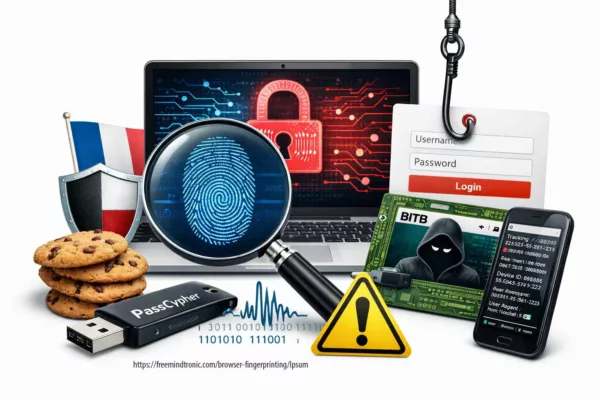
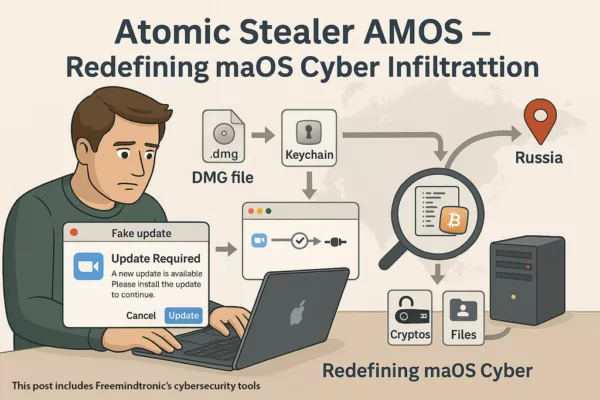
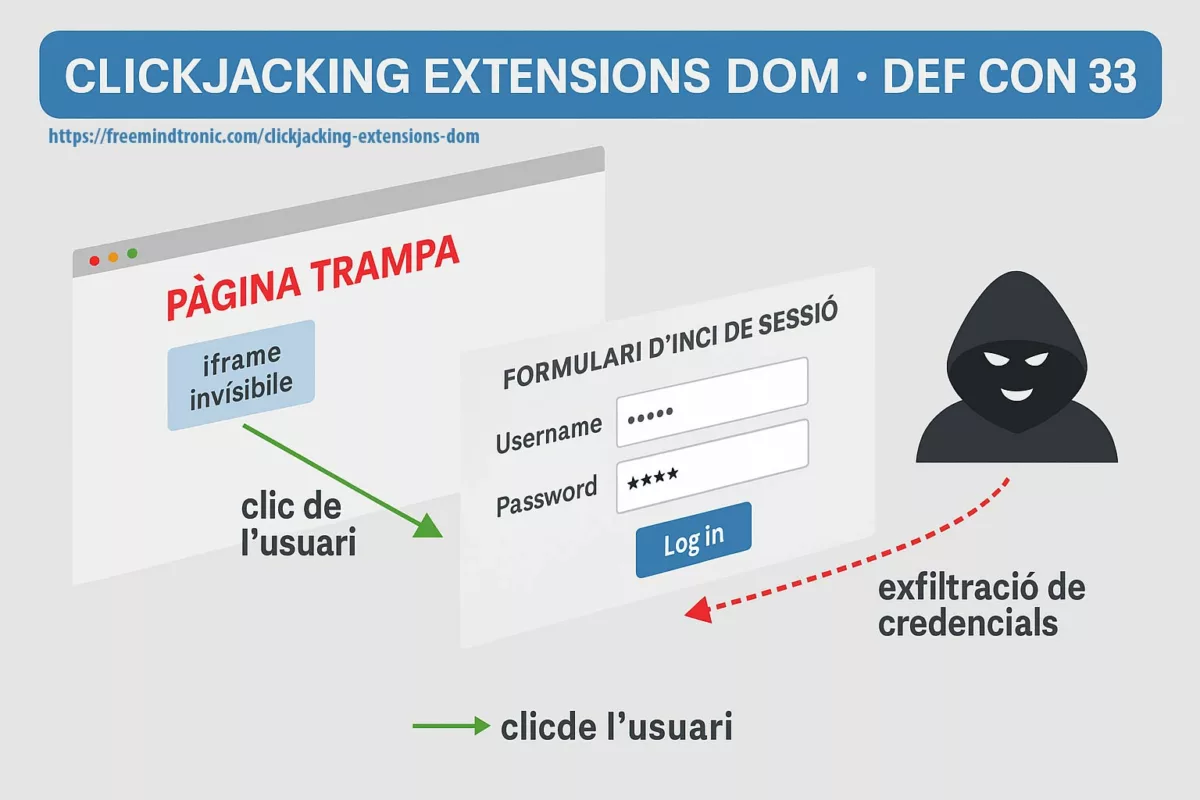
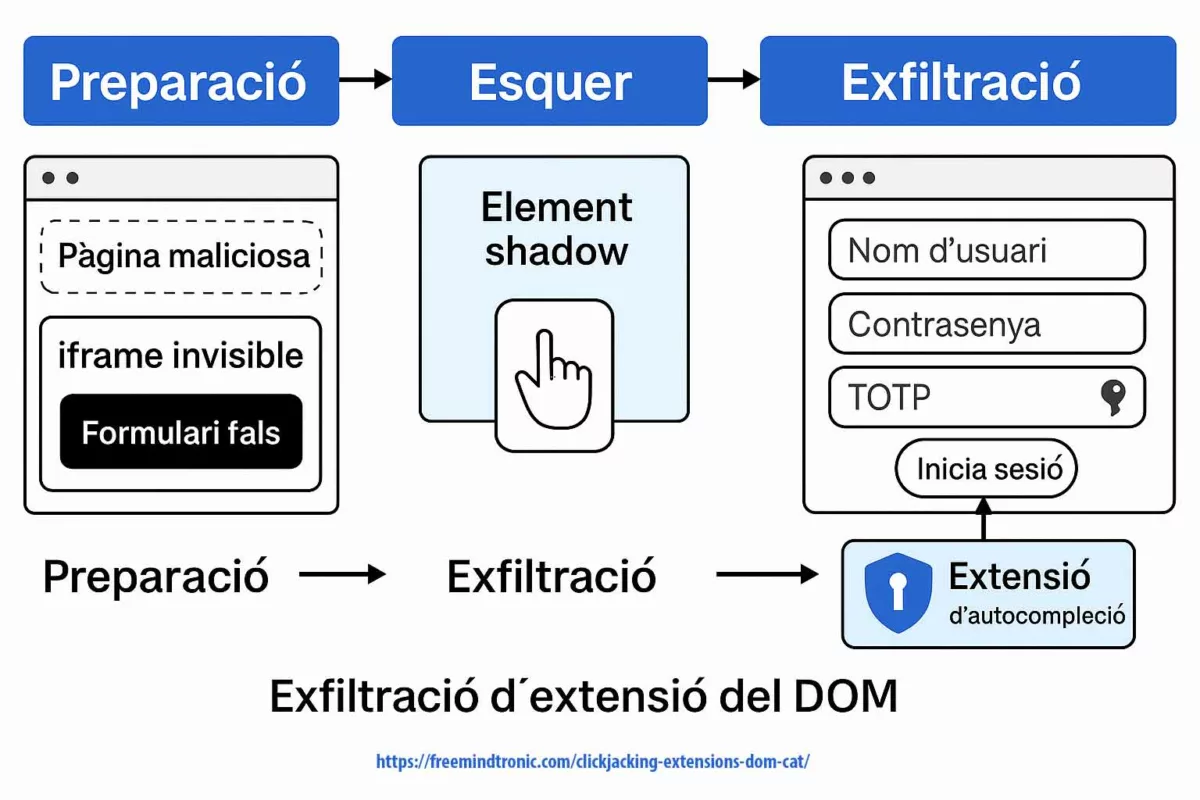
DOM extension clickjacking — a technical chronicle of DEF CON 33 demonstrations, their impact, and Zero-DOM countermeasures. See the Executive Summary below for a 4-minute overview.
Executive Summary — DOM Extension Clickjacking
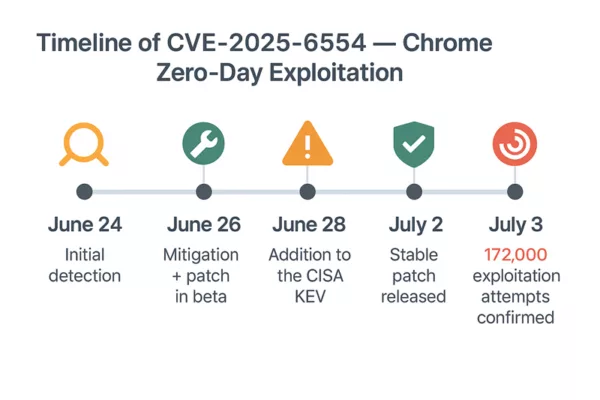
Snapshot (17 Sep 2025):At DEF CON 33, live demos showed DOM-based extension clickjacking and overlay attacks that can exfiltrate credentials, TOTP codes, synced passkeys and crypto keys from browser extensions and wallets. Initial testing reported ~40M exposed installations. Several vendors published mitigations in Aug–Sep 2025 (e.g. Bitwarden, Dashlane, Enpass, NordPass, ProtonPass, RoboForm); others remained reported vulnerable (1Password, LastPass, iCloud Passwords, KeePassXC-Browser). See the status table for per-product details.
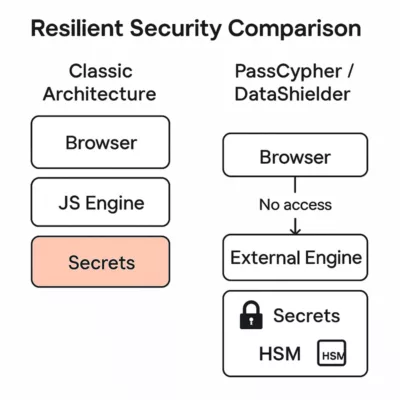
Impact: systemic — secrets that touch the DOM can be covertly exfiltrated; overlays (BITB) make synced passkeys phishable. Recommended mitigation: move to Zero-DOM hardware flows (HSM/NFC) or adopt structural injection re-engineering. See §Sovereign Countermeasures for options.
⚡ The Discovery
Las Vegas, early August 2025. DEF CON 33 takes over the Las Vegas Convention Center. Between hacker domes, IoT villages, Adversary Village, and CTF competitions, the atmosphere turns electric. On stage, Marek Tóth simply plugs in his laptop, launches the demo, and presses Enter.
