Le bot Telegram Usersbox n’était pas un simple outil d’OSINT « pratique » pour curieux russophones. Il servait de vitrine à un écosystème probiv, ce marché noir de données personnelles russes qui interroge des bases d’opérateurs, de banques ou d’administrations en quasi temps réel. Pourtant, derrière l’image d’une machine d’espionnage russe disciplinée et centralisée, l’affaire Usersbox révèle surtout une illusion de contrôle des données : des téraoctets de PII fuient via Telegram, nourris par la corruption interne et des usages obscurs des services, ainsi que par l’industrialisation de bots Telegram de type probiv présentés abusivement comme des “bots OSINT”.
Résumé express — Ce qu’il faut retenir du bot Telegram Usersbox
Lecture rapide ≈ 4 min — Le bot Telegram Usersbox illustre une contradiction au cœur du modèle russe de gestion des données. D’un côté, le récit officiel met en avant un État tout-puissant en matière de renseignement. De l’autre, la réalité montre un marché noir probiv alimenté par des fuites internes massives. Pendant des années, des téraoctets de données personnelles ont été vendus à la demande via une simple interface Telegram. Les autorités ont laissé prospérer ce modèle, jusqu’au basculement. L’arrestation de son administrateur et la saisie de ses serveurs deviennent alors le symptôme d’un chaos de maîtrise des bases étatiques.
Principe — Un bot vitrine d’un marché noir déjà ancien
Pour comprendre Usersbox, il faut d’abord rappeler que le probiv n’est pas nouveau. Usersbox n’invente ni la vente de rapports, ni la mise en fiche de citoyens sur demande. Il en devient en revanche la vitrine la plus visible. Depuis une simple interface de chat Telegram, le bot peut agréger des informations issues de multiples bases. Celles-ci proviennent d’opérateurs télécom, de registres administratifs, de données bancaires ou encore d’historiques de déplacements. Pour l’utilisateur, tout tient dans quelques messages. En arrière-plan, c’est un accès industrialisé aux PII qui s’organise, adossé à des fuites internes et à des accès privilégiés monétisés.
Fondement — Des bases étatiques poreuses et des insiders rémunérés
Ensuite, il faut regarder le socle technique et humain. Le cœur du modèle probiv repose sur un constat simple. Les bases de données étatiques, bancaires ou opérateurs sont massives et centralisées. Elles restent mieux protégées contre les attaques externes que contre la corruption interne. Des employés, des sous-traitants ou des agents disposant d’accès légitimes extraient, copient ou interrogent ces données contre rémunération. Usersbox sert alors de façade Telegram à ce marché. L’utilisateur voit un bot. Derrière, on trouve des accès internes, des dumps, des scripts d’interrogation et une chaîne de valeur entièrement clandestine.
Constat — Le mythe de la machine d’espionnage disciplinée se fissure
À ce stade, une contradiction apparaît. Officiellement, la Russie se présente comme un État qui maîtrise tout. Les discours soulignent des bases centralisées, une surveillance de bout en bout et des services de renseignement omniprésents. L’existence même de Usersbox raconte l’inverse. Elle montre des bases massivement fuyardes, un marché noir organisé à grande échelle et des services qui ont toléré ces canaux tant que l’équilibre leur était favorable. Quand un bot accessible au grand public permet d’obtenir en quelques secondes ce qu’un service de renseignement exigerait normalement d’une procédure interne stricte, c’est l’architecture de confiance de l’État qui se trouve exposée.
Enjeu — Pourquoi frapper Usersbox maintenant ?
Vient alors la question décisive. L’arrestation de l’administrateur de Usersbox n’intervient pas dans un vide juridique ou technique. Elle suit le durcissement des lois russes sur les données personnelles. Elle s’inscrit aussi dans la création d’infractions pénales qui ciblent directement les « ressources destinées à la vente de bases illégales ». En parallèle, plusieurs affaires montrent que certaines plateformes probiv commencent à exposer des militaires, des fonctionnaires et des élites. Le problème ne se limite plus à des citoyens vendus « au détail ». Le même outil permet désormais de regarder l’appareil d’État de l’intérieur. Dans ce contexte, Usersbox devient une cible exemplaire. Il s’intègre dans une campagne de recentralisation du marché noir des données au profit du centre politique.
