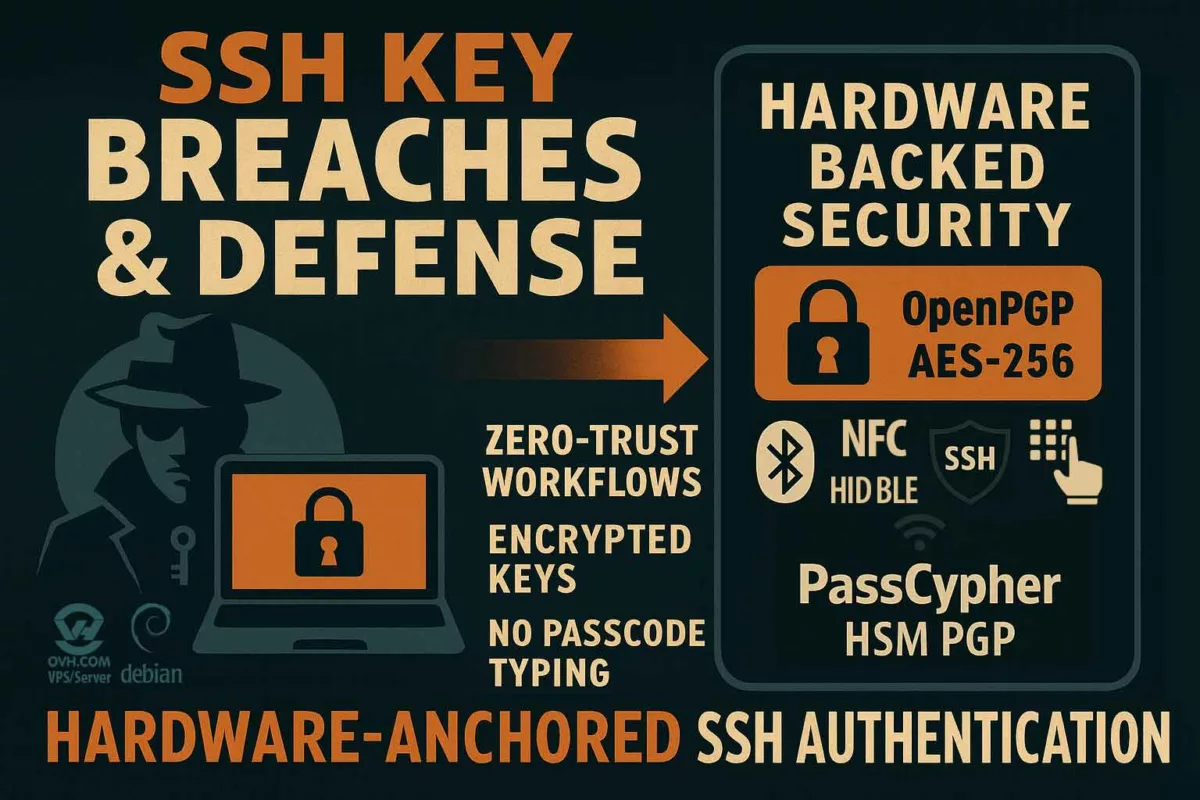
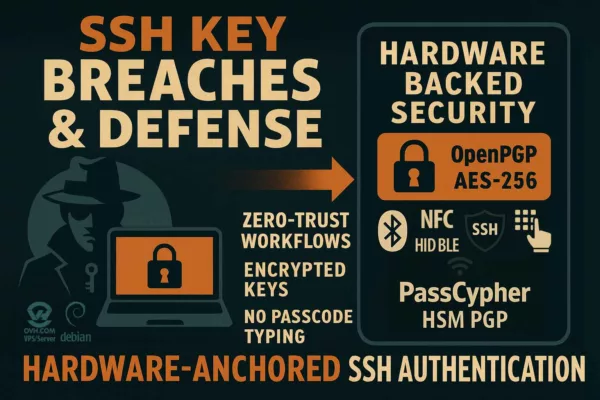
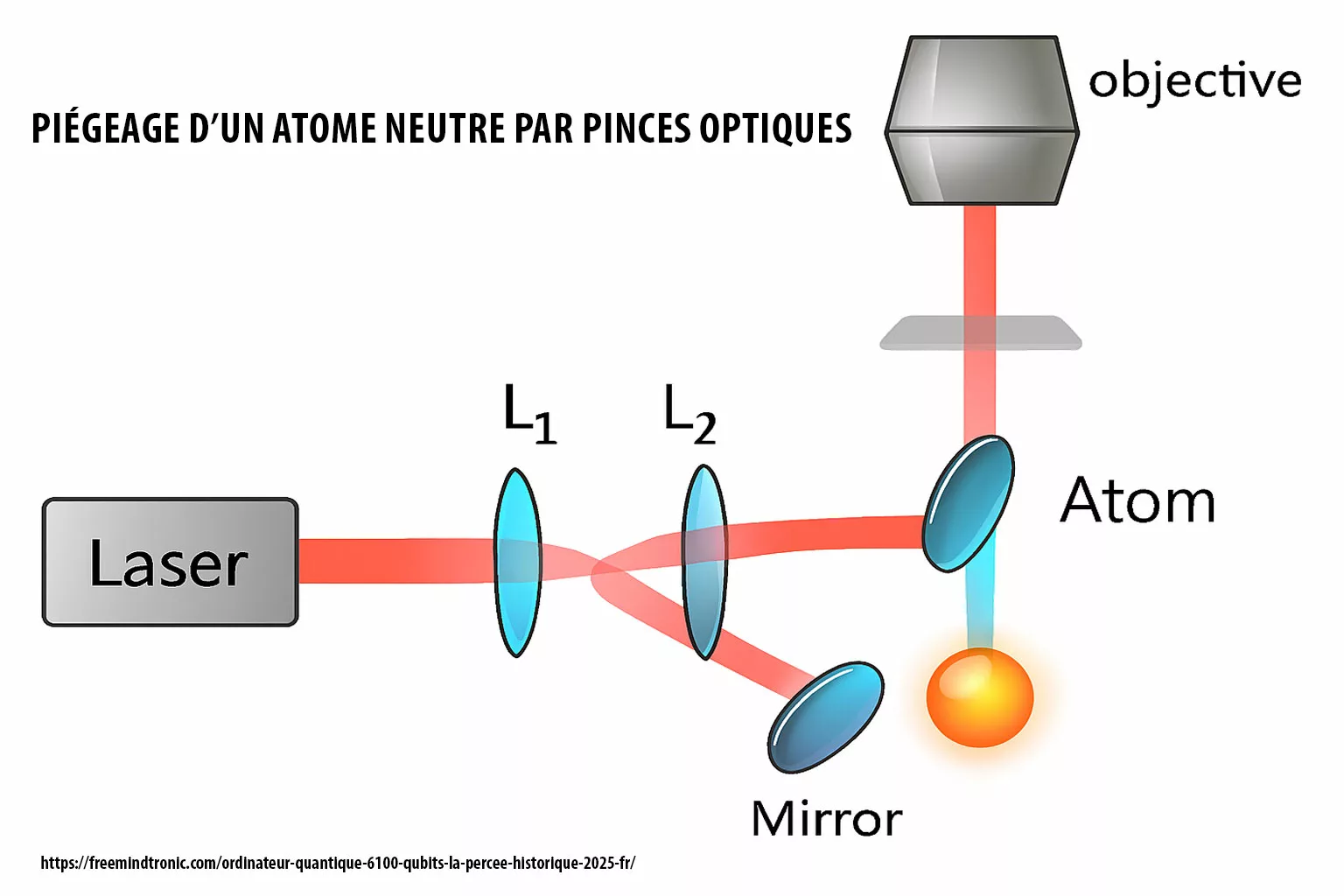
SSH Key PassCypher HSM PGP establishes a sovereign SSH authentication chain for zero-trust infrastructures, where keys are generated and sealed inside a hardware HSM under OpenSSH AES-256 encryption. It demonstrates how to secure an SSH key — or, in French, comment sécuriser une clé SSH — by ensuring that the private key is never exposed in the clear, neither on disk nor in memory. Through BLE-HID passphrase injection, it eliminates keylogger risks and enforces a zero-clear-key policy, bringing hardware-anchored SSH security to Debian, macOS, and Windows environments. This sovereign method combines OpenSSH encryption, hardened KDFs such as bcrypt, and NFC-triggered hardware interactions to protect SSH credentials across multi-OS infrastructures.
Express Summary — Sovereign SSH Authentication for All Operating Systems
⮞ In Brief
Quick read (≈ 4 minutes): generate your SSH key pair directly inside PassCypher HSM PGP, export only the public key to the server, and keep the private key sealed in an OpenSSH-encrypted private key file (id_ed25519, id_rsa, etc.). The private key is never stored in the clear. During connection, it is decrypted ephemerally in RAM using a passphrase injected either manually or through the PassCypher NFC HSM via its BLE-HID hardware keyboard emulator. This sovereign SSH authentication model eliminates the risk of keyloggers and clipboard theft while supporting long, post-quantum-ready passphrases (≥256 bits).
⚙ Core Concept
Key generation inside HSM → OpenSSH passphrase encryption (AES-256 + hardened KDF) → export of public key (.pub OpenSSH) → safe storage and duplication of encrypted private key (id_ed25519 (ou id_rsa, selon le cas)) → ephemeral local decryption via NFC / BLE-HID injected passphrase → authenticated SSH session.
Interoperability
Fully compatible with Debian, Ubuntu, Fedora, FreeBSD, macOS, Windows (WSL, PuTTY), Android (Termux) and iOS (Blink Shell). Native OpenSSH format ensures universal portability and sovereign SSH key management across environments.
Reading Parameters
Express summary reading time: ≈ 4 minutes
Advanced summary reading time: ≈ 6 minutes
Full chronicle reading time: ≈ 35 minutes
Last updated: 2025-10-02
Complexity level: Advanced / Expert
Technical density: ≈ 73 %
Languages available: CAT · EN · ES · FR
Linguistic specificity: Sovereign lexicon — high technical density
Reading order: Summary → Architecture → Security → Workflow → Rotation → EviSSH → Resources
Accessibility: Screen-reader optimized — semantic anchors included
Editorial type: Strategic Chronicle — Digital Security · Technical News
Author: Jacques Gascuel — inventor and founder of Freemindtronic Andorra, expert in NFC HSM technologies, embedded cryptography, and zero-trust architectures. His research focuses on digital sovereignty and post-quantum resilience.
