Chrome v8 confusion RCE: This edition addresses impacts and guidance relevant to major English-speaking markets — United States, United Kingdom, Canada, Australia and India — with region-specific guidance, compliance pointers and references.
Quick summary
Chrome V8 confusion RCE is a live, exploitable V8 type-confusion that enables drive-by remote code execution. You open a tab and the page looks ordinary; inside V8 one value impersonates another, pointers slip, memory integrity collapses, and a crafted script executes. Google’s Threat Analysis Group confirmed active exploitation. Patches landed on Stable: 140.0.7339.185/.186 (Windows/Mac) and 140.0.7339.185 (Linux); Android: 140.0.7339.155.
🚨 Bottom line — update now. Treat the browser as a hostile runtime. Separate sensitive tasks from everyday browsing. Adopt a Zero-DOM posture — install PassCypher HSM (free PGP) and enable the anti-“BITB” feature.
Recommended read
Summary read time: 3–4 minutes
Estimated full read: 36–38 minutes
Last updated: 2025-09-19
Complexity: Advanced / Expert
Linguistic note: Sovereign lexicon — high technical density
Technical density: high ≈ 72%
Languages: CAT · EN · ES · FR
Accessibility: Screen-reader optimized — semantic anchors included
Editorial type: Strategic column (narrative)