Immediately, the star attack emerges: DOM extension clickjacking. Easy to code yet devastating to execute, it relies on a booby-trapped page, invisible iframes, and a malicious focus() call. These elements trick autofill managers into pouring credentials, TOTP codes, and passkeys into a phantom form. As a result, DOM-based extension clickjacking surfaces as a structural threat.
⧉ Second Demo — Phishable Passkeys (overlay)
At DEF CON 33, Allthenticate showed that synced passkeys can also be phished through simple overlay and redirection — no DOM injection required.
We cover the full implications in the dedicated section Phishable Passkeys and in attribution & sources. Also worth noting: DEF CON 33 and Black Hat 2025 highlighted another critical demonstration — BitUnlocker — targeting BitLocker via WinRE (see here)
⚠ Strategic Message — Systemic Risks
With just two demos — one targeting password managers and wallets, the other aimed directly at passkeys — two pillars of cybersecurity collapsed. The message is clear: as long as secrets reside in the DOM, they remain vulnerable. Moreover, as long as cybersecurity depends on the browser and the cloud, a single click can overturn everything. As OWASP reminds us, clickjacking has always been a well-known threat. Yet here, the extension layer itself collapses.
⎔ The Sovereign Alternative — Zero-DOM Countermeasures
Fortunately, another way has existed for more than a decade — one that does not rely on the DOM.
With PassCypher HSM PGP, PassCypher NFC HSM, and SeedNFC for hardware backup of cryptographic keys, your credentials, passwords, and TOTP/HOTP secrets never touch the DOM. Instead, they remain encrypted in offline HSMs, securely injected via URL sandboxing or manually entered through the Android NFC application, and always protected by anti-BITB safeguards.
Therefore, this is not a patch, but a patented sovereign passwordless architecture: decentralized, with no server, no central database, and no master password. It frees secret management from centralized dependencies such as FIDO/WebAuthn.
Chronicle to Read
Estimated reading time: 37–39 minutes
Date updated: 2025-10-02
Complexity level: Advanced / Expert
Linguistic specificity: Sovereign lexicon — high technical density
Available languages: CAT ·EN ·ES ·FR
Accessibility: Screen-reader optimized — semantic anchors included
Editorial type: Strategic Chronicle
About the author: Jacques Gascuel, inventor and founder of Freemindtronic®.
As a specialist in sovereign security technologies, he designs and patents hardware systems for data protection, cryptographic sovereignty, and secure communications. His expertise also includes compliance with ANSSI, NIS2, GDPR, and SecNumCloud frameworks, as well as defense against hybrid threats via sovereign-by-design architectures.
Key takeaways —
- DOM injection by extensions enables stealth exfiltration (credentials, TOTP, passkeys, keys).
- Some vendors released mitigations (Aug–Sep 2025); structural fixes are rare.
- Long term: adopt Zero-DOM hardware flows or re-engineer injection logic.
Anatomy of DOM extension clickjacking: a malicious page, hidden iframe, and autofill hijack exfiltrating credentials, passkeys, and crypto-wallet keys.
In sovereign cybersecurity ↑ This chronicle is part of the Digital Security section, continuing our research into exploits, systemic vulnerabilities, and hardware-based zero trust countermeasures.
- Executive Summary
- History of Clickjacking (2002–2025)
- What is DOM-Based Extension Clickjacking?
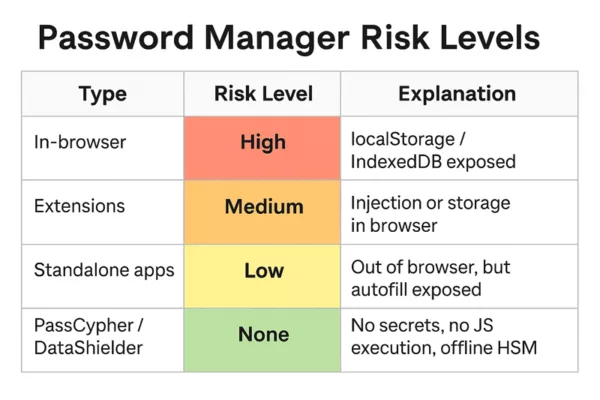
- Vulnerable Password Managers
- Technologies of Correction Used
- Correction Technologies — Technical & Doctrinal Analysis
- Systemic Risks & Exploitation Vectors
- Regional Exposure & Linguistic Impact
- Exposed Crypto Wallet Extensions
- Fallible Sandbox & Browser-in-the-Browser (BITB)
- BitUnlocker — Attacks on BitLocker via WinRE
- Phishable Passkeys — Overlay Attacks at DEF CON 33
- Strategic Signals from DEF CON 33
- Sovereign Countermeasures (Zero DOM)
- PassCypher HSM PGP — Patented Zero-DOM
- PassCypher NFC HSM — Passwordless Sovereign Manager
- SeedNFC + HID Bluetooth — Secure Wallet Injection
- Exploitation Scenarios & Mitigation
- Strategic Synthesis
- Glossary
🚨 DEF CON 33 — Key points
- Two live demos: DOM extension clickjacking (password managers/wallets) and phishable synced passkeys (overlay attacks).
- ~11 managers tested; initial impact estimated at ~40M exposed installations.
- Mitigation direction: fast UI/conditional fixes vs. rare structural Zero-DOM solutions.
- See the status table and §Sovereign Countermeasures for details.
What is DOM-based extension clickjacking?
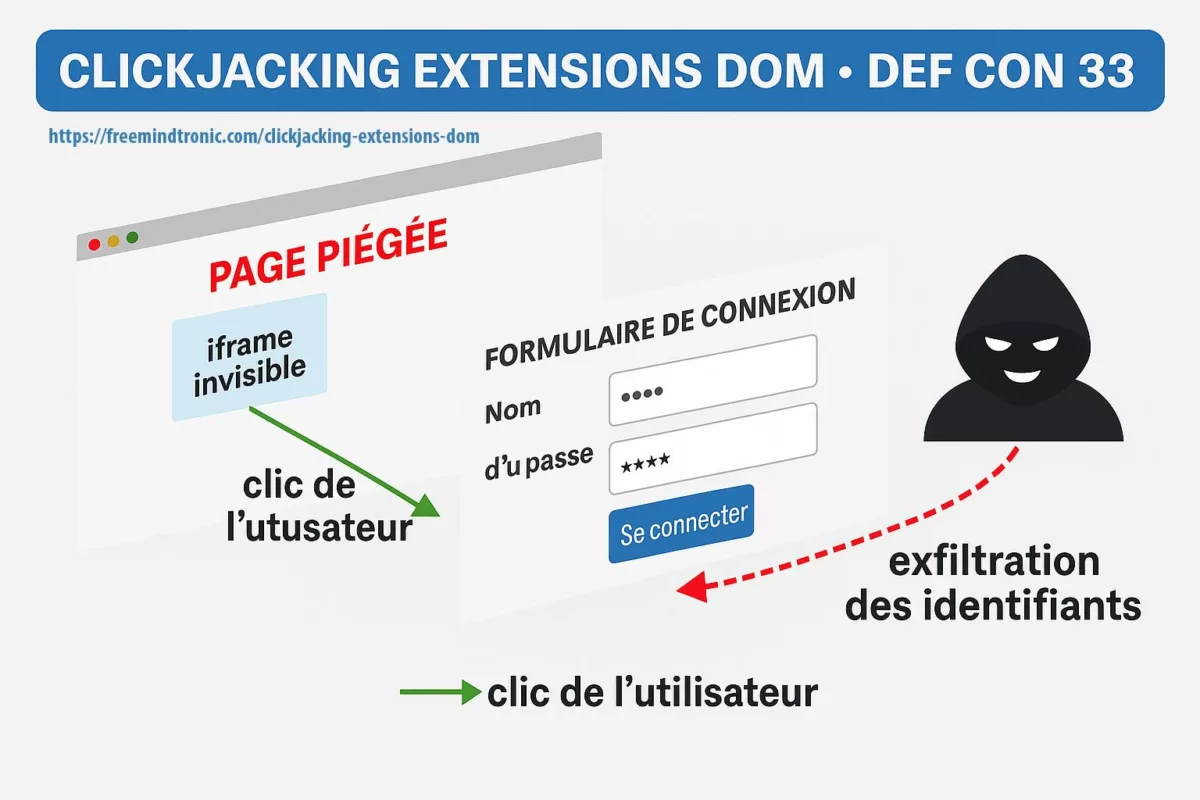
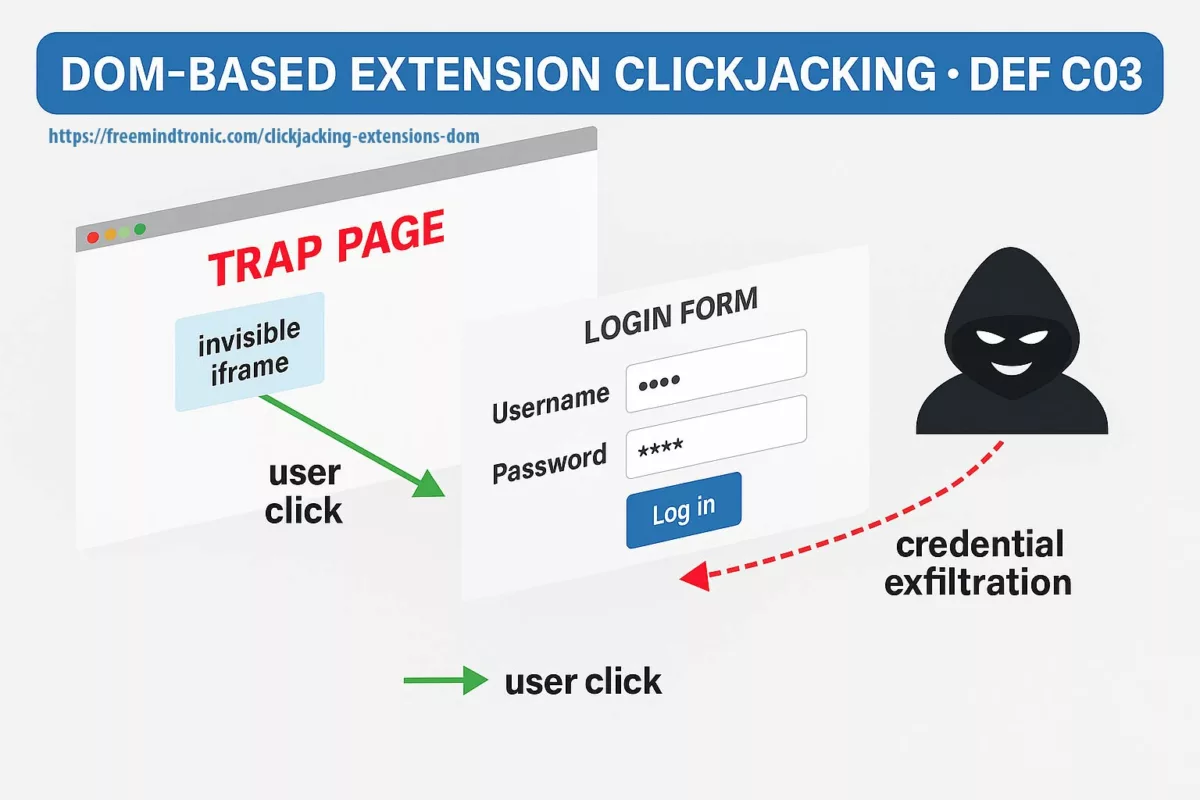
DOM-based extension clickjacking hijacks a browser extension (password manager or crypto wallet) by abusing the browser’s Document Object Model. A deceptive page chains invisible iframes, Shadow DOM and a malicious focus() call to trigger autofill into an invisible form. The extension “believes” it is interacting with a legitimate field and pours secrets there — credentials, TOTP/HOTP codes, passkeys, even private keys. Because these secrets touch the DOM, they can be exfiltrated silently.