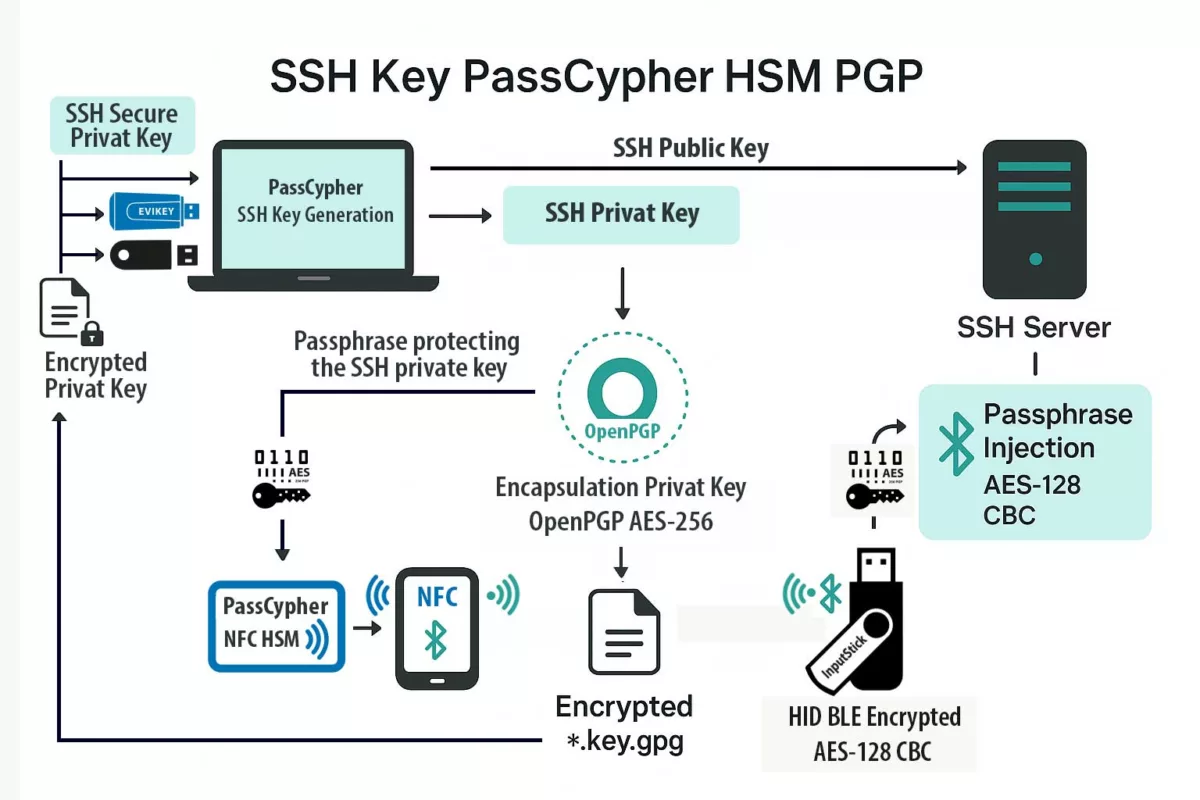
Advanced Summary — Architecture and Secure SSH Workflow with Sovereign SSH Authentication via PassCypher HSM PGP
⮞ In Detail
The workflow for sovereign SSH authentication follows a secure and repeatable pattern. First, PassCypher HSM PGP generates the SSH key pair internally. Then, the system encrypts the private key in an OpenSSH private key format using AES-256 encryption and a hardened KDF. Only the public key (.pub) is exported for server use. The encrypted private key (id_ed25519 or id_rsa) stays sealed inside the HSM. When needed, the HSM decrypts the key ephemerally in RAM using an injected passphrase via NFC or BLE-HID. The SSH connection then proceeds without exposing any clear-text key. This step-by-step model keeps each process verifiable, auditable, and sovereign.
Hardware-Based SSH Key Management
Unlike cloud solutions, PassCypher HSM PGP provides SSH key management entirely within a hardware module. It enables complete SSH key rotation and ephemeral decryption while maintaining a zero-clear-key security posture. This architecture ensures that SSH private keys never exist in plaintext — not on disk, not in memory, and not in any centralized vault — thereby delivering hardware-anchored sovereignty for critical systems.
Beyond Conventional SSH Key Management Platforms
While many SSH key management solutions rely on cloud-based vaults or software-only zero-knowledge models, PassCypher HSM PGP introduces a sovereign alternative that removes every intermediary layer. All cryptographic operations — from SSH key generation to rotation and lifecycle management — occur inside the hardware HSM. No agent, vault, or remote API ever handles private keys or passphrases.
This approach merges the benefits of zero-knowledge architectures with hardware-level isolation. Each SSH credential is locally created, Encrypted with OpenSSH AES-256 encryption, and stored in a zero-clear-key state. Unlike software-based systems that synchronize secrets through cloud or network vaults, PassCypher’s design ensures no key leaves the trusted hardware perimeter.
The result is a hardware-anchored SSH key management solution that delivers the same usability and automation found in traditional secrets managers — including key rotation, team access control, auditability, and lifecycle orchestration — but under a sovereign, offline-capable, zero-cloud architecture.
Why Secure SSH with a Hardware HSM
Unencrypted SSH keys remain vulnerable to theft, duplication, and accidental backup. Attackers can exploit them silently for persistence. PassCypher HSM PGP solves this by locking the private key inside a hardware-based trust boundary. Each operation requires hardware confirmation. Decryption occurs only when an authenticated passphrase is injected. This removes dependence on software agents and delivers hardware-anchored sovereignty for SSH authentication. As a result, even on untrusted machines, administrators maintain cryptographic control of their access credentials.
HSM PGP Architecture — Technical Components
The sovereign SSH authentication architecture combines proven OpenSSH native encryption with hardware isolation. Each component plays a specific role in the zero-clear-key chain.
- OpenSSH private key format: Encrypts with AES-256 (CTR, CBC, or GCM) and ensures data integrity with MDC.
- Hardened KDF: Uses PBKDF2 (≥200k iterations) or bcrypt (default) to resist brute force.
- Passphrase: Randomly generated inside the HSM. Recommended entropy ≥256 bits for PQC readiness.
- Injection: Delivered through NFC trigger or BLE-HID emulation. This prevents typing and blocks keyloggers.
- Secure duplication: The encrypted id_ed25519 or id_rsa can be safely stored on EviKey NFC HSM, USB, or NAS. It remains secure as long as the KDF and passphrase are protected.
Deploying Sovereign SSH Authentication with PassCypher HSM PGP on Debian VPS and Beyond
⮞ TL;DR
This section explains how to deploy SSH Key PassCypher HSM PGP for secure remote access on Debian VPS, OVHcloud, and hybrid infrastructures. The HSM generates SSH key pairs internally and encrypts the private key as id_ed25519 or id_rsa. The system exports only the public key for registration. When connecting, the HSM decrypts the private key temporarily in RAM. A passphrase from PassCypher NFC HSM injects via BLE-HID keyboard emulation using AES-128 CBC encryption. No plaintext key ever touches disk or memory. This design removes keyloggers, clipboard theft, and man-in-the-browser risks.
It guarantees zero-clear-key SSH authentication across platforms.
Operational Alert — BLE-HID Pairing Security
Avoid using the “Just Works” pairing mode in Bluetooth Low Energy. Instead, enforce Secure Connections mode with AES-128 CBC encryption. Always use numeric authentication by PIN or code confirmation. This configuration prevents unauthenticated pairing. It also blocks MITM attacks during BLE initialization. In air-gapped or classified setups, BLE-HID provides direct passphrase transfer with zero dependency on cloud middleware. This maintains operational sovereignty, even under isolation.
In sovereign cybersecurity ↑ This chronicle belongs to Digital Security and Tech Fixes & Security Solutions. Explore related content such as EviSSH — SSH Key Management in HSM, EviKey NFC HSM, Secure SSH VPS with PassCypher HSM and PassCypher HSM PGP — Technical Note.
Chronicle — EviSSH: Embedded Engine Inside PassCypher HSM PGP
EviSSH is the embedded technology within PassCypher HSM PGP dedicated to sovereign SSH key generation, management, and storage. It relies on the EviEngine to execute all cryptographic operations locally. Every SSH key pair creation and OpenSSH passphrase encryption happens client-side. No data, keys, or metadata ever leave the user’s environment.
Role and Operation
- Integrated Interface — EviSSH is directly accessible through the PassCypher HSM PGP browser extension.
- Local Generation — SSH key pairs are generated using Git for Windows or its Linux/macOS equivalent under EviEngine orchestration.
- Encryption — The private key is automatically wrapped in an OpenSSH private key format encrypted with AES-256 and a hardened KDF.
- Sovereign Storage — Users choose the storage path: local .ssh folder, EviKey NFC HSM, NAS, or external drive.
- Interoperability — Public keys export in standard OpenSSH format and work across Debian, Ubuntu, macOS, Windows, Android, and iOS.
EviEngine — Core Orchestrator
EviEngine coordinates secure communication between the browser, the OS, and HSM components. It generates SSH keys via Git, manages PassCypher extension licensing, and runs entirely offline. Every operation executes locally on the user’s device, ensuring full sovereignty and auditability.
HSM Integration
- PassCypher NFC HSM — Injects passphrases through a BLE-HID channel encrypted with AES-128 CBC.
- EviKey NFC HSM — Stores encrypted key containers (
id_ed25519orid_rsa) protected by the user-defined passphrase.
Generating a Sovereign SSH Key with PassCypher HSM PGP
SSH key creation occurs through the EviSSH module embedded in PassCypher HSM PGP using the EviEngine. It leverages Git to build the SSH key pair, then encrypts it instantly through PassCypher HSM PGP. The entire process stays local and offline.