Enjeu souverain — Ce que révèle Usersbox pour les autres États
Enfin, l’affaire Usersbox agit comme un avertissement pour les États qui se veulent souverains. Plus les PII sont concentrées dans des silos centralisés au sein de structures peu auditables, plus un probiv local finit par émerger. Le vecteur pourra changer. Aujourd’hui, il s’agit de Telegram. Demain, ce pourrait être une autre messagerie ou une autre interface. La véritable protection ne consiste pas seulement à multiplier les sanctions a posteriori. Elle suppose de revoir l’architecture elle-même. Cela signifie minimiser les données stockées, cloisonner les accès, renforcer la journalisation et recourir à des HSM. Cela implique aussi des solutions où les secrets critiques ne vivent jamais en clair dans des bases interrogées à distance.
⮞ En résumé
Usersbox n’est pas une anomalie dans un système supposément maîtrisé. Il révèle un écosystème probiv structurel où l’État perd une partie de la main sur ses propres bases. Il tente ensuite de reprendre le contrôle par la répression, lorsque ces outils commencent à servir à d’autres que lui. La vraie question n’est donc pas « pourquoi ce bot ? ». Elle devient plutôt : « comment a-t-on pu laisser les données d’un pays entier se retrouver derrière une simple interface Telegram ? »
Paramètres de lecture
Résumé express : ≈ 4 min
Résumé avancé : ≈ 6 min
Chronique complète : ≈ 32 min
Date de publication : 2025-11-28
Dernière mise à jour : 2025-11-28
Niveau de complexité : Souverain & Géopolitique
Densité technique : ≈ 72 %
Langues disponibles : FR · EN · ES · CAT
Focal thématique : Telegram, probiv, données personnelles, Russie
Type éditorial : Chronique — Freemindtronic Cyberculture Series
Niveau d’enjeu : 8.1 / 10 — souveraineté & données
Dans la doctrine Freemindtronic, la souveraineté ne se prouve pas par la seule accumulation de lois répressives ou de capacités d’interception. Elle se démontre par la conception même des systèmes d’information. Là où l’écosystème probiv russe révèle les effets toxiques de bases centralisées et peu contrôlées, des solutions comme DataShielder HSM PGP et PassCypher NFC HSM et CryptPeer illustrent une approche inverse. Elles s’appuient sur un chiffrement local, des HSM hors ligne et une réduction maximale des risques liés à la centralisation.
Transposé au contexte des bases nationales, ce paradigme rappelle une exigence simple. Un État souverain ne devrait jamais permettre qu’un « Usersbox local » puisse, un jour, exister.
Sommaire
- Résumé express — Ce qu’il faut retenir
- Résumé avancé — Probiv, illusion de contrôle et ligne rouge
- Chronique — Probiv, État et perte de maîtrise
- Probiv — Modèle économique et techniques
- Usersbox — Arrestation, mise en scène et signaux
- Pourquoi maintenant ? Changement de rapport de force
- Machine d’espionnage ou illusion de contrôle ?
- OSINT bots — De quoi s’agit-il vraiment ?
- Risques OSINT — Dépendance aux bots Telegram
- Contre-mesures souveraines — Architectures anti-probiv
- Signaux faibles — Vers de nouveaux probiv hors Russie
- Perspective souveraine — Ce que Usersbox annonce pour demain
- FAQ — Usersbox, probiv et souveraineté des données
Points saillants — Lignes de force
- Usersbox n’est pas un cas isolé mais la vitrine la plus visible d’un probiv russe ancien et structuré.
- Le mythe d’une machine d’espionnage parfaite masque une réalité de bases centralisées, poreuses et mal auditées.
- Le durcissement légal intervient quand le probiv commence à exposer des militaires, des fonctionnaires et des élites.
- Les bots Telegram créent une dépendance dangereuse pour l’OSINT : insécurité juridique, traçabilité, perte de souveraineté de l’enquête.
- Seules des architectures souveraines (segmentation, HSM, chiffrement local) rendent structurellement impossible un « Usersbox local ».
Résumé avancé — Probiv russe, illusion de contrôle et ligne rouge Usersbox
Cette chronique interroge le contraste entre le mythe d’une machine d’espionnage russe hyper-disciplinée et la réalité d’un système beaucoup plus chaotique. D’un côté, le discours officiel insiste sur l’ordre, la centralisation et la maîtrise. De l’autre, les enquêtes montrent un environnement où les mêmes structures qui prétendent tout contrôler laissent fuir et monétiser leurs propres bases. Usersbox n’est qu’un révélateur dans ce paysage. Il montre à quel point un État peut perdre la main sur ses données lorsqu’il mise tout sur la centralisation et trop peu sur la conception souveraine de ses systèmes.