How dangerous is it?
This vector is far from minor: it exploits the autofill logic itself and operates without user awareness. The attacker does not merely overlay an element; they force the extension to fill a fake form as if nothing were wrong, making exfiltration undetectable by superficial inspection.
Typical attack flow
- Preparation — the malicious page embeds an
iframethat is invisible and a Shadow DOM that masks the real context; inputs are rendered non-visible (opacity:0,pointer-events:none). - Bait — the victim clicks a benign element; redirections and a malicious
focus()redirect the event to an attacker-controlled input. - Exfiltration — the extension believes it is interacting with a legitimate field and automatically injects credentials, TOTP, passkeys or private keys into the fake DOM; the data is immediately exfiltrated.
This mechanism spoofs visual cues, bypasses classic protections (X-Frame-Options, Content-Security-Policy, frame-ancestors) and turns autofill into an invisible data-exfiltration channel. Browser-in-the-Browser (BITB) overlays and Shadow DOM manipulation further increase the risk, making synced passkeys and credentials phishable.
⮞ Summary
The attack combines invisible iframes, Shadow DOM manipulation and focus() redirections to hijack autofill extensions. Secrets are injected into a phantom form, giving the attacker direct access to sensitive data (credentials, TOTP/HOTP, passkeys, private keys). Bottom line: as long as secrets transit the DOM, the attack surface remains open.
History of Clickjacking (2002–2025)
Clickjacking has become the persistent parasite of the modern web. The term emerged in the early 2000s, when Jeremiah Grossman and Robert Hansen described a deceptive scenario: tricking a user into clicking on something they cannot actually see. An optical illusion applied to code, it quickly became a mainstream attack technique (OWASP).
- 2002–2008: Emergence of “UI redressing”: HTML layers + transparent iframes trapping users (Hansen Archive).
- 2009: Facebook falls victim to Likejacking (OWASP).
- 2010: Cursorjacking emerges — shifting the pointer to mislead user clicks (OWASP).
- 2012–2015: Exploitation via iframes, online ads, and malvertising (MITRE CVE) (Infosec).
- 2016–2019: Tapjacking spreads on mobile platforms (Android Security Bulletin).
- 2020–2024: Rise of “hybrid clickjacking” combining XSS and phishing (OWASP WSTG).
- 2025: At DEF CON 33, Marek Tóth unveils a new level: DOM-Based Extension Clickjacking. This time, not only websites, but browser extensions (password managers, crypto wallets) inject invisible forms, enabling stealth exfiltration of secrets.
At DEF CON 33, Marek Tóth publicly revealed DOM extension clickjacking, marking a structural shift from visual trickery to systemic weakness in password managers and crypto wallets.
❓How long have you been exposed?
Clickjacking and invisible iframes have been known for years; Shadow DOM usage is not new. The DEF CON 33 findings reveal a decade-old design pattern: extensions that trust the DOM for secret injection are inherently exposed.
In just 20 years, clickjacking evolved from a simple visual trick into a systemic sabotage of identity managers. DEF CON 33 marks a breaking point: the threat is no longer just malicious websites, but the very core of browser extensions and autofill. Hence the urgency of Zero-DOM approaches anchored in sovereign hardware like PassCypher.
Vulnerable Password Managers & CVE disclosure (snapshot — 2 Oct 2025)
Updated: 2 October 2025
Following Marek Tóth’s disclosure at DEF CON 33, several vendors have issued patches or mitigations, but response times vary widely. The new column indicates the estimated time between the presentation (8 August 2025) and the release of a patch/mitigation.
| Manager | Credentials | TOTP | Passkeys | Status | Official patch / note | ⏱️ Patch delay |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1Password | Yes | Yes | Yes | Mitigations (v8.11.x) | Blog | 🟠 >6 weeks (mitigation) |
| Bitwarden | Yes | Yes | Partial | Patched (v2025.8.2) | Release | 🟢 ~4 weeks |
| Dashlane | Yes | Yes | Yes | Patched | Advisory | 🟢 ~3 weeks |
| LastPass | Yes | Yes | Yes | Patched (Sep 2025) | Release | 🟠 ~6 weeks |
| Enpass | Yes | Yes | Yes | Patched (v6.11.6) | Release | 🟠 ~5 weeks |
| iCloud Passwords | Yes | No | Yes | Vulnerable (under review) | – | 🔴 >7 weeks (no patch) |
| LogMeOnce | Yes | No | Yes | Patched (v7.12.7) | Release | 🟢 ~4 weeks |
| NordPass | Yes | Yes | Partial | Patched (mitigations) | Release | 🟠 ~5 weeks |
| ProtonPass | Yes | Yes | Partial | Patched (mitigations) | Releases | 🟠 ~5 weeks |
| RoboForm | Yes | Yes | Yes | Patched | Update | 🟢 ~4 weeks |
| Keeper | Partial | No | No | Partial patch (v17.2.0) | Release | 🟠 ~6 weeks (partial) |
⮞ Key insight:
Even after patches, the problem remains architectural: as long as secrets transit the DOM, they remain exposed.
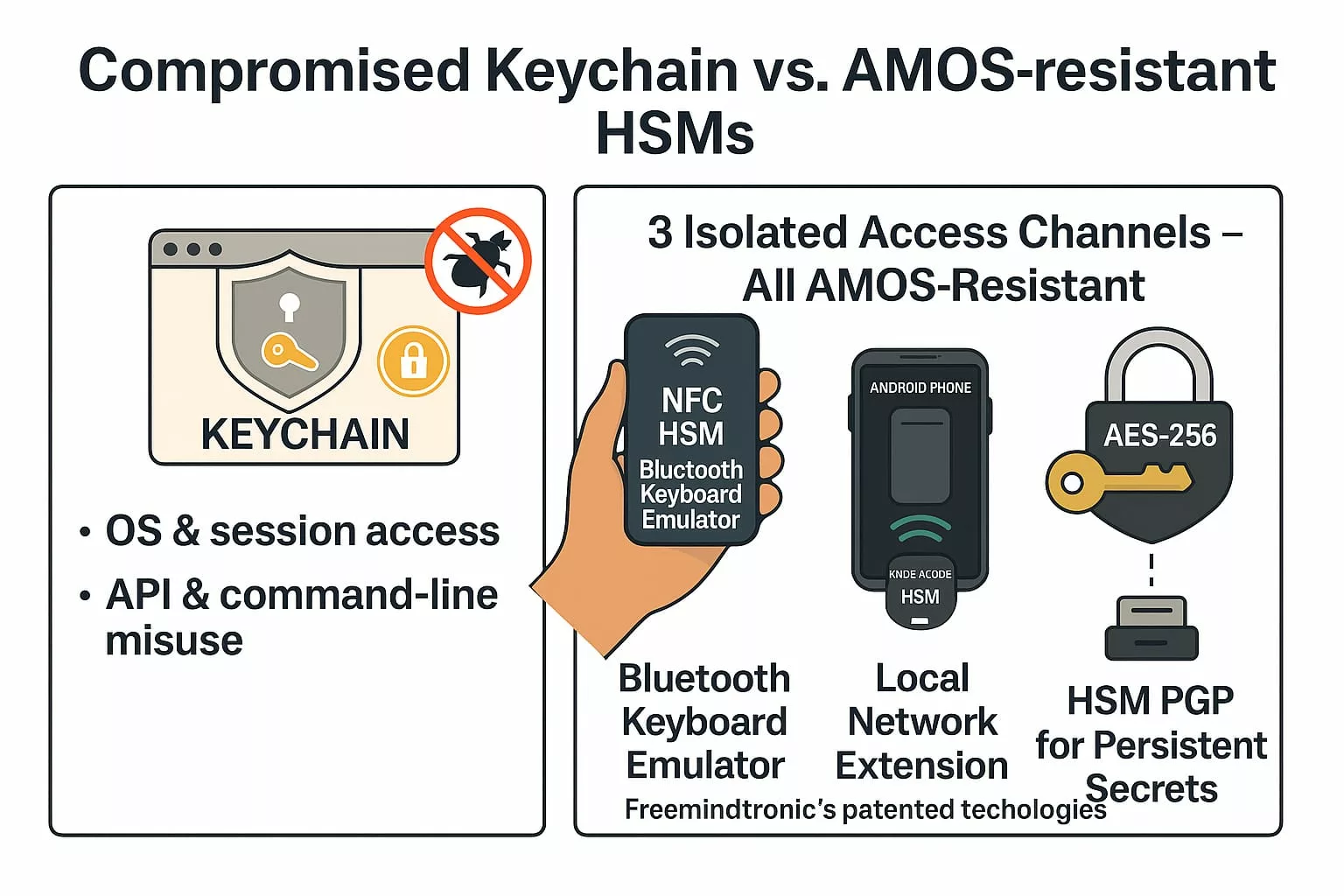
Zero-DOM solutions (PassCypher HSM PGP, PassCypher NFC HSM, SeedNFC) eliminate the attack surface by ensuring secrets never leave their encrypted container.
Zero-DOM = zero attack surface.