About the author: Jacques Gascuel, inventor and founder of Freemindtronic®.
Key points
- One page is enough: drive-by RCE via V8 type confusion.
- Exploitation confirmed at time of patch release.
- Patched versions: 140.0.7339.185/.186 (Win/Mac) · 140.0.7339.185 (Linux) · Android 140.0.7339.155.
- Sovereign reflex: isolate critical use, reduce browser trust, adopt hardware Zero-DOM flows (HSM/NFC).
Got three minutes? Read the extended summary: how compromise becomes routine.
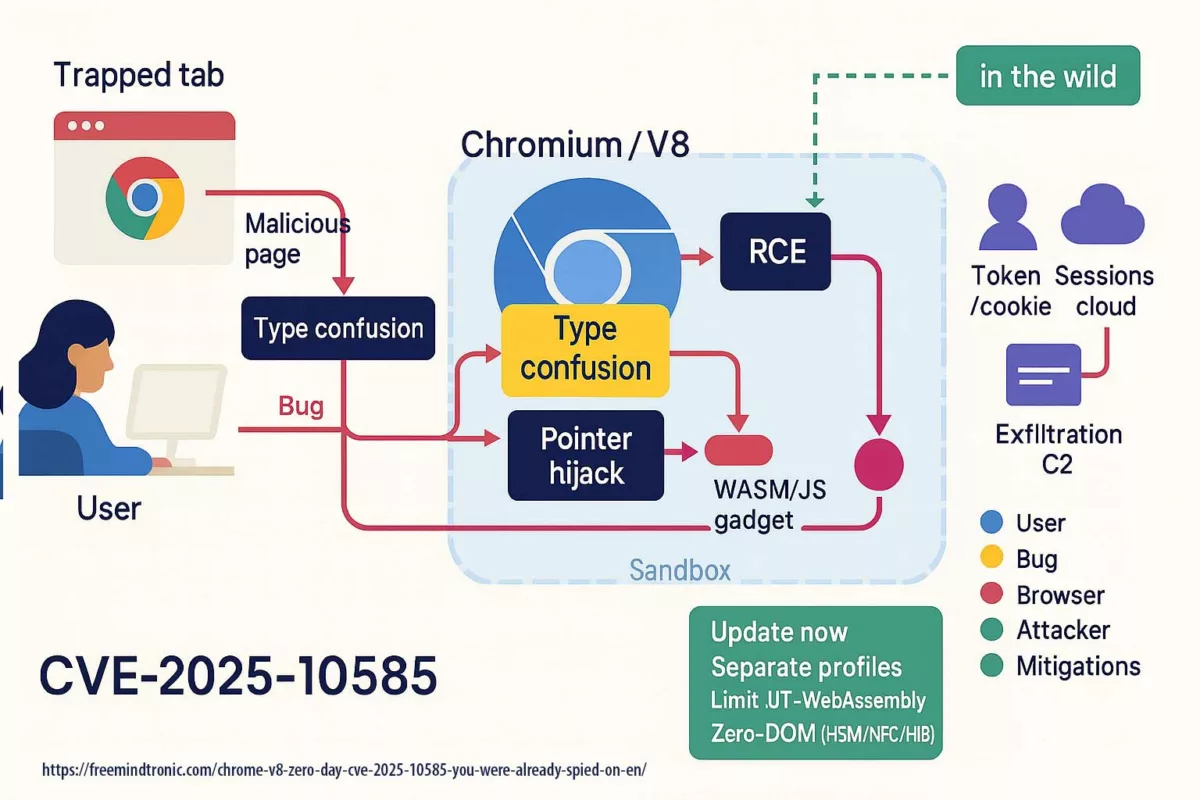
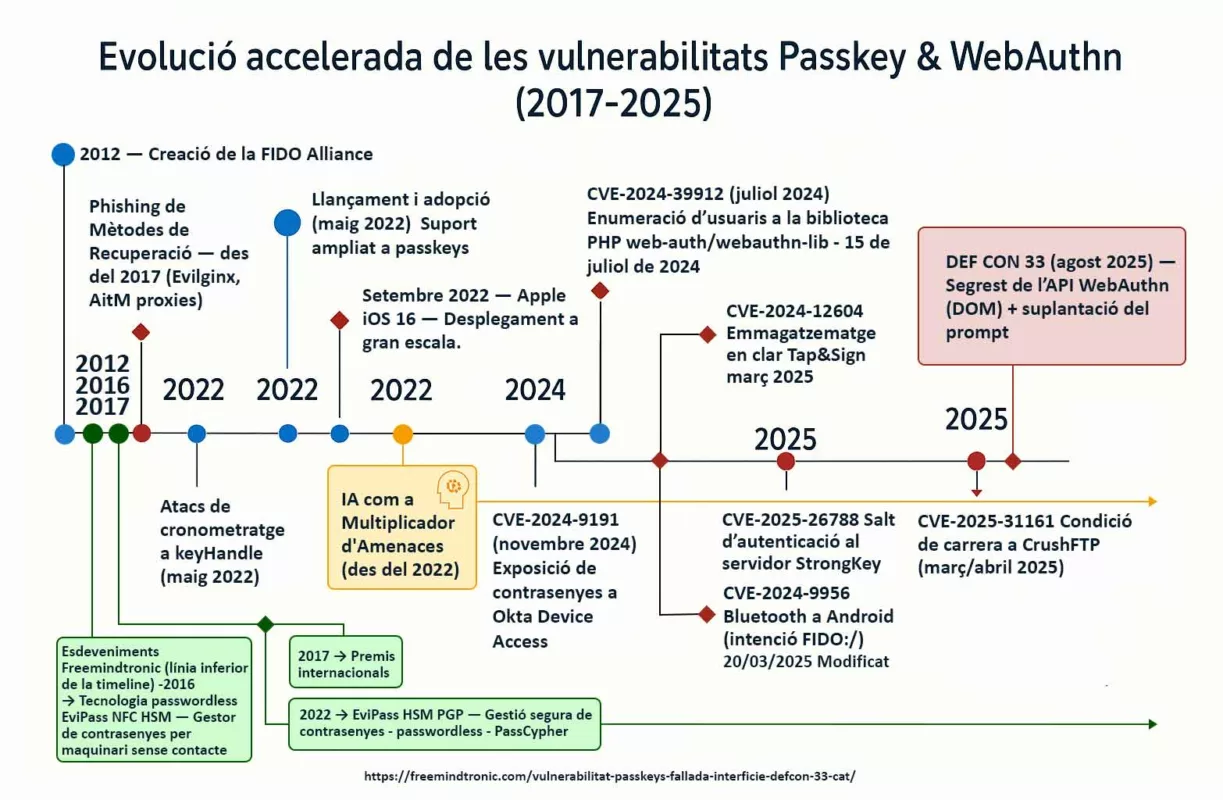
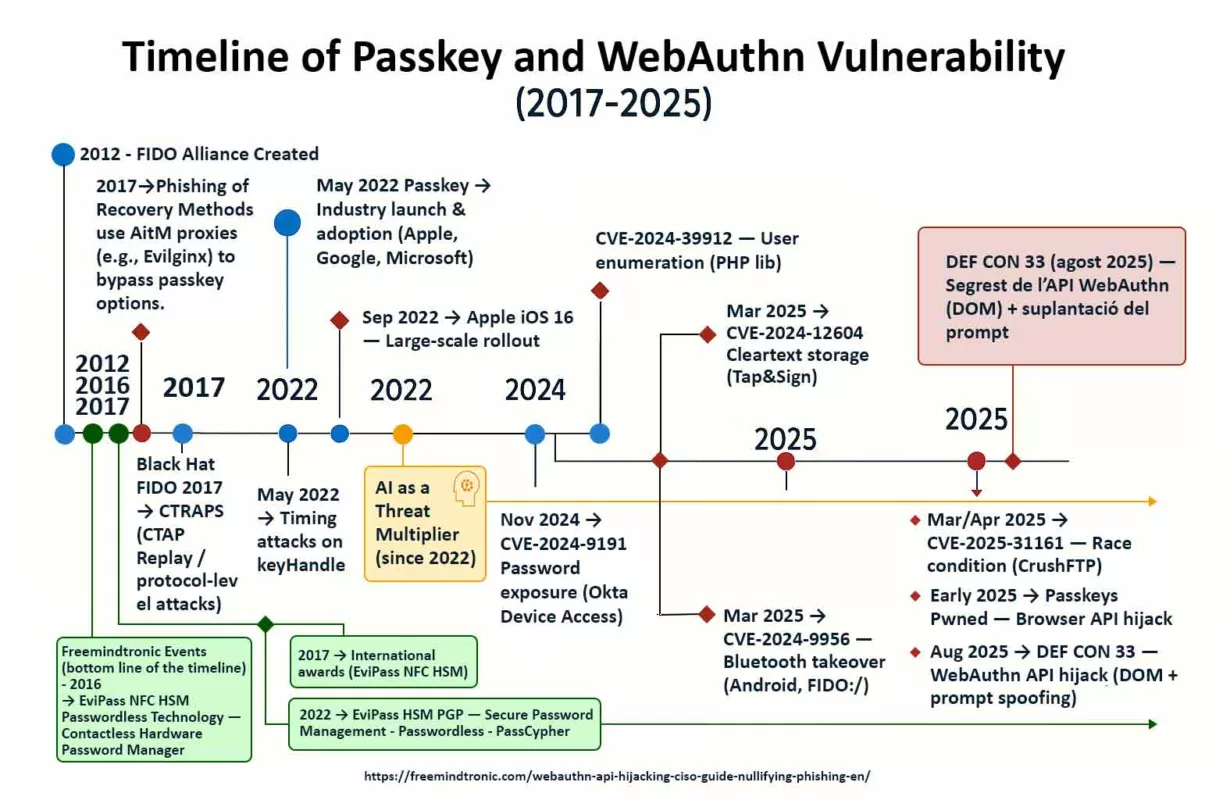
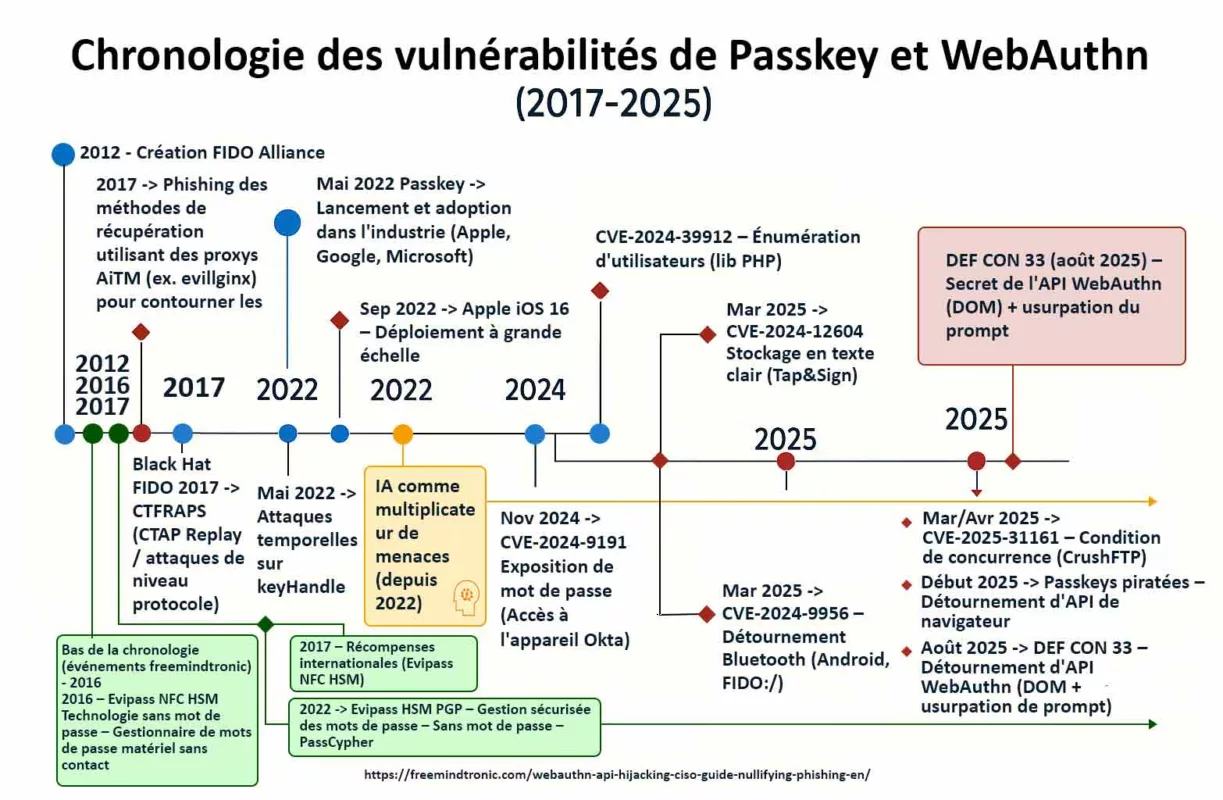
Serial flaws, lagging defenses — Zero-DOM posture
2025 reads like a spy series where attackers stay one step ahead. CVE-2025-2783 in March, CVE-2025-4664 in May, CVE-2025-5419 in June, and the Chrome V8 zero-day CVE-2025-10585 in September. Each episode follows the same script: bend memory just enough to gain a foothold. On the market, a stable RCE can fetch north of $500,000. Defenders meanwhile buy time: patches ship after campaigns are already under way.
Regional highlights
- US — Prioritise CISA/NIST guidance and enterprise patching.
- UK — Align with NCSC guidance; review high-risk finance/admin consoles.
- Canada — Follow CCCS advisories for public-sector rollouts; isolate e-gov consoles.
- Australia — Map to ACSC Essential Eight; accelerate patch + restarts.
- India — Prioritise Android Chrome 140.0.7339.155 across enterprise fleets.
In Sovereign Cybersecurity ↑ This column belongs to the Digital Security section, focused on exploits, systemic vulnerabilities and hardware countermeasures for zero-trust environments.
Chrome V8 zero-day CVE-2025-10585: why this pivot changes everything
Chrome V8 confusion RCE is not a one-off accident but the symptom of a model where the browser executes untrusted code next to your secrets. As long as identities, sessions and keys cross the DOM or linger in browser memory, a drive-by remote code execution via a V8 type confusion exploit is enough to expose them. The next sections unpack what actually happens, who is exploiting it, and how to regain the upper hand—starting with updating to Chrome Stable 140.0.7339.185/.186c and tightening browser runtime hardening under a Zero-DOM posture.
- Executive summary — CVE-2025-10585
- Regional highlights
- Serial flaws, lagging defenses — Zero-DOM posture
- Why this pivot changes everything
- What the zero-day reveals
- Zero-day Chrome V8 in 2025 — the cadence
- Who is exploiting it?