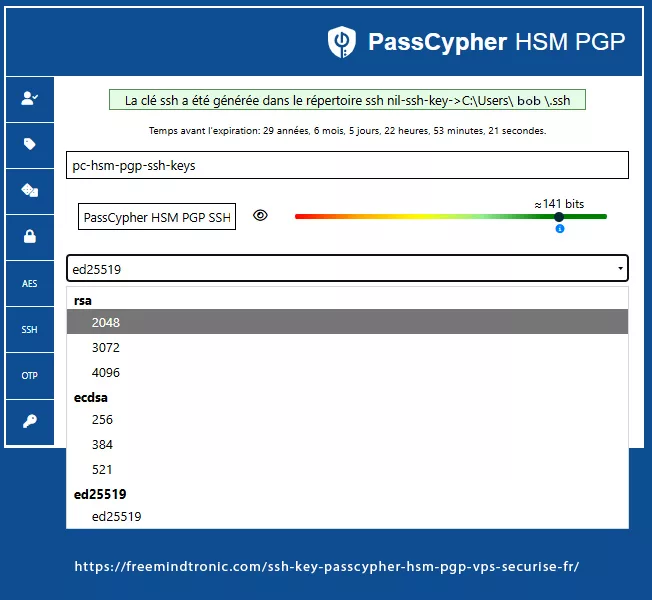
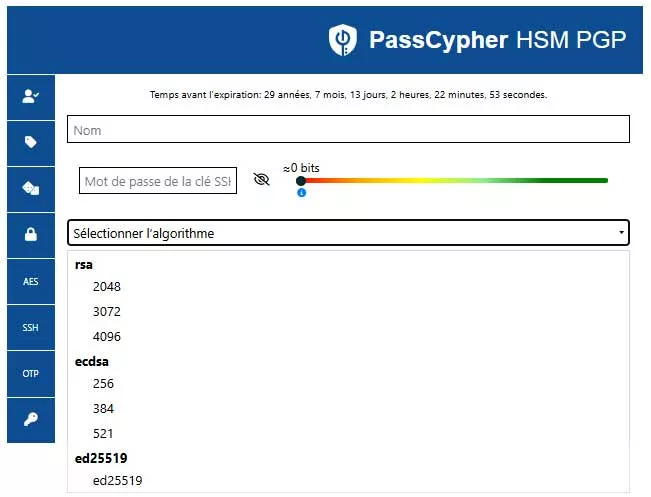
Algorithm Selection — Cryptographic Choice within PassCypher
The user selects algorithm and key size directly in the PassCypher HSM PGP interface. Available families include:
- RSA: 2048 bits · 3072 bits · 4096 bits
- ECDSA: 256 bits (p-256) · 384 bits (p-384) · 521 bits (p-521)
- EdDSA: ed25519 — recommended for its robustness, compactness, and native OpenSSH support
Generation Steps — Transparent Workflow
- Open the SSH module inside PassCypher HSM PGP.
- Define a unique key label, for example
pc-hsm-pgp-ssh-key. - Select the desired algorithm (
ed25519orrsa-4096). - Set a passphrase, either typed manually or injected via PassCypher NFC HSM using its BLE-HID AES-128 CBC emulator. This passphrase encrypts the private key container.
- Validate the action. EviSSH generates the pair through Git, and PassCypher HSM PGP encrypts the private key. Files save automatically in the chosen path, by default
~/.ssh/or an EviKey NFC HSM.
Result — Exported Artifacts
id_ed25519.pub— public key copied to the remote server.id_ed25519 — private key encrypted by PassCypher HSM PGP in native OpenSSH format (AES-256 + bcrypt KDF)
The passphrase, ideally ≥ 256 bits of entropy, can be typed or injected from the HSM via BLE-HID, avoiding exposure to keyloggers.
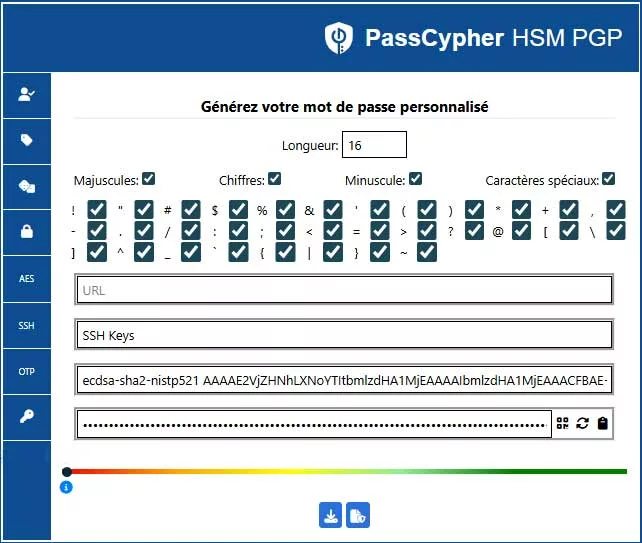
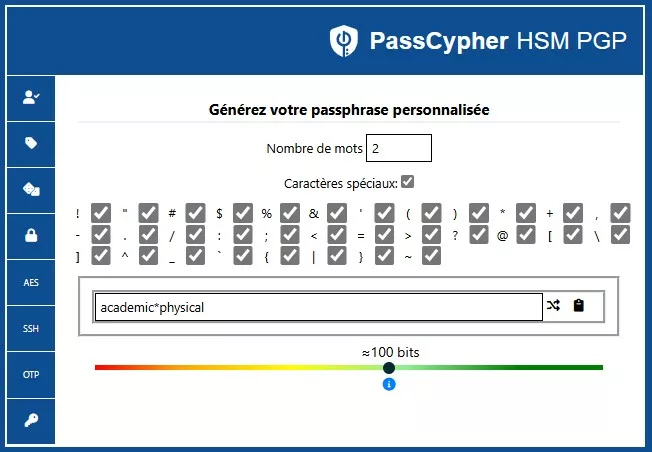
Memorable Passphrase Generator — “Two Words + Symbol” Option
The built-in generator:
- Selects random words from an embedded wordlist.
- Inserts 1–3 special characters between or around words.
- Displays an estimated entropy score.
- Optionally stores the passphrase in the HSM or injects it via BLE-HID during container encryption.
Practical Example
Generate a 3-word passphrase with two special characters:
# Example (PassCypher interface)
1) Choose wordlist: common-wordlist-16k
2) Words: 3
3) Separator: '-'; special chars: '#!'
→ Example output: atlas-siren#!
Use PassCypher NFC HSM to inject it via BLE-HID during encryption:
ssh-keygen -p -o -a 16 -t ed25519 -f ~/.ssh/id_ed25519 --output id_ed25519.key.gpg --compress-level 0 id_ed25519
# Passphrase is injected by PassCypher BLE-HID at pinentry prompt
Operational Recommendations
- For critical servers or bastions, prefer HSM generation or increase word count.
- Enable bcrypt with m ≥ 512 MB, t ≥ 3, p ≥ 4 during encryption.
- Never store the passphrase in plain text or unprotected form.
- Check entropy estimation in UI and adjust with extra words or symbols if required.
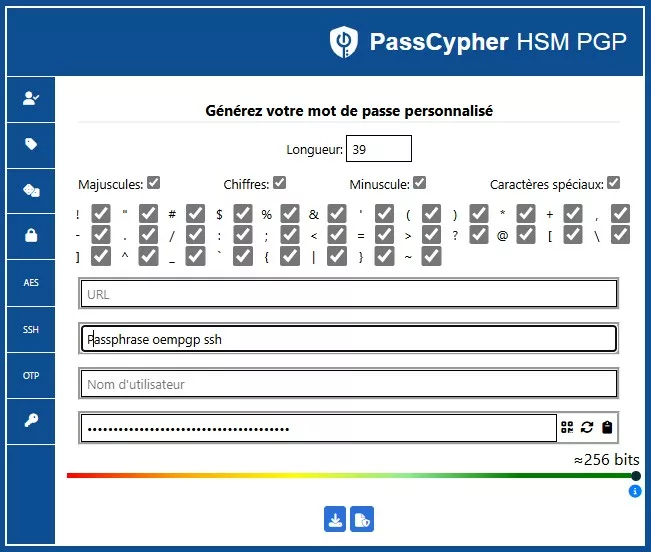
ASCII-95 Generator — High-Entropy Password / Passphrase Mode
The interface below creates ultra-secure passwords or passphrases using all 95 printable ASCII characters. Unlike word-based modes, this option targets maximum entropy and granular control over character classes. It provides real-time entropy estimation, often ≥ 256 bits depending on length. It is meant for use cases where the secret remains encrypted (QR or HSM) and is injected via PassCypher ecosystem (BLE-HID / NFC) without screen display.
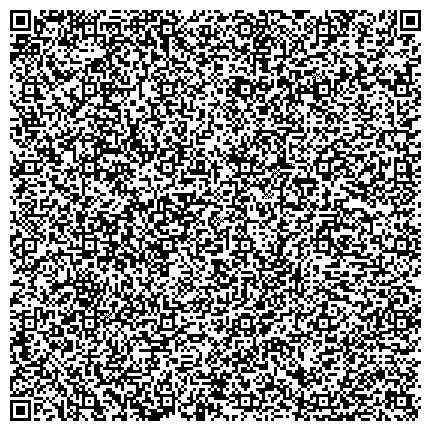
QR Code Export — Direct Transfer to PassCypher NFC HSM
Once a high-entropy password or passphrase is generated through the ASCII-95 module, the user can export the secret as an encrypted QR Code. This code can then be scanned by an Android smartphone with NFC running the Freemindtronic app that includes PassCypher NFC HSM. This sovereign interoperability enables direct transfer from the software HSM to the hardware HSM without network exposure or disk writes. Afterward, PassCypher NFC HSM can inject the secret through its Bluetooth HID keyboard emulator for authentication on any SSH client.
Real-World Example — RSA 4096-bit Private Key Protected by Passphrase
Even an RSA 4096-bit key becomes vulnerable if stored unencrypted. Within PassCypher HSM PGP, the key remains encapsulated and protected by a 141-bit entropy passphrase by default, making brute-force or exfiltration mathematically infeasible. Below is what an OpenSSH-formatted RSA 4096-bit private key looks like once encrypted by passphrase:
-----BEGIN OPENSSH PRIVATE KEY-----
b3BlbnNzaC1rZXktdjEAAAAACmFlczI1Ni1jdHIAAAAGYmNyeXB0AAAAGAAAABA+ghFLmp
Oiw0Z3A4NKn2gHAAAAGAAAAAEAAAIXAAAAB3NzaC1yc2EAAAADAQABAAACAQDK4d0ntIeb
... (truncated for readability) ...