Technologies of Correction Used
Since the public disclosure of DOM Extension Clickjacking at DEF CON 33, vendors have rushed to release patches. Yet these fixes remain uneven, mostly limited to UI adjustments or conditional checks. No vendor has yet re-engineered the injection engine itself.
Before diving into the correction methods, here’s a visual overview of the main technologies vendors have deployed to mitigate DOM Extension Clickjacking. This image outlines the spectrum from cosmetic patches to sovereign Zero-DOM solutions.

Objective
This section explains how vendors attempted to fix the flaw, distinguishes cosmetic patches from structural corrections, and highlights sovereign Zero-DOM hardware approaches.
Correction Methods Observed (as of August 2025)
| Method | Description | Affected Managers |
|---|---|---|
| Autofill Restriction | Switch to “on-click” mode or default deactivation | Bitwarden, Dashlane, Keeper |
| Subdomain Filtering | Blocking autofill on non-authorized subdomains | ProtonPass, RoboForm |
| Shadow DOM Detection | Refusal to inject if the field is encapsulated inside Shadow DOM | NordPass, Enpass |
| Contextual Isolation | Checks before injection (iframe, opacity, focus) | Bitwarden, ProtonPass |
| Hardware Sovereign (Zero DOM) | Secrets never transit through the DOM: NFC HSM, HSM PGP, SeedNFC | PassCypher, EviKey, SeedNFC (non-vulnerable by design) |
📉 Limits Observed
- Patches did not change the injection engine, only its activation triggers.
- No vendor introduced a structural separation between UI and secret flows.
- Any manager still tied to the DOM remains structurally exposed to clickjacking variants.
These patches show reaction, not rupture. They address symptoms, not the structural flaw.
To understand what separates a temporary patch from a doctrinal fix, let’s move to the next analysis.
Correction Technologies Against DOM Extension Clickjacking — Technical & Doctrinal Analysis
DOM extension clickjacking is a structural design flaw: secrets injected into a manipulable DOM can be hijacked unless the injection flow is architecturally separated from the browser.
What Current Fixes Do Not Address
- No vendor has rebuilt its injection engine.
- Fixes mostly limit activation (disable autofill, subdomain filters, detect some invisible elements) rather than change the injection model.
What a Structural Fix Would Require
- Remove dependency on the DOM for secret injection.
- Isolate the injection engine outside the browser (hardware or separate secure process).
- Use hardware authentication (NFC, PGP, secure enclave) and require explicit physical/user validation.
- Forbid interaction with invisible or encapsulated elements by design.
Typology of Fixes
| Level | Correction Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Cosmetic | UI/UX, autofill disabled by default | No change to injection logic, only its trigger |
| Contextual | DOM filtering, Shadow DOM, subdomains | Adds conditions, but still relies on the DOM |
| Structural | Zero DOM, hardware-based (PGP, NFC, HSM) | Eliminates DOM use for secrets, separates UI and secret flows |
Doctrinal Tests to Verify Patches
To check whether a vendor’s fix is structural, researchers can:
- Inject an invisible field (
opacity:0) inside an iframe and verify injection behavior. - Check whether extensions still inject secrets into encapsulated or non-visible inputs.
- Verify whether autofill actions are auditable or blocked when context mismatches occur.
There is currently no widely adopted industry standard (NIST/OWASP/ISO) governing extension injection logic, separation of UI and secret flows, or traceability of autofill actions.
Current fixes are largely stopgaps. The durable solution is architectural: remove secrets from the DOM using Zero-DOM patterns and hardware-backed isolation (HSM/NFC/PGP), rather than piling UI patches on top of a flawed injection model.
Systemic Risks & Exploitation Vectors
DOM extension clickjacking is not an isolated bug but a systemic design flaw. When an extension’s injection flow is compromised, the impact goes well beyond a single leaked password: it can cascade through authentication layers and core infrastructure.
Critical scenarios
- Persistent access — cloned TOTP or recovered session tokens can re-register “trusted” devices and preserve access after resets.
- Passkey replay — an exfiltrated passkey can act as a reusable master token outside normal control boundaries.
- SSO compromise — leaked OAuth/SAML tokens from an enterprise extension can expose entire IT systems.
- Supply-chain exposure — weak or malicious extensions create a structural browser-level attack surface.
- Crypto-asset theft — wallet extensions that rely on DOM injection can leak seed phrases, private keys, or sign malicious transactions.
⮞ Summary
The consequences reach far beyond credential theft: cloned TOTPs, replayed passkeys, compromised SSO tokens and exfiltrated seed phrases are all realistic outcomes. As long as secrets transit the DOM, they remain an exfiltration vector.
Sovereign threat comparison
| Attack | Target | Secrets | Sovereign countermeasure |
|---|---|---|---|
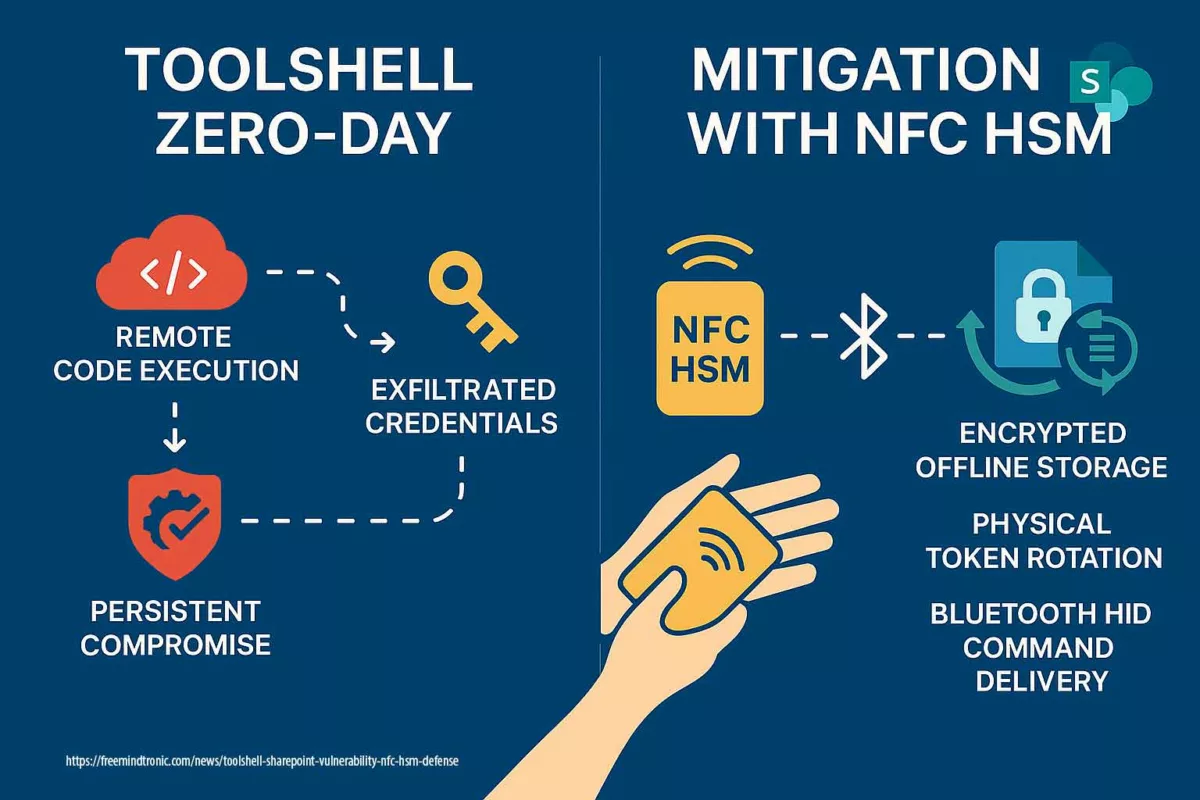
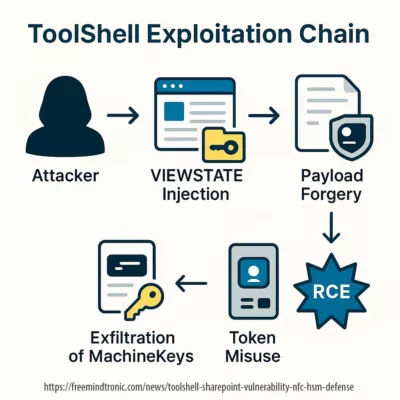
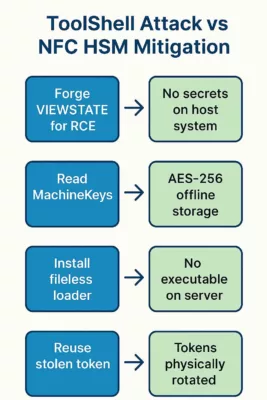
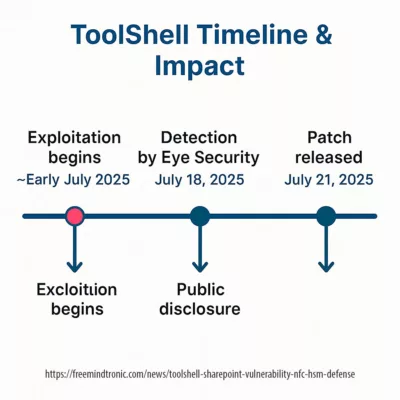
| ToolShell RCE | SharePoint / OAuth | SSL certs, SSO tokens | Hardware-backed storage & signing (HSM/PGP) |
| eSIM hijack | Mobile identity | Carrier profiles | Hardware anchoring (SeedNFC) |
| DOM clickjacking | Browser extensions | Credentials, TOTP, passkeys | Zero-DOM + HSM / sandboxed autofill |
| Crypto-wallet hijack | Wallet extensions | Private keys, seed phrases | HID/NFC injection from HSM (no DOM, no clipboard) |
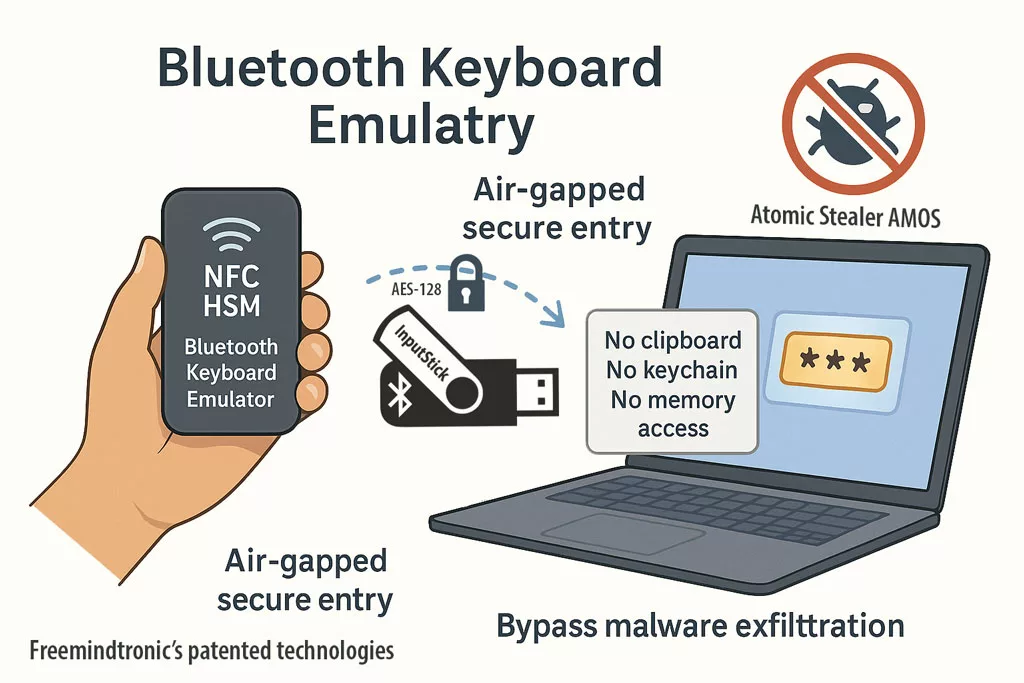
| Atomic Stealer | macOS clipboard | PGP keys, wallet data | Encrypted channels + HSM input (no clipboard) |
Regional Exposure & Linguistic Impact — Anglophone World
| Region | Estimated Anglophone Users | Password-Manager Adoption | Sovereign Zero-DOM Countermeasures |
|---|---|---|---|
| Global English-speakers | ≈1.5 billion users | Strong (North America, UK, Australia) | PassCypher HSM PGP, SeedNFC |
| North America (USA + Canada Anglophone) | ≈94 million users (36 % of US adults) | Growing awareness; still low uptake | PassCypher HSM PGP, NFC HSM |
| United Kingdom | High internet and crypto-wallet penetration | Maturing adoption; rising regulations | PassCypher HSM PGP, EviBITB |
Strategic insight: the Anglophone sphere represents a large exposure surface; prioritize Zero-DOM, hardware-anchored mitigations in regional roadmaps. Sources: ICLS, Security.org, DataReportal.