- Sectoral risk & examples
- User impact
- What to do now
- Fixed versions & timeline
- Exposure & regional impact
- Anatomy — V8 type confusion
- Regulatory & compliance guidance
- After the breach — from container to corridor
- Actors & incentives
- Sovereign rewrite (Zero-DOM)
- Weak signals
- Related reading…
- MDM/GPO quick controls
- What we did not cover
- FAQ CVE-2025-10585
- Glossary
- Changelog
- Admin checklist (enterprise)
What the Chrome V8 zero-day CVE-2025-10585 reveals
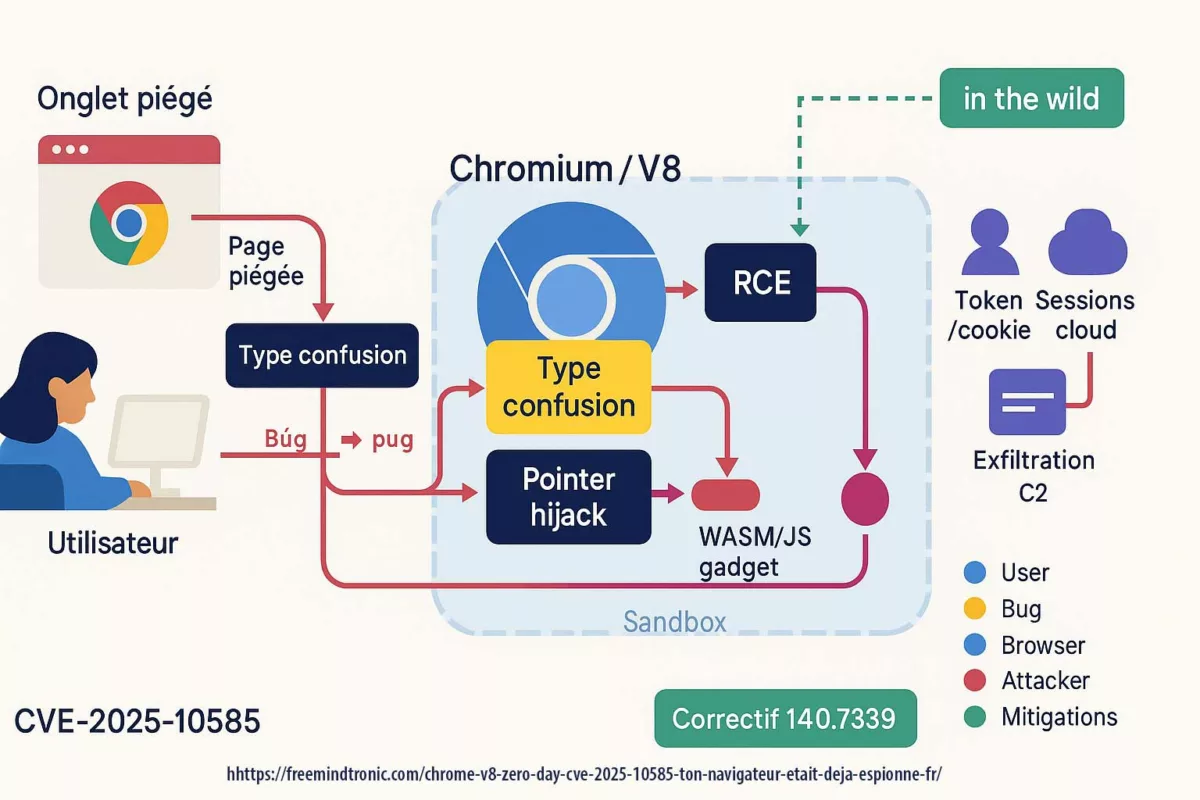
CVE-2025-10585 is a memory flaw in the V8 engine — a type confusion in the JavaScript/WebAssembly runtime. One value is mistaken for another, opening a corridor where a crafted script can execute code as soon as you visit a booby-trapped page. Google’s Threat Analysis Group confirmed active exploitation at the time Stable shipped 140.0.7339.185/.186 (Windows/Mac) and 140.0.7339.185 (Linux); Android 140.0.7339.155. In short: exploitation preceded the patch.
Two consequences follow. First, compromise can stay silent: nothing on screen signals the browser just crossed a boundary. Second, once code runs, the browser stops being a container and turns into a corridor: cookies, tokens, extensions and cloud sessions become side doors within reach.
Zero-day Chrome V8 in 2025: the cadence
In 2025 the pattern repeats: V8 memory flaws punctuate the year and sync with already-moving campaigns. This cadence sustains a persistent gap between exploitation and patching, especially when the bug enables RCE.
| CVE | Type | Fix window | Official link |
|---|---|---|---|
| CVE-2025-2783 | Memory corruption | March 2025 | Record cve.org |
| CVE-2025-4664 | Use-after-free / policy (Loader) | May 14, 2025 | Chrome Releases — Desktop |
| CVE-2025-5419 | Out-of-bounds R/W | June 3, 2025 | Chrome Releases — Extended Stable |
| CVE-2025-10585 | Type confusion (V8) | Sept 17, 2025 | Chrome Releases — Desktop · Android |
On the grey/black markets, a reliable Chrome V8 zero-day (RCE/sandbox escape) often fetches $500,000+.
Who exploits a Chrome V8 zero-day like CVE-2025-10585?
Three spheres intersect. Cybercrime crews monetise access to sessions and accounts via malvertising and compromised sites. State-aligned actors use the flaw sparingly and precisely to cross technical borders inside selected organisations. Between them, brokers assess reliability and reach before chaining a full exploit kit. The TAG attribution suggests CVE-2025-10585 sits in this state-actor theatre.
Sectoral risk & examples
- US — federal agencies, healthcare providers, cloud admin consoles
- UK — financial services, legal/finance SaaS tenants
- Canada — provincial e-gov portals, health networks
- Australia — mining/energy operators, identity federation portals
- India — mobile-first services, large telcos, payment platforms
Illustrative targets only — avoid attribution without official confirmation.
User impact: from an ordinary click to loss of sovereignty
A single page may plant code that observes and diverts the life of a tab. The user sees nothing; the browser carries cookies, tokens and extensions — all become levers for elevation and persistence. Across the English-speaking sphere the risk is systemic: public services, messaging, and admin consoles rely on the browser as if it were trusted land. A Chrome V8 zero-day is a reminder it is not.
What to do against CVE-2025-10585: treat the browser as a hostile runtime
Update to 140.0.7339.185/.186 (Windows/Mac) or 140.0.7339.185 (Linux) via Help → About Google Chrome; Android: 140.0.7339.155. Separate uses (dedicated profile/VM for administrative and sensitive ops), reduce surface (disable WebAssembly where possible, limit JIT on sensitive third-party sites), strictly govern extensions (allow-list, audit, no sideloading) and follow official advisories.
In one line: patch fast, isolate what matters, declutter the browser.
google-chrome --version (or chromium --version depending on distro). Android: Google Play → Updates → Chrome, then relaunch.IT block — example enterprise policies
{ "ExtensionInstallAllowlist": ["<IDs>"], "ExtensionInstallBlacklist": ["*"], "URLAllowlist": ["https://intra.example.tld/*"], "URLBlacklist": ["*"], "DefaultPopupsSetting": 2, "JavascriptAllowedForUrls": ["https://intra.example.tld/*"], "AutofillAddressEnabled": false, "PasswordManagerEnabled": false, "WebAssemblyEnabled": false }
Adapt as needed; deploy via GPO, Intune/MDM or managed policies JSON.