55XA==
-----END OPENSSH PRIVATE KEY-----
BEGIN OPENSSH PRIVATE KEY and a base64-encoded payload. Field b3BlbnNzaC1rZXktdjE= identifies OpenSSH v1 with encryption enabled. Depending on configuration, the engine uses aes256-ctr or aes256-cbc.After securing key generation and encapsulation, administrators can integrate the sovereign SSH key into their virtual servers. The next section explains how to deploy it on Debian-based VPS instances like OVHcloud.
Integration on VPS (Example – OVH Debian 12)
Integrating a PassCypher HSM PGP SSH key into a VPS involves placing the public key (.pub) inside the server’s authorized_keys file.
OVHcloud allows inserting it directly during VPS creation through its dashboard.
Manual Insertion After Deployment
ssh -p 49152 debian@IPVPS "mkdir -p ~/.ssh && chmod 700 ~/.ssh && cat >> ~/.ssh/authorized_keys" < id_ed25519.pub
Then decrypt the private key locally from its encrypted container:
ssh -i ~/.ssh/id_ed25519 --output ~/.ssh/id_ed25519 ~/.ssh/id_ed25519.key.gpg
chmod 600 ~/.ssh/id_ed25519
ssh -i ~/.ssh/id_ed25519 -p 49152 debian@IPVPS
The decrypted file exists only temporarily. It can self-erase after the SSH session or stay in RAM if mounted on tmpfs.
This “zero-clear-text” approach ensures that no sensitive data persist on disk.
No keystroke is capturable. Even on a compromised host, the private key remains unusable without the physical HSM and its secured pairing session.
Once integrated on a server, the same sovereign SSH key can authenticate securely across multiple operating systems.
The following section details how PassCypher HSM PGP maintains this universal compatibility.
Cross-OS compatibility — Universal authentication
The OpenSSH format used by PassCypher HSM PGP guarantees full compatibility with major operating systems. The sovereign design is based on open standards only — no cloud dependencies, no third-party identity services.
| OS | SSH client | Highlights |
|---|---|---|
| Debian / Ubuntu | OpenSSH | Native support for encrypted private keys. |
| macOS | Built-in OpenSSH | Managed via ssh-add or BLE-HID injection. |
| Windows 10 / 11 | PuTTY / OpenSSH | Optional conversion via PuTTYgen. |
| Android | Termux / JuiceSSH | HID injection support from a paired NFC/BLE device. |
| iOS | Blink Shell | Automatic BLE-HID injection after trusted pairing. |
authorized_keys, administrators_authorized_keys).Official reference — Microsoft: Key-based SSH authentication on Windows (March 10, 2025)
On March 10, 2025 Microsoft updated guidance for OpenSSH key-based authentication on Windows. The document covers creating and managing public/private key pairs and recommends modern asymmetric algorithms (Ed25519, ECDSA, RSA, DSA).
- Published: March 10, 2025 — Microsoft Learn
- Scope: OpenSSH key management and secure key storage on Windows
- Tools & commands:
ssh-keygen,ssh-agent,ssh-add,sshd, PowerShell automation,scp,sftp - Key files:
authorized_keys,administrators_authorized_keys,id_ecdsa.pub, default folderC:\Users\username\.ssh\ - Algorithms supported: Ed25519, ECDSA, RSA, DSA
- Best practices: strong passphrase encryption, MFA where applicable, strict file permissions
- Limitation: passphrases are typically typed or managed by software agents — an exposure vector in conventional setups
C:\ProgramData\ssh\administrators_authorized_keys. Protect this file with NTFS ACLs (Administrators & SYSTEM only). In non-localized setups use the SID S-1-5-32-544 to target Administrators.Read Microsoft — OpenSSH key-based authentication
Sovereign extension of the model
- Passphrases are injected from hardware (NFC / BLE-HID) — no manual typing, no clipboard exposure.
- Private keys are protected in an OpenSSH private key format (AES-256 + hardened KDF), preventing any cleartext private key from leaving ephemeral memory.
Combined with OpenSSH on Windows, PassCypher HSM PGP converts Microsoft’s key-based flow into a hardware-anchored sovereign SSH suitable for Zero-Trust and PQ-aware postures.
PowerShell SSH
PowerShell (Windows 11 / Windows Server 2025) includes native OpenSSH integration and automation capabilities. When combined with PassCypher HSM PGP, remote operations can be automated while keeping the passphrase bound to hardware (HSM), avoiding exposure in process memory — an auditable, sovereign automation model.
Sovereign SSH
The hybrid hardware approach embodied by PassCypher HSM PGP implements Sovereign SSH: local key generation inside HSM, OpenSSH passphrase encryption (AES-256), hardened KDFs, typological key rotation — all without cloud or federated identity dependencies. This layer strengthens Microsoft OpenSSH’s trust chain with an auditable, PQ-aware hardware boundary.
Git for Windows integration — SSH key generation
PassCypher HSM PGP uses the Git for Windows environment to generate and manage SSH key pairs. Git for Windows ships ssh-keygen.exe, enabling creation of keys protected by a passphrase. By default keys are placed in the user folder:
C:\Users\\.ssh\This default placement ensures full compatibility with PowerShell SSH and OpenSSH on Windows while allowing PassCypher to add an additional sovereign protection layer (OpenSSH passphrase encryption + HSM-based passphrase injection), producing a double barrier consistent with the zero-clear-key principle.
Functional SSH Key Separation — Authentication vs Signature
In a sovereign SSH architecture, each key must serve a clearly defined function to minimize exposure risks and enhance traceability. PassCypher HSM PGP enforces this typological separation by encrypting each private key individually within an OpenSSH private key format (AES-256 + hardened KDF), each labeled and fingerprinted according to its role:
- Authentication key: used exclusively to establish secure SSH connections to remote servers. The private key’s passphrase is injected via BLE-HID from a PassCypher NFC HSM, entered manually, or pasted locally. PassCypher never displays or transmits this passphrase in cleartext—neither on disk nor in persistent memory—ensuring strict compliance with the Zero-Clear-Key principle. The user remains responsible for clipboard and terminal security when typing or pasting manually.
- Signature key: used for cryptographic validation of files, scripts, or Git commits. It is encapsulated in a separate OpenSSH private key format, traceable and revocable without affecting SSH access.
This encrypted separation enables:
- Targeted revocation without disrupting active SSH sessions (revocation date management is planned in future PassCypher SSH releases)
- Enhanced auditability through functional labeling and local logging
- Native DevSecOps compatibility (Git, CI/CD, signed pipelines)
ssh-keygen -C "auth@vps" or sign@repo") to simplify management within authorized_keys files and PassCypher append-only ledgers.Server Hardening and Best Practices for SSH Key PassCypher HSM PGP
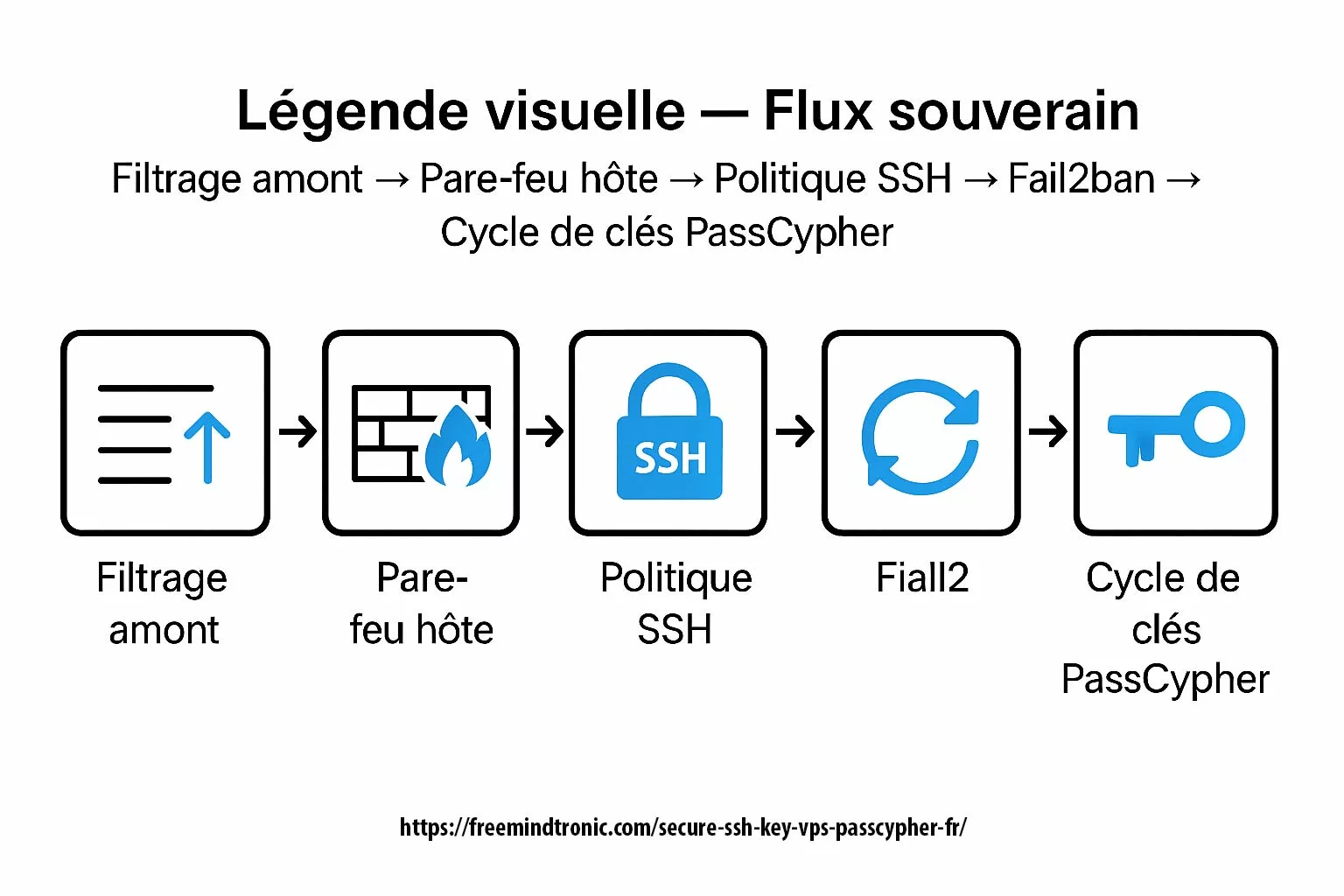
Even with a PassCypher HSM PGP SSH key, overall security depends on server configuration. Key recommendations for a sovereign posture include:
-
-
- Disable root login:
PermitRootLogin no - Forbid password authentication:
PasswordAuthentication no - Restrict SSH users:
AllowUsers admin - Change default port: use
49152and block 22 via firewall. - Configure UFW or iptables: default
DROPpolicy with targeted exceptions. - Enable Fail2ban: maxretry = 3, bantime = 30 min to block brute-force attacks.