Exposed Crypto Wallet Extensions
Crypto wallet extensions (MetaMask, Phantom, TrustWallet) often rely on DOM interactions; overlays or invisible iframes can trick users into signing malicious transactions or exposing seed phrases. See §Sovereign Countermeasures for hardware mitigations.
SeedNFC HSM — hardware mitigation (concise)
Sovereign countermeasure: SeedNFC HSM provides hardware-backed storage for private keys and seed phrases kept outside the DOM. Injection is performed via secure NFC↔HID BLE channels and requires a physical user trigger, preventing DOM redressing and overlay-based signing attacks. See the full SeedNFC technical subsection for implementation details and usage flows.
Fallible Sandbox & Browser-in-the-Browser (BITB)
Browsers present their sandbox as a strong boundary — but DOM extension clickjacking and Browser-in-the-Browser (BITB) attacks show that UI-level illusions can still deceive users. A fake authentication frame or overlay can impersonate a trusted provider (Google, Microsoft, banks) and cause users to approve actions that release secrets or sign transactions. Standard directives such as frame-ancestors or some CSP rules do not necessarily block these interface forgeries.
Sandbox URL mechanism (technical): a robust Zero-DOM approach binds each credential or cryptographic reference to an expected URL (the “sandbox URL”) stored inside an encrypted HSM. Before any autofill or signing operation, the active page URL is compared to the HSM reference. If the URLs do not match, the secret is not released. This URL-level validation prevents exfiltration even when overlays or hidden frames evade visual detection.
Anti-iframe detection & mitigation (technical): real-time defenses inspect and neutralize suspicious iframe/overlay patterns (e.g., invisible elements, nested Shadow DOM, anomalous focus() sequences, unexpected pointer-events overrides). Detection heuristics include opacity, stacking context, focus redirections, and iframe ancestry checks; mitigation can remove or isolate the forged UI before any user interaction is processed.
For desktop flows, secure pairing between an Android NFC device and an HSM-enabled application allows secrets to be decrypted only in volatile RAM for a fraction of a second and injected outside the browser DOM, reducing persistence and exposure on the host system.
⮞ Technical Summary (attack defeated by sandbox URL + iframe neutralization)
The DOM extension clickjacking chain typically uses invisible CSS overlays (opacity:0, pointer-events:none), embedded iframes and encapsulated Shadow DOM nodes. By chaining focus() calls and cursor tracking, an extension may be tricked into autofilling credentials or signing transactions into attacker-controlled fields that are immediately exfiltrated. URL-based sandboxing plus real-time iframe neutralization closes this vector.

✪ Illustration – Sandbox URL and iframe-neutralization protect credentials from clickjacking-trapped login forms.
⮞ Practical referenceFor a practical Zero-DOM implementation and product-level details (antiframe tooling, HSM URL binding and desktop pairing), see §PassCypher HSM PGP and §Sovereign Countermeasures.
BitUnlocker — Attaque sur BitLocker via WinRE
At DEF CON 33 and Black Hat USA 2025, the research team STORM presented a critical attack against BitLocker called BitUnlocker. This technique bypasses BitLocker protections by exploiting logical weaknesses in the Windows Recovery Environment (WinRE).
Attack vectors
- boot.sdi parsing — manipulation of the boot loading process
- ReAgent.xml — modification of the recovery configuration file
- Tampered BCD — exploitation of Boot Configuration Data settings
Methodology
The researchers targeted the boot chain and its recovery components to:
- Identify logical vulnerabilities in WinRE;
- Develop exploits capable of exfiltrating BitLocker secrets;
- Propose countermeasures to reinforce BitLocker and WinRE security.
Strategic impact
This attack demonstrates that even encryption systems considered robust can be undermined via indirect vectors — in this case, the Windows recovery chain. It highlights the need for a defense-in-depth approach that protects not only cryptographic primitives but also the integrity of boot and recovery environments.
Phishable Passkeys — Overlay Attacks at DEF CON 33
At DEF CON 33, an independent demonstration showed that synced passkeys — often presented as “phishing-resistant” — can be silently exfiltrated using a simple overlay + redirect. Unlike DOM extension clickjacking, this vector requires no DOM injection: it abuses UI trust and browser-rendered frames to trick users and harvest synced credentials.
How the overlay attack works (summary)
- Overlay / redirect: a fake authentication frame or overlay is shown that mimics a platform login.
- Browser trust abused: the UI appears legitimate, so users approve actions or prompts that release synced passkeys.
- Synced export: once the attacker gains access to the password manager, synced passkeys and credentials can be exported and reused.
Synced vs device-bound — core difference
- Synced passkeys: stored and replicated via cloud/password-manager infrastructure — convenient but a single point of failure and phishable by UI-forgery attacks.
- Device-bound passkeys: stored in a device secure element (hardware) and never leave the device — not subject to cloud-sync export, therefore far more resistant to overlay phishing.
Proofs & evidence
- Allthenticate demonstration and living repository: yourpasskeyisweak.com.
- DEF CON technical slides / research: Passkeys Pwned — DEF CON 33 (PDF).
- Press coverage summarizing the demonstration: MENAFN / PR Newswire.
Phishable Passkeys @ DEF CON 33 — Attribution & Technical Note
Principal Researcher: Dr. Chad Spensky (Allthenticate)
Technical Co-authors: Shourya Pratap Singh, Daniel Seetoh, Jonathan (Jonny) Lin — Passkeys Pwned: Turning WebAuthn Against Itself (DEF CON 33)
Contributors acknowledged: Shortman, Masrt, sails, commandz, thelatesthuman, malarum (intro slide)
References:
Strategic Signals from DEF CON 33
DEF CON 33 crystallised a shift in assumptions about browser security. Key takeaways below are concise and action-oriented.
- Browsers are unreliable trust zones. The DOM should not be treated as a safe place for secrets.
- Synced passkeys & DOM-injected secrets are phishable. UI-forgery and overlay techniques can defeat cloud-synced credentials.
- Vendor responses vary; structural fixes are rare. Quick UI patches help, but few vendors have adopted architectural changes.
- Prioritise hardware Zero-DOM approaches. Offline, hardware-anchored flows reduce exposure and belong in security roadmaps.
Summary
Rather than relying on cosmetic fixes, organisations should plan for doctrinal changes: treat any secret that touches the DOM as suspect and accelerate adoption of hardware-backed, Zero-DOM mitigations in product and policy roadmaps.