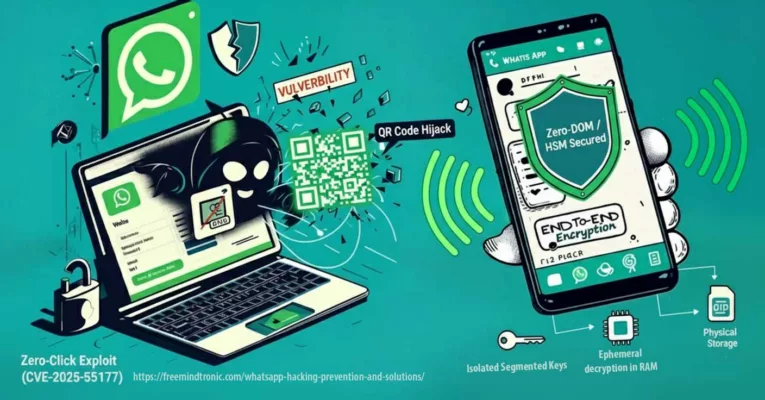
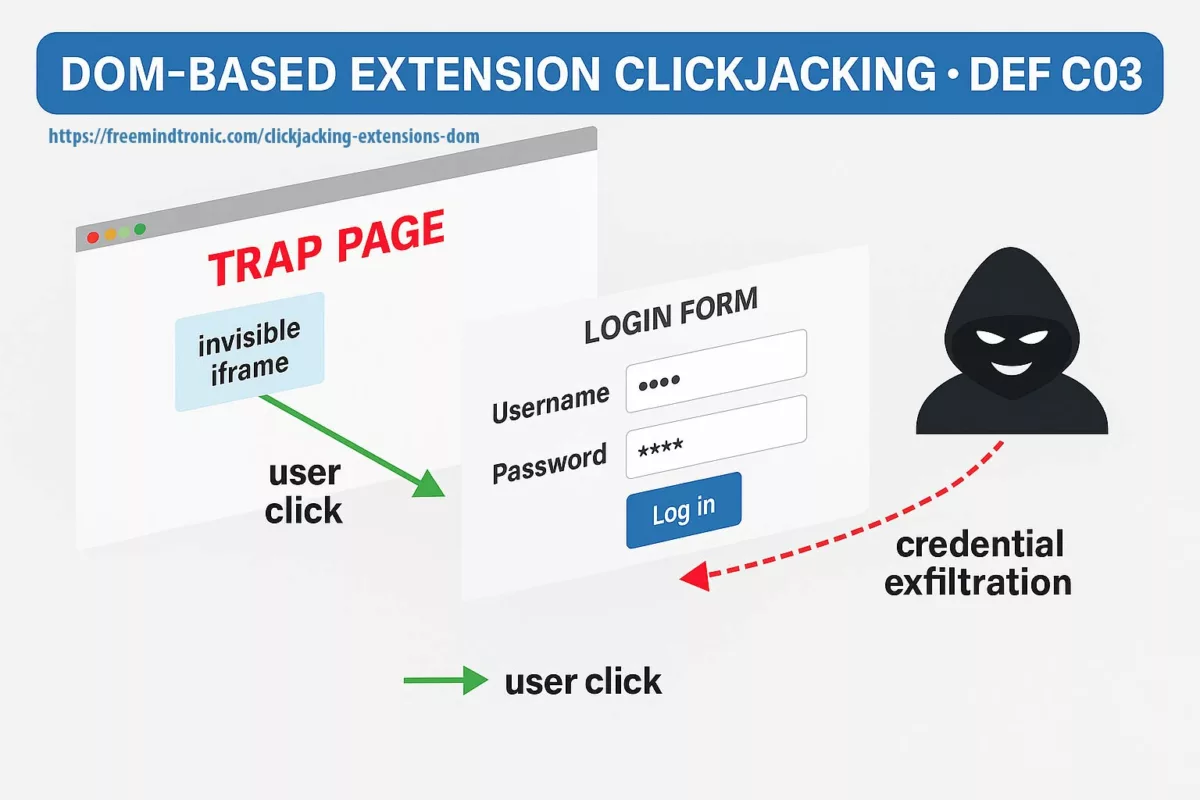
Why it’s tied to the DOM — and to our Clickjacking column
V8 remote code execution (CVE-2025-10585) and DOM-based extension clickjacking end the same way: if secrets cross the DOM or live in browser memory, they become accessible. The first path (V8 RCE) takes over the process; the second (UI redressing/BITB) forces secrets into a trapped DOM. Either way, the DOM is the exfiltration surface.
- Common surface: DOM & browser memory (autofill, cookies, tokens, synced passkeys, extensions).
- Attack paths: engine (V8 RCE) or interface (overlays, iframes,
focus(), Shadow DOM). - Convergent mitigation: isolate uses, govern extensions, and adopt Zero-DOM (secrets off-DOM/off-process, ephemeral RAM, physical consent).
Related read… ⤵
WebAuthn API Hijacking: A CISO’s Guide to Nullifying Passkey Phishing
Fixed versions & timeline
| Date | Channel / Platform | Version | Note |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sept 17, 2025 | Stable Desktop (Win/Mac) | 140.0.7339.185/.186 | CVE-2025-10585 listed; in-the-wild exploitation acknowledged. |
| Sept 17, 2025 | Stable Desktop (Linux) | 140.0.7339.185 | Progressive rollout. |
| Sept 17, 2025 | Chrome for Android | 140.0.7339.155 | Security fixes aligned with Desktop. |
Exposure & regional impact
Chrome holds roughly ~69.23% global browser share (source: StatCounter — Global, Aug 2025).
A Chrome V8 confusion RCE therefore reaches a very large share of English-speaking users and enterprises.
- United States — 52.85% (desktop/mobile combined)
Source: StatCounter US — Aug 2025 - United Kingdom — 51.9%
Source: StatCounter UK — Aug 2025 - Canada — 60.69% (desktop)
Source: Similarweb Canada — Aug 2025 - Australia — 61.94%
Source: StatCounter Australia — Aug 2025 - India (mobile) — 90.77%
Source: StatCounter India Mobile — Aug 2025
Anatomy — V8 type confusion
The cursor blinks. Behind the screen, the script has staged memory: groomed heaps, mislabeled objects, guardrails nudged aside. V8 mistakes a value for what it is not; the page becomes a vehicle. No pop-ups, no warning. The exploit speaks the web’s ordinary language — events, focus, rendering — and leverages it to land execution.