Dans les sections suivantes, le Résumé avancé va d’abord revenir sur le fonctionnement général du probiv. Il décrira ensuite la place précise de Usersbox dans cet écosystème. Enfin, il préparera le terrain pour la partie « Pourquoi maintenant ? » de la Chronique, où l’arrestation n’apparaît plus comme un accident, mais comme un changement d’arbitrage stratégique.
Probiv russe — Un marché structuré, pas un folklore pirate
Pour aller plus loin, il faut d’abord clarifier ce qu’est le probiv. Le terme désigne la vente de « vérifications » à la demande. Un client fournit un numéro, un nom ou une plaque. En retour, il obtient un rapport détaillé sur la personne ciblée. Cette pratique existe depuis des années en Russie. Elle ne relève pas d’un folklore marginal. Elle constitue un marché structuré, avec des intermédiaires, des tarifs récurrents et des canaux stables.
Concrètement, les informations vendues proviennent de plusieurs couches. On retrouve des dumps historiques de bases fuitées, mais aussi des accès actifs. Ces accès dépendent souvent d’employés ou de sous-traitants qui disposent de droits légitimes dans les systèmes. Le probiv ne contourne donc pas toujours la sécurité périmétrique. Il exploite d’abord la porosité interne des organisations et la faiblesse du contrôle des accès.
Dans ce paysage, Telegram joue un rôle de vitrine et de bus. Les canaux, bots et groupes privatisent une activité déjà ancienne. Ils la rendent plus rapide, plus confortable et plus industrialisée. Usersbox s’inscrit exactement à ce niveau : l’interface visible d’un back-office de fuites et d’insiders.
Usersbox — Une interface Telegram au-dessus d’un chaos de bases
Sur cette base, la place de Usersbox apparaît plus clairement. Le bot ne crée pas la fuite. Il l’orchestre. Il mutualise plusieurs sources dans une seule interface de chat. Pour l’utilisateur, le geste reste trivial. Il envoie une requête, attend quelques secondes, puis lit un rapport structuré.
En coulisse, la situation est beaucoup plus complexe. Des scripts interrogent des bases différentes. Certains modules piochent dans des dumps anciens. D’autres utilisent des accès toujours actifs dans les systèmes d’opérateurs ou d’administrations. Usersbox agit comme un routeur clandestin entre ces silos et le front Telegram.
C’est précisément ce qui le rend si intéressant pour l’analyse. Le bot révèle l’ampleur du problème. Il agrège ce qui, jusqu’ici, restait fragmenté et peu visible. Il montre qu’un simple canal Telegram peut concentrer une capacité de renseignement interne que l’État pensait réservée à ses propres structures.
Nouveau cadre juridique — Une arme taillée pour frapper les probiv
Le basculement ne se comprend pas sans le volet légal. Pendant longtemps, les autorités russes ont réprimé le probiv à la marge. Elles utilisaient des articles génériques. Corruption, abus de fonctions, accès illégal à un système. Ces incriminations restaient souvent fragmentaires.
À partir de 2024, le cadre change. De nouvelles dispositions visent directement les bases de données illégales et les plateformes qui les exploitent. La loi introduit des peines lourdes pour la collecte, le stockage et la vente de données personnelles. Elle cible aussi les « ressources » créées pour faciliter cette activité. Les bots et sites probiv entrent clairement dans cette catégorie.
Ce durcissement a deux effets. Il fournit d’abord aux autorités une boîte à outils juridique spécialisée. Il leur permet ensuite de mener des opérations plus visibles. L’arrestation d’un administrateur de bot, avec saisie de serveurs et communication encadrée, devient un message politique autant qu’un acte judiciaire.
Ligne rouge — Quand le probiv commence à se retourner contre l’État
Reste la question centrale : pourquoi maintenant. Le probiv existe depuis longtemps. Les services en connaissent parfaitement l’existence. Ils en subissent certains effets. Ils en tirent aussi parfois parti. Tant que l’équilibre reste maîtrisé, l’État peut fermer les yeux ou frapper ponctuellement.
Le cas Usersbox suggère un changement de phase. D’une part, le volume de données en circulation atteint des niveaux critiques. D’autre part, les usages débordent le périmètre toléré. Des journalistes, des militants anticorruption et des analystes OSINT utilisent ces mêmes canaux. Ils les emploient pour documenter des affaires sensibles. Ils peuvent exposer des militaires, des policiers ou des responsables locaux.
À partir de là, le probiv cesse d’