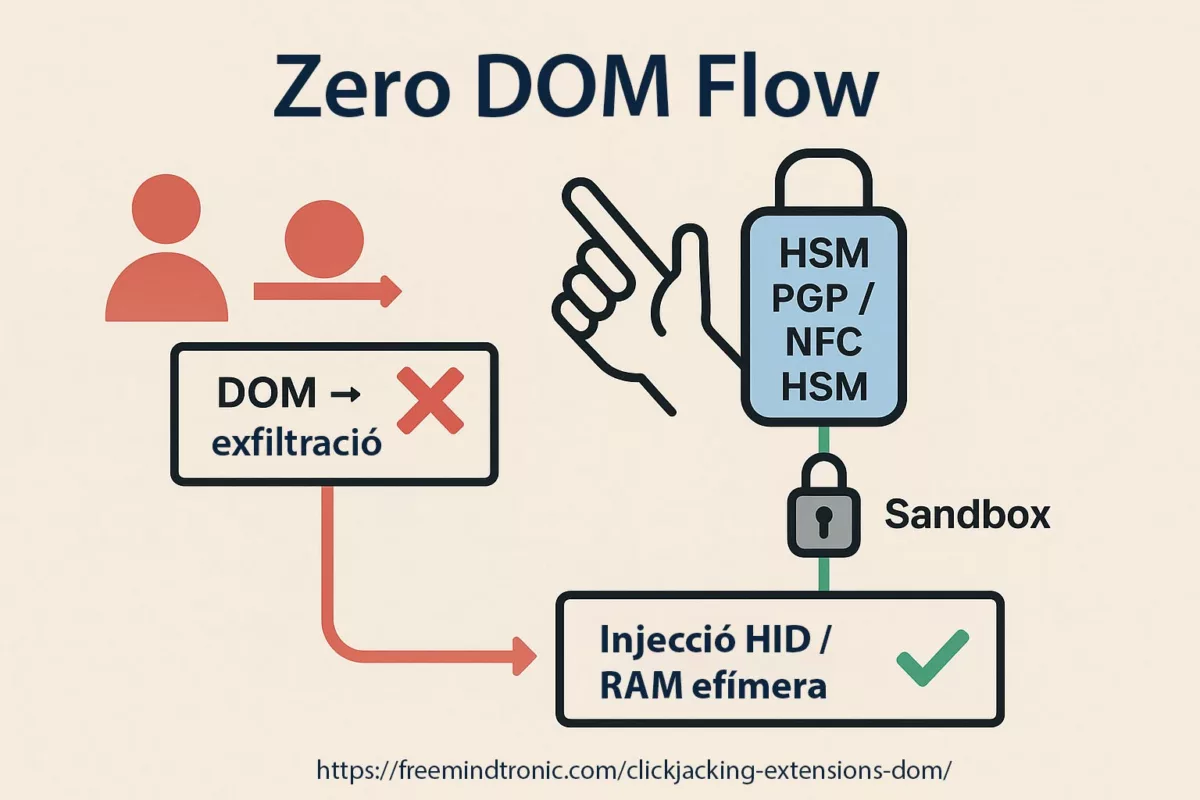
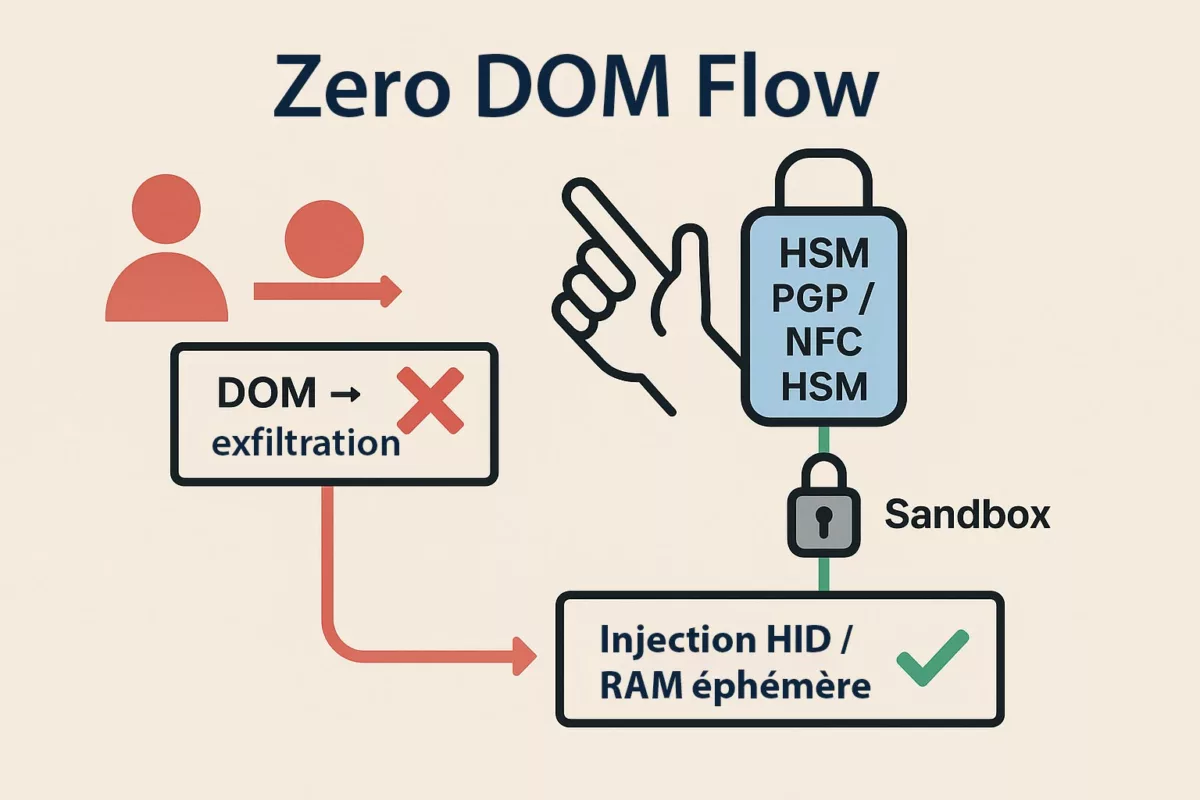
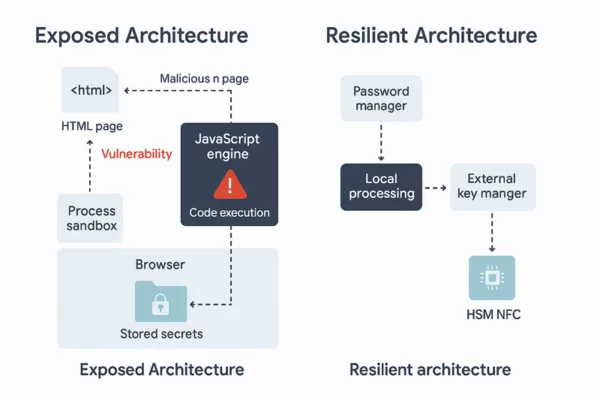
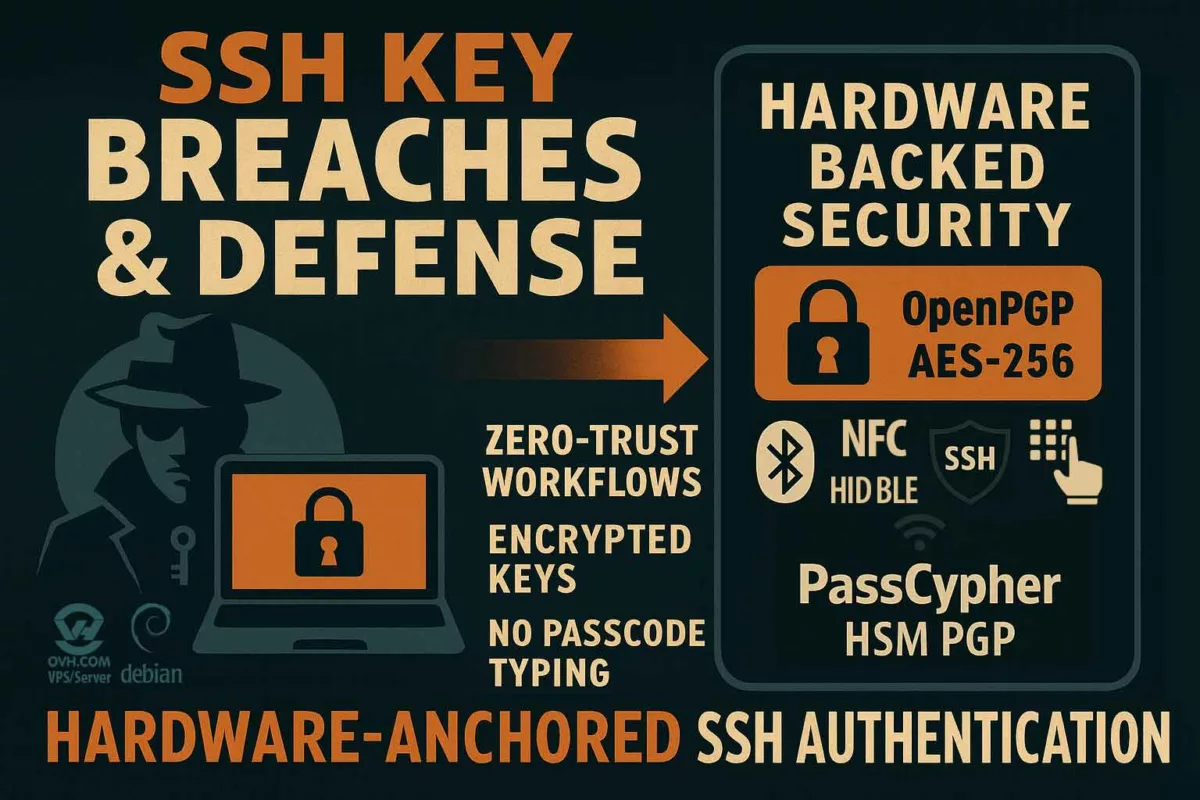
Sovereign Countermeasures (Zero DOM)
Vendor patches can reduce immediate risk but do not remove the root cause: secrets flowing through the DOM. Zero DOM means secrets should never reside in, transit through, or depend on the browser. The durable defence is architectural — keep credentials, TOTP, passkeys and private keys inside offline hardware and only expose them briefly in volatile memory when explicitly activated.
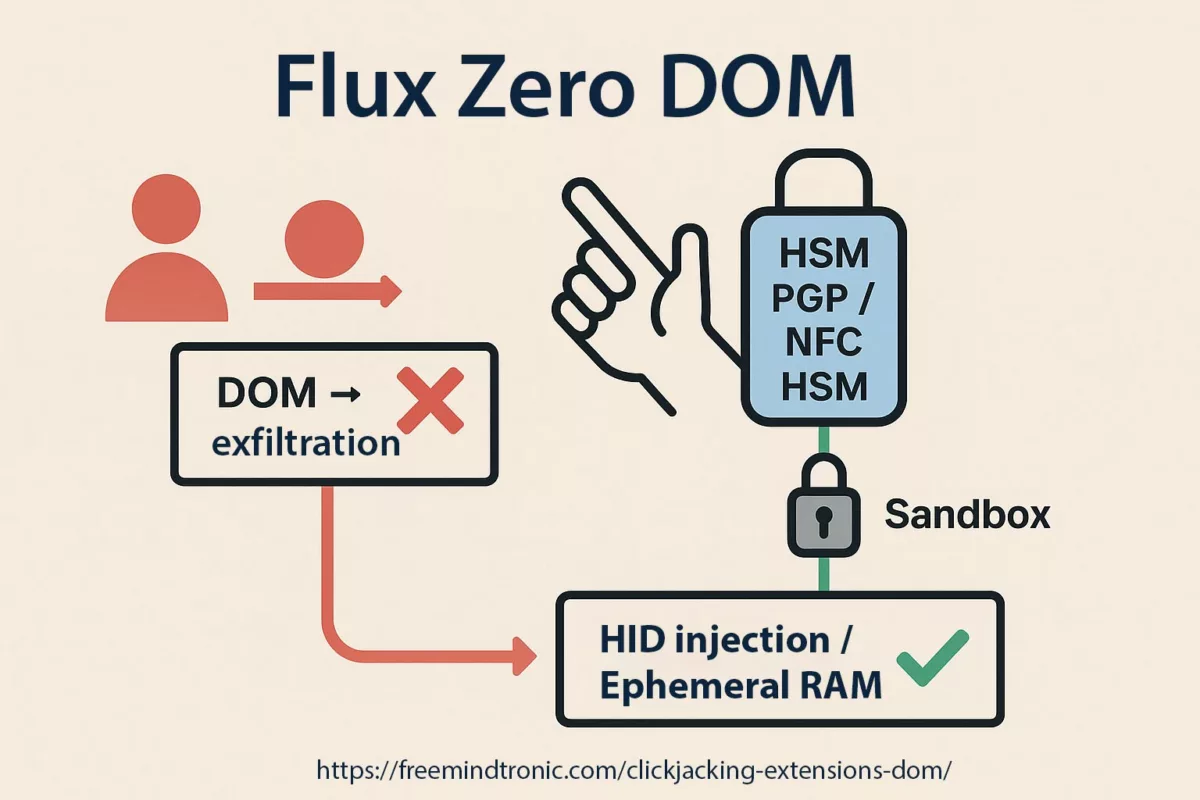
✪ Illustration — Zero DOM Flow: secrets remain inside the HSM, injected via HID into ephemeral RAM, making DOM exfiltration impossible.