- Activate audit logs:
journalctl -u sshwith rotation and ledger tracking.
- Disable root login:
-
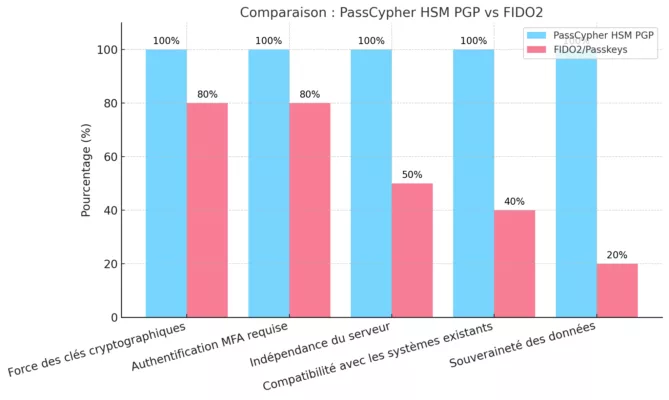
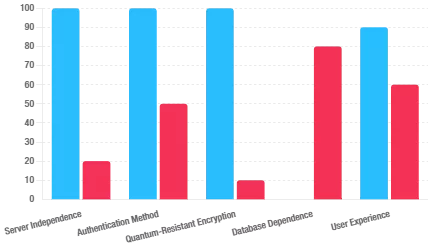
FIDO vs SSH — Two Paradigms, Two Security Postures
In the evolving cybersecurity landscape, confusion between FIDO2/WebAuthn and SSH remains common. These two systems rely on fundamentally different trust models and authentication paradigms. FIDO secures a human identity in the browser, while SSH secures a machine identity within the network. Their purposes, exposure surfaces, and sovereignty principles diverge completely.
FIDO2 / WebAuthn — Human-Centric Authentication
-
-
- ↳ Designed to authenticate a user to a web service (browser ↔ server via WebAuthn).
- ↳ The private key stays sealed within a hardware authenticator (YubiKey, TPM, Secure Enclave, etc.).
- ↳ Each site or domain creates a unique key pair — ensuring identity isolation.
- ↳ Relies on an authentication server (RP) and the browser ecosystem.
- ↳ Requires human presence (biometric, touch, or gesture).
- ↳ Non-exportable key: strong security but minimal portability.
- ↳ No local audit trail or autonomous key rotation.
-
SSH — Machine-Centric Authentication
-
-
- ↳ Designed to authenticate a client system to a remote host (VPS, server, or cluster).
- ↳ Uses a persistent key, reusable across hosts according to trust policy.
- ↳ Operates outside browsers — native SSH protocol with encrypted machine-to-machine exchanges.
- ↳ Allows duplication and backup of keys when securely encrypted.
- ↳ Relies on a passphrase or hardware HSM for local or injected authentication.
- ↳ Supports native logging, rotation, and revocation controls.
- ↳ Fully independent of cloud or third-party identity providers.
-
⮞ What PassCypher HSM PGP with EviSSH Brings
The SSH Key PassCypher HSM PGP solution extends classic SSH by introducing hardware security and auditability similar to FIDO2 — but within a cloudless sovereign architecture. It brings trust, portability, and compliance into a unified zero-trust framework:
-
-
- → Local SSH key pair generation through PassCypher Engine / EviSSH.
- → Private key encrypted in its OpenSSH private key format (AES-256 + bcrypt KDF).
- → Key always encrypted on disk — decryption happens only in volatile memory.
- → Hardware passphrase injection via PassCypher NFC HSM or BLE-HID emulator using AES-128 CBC encryption.
- → Optional physical presence adds a “sovereign gesture” equivalent to FIDO authentication.
- → Full cross-platform support: Linux, macOS, Windows, Android, and iOS.
- → No dependency on browsers, WebAuthn servers, or cloud identity accounts.
- → Orchestrated key rotation and archival via EviSSH for industrial or defense-grade use.
-
Strategic Summary
-
-
- FIDO2: Cloud-centric, non-exportable — ideal for web identity, but limited outside browsers.
- SSH PassCypher: Sovereign, portable — ideal for servers, VPS, and critical infrastructure access.
- PassCypher merges the hardware assurance of authenticators with the flexibility of native SSH.
- BLE-HID injected passphrases (≥ 256 bits) ensure post-quantum symmetric resistance.
- Local audit trails and key rotation enable off-cloud traceability.
- Both pursue digital trust, but through opposite paths — dependence vs. sovereignty.
-
Threat Model — Understanding SSH Risks
Before addressing mitigation, it is essential to understand how traditional SSH keys introduce vulnerabilities. Standard SSH connections rely on local files containing private keys. Without hardware protection, these files can be copied, exfiltrated, or reused remotely. The sovereign model deployed in SSH Key PassCypher HSM PGP neutralizes these vectors through zero-clear-key architecture and strict secret segmentation.
Identified Threats
-
-
- Private key theft — exfiltration of
~/.ssh/id_*or cloud-synced copies. - Memory dump — retrieval of a key temporarily decrypted in RAM.
- Keylogger — passphrase capture during manual keyboard entry.
- BLE MITM — interception during insecure “Just Works” pairing.
- Unencrypted backup — uncontrolled duplication of the container file.
- Human error — key reuse or unintended disclosure.
- Private key theft — exfiltration of
-
SSH Private Key Breaches (2021–2025) — Why OpenSSH AES-256 + HSM-injected passphrase would have prevented them
⮞ Documented Incidents
Codecov — CI Supply Chain Compromise (Jan–Apr 2021)
- Attackers modified Bash scripts to exfiltrate environment variables and plaintext SSH credentials.
- Codecov post-mortem · CISA alert
Lesson: Plaintext secrets in CI pipelines are a critical vulnerability.
PassCypher mitigation: OpenSSH-encrypted keys with HSM-injected passphrases would have rendered exfiltrated keys cryptographically unusable.
Ebury — Persistent SSH Backdoor Campaign (2009–2024)
- Malware implanted in SSH daemons stole credentials from over 400,000 Linux servers.
- ESET analysis
Lesson: Keys loaded in memory are vulnerable to persistent malware.
PassCypher mitigation: Keys are decrypted only ephemerally in RAM, never stored persistently.
GitHub — SSH Host Key Exposure (March 2023)
- An internal SSH host key was accidentally committed to a public repository.
- GitHub blog
Lesson: Even trusted providers can leak long-lived keys.
PassCypher mitigation: OpenSSH private key formats (id_ed25519 (ou id_rsa, selon le cas)) remain cryptographically inert if published without the HSM.
Cloudflare — Credential Leakage via Logs (2024)
- A misconfigured worker exposed SSH-related secrets in debug logs.
- Cloudflare blog
Lesson: Logging and debugging can inadvertently expose secrets.
PassCypher mitigation: Passphrases are injected via BLE-HID and never typed or logged.
OpenSSH — CVE-2025-26465 & CVE-2025-26466 (Feb 2025)
- Critical flaws allowed MitM and DoS attacks on SSH servers.
- CERT-FR advisory
Lesson: Protocol-level flaws can bypass host key trust.
PassCypher mitigation: Host key pinning and hardware-bound passphrase injection neutralize MitM vectors.
GitHub Actions — CI/CD Secret Exposure (Q2 2025)
- Multiple open-source projects committed `.env` files containing SSH private keys.
Lesson: Plaintext key reuse across environments remains widespread.
PassCypher mitigation: Encrypted key containers (id_ed25519 (ou id_rsa, selon le cas)) are unusable without the physical HSM and injected passphrase.
Operational Conclusion
None of the compromised keys in these incidents were protected by OpenSSH native encryption or hardware-injected passphrases. Each breach exploited plaintext exposure — in scripts, logs, memory, or repositories.
PassCypher HSM PGP Architecture:
- Private keys are always encrypted at rest (AES-256 OpenSSH)
- Decryption occurs only ephemerally in RAM
- Passphrases are injected via sovereign hardware — never typed or logged
- Even if the encrypted key is exfiltrated, it remains cryptographically inert without the HSM
This model neutralizes every known attack vector used in SSH key compromises to date.
AI-Assisted Breach Vectors — and Why Hardware Sovereignty Matters
Short summary: Since 2021, multiple public incidents have exposed a recurring vulnerability: plaintext secrets or private keys accessible in CI pipelines, memory, or logs. Today, AI-assisted IDEs and Copilot-like assistants extend that exposure surface by indexing local workspace data, terminal outputs, and editor buffers. When an AI assistant can read or summarize visible code or system logs, any plaintext secret becomes an implicit exfiltration vector.
Documented, verifiable examples
-
-
- Codecov supply-chain compromise (2021) — CI scripts leaked plaintext credentials. Hardware encryption (OpenSSH AES-256 + HSM passphrase injection) would have rendered them useless.
- Ebury SSH backdoors (2009 – 2024) — malware stole SSH keys in memory. Zero-clear-key workflows prevent such exfiltration.
- Public key leaks (GitHub, 2023 – 2024) — accidental commits of secrets. OpenSSH-encrypted private key files remain inert if exposed.