Regulatory & compliance guidance
United States (CISA / NIST)
Follow CISA emergency directives and NIST/NVD advisories: document patch status, prioritise high-privilege endpoints, and report incidents per CISA guidance.
Refs: CISA Advisory · NIST NVD
United Kingdom (NCSC)
Apply NCSC browser-hardening and BYOD guidance; include the incident in your Cyber Essentials review.
Ref: NCSC Guidance
Canada (CCCS)
Align public-sector patch windows with CCCS advisories; escalate risks to provincial IT for e-services.
Ref: CCCS Advisory
Australia (ACSC)
Map fixes to ACSC Essential Eight priorities; accelerate patch + restart cadence in OT/IT.
India (CERT-IN)
Prioritise Android Chrome 140.0.7339.155 rollouts (MDM/Play), validate restarts, and track compliance.
Ref: CERT-IN Advisory
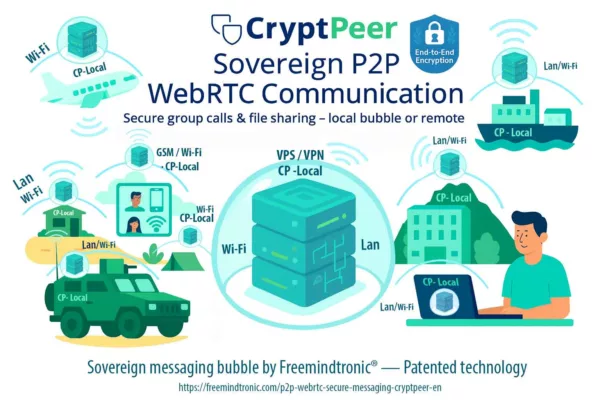
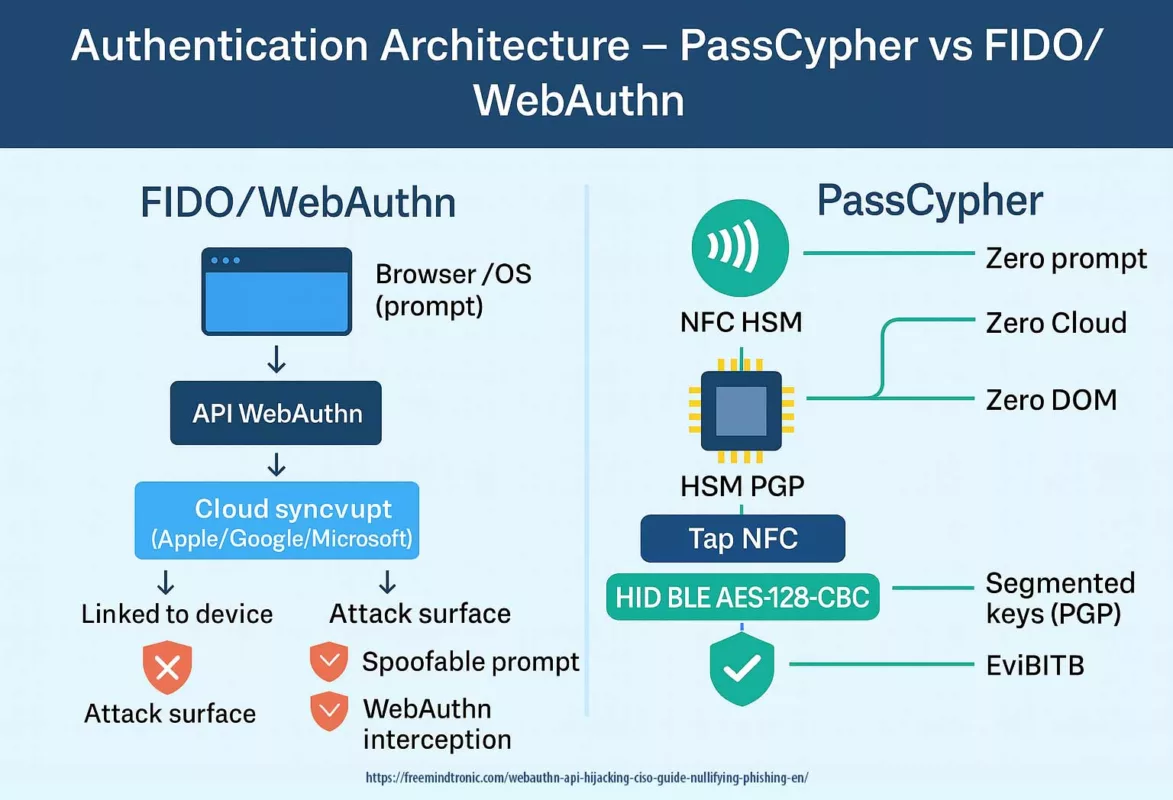
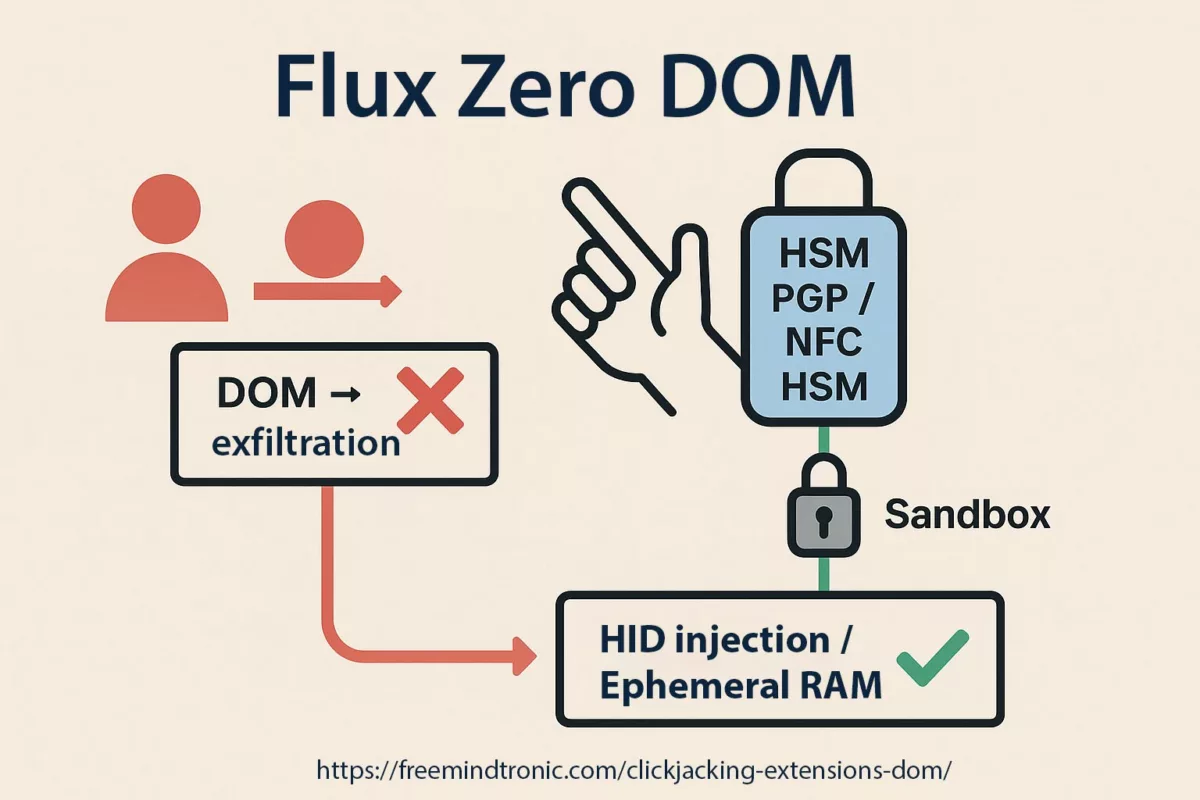
Sovereign rewrite (Zero-DOM)
There’s a version of this story where the tab compromises the browser — and finds nothing worth stealing.