In a Zero-DOM design, secrets are stored in offline HSMs and released only after an explicit physical action (NFC tap, HID pairing, local confirmation). Decryption happens in volatile RAM for the minimal time required to fill a field; nothing persists in the DOM or on disk.
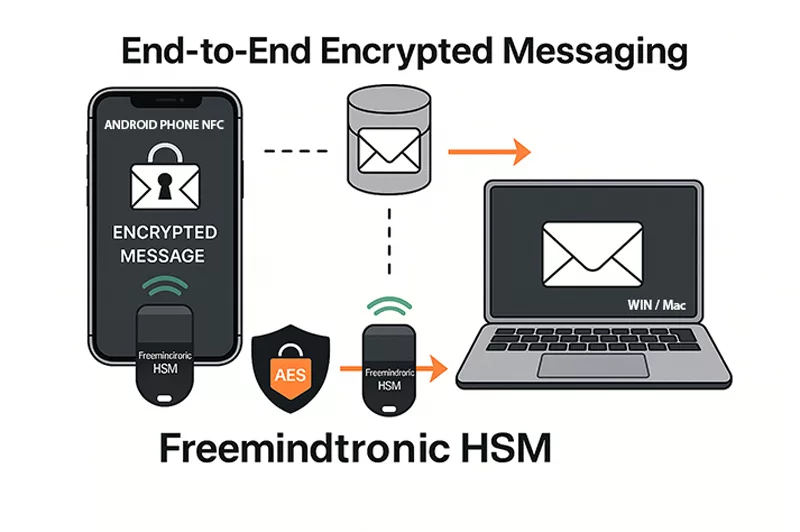
⮞ Sovereign operation: NFC HSM, HID-BLE and HSM-PGP
NFC HSM ↔ Android ↔ Browser: the user physically presents the NFC HSM to an NFC-enabled Android device. The companion app verifies the request from the host, activates the module, and transmits the encrypted secret contactlessly to the host. Decryption occurs only in volatile RAM; the browser never holds the secret in clear.
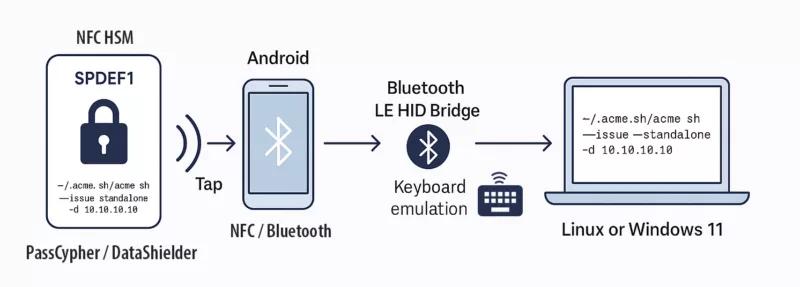
NFC HSM ↔ HID-BLE: when paired with a Bluetooth HID emulator, the system types credentials straight into the target field over an AES-128-CBC encrypted BLE channel, avoiding clipboard, keyboard logging, and DOM exposure.
Local HSM-PGP activation: on desktop, a PassCypher-style HSM-PGP container decrypts locally (AES-256-CBC PGP) into RAM on a single user action. The secret is injected without traversing the DOM and is erased immediately after use.
This architecture removes the injection surface rather than patching it: no central server, no master password to extract, and no persistent cleartext inside the browser. Implementations should combine sandboxed URL checking, minimal ephemeral memory windows, and auditable activation logs to verify each autofill operation.
⮞ Summary
Zero DOM is a structural defence: keep secrets in hardware, require physical activation, decrypt only in RAM, and block any DOM-based injection or exfiltration.
passcypher-hsm-pgp
PassCypher HSM PGP — Patented Zero-DOM Technology & Sovereign Anti-Phishing Key Management
Long before DOM Extension Clickjacking was publicly exposed at DEF CON 33, Freemindtronic adopted a different approach. Since 2015 our R&D has followed a simple founding principle: never use the DOM to carry secrets. That Zero-Trust doctrine produced the patented Zero-DOM architecture behind PassCypher HSM PGP, which keeps credentials, TOTP/HOTP, passkeys and cryptographic keys confined in hardware HSM containers — never injected into a manipulable browser environment.
A unique advance in password managers
- Native Zero-DOM — no sensitive data ever touches the browser.
- Integrated HSM-PGP — AES-256-CBC encrypted containers with patented segmented-key protection.
- Sovereign autonomy — no server, no central database, no cloud dependency.
Reinforced BITB protection (EviBITB)
Since 2020 PassCypher HSM PGP embeds EviBITB, a serverless engine that neutralizes Browser-in-the-Browser (BITB) attacks in real time by detecting and destroying malicious iframes and fraudulent overlays and validating UI context anonymously. EviBITB can operate manually, semi-automatically or fully automatically to drastically reduce BITB and invisible DOM-hijacking risk.
Why it resists DEF CON-style attacks
Nothing ever transits the DOM, there is no master password to extract, and containers remain encrypted at rest. Decryption occurs only in volatile RAM for the brief instant required to assemble key segments; after autofill the data is erased, leaving no exploitable trace.
Key features
- Shielded autofill — single-click autofill via sandboxed URL, never exposed in cleartext in the browser.
- Embedded EviBITB — real-time iframe/overlay neutralization (manual / semi / automatic), fully serverless.
- Integrated crypto tooling — segmented AES-256 key generation and PGP key management without external dependencies.
- Universal compatibility — works with any website via the extension; no additional plugins required.
- Sovereign architecture — zero server, zero central DB, zero DOM; designed to remain resilient where cloud managers fail.
Immediate implementation
No complex setup is required. Install the PassCypher HSM PGP extension from the Chrome Web Store or Edge Add-ons, enable the BITB option, and benefit instantly from Zero-DOM sovereign protection.
⮞ Summary
PassCypher HSM PGP redefines secret management: permanently encrypted containers, segmented keys, ephemeral decryption in RAM, Zero-DOM and zero-cloud. A hardware-centric, passwordless solution engineered to resist current threats and anticipate quantum-era risks.
PassCypher NFC HSM — Sovereign Passwordless Manager
Software password managers fall into the trap of a simple iframe, but PassCypher NFC HSM follows a different path: it never lets your credentials and passwords transit through the DOM. The nano-HSM keeps them encrypted offline and only releases them for a fleeting instant in volatile memory — just long enough to authenticate.
User-side operation:
- Untouchable secrets — the NFC HSM encrypts and stores credentials so they never appear or leak.
- TOTP/HOTP — the PassCypher NFC HSM Android app or the PassCypher HSM PGP on desktop generates and displays them instantly on demand.
- Manual entry — the user enters a PIN or TOTP directly into the login field on a computer or Android NFC phone. The PassCypher app shows the code generated by the NFC HSM module. The same process applies to credentials, passkeys, and other secrets.
- Contactless autofill — the user simply presents the PassCypher NFC HSM module to a smartphone or computer, which executes autofill seamlessly, even when paired with PassCypher HSM PGP.
- Desktop autofill — with PassCypher HSM PGP on Windows or macOS, the user clicks the integrated login field button to auto-complete login and password, with optional auto-validation.
- Distributed anti-BITB — the NFC ↔ Android ↔ browser (Win/Mac/Linux) secure pairing triggers EviBITB to destroy malicious iframes in real time.
- HID BLE mode — a paired Bluetooth HID keyboard emulator injects credentials outside the DOM, blocking both DOM-based attacks and keyloggers.
⮞ Summary
PassCypher NFC HSM embodies Zero Trust (every action requires physical validation) and Zero Knowledge (no secret is ever exposed). A sovereign hardware identity safeguard by design, it neutralizes clickjacking, BITB attacks, typosquatting, keylogging, IDN spoofing, DOM injections, clipboard hijacking, malicious extensions, while anticipating quantum attacks.