-
AI / IDE assistants — new attack surface
Modern code assistants (GitHub Copilot, Amazon CodeWhisperer, etc.) scan active projects and terminals to provide context-aware suggestions. If plaintext secrets exist in that context, they may be processed or exposed inadvertently. Independent audits and vendor advisories highlight potential privacy and data-leak risks when assistants index developer environments without isolation.
Why hardware sovereignty eliminates this risk
-
-
- Private keys remain sealed in OpenSSH AES-256 containers.
- Decryption requires a hardware-held passphrase injected via BLE-HID or NFC.
- No plaintext key or passphrase ever appears on screen, disk, or in clipboard memory.
-
Even if an AI assistant, IDE plugin, or CI process is compromised, it cannot extract usable secrets — because none exist in cleartext. PassCypher HSM PGP enforces this “zero-clear-key” model from key generation to authentication.
Protection Mechanisms — OpenSSH, KDF, and BLE-HID Layers
After defining the threat surface, PassCypher HSM PGP establishes a defense-in-depth model built on three pillars: robust asymmetric encryption, hardened key derivation, and secure physical passphrase injection. Together, these mechanisms ensure that no private key can be extracted — even from a compromised endpoint.
OpenSSH private key format and Integrity Assurance
The private key is stored directly in OpenSSH’s native encrypted format (AES-256 + bcrypt).
-
-
- Encryption: AES-256 (CTR, CBC, or GCM depending on configuration)
- Integrity: Active MDC (Modification Detection Code).
- Unique salt: generated by the engine during initial encryption.
- Optional compression: reduces memory footprint and transmission load.
-
Key Derivation Function (KDF) and Symmetric Resistance
The OpenSSH encryption key derives from an HSM-generated passphrase:
-
-
- bcrypt: default mode (m=512MB, t=3, p=4) hardened against GPU attacks.
- PBKDF2 fallback: 250,000 SHA-512 iterations when bcrypt is unavailable.
- Post-quantum awareness: ≥256-bit entropy ensures symmetric strength equivalent to 2¹²⁸ under Grover’s bound.
-
BLE-HID Injection Channel — Passphrase Security at the Hardware Layer
The passphrase travels through a Bluetooth Low Energy HID channel emulating a hardware keyboard.
-
-
- Secure pairing mode: Secure Connections enforced with numeric authentication (PIN or code), bonding activated for persistence.
- Communication encryption: AES-128 CBC applied at HID application level.
- First AES-128 key stored in a secure enclave embedded in the Bluetooth keyboard emulator.
- Second AES-128 key stored inside Android Keystore (Android ≥ 10) managed by the PassCypher NFC HSM app.
- Residual risk: a MITM vulnerability can appear if “Just Works” mode is allowed — this mode is strictly forbidden under sovereign policy.
-
Rotation and Revocation — SSH Key PassCypher HSM PGP Lifecycle Management
Within sovereign SSH authentication infrastructures, key rotation ensures continuity and traceability without exposing secrets. Unlike simple rotation commands, SSH Key PassCypher HSM PGP follows a four-step operational process: regenerate, deploy, validate, revoke. This method fully preserves the zero-clear-key principle — private keys stay encrypted at rest and are decrypted only in volatile memory.
1) Regeneration — Creating a New Sovereign SSH Key Pair
From the integrated EviSSH interface, users regenerate SSH key pairs through Git. The PassCypher Engine automatically encapsulates and encrypts them.
-
-
- Select the algorithm —
ed25519for resilience and interoperability, orrsa-4096for specific requirements. - Assign a distinct label (e.g.,
pc-hsm-ssh-2025-10) to ensure traceability and simplify future revocation. - The private key is encapsulated in an OpenSSH AES-256 encrypted container (id_ed25519 or id_rsa) using a hardened KDF (bcrypt).
- The public key (
*.pub) is generated with a unique comment identifier for use inauthorized_keys.
- Select the algorithm —
-
2) Controlled Deployment — Adding Without Downtime
Append the new .pub key to ~/.ssh/authorized_keys on each server without removing the previous one.
# Append-only deployment (port 49152, Debian user)
scp -P 49152 ~/.ssh/id_ed25519_2025-10.pub debian@IPVPS:/tmp/newkey.pub
ssh -p 49152 debian@IPVPS 'umask 077; mkdir -p ~/.ssh; touch ~/.ssh/authorized_keys
&& grep -qxF -f /tmp/newkey.pub ~/.ssh/authorized_keys || cat /tmp/newkey.pub >> ~/.ssh/authorized_keys
&& rm -f /tmp/newkey.pub && chmod 600 ~/.ssh/authorized_keys'
3) Validation — Canary Phase
Test connectivity with the new key. The passphrase is injected securely via BLE-HID from the HSM.
ssh -o IdentitiesOnly=yes -i ~/.ssh/id_ed25519_2025-10 -p 49152 debian@IPVPS
Maintain both keys for 24–72 hours to ensure seamless operational continuity.
4) Revocation — Retiring the Old Key
Remove the previous key entry using its label comment.
# Remove key by label match
ssh -p 49152 debian@IPVPS "sed -i.bak '/ pc-hsm-ssh-2025-04$/d' ~/.ssh/authorized_keys"
Repeat across all target hosts. Archive authorized_keys.bak for forensic traceability.
Audit Ledger — Append-Only Record
Maintain a timestamped ledger of key lifecycle operations.
mkdir -p ~/audit && touch ~/audit/ssh-keys-ledger.tsv
printf "%stNEWt%st%sn" "$(date -Iseconds)"
"$(ssh-keygen -lf ~/.ssh/id_ed25519_2025-10.pub | awk '{print $2}')" "pc-hsm-ssh-2025-10"
>> ~/audit/ssh-keys-ledger.tsv
printf "%stREVOKEt%st%sn" "$(date -Iseconds)"
"$(ssh-keygen -lf ~/.ssh/id_ed25519_2025-04.pub | awk '{print $2}')" "pc-hsm-ssh-2025-04"
>> ~/audit/ssh-keys-ledger.tsv
Multi-Host Orchestration Script — Without Third-Party Tools
#!/usr/bin/env bash
set -euo pipefail
PORT=49152
USER=debian
NEWPUB="$HOME/.ssh/id_ed25519_2025-10.pub"
OLD_LABEL="pc-hsm-ssh-2025-04"
while read -r HOST; do
echo "[*] $HOST :: install new key"
scp -P "$PORT" "$NEWPUB" "$USER@$HOST:/tmp/newkey.pub"
ssh -p "$PORT" "$USER@$HOST" '
umask 077
mkdir -p ~/.ssh
touch ~/.ssh/authorized_keys
grep -qxF -f /tmp/newkey.pub ~/.ssh/authorized_keys || cat /tmp/newkey.pub >> ~/.ssh/authorized_keys
rm -f /tmp/newkey.pub
chmod 600 ~/.ssh/authorized_keys
'
done < hosts.txt
echo "[] Validate the new key on all hosts, then retire the old key:"
while read -r HOST; do
echo "[] $HOST :: remove old key by label"
ssh -p "$PORT" "$USER@$HOST" "sed -i.bak '/ ${OLD_LABEL}$/d' ~/.ssh/authorized_keys"
done < hosts.txt
Sovereign Methods for Passphrase or Password Recovery
PassCypher HSM PGP provides several sovereign recovery mechanisms for SSH authentication secrets. Each method follows the zero-clear-key rule and adapts to operational contexts:
-
-
- Encrypted QR Code (GIF/PNG) — Import a passphrase without display. Ideal for printed backups or planned rotations. → Injects directly into secure input fields.
- NFC Retrieval from PassCypher HSM — Contactless recovery from sovereign hardware (EviKey or EviPass). → Automatic encrypted injection through BLE-HID channel.
- Bluetooth or USB Keyboard Emulator (BLE-HID) — AES-128 CBC encrypted keystroke emulation. Works on Linux, macOS, Windows, Android, and iOS, even air-gapped. → Leaves no persistent trace.
- Manual Memory Entry — Expert-only option: direct entry in secure pinentry. → Sovereign if no autocomplete or logging is active.
-
⮞ Recommended Procedure — Restore a Passphrase from a QR Backup
- Open the Recovery interface in PassCypher, preferably offline.
- Import the QR image (GIF/PNG). Decryption runs locally with no network connection.
- Select the usage mode: BLE-HID injection or ephemeral clipboard (auto-clear).
- Validate, then purge clipboard memory. Log the action (timestamp, hash, QR source).
Warning: Never paste a passphrase into editors or terminals. Use only ephemeral, auditable input methods.
Advanced CLI FIFO Example — For Expert Linux Operators
# 1. Create a secure FIFO
mkfifo /tmp/pc_pass.fifo
chmod 600 /tmp/pc_pass.fifo
# 2. Decrypt via FIFO without storing passphrase
gpg --batch --yes --passphrase-fd 0 --decrypt --output ~/.ssh/id_ed25519 ~/.ssh/id_ed25519.key.gpg < /tmp/pc_pass.fifo & # 3. Write the passphrase transiently, then destroy FIFO printf '%s' "THE_PASSPHRASE" > /tmp/pc_pass.fifo
shred -u /tmp/pc_pass.fifo || rm -f /tmp/pc_pass.fifo
CLI Security Notes:
- Never store passphrases in environment variables or shell history.
- Prefer BLE-HID injection via pinentry to avoid process or clipboard exposure.
- Record each recovery event in the audit ledger (key fingerprint, host, operator, timestamp).
Operational Flow — From Generation to Authentication (SSH Key PassCypher HSM PGP)
The operational flow defines how PassCypher Engine, PassCypher HSM PGP, and optionally the PassCypher NFC HSM with its BLE-HID keyboard emulator collaborate to generate, protect, transport, and authenticate an SSH key whose private component remains encrypted and is only unlocked ephemerally in RAM.
This architecture forms the backbone of the sovereign SSH authentication lifecycle.
⮞ One-Line Summary: Generate → protect private key with passphrase → export .pub → securely store encrypted key → inject passphrase (via PassCypher NFC HSM over BLE-HID or manual input) → decrypt in RAM → SSH connect → immediate purge.