In that version, secrets:
- never touch the DOM,
- do not reside in the browser process,
- never travel in cleartext.
IDs, OTPs, passkeys and private keys live in offline hardware. They appear only as ephemeral ghosts in RAM, triggered by a physical user action.
sovereign technologies
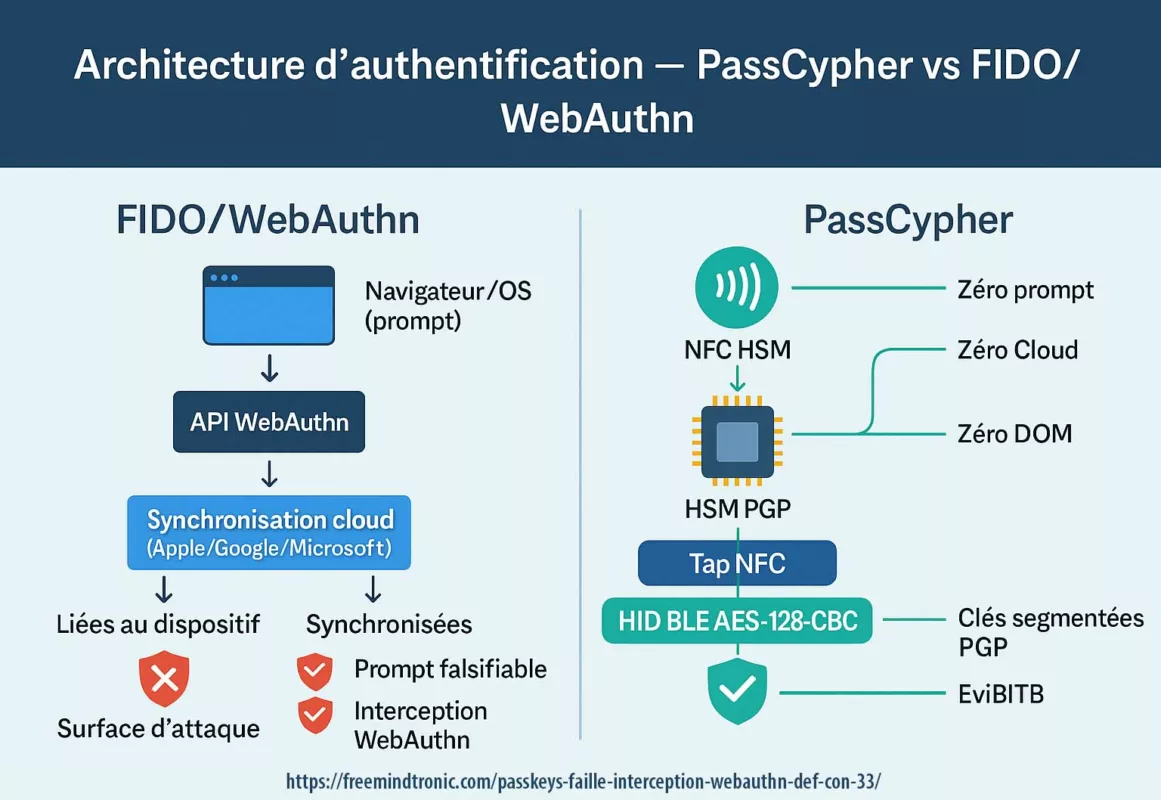
- PassCypher HSM PGP: every secret is bound to an expected URL. Deviations are refused. Containers remain encrypted until a verifiable physical decision.
- PassCypher NFC HSM: a physical tap (NFC) before any injection. The browser sees transport, never content.
- SeedNFC HSM: simplified NFC cold-wallet HSM. Paired with an Android NFC phone + HID-BLE emulator, it injects cryptocurrency public/private keys without clipboard or DOM.
- Bluetooth keyboard emulator (HID-BLE) — EviKeyboard BLE: BLE signal encrypted with AES-128-CBC. Paired with Freemindtronic apps (PassCypher, SeedNFC, DataShielder), it injects secrets over HID-BLE, off-DOM and off-clipboard. Overlays and UI-redressing techniques become ineffective.