✪ Attacks Neutralized by PassCypher NFC HSM
| Attack Type | Description | Status with PassCypher |
|---|---|---|
| Clickjacking / UI Redressing | Invisible iframes or overlays that hijack user clicks | Neutralized (EviBITB) |
| BITB (Browser-in-the-Browser) | Fake browser frames simulating login windows | Neutralized (sandbox + pairing) |
| Keylogging | Keystroke capture by malware | Neutralized (HID BLE mode) |
| Typosquatting | Lookalike URLs mimicking legitimate domains | Neutralized (physical validation) |
| Homograph Attack (IDN spoofing) | Unicode substitution deceiving users on domain names | Neutralized (Zero DOM) |
| DOM Injection / DOM XSS | Malicious scripts injected into the DOM | Neutralized (out-of-DOM architecture) |
| Clipboard Hijacking | Interception or modification of clipboard data | Neutralized (no clipboard usage) |
| Malicious Extensions | Browser compromised by rogue plugins | Neutralized (pairing + sandbox) |
| Quantum Attacks (anticipated) | Massive computation to break crypto keys | Mitigated (segmented keys + AES-256 CBC + PGP) |
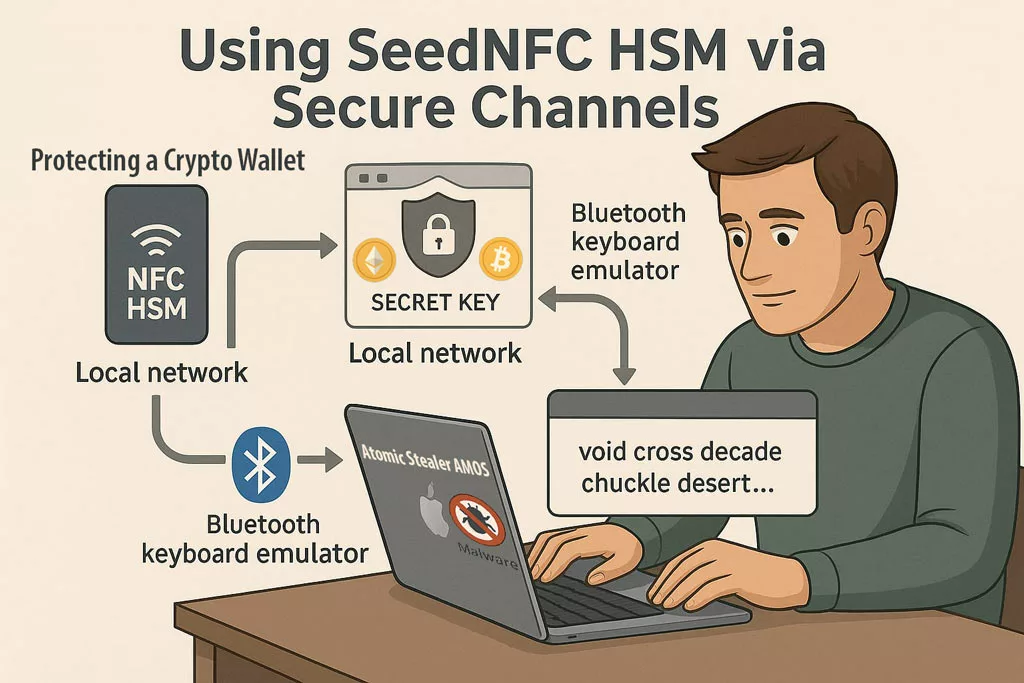
SeedNFC + HID Bluetooth — Secure Wallet Injection
Browser wallet extensions thrive in the DOM — and attackers exploit that weakness. With SeedNFC HSM, the logic flips: the enclave never releases private keys or seed phrases. When users initialize or restore a wallet (web or desktop), the system performs input through a Bluetooth HID emulation — like a hardware keyboard — with no clipboard, no DOM, and no trace for private keys, public keys, or even hot wallet credentials.
Operational flow (anti-DOM, anti-clipboard):
- Custody — the SeedNFC HSM encrypts and stores the seed/private key (never exports it, never reveals it).
- Physical activation — the NFC HSM authorizes the operation when the user presents it contactlessly via the Freemindtronic app (Android NFC smartphone).
- HID BLE injection — the system types the seed (or required fragment/format) directly into the wallet input field, outside the DOM and outside the clipboard, resisting even software keyloggers.
- BITB protection — users can activate EviBITB (anti-BITB iframe destroyer) inside the app, which neutralizes overlays and malicious redirections during onboarding or recovery.
- Ephemerality — volatile RAM temporarily holds the data during HID input, then instantly erases it.
Typical use cases:
- Onboarding or recovery of wallets (MetaMask, Phantom, etc.) without ever exposing the private key to the browser or DOM. The HSM keeps the secret encrypted and decrypts it only in RAM, for the minimal time required.
- Sensitive operations on desktop (logical air-gap), with physical validation by the user: the user presents the NFC HSM module under an Android NFC smartphone to authorize the action, without keyboard interaction or DOM exposure.
- Secure multi-asset backup: an offline hardware HSM stores seed phrases, master keys, and private keys, allowing reuse without copying, exporting, or capturing. Users perform activation exclusively through physical, sovereign, and auditable means.
⮞ Summary
First of all, SeedNFC HSM with HID BLE injects private or public keys directly into hot wallet fields via a Bluetooth Low Energy HID emulator, thereby bypassing both keyboard typing and clipboard transfer. Moreover, the channel encrypts data with AES-128 CBC, while the NFC module physically triggers activation, ensuring a secure and verifiable process.
In addition, users can enable anti-BITB protection to neutralize malicious overlays and deceptive redirections.
Finally, the HSM enclave keeps secrets strictly confined, outside the DOM and beyond the reach of malicious extensions, thus guaranteeing sovereign protection by design.
Exploitation Scenarios & Mitigation Paths
The DEF CON 33 revelations are a warning — threats will evolve beyond simple patches. Key near-term scenarios to watch:
- AI-driven clickjacking: LLMs and automation create realistic, real-time DOM overlays and Shadow-DOM traps at scale — making phishing + DOM hijack far more scalable and convincing.
- Hybrid mobile tapjacking: stacked UI elements, invisible gestures, and background app interactions enable large-scale mobile validation/exfiltration (OTP, transaction approvals).
- Post-quantum HSMs: long-term mitigation requires hardware anchors and quantum-resistant key management — move the security boundary into certified HSMs and out of the browser. See §Sovereign Countermeasures for architectural guidance.
⮞ Summary
Future attackers will bypass browser fixes. Mitigation requires a rupture: offline hardware anchors, post-quantum HSM planning, and Zero-DOM designs rather than incremental software band-aids.
Strategic Synthesis
DOM extension clickjacking shows that browsers and extensions cannot be treated as trusted execution zones for secrets. Patches reduce risk but do not eliminate the structural exposure.
The sovereign path — three priorities
- Governance: treat extensions and autofill engines as critical infrastructure — tighten development controls, mandatory audits, and incident disclosure rules.
- Architectural change: adopt Zero-DOM designs so secrets never transit the browser; require physical activation for sensitive operations.
- Hardware resilience: invest in hardware anchors and post-quantum HSM roadmaps to remove single-point failures in cloud/sync models.
Doctrine — concise
- Consider any secret that touches the DOM as potentially compromised.
- Prefer physical activation (NFC, HID BLE, HSM flows) for high-value operations.
- Audit and regulate extension injection logic as a security-critical function.
Glossary
-
DOM (Document Object Model)
- In-memory representation of a web page’s HTML/JS structure; allows scripts and extensions to access and modify page elements.
-
Shadow DOM
- Encapsulated DOM subtree used to isolate web components; can hide elements from the rest of the document.
-
Clickjacking
- UI redressing technique that tricks users into clicking hidden or overlaid elements.
-
DOM-Based Extension Clickjacking
- Attack variant where a malicious page chains invisible iframes, Shadow DOM and
focus()redirects to coerce an extension into injecting secrets into a fake form. -
Autofill
- Mechanism used by password managers and browser extensions to automatically populate credentials, OTPs or passkeys into web fields.
-
Passkey
- WebAuthn authentication credential (public-key based). Passkeys are phishing-resistant when stored device-bound in a secure element; cloud-synced passkeys are more exposed.
-
WebAuthn / FIDO
- Public-key authentication standard (FIDO2) for passwordless logins; security depends on storage model (synced vs device-bound).
-
TOTP / HOTP
- One-time codes generated by time-based (TOTP) or counter-based (HOTP) algorithms for two-factor authentication.
-
HSM (Hardware Security Module)
- Hardware device that securely generates, stores and uses cryptographic keys without exposing them in cleartext outside the enclave.
-
PGP (Pretty Good Privacy)
- Hybrid encryption standard using public/private keys; here used to protect AES-256-CBC encrypted containers.
-
AES-256 CBC
- Symmetric encryption algorithm (CBC mode) with 256-bit keys — used to encrypt secret containers.
-
Segmented keys
- Key fragmentation approach: keys are split into segments to increase resistance and are assembled securely in ephemeral RAM.
-
Ephemeral RAM
- Volatile memory where secrets are briefly decrypted for an autofill operation and immediately erased — no persistence to disk or DOM.
-
NFC (Near Field Communication)
- Contactless technology used to physically activate an HSM and authorize local secret release.
-
HID-BLE (Bluetooth Low Energy HID)
- BLE keyboard emulation mode to inject data directly into fields without using the DOM or clipboard.
-
Sandbox URL
- Mechanism binding each secret to an expected URL stored inside the HSM; if the active URL does not match, autofill is blocked.
-
Browser-in-the-Browser (BITB)
- Overlay attack that simulates a browser window inside an iframe — tricks users into interacting with a fake authentication frame.
-
EviBITB
- Serverless anti-BITB engine that detects and destroys malicious iframes/overlays in real time and validates UI context anonymously.
-
SeedNFC
- Hardware HSM solution for seed phrase / private key custody; performs out-of-DOM injection via HID/NFC.
-
Iframe
- HTML frame embedding another page; invisible iframes (opacity:0, pointer-events:none) are commonly used in UI redressing attacks.
focus()- JavaScript call that sets focus on a field. Abused to redirect user events to attacker-controlled inputs.
-
Overlay
- Visual layer (fake window/frame) that masks the real interface and deceives the user about the origin of an action.
-
Exfiltration
- Unauthorized extraction of sensitive data from the target (credentials, TOTP, passkeys, private keys).
-
Phishable
- Describes a mechanism (e.g., cloud-synced passkeys) that can be compromised by UI forgery or overlays — therefore vulnerable to phishing.
-
Content-Security-Policy (CSP)
- Web policy controlling resource origins; useful but alone insufficient against advanced clickjacking variants.
-
X-Frame-Options / frame-ancestors
- HTTP headers / CSP directives intended to limit iframe inclusion; can be bypassed in complex attack scenarios.
-
Keylogging
- Malicious capture of keystrokes; mitigated by secure HID injection (no software keyboard or clipboard use).
Note: this glossary standardises terms used in the chronicle. For normative definitions and standards, consult OWASP, NIST and FIDO/WebAuthn specifications.
⮞ Note — What this chronicle does not cover:
This article does not provide exploitable PoCs or step-by-step attack instructions for DOM clickjacking or passkey phishing. It also does not analyse cryptocurrency economics or specific legal cases beyond a strategic security viewpoint.
The objective: explain structural flaws, quantify systemic risks, and outline Zero-DOM hardware countermeasures as the robust mitigation path. For implementation details, see §Sovereign Countermeasures and the product subsections collected there.