Detailed Steps (Flow)
Generation (EviSSH Integrated in PassCypher HSM PGP, Orchestrated by PassCypher Engine)
▸ The user launches PassCypher Engine or the extension → “SSH Key Generator.”
▸ Selects algorithm (ed25519 recommended).
▸ Defines a label and passphrase method (generated by the HSM or user-specified).
▸ Result: key pair → id_ed25519 (OpenSSH private key encrypted with passphrase) + id_ed25519.pub (public key).
▸ EviSSH suggests secure storage (local folder, EviKey, encrypted NAS). No automatic unlock is performed.
Export & Secure Storage
▸ Export only the public key (.pub) to the server (e.g., OVH, Scaleway, etc.).
▸ Store the encrypted private key (OpenSSH PEM block protected by passphrase) securely: on EviKey NFC, encrypted NAS, or USB drive. The file remains encrypted at rest.
Client Preparation Before Use
▸ Copy the encrypted private key to a controlled directory on the client (e.g., ~/secure/id_ed25519).
▸ Optionally, mount a tmpfs to avoid disk persistence during temporary decryption:
sudo mkdir -p /mnt/ssh-tmp && sudo mount -t tmpfs -o mode=700 tmpfs /mnt/ssh-tmp▸ Disable or encrypt swap: sudo swapoff -a.
Passphrase Injection (PassCypher NFC HSM → BLE-HID)
▸ The user triggers passphrase injection by bringing the PassCypher NFC HSM near the smartphone or pairing the BLE-HID if not yet bonded.
▸ Security Note — never allow “Just-Works” pairing. Require Secure Connections (Numeric Comparison or PIN) and enforce bonding.
▸ The BLE channel transmits encrypted packets (AES-128 CBC). The device injects the passphrase as a virtual keyboard input — no manual typing.
Ephemeral Decryption in RAM
▸ The OpenSSH prompt requests the passphrase; PassCypher BLE-HID injects it securely.
▸ The private key decrypts only in volatile memory for immediate use.
▸ The id_ed25519 or id_rsa container remains encrypted and intact.
▸ For temporary files, enforce chmod 600 and avoid disk writes when possible.
SSH Authentication
▸ SSH uses the decrypted key in memory:
ssh -i /path/to/id_ed25519 -p 49152 user@IPVPS▸ Once authenticated, purge the key immediately from memory.
Purge & Post-Usage
▸ If a temporary file was used, delete and unmount it:
shred -u /mnt/ssh-tmp/id_ed25519 || rm -f /mnt/ssh-tmp/id_ed25519
sudo umount /mnt/ssh-tmp▸ Remove SSH agent sessions: ssh-add -D and eval "$(ssh-agent -k)".
▸ Reactivate swap if needed: sudo swapon -a.
Critical Security Points & Recommendations
- Never use “Just-Works” BLE pairing — enforce Secure Connections, numeric verification, and bonding.
- The private key always stays encrypted; only ephemeral RAM decryption occurs.
- ssh-agent extends exposure time — limit lifetime and purge after use.
- Disable swap and prevent core dumps:
sudo swapoff -a,ulimit -c 0. - Enable audit logging for key rotations and passphrase injections.
- Use hardened cryptography: bcrypt or PBKDF2 with strong parameters and AES-256 encryption. Random ≥256-bit passphrases ensure post-quantum-aware resilience.
Quick Command Examples
# Example: temporary RAM decryption
sudo mkdir -p /mnt/ssh-tmp && sudo mount -t tmpfs -o mode=700 tmpfs /mnt/ssh-tmp
cp /media/evikey/id_ed25519 /mnt/ssh-tmp/id_ed25519
ssh -i /mnt/ssh-tmp/id_ed25519 -p 49152 user@vps.example.com
shred -u /mnt/ssh-tmp/id_ed25519 || rm -f /mnt/ssh-tmp/id_ed25519
sudo umount /mnt/ssh-tmp
EviSSH — Integrated Management & Orchestration
EviSSH is not an external utility but an integrated part of PassCypher HSM PGP. It automates SSH key generation, rotation, and management locally while maintaining universal compatibility across Linux, macOS, and Windows. It operates under EviEngine, orchestrating system-level actions with no cloud or third-party dependency — ensuring trusted and sovereign SSH key management.
Main Capabilities
-
-
- SSH Key Generation via Git, directly within the PassCypher HSM PGP interface.
- Automatic Encryption of the private key into an OpenSSH private key format (AES-256 + bcrypt).
- Sovereign Storage on local drives, EviKey NFC HSM, or encrypted NAS devices.
- Simple Rotation: creation, deployment, and revocation without handling plaintext keys.
- Full Interoperability: OpenSSH-compatible keys across all major platforms.
-
Security and Hardware Integration
-
-
- Passphrase Injection via PassCypher NFC HSM using an AES-128 CBC encrypted BLE-HID channel.
- Optional Hardware Storage on EviKey NFC HSM — encrypted containers remain inaccessible without the defined passphrase.
-
Sovereign Use Case — PassCypher HSM PGP × PassCypher NFC HSM & BLE-HID
This scenario illustrates a full sovereign SSH authentication use case across multi-OS and multi-site environments:
- ✓ PassCypher HSM PGP generates and encapsulates SSH pairs inside an OpenSSH AES-256 container hardened with bcrypt.
- ✓ PassCypher NFC HSM stores and secures the sovereign passphrase, enabling encrypted BLE-HID injection on any compatible system.
- ✓ The Bluetooth HID emulator acts as an encrypted virtual keyboard (AES-128 CBC), injecting passphrases locally without manual input — eliminating keylogger risk.
- ✓ Example: an administrator connects to a Debian VPS from macOS or Android by simply tapping the PassCypher NFC HSM. The passphrase is securely injected over BLE-HID and decrypted in RAM only.
- ✓ Operational Benefit: portable, audit-ready, and cloud-independent sovereign SSH authentication across Linux, macOS, Windows, Android, and iOS.
This integration — PassCypher HSM PGP × PassCypher NFC HSM & BLE-HID — embodies Freemindtronic’s zero-clear-key model:
no private key ever exists in plaintext on disk or network, and access requires both the physical HSM and secure BLE pairing.
Key Insights
- PassCypher HSM PGP → zero private key exposure, even temporarily.
- AES-128 BLE-HID injection → neutralizes keyloggers and keyboard injection attacks.
- OpenSSH AES-256 + bcrypt → robust symmetric defense, post-quantum-ready posture.
- Rotation, audit, timestamped ledger → complete traceability of machine identities.
- EviSSH orchestration → multi-HSM sovereign management, no cloud or third-party dependency.
Weak Signals — Emerging Trends in Sovereign SSH Security
⮞ Weak Signals to Watch
- Rapid adoption of BLE-HID workflows across multi-OS DevSecOps environments.
- Early experiments with hardware-accelerated bcrypt KDF inside next-gen HSMs.
- Growth of OpenPGP v6 projects embedding hybrid PQC-ready modules.
- Increasing NIS2/DORA regulatory pressure for mandatory machine-access logging.
- A visible convergence between SSH, FIDO2, and PQC in emerging sovereign access architectures.
What We Haven’t Covered — Beyond SSH Key PassCypher HSM PGP
⧉ Areas Not Covered in This Chronicle
This article focused on sovereign SSH authentication for VPS access and secure key lifecycle management.
However, several advanced topics remain for future deep-dives:
- Direct integration into CI/CD pipelines and automated DevOps flows.
- Upcoming FIDO2 extensions and hybrid post-quantum support.
- Automated BLE security audits on mobile systems.
- Real-time inter-HSM synchronization for distributed infrastructures.
These aspects will be detailed in the upcoming series Tech Fixes & Security Solutions.
FAQ — SSH Key PassCypher HSM PGP
A Hybrid HSM for Sovereign SSH Key Management
PassCypher HSM PGP is a hybrid hardware/software security module by Freemindtronic.
It generates, encrypts, and protects SSH and OpenPGP keys using AES-256 encryption and memory-hardened KDFs (PBKDF2 or bcrypt).
Through its NFC and BLE-HID interfaces, passphrases are injected securely without ever exposing private keys — ensuring a zero-trust and sovereign SSH authentication posture.
Secure Duplication Without Losing Sovereignty
Yes. The encrypted id_ed25519 or id_rsa file can be copied across multiple sovereign media (EviKey NFC, encrypted NAS, printed QR).
It remains unusable without the matching passphrase and KDF — ensuring secure SSH key storage even under physical breach.
Cryptographic Resilience in a PQ-Aware Context
A random ≥256-bit passphrase combined with a hardened KDF and AES-256 encryption provides strong symmetric resistance, even against Grover-based quantum attacks.
However, it does not replace PQC algorithms for asymmetric operations.
This model offers robust, yet transitional, post-quantum-aware SSH security.
Sovereign Recovery Without Cloud Dependency
If the encrypted key file (id_ed25519 or id_rsa) was backed up — via printed QR, EviKey NFC, or encrypted media — it can be restored.
The passphrase injection via PassCypher NFC HSM enables full recovery without external servers or cloud reliance.
Local Use Only — Maintain Zero-Clear-Key Posture
While `ssh-agent` offers convenience, it increases memory exposure.
It’s safer to rely on direct BLE-HID passphrase injection — ensuring ephemeral decryption only in RAM and compliance with zero-clear-key SSH architecture.
Local Operations, Zero Private-Key Export
Yes. Sensitive operations (signing, partial decryption) execute directly inside the HSM engine.
The private key never leaves the secure process, ensuring full hardware-anchored SSH authentication.
Incompatible with Sovereign SSH Key Architecture
Agent forwarding conflicts with the zero-trust SSH access model.
Passphrases and private keys must never transit remotely.
Keep SSH-agent sessions strictly local, favoring hardware injection over forwarding.
Best Practices for Secure BLE Pairing
Even with Secure Connections Only, downgrade risks exist on some platforms.
To mitigate them:
-
-
- Always require numeric-code authentication (6-digit PIN or comparison).
- Enforce bonding and store pairing keys securely (Secure Enclave / Android Keystore).
- Ensure BLE-HID channels use AES-128 CBC encryption.
- Regularly review paired device lists and revoke unused entries.
-
This ensures true end-to-end BLE encryption for sovereign SSH workflows.