Weak signals
MDM/GPO quick controls
- Force update & relaunch — Intune/JAMF/Workspace ONE: push Chrome update policy; enforce relaunch deadline.
- Android fleets (India focus) — Managed Play rollout to 140.0.7339.155; verify via device compliance reports.
- Disable WebAssembly where not required; restrict JIT on critical scopes.
- Extensions governance — allow-list only; block sideloading; audit permissions.
What we did not cover
This column deliberately omits exploitation PoCs and step-by-step reproductions. It also leaves out sector-specific hardening baselines and a deep dive into exploit-market economics. The goal is to expose the systemic risk and show why a hardware Zero-DOM approach changes the outcome. Perspective — Design for graceful failure: assume the browser can fall without taking your identity with it. Anchor secrets in hardware, require physical consent, and treat every tab as disposable.
FAQ CVE-2025-10585
Open Menu → Help → About Google Chrome. Look for 140.0.7339.185/.186 (Win/Mac) or .185 (Linux).
Update to 140.0.7339.155 via Google Play, then relaunch the app. Check in Settings → About → Version.
Yes — these Chromium-based browsers embed V8. Apply each vendor’s update without delay and confirm that CVE-2025-10585 is included in the release notes.
If your sensitive workflows allow it, yes: it reduces attack surface. In enterprises, enforce via GPO/MDM, and limit JIT for high-risk profiles.
Secrets never transit the DOM nor live in the browser process. They remain in offline hardware (HSM) and only appear ephemerally in RAM on a physical user action. A Chrome V8 confusion RCE then has little or nothing to exfiltrate.
SeedNFC is an NFC HSM cold wallet (based on EviPass NFC HSM). PassCypher NFC HSM and DataShielder NFC HSM embed the same sovereign core.
What this brings against CVE-2025-10585 (V8) and BITB/overlays:
- Secrets off-browser: IDs, OTP, private keys never stored in the browser process/DOM.
- Physical consent: each use requires an NFC/HSM action; without it, nothing leaves.
- URL binding (PassCypher/DataShielder): secrets are bound to expected URLs; on deviation (phishing/BITB) the HSM refuses.
- Anti-keylogger injection: HID-BLE mode via USB; BLE signal encrypted with AES-128-CBC; no clipboard, no DOM.
- Ephemeral RAM: nothing persists on the host; drive-by RCE finds little to steal.
Usage modes:
- Android NFC + Freemindtronic app (PassCypher, SeedNFC, DataShielder) to drive the HSM.
- HID-BLE: Bluetooth Low Energy keyboard emulation to the host; works with standard input fields.
Bottom line:
- Does not replace Chrome/Chromium updates; it complements them by removing secrets from the browser.
- Ideal for privileged accounts, admin consoles, sensitive messaging and critical transactions.
Prereqs: Android NFC smartphone, Freemindtronic app, HSM device (SeedNFC / PassCypher NFC HSM / DataShielder NFC HSM). Secrets are not stored on the phone; they stay sealed inside the NFC HSM.
Read official advisories and compare your version to fixed builds. See: Chrome Releases (June 17, 2025) and CERT-FR on CVE-2025-10585.
Switching alone won’t cut it. All Chromium browsers share V8. A Zero-DOM posture and role separation are more effective than simply changing brand.
Yes. Follow CISA emergency directives, document patch status and restart compliance, and report incidents as required. See: CISA advisory.
Yes. Apply NCSC browser-hardening and BYOD controls; align with Cyber Essentials and sector regulators. See: NCSC guidance.
Use managed Play + MDM for staged rollouts, enforce restarts, and verify version 140.0.7339.155. See: CERT-IN.
Prioritise application patching, app control and configuration hardening; document restarts. See: ACSC E8.
Follow CCCS advisories, coordinate with provincial IT for e-services, and enforce restarts. See: CCCS.
Glossary
V8 — Chrome’s JavaScript/WebAssembly engine (also used by Chromium browsers).
Type confusion — Memory bug where an object is treated as another type; leads to controlled corruption.
HID-BLE — Bluetooth Low Energy keyboard emulation; injects secrets “as if typed,” off-clipboard and off-DOM.
RCE — Remote Code Execution: arbitrary code runs remotely. Zero-day — Vulnerability exploited before a public fix.
DOM — Document Object Model: the in-memory structure of web pages.
BITB — Browser-in-the-Browser: fake frames imitating auth windows.
WebAssembly — Portable binary format executed in browsers.
JIT — Just-in-Time compilation: speeds execution but expands attack surface.
Zero-DOM — Freemindtronic doctrine: no secrets in DOM/process; ephemeral RAM, hardware anchoring (HSM/NFC).
Official references:
• Chrome Releases — Stable Desktop (Sept 17, 2025) (CVE-2025-10585).
• Chrome Releases — Android (Sept 17, 2025).
• Chrome Releases — Stable Desktop (May 14, 2025) (CVE-2025-4664).
• Chrome Releases — Extended Stable (June 3, 2025) (CVE-2025-5419).
• cve.org — CVE-2025-2783.
• Stats: StatCounter — Global (Aug 2025).
Changelog
- 2025-09-19 (v1.2) — Added official links per CVE; consolidated Android FAQ; stats section; color-bar signal blocks; enterprise policy block; “check your version” snippet; structured timeline.
- 2025-09-19 (v1.1) — Harmonised 140.0.7339.x versions (Desktop/Android); FR anchors.
- 2025-09-19 (v1.0) — Initial publication: “Your browser was already spying.”
Admin checklist (enterprise)
- Force a browser relaunch post-update; control the restart window.
- Disable autofill on sensitive scopes; audit extension permissions; no sideloading.
- Segment by profile/VM: general browsing vs privileged operations (consoles, critical IS).
- Disable WebAssembly where unnecessary; limit JIT on critical scopes.
- Deploy an off-browser secrets solution (HSM/NFC) for MFA and credential management.