Multi-Device Backups with Full Sovereignty
Yes — if the passphrase and KDF remain confidential.
The encrypted key file can reside on EviKey NFC, NAS, USB drive, or printed QR.
This enables secure cold backups with zero cloud exposure.
100% Offline Operation — Full Sovereign Mode
Yes. All operations (generation, encryption, injection, rotation) are performed locally, with no network connection required.
Ideal for air-gapped SSH environments or classified infrastructures.
Recommended SSH Key Lifecycle Management
Key rotation every 6–12 months is recommended for administrative access.
PassCypher automates this through its four-step rotation process — each event logged in the local audit ledger for compliance verification.
Full Interoperability with OpenSSH and Industry Standards
Yes. Keys generated by PassCypher follow OpenSSH format standards.
They can be used in PuTTY, Git Bash, Termux, or native OpenSSH clients — maintaining multi-OS SSH key interoperability.
Real-World Key Theft Techniques & Incidents
Several incident reports and security analyses reveal how SSH private keys have been compromised:
-
-
- Malware / Rootkit extraction: Once an attacker achieves code execution or root privileges, they can exfiltrate key files (commonly stored in ~/.ssh). Notable examples include Careto and Windigo malware.
- Memory scraping of ssh-agent: An attacker with root or debugging privileges can dump memory and recover decrypted private keys or agent cache. > “If you can run code as root, it’s game over”
- Accidental public exposure (git commits): A well-known case: a deploy SSH private key got committed via a CI/CD auto-format script.
- Malicious packages stealing credentials: Some npm / PyPI trojan packages have been observed harvesting SSH keys from developers’ workstations. :contentReference
- Fault / side-channel recovery: Researchers recovered SSH private keys from ephemeral computational errors during protocol execution over multiple captures.
- Insider threats or misconfiguration: In compromised SSH host reports, malicious keys added to `authorized_keys` allowed lateral movement.
-
These cases illustrate high-risk attack vectors such as memory dumps, keylogging bypass, supply chain trojans, protocol-level flaws, and insider injection.
Incorporating defense against them is critical for any robust SSH key architecture.
SSH Protocol Weaknesses & Attacks
Yes — recent academic work shows that subtle protocol-level flaws can be exploited:
-
-
- Terrapin Attack (prefix truncation): Allows partial truncation of encrypted SSH packets during handshake, enabling attacker to downgrade public-key authentication or hijack sessions.
- Strict KEX violations: Some SSH server implementations do not enforce the “strict key exchange” mode, making them vulnerable to handshake manipulations or rogue session takeover.
- Weak randomness or biased nonce reuse: In ECDSA or deterministic signature schemes, poorly generated nonces or biases may leak private key bits. A recent study revealed even PuTTY keys became recoverable from just 58 signatures.
-
These attacks underscore the importance of using hardened, current SSH versions, enforcing latest mitigations (strict KEX), and avoiding signature schemes with weak nonce behaviors.
Public Key Theft is Harmless (if private key and passphrase are safe)
No — possessing the public key alone does not enable SSH login. The public key is, by design, meant to be shared.
However, public-key knowledge can aid an attacker in:
-
-
- Performing cryptanalysis or side-channel attacks if private key generation was flawed.
- Launching chosen-ciphertext or protocol downgrade attacks — e.g., leveraging protocol flaws like Terrapin to force weaker algorithms.
-
Therefore, the core protection lies in safeguarding the private key and controlling its exposure.
Memory & Agent Exposure — Key Risk in Conventional SSH
Using `ssh-agent` or unencrypted key caching often increases exposure risk because:
-
-
- The agent stores decrypted keys in memory (RAM), which can be dumped by a local attacker with high privileges.
- Agent forwarding can propagate that risk across hops if an intermediary is compromised.
- Even if the key is encrypted at rest, once loaded into agent, subsequent use is vulnerable.
-
Thus, many advanced architectures avoid persistent agent usage, instead relying on ephemeral decryption and non-forwardable injected secrets.
Supply Chain & Library Backdoor Risks
Yes — indirect attacks via compromised software are a known vector:
-
-
- Backdoored compression library (XZ Utils): In 2024, a malicious backdoor was injected into the `xz` utility which, under specific conditions, could hijack `sshd` authentication to allow remote root compromise.
- Trojanized OSS dependencies: Attackers may infiltrate software libraries used in buildchains or CI/CD to introduce key leakage routines or drift into binaries.
-
To defend, one must enforce supply chain assurance, reproducible builds, binary verification, and minimal trusted dependencies.
Real incidents and evidence
Yes. See documented cases and official reports in the section Documented SSH / Credential Breaches.
Glossary — SSH Key PassCypher HSM PGP
SSH Key Pair
A cryptographic identity composed of a public and a private key. PassCypher generates them locally using Ed25519, ECDSA, or RSA.
The private key is encrypted directly by OpenSSH using a passphrase (bcrypt KDF + AES-256), while the public key is exported in OpenSSH format for use in authorized_keys or administrators_authorized_keys.
Authorized Keys
OpenSSH file used to validate public keys during authentication. On Linux it resides under ~/.ssh/authorized_keys; on Windows, under C:\Users\username\.ssh\. PassCypher supports hardware-based injection into this file.
administrators_authorized_keys
File used by Windows Server 2019 / 2022 / 2025 for administrative SSH access, located in C:\ProgramData\ssh\. It must be protected by NTFS ACLs allowing access only to Administrators and SYSTEM. The SID S-1-5-32-544 corresponds to the Administrators group.
SSH Key Management
Lifecycle of key identities — generation, encryption, injection, rotation, and recovery — performed locally without cloud dependency.
PassCypher manages OpenSSH-encrypted keys and injects passphrases via NFC or BLE-HID hardware channels.
SSH Key Rotation
Lifecycle of SSH credentials (generate → deploy → validate → revoke). Managed by PassCypher’s append-only ledger for full traceability across Ed25519, ECDSA, and RSA formats.
SSH Key Recovery
Sovereign restoration of encrypted SSH keys or passphrases using QR codes, NFC HSM, or BLE-HID injection — without plaintext exposure, fully compatible with OpenSSH workflows.
SSH Key Injection
Hardware-based transmission of encrypted passphrases via BLE-HID or NFC.
Reduces interception risks during authentication, compatible with scp, sftp, and OpenSSH clients across Windows and Linux.
SSH Key Security
Best practices for SSH hardening: AES-256 encryption, bcrypt KDF, local key generation, audit trails, and enforcement of zero-clear-key.
Avoids unsupported directives (AuthorizedKeysCommand) on Windows.
SSH-Agent / ssh-add
Volatile memory service that temporarily caches decrypted keys. PassCypher replaces this with hardware injection and ephemeral decryption, ensuring no keys persist in memory.
ssh-keygen
Standard OpenSSH utility for key generation. PassCypher automates it through its EviEngine, producing OpenSSH-native private keys encrypted by passphrase, and OpenSSH-compatible public keys.
Public Key Authentication
Login mechanism based on asymmetric cryptography.
PassCypher enhances it with hardware-based passphrase delivery, sovereign audit logging, and offline key generation (no OpenSSH passphrase encryption).
Fingerprint
SHA-256 hash uniquely identifying an SSH key. Used for authenticity verification and recorded in PassCypher’s audit ledger. Matches ssh-keygen -lf output.
Tmpfs
RAM-based filesystem used for temporary decryption, ensuring no persistent storage of decrypted keys.
Zero-Clear-Key
Freemindtronic’s sovereign principle: private keys never exist unencrypted on disk or network.
Decryption occurs only in volatile memory (RAM).
Secure VPS Access
Remote server authentication using locally generated and encrypted OpenSSH keys.
Removes the need for SSH agent forwarding, fully offline and cross-platform.
SSH Key Audit Trail
Append-only chronological record of SSH key events — generation, rotation, revocation, recovery — providing local forensic traceability.
ACL (Access Control List)
Windows NTFS security model defining granular file access. PassCypher enforces restrictive ACLs on SSH key files (authorized_keys, administrators_authorized_keys) to align with Microsoft OpenSSH guidelines.
SID (Security Identifier)
Windows internal numeric identifier representing users or groups. The SID S-1-5-32-544 designates the Administrators group. Used by PassCypher to assign access in non-localized systems.
Git for Windows
Windows environment bundling ssh-keygen.exe and OpenSSH utilities. Used by PassCypher to generate SSH key pairs natively and store them in C:\Users\\.ssh\, maintaining compatibility with PowerShell SSH.
PowerShell SSH
Native Windows 11 / Server 2025 module allowing SSH automation through PowerShell. Integrated with PassCypher HSM for secure remote execution while retaining passphrase protection inside hardware.
Sovereign SSH
Freemindtronic’s sovereign model for SSH identity management — local generation, OpenSSH AES-256 encryption, bcrypt KDF, typological key rotation, and auditability, fully cloud-independent and sovereignty-compliant.
Windows Server 2025 / 2022 / 2019
Microsoft server platforms with native OpenSSH integration. PassCypher extends their capabilities with hardware-based passphrase management and OpenSSH-native key encryption for sovereign compliance.
OpenSSH for Windows
Microsoft-integrated implementation of OpenSSH. Fully compatible with PassCypher’s sovereign modules, enhancing key-based authentication via secure BLE-HID/NFC passphrase delivery.
It ensures semantic alignment across the PassCypher, EviKey, and DataShielder ecosystems, supporting technical precision and sovereign consistency within this chronicle.
Strategic Outlook — Toward Post-Quantum Sovereign SSH Authentication
The SSH Key PassCypher HSM PGP framework anticipates the next evolution of secure access: a convergence between hardware sovereignty, quantum-resilient cryptography, and zero-trust architectures. By merging hardware-backed SSH authentication, memory-hardened encryption, and physical key injection, PassCypher bridges classical cryptography with future PQC-hybrid designs.
Future versions will introduce:
-
-
- Hybrid primitives (ed25519 + CRYSTALS-Dilithium) for quantum-safe SSH signatures.
- BLE 5.3 channels with AES-256 GCM encryption.
- Native signed-ledger integration using embedded blockchain audit trails.
-
Until PQC becomes mainstream, the zero-clear-key model remains the strongest defense: never let a private key exist outside encrypted volatile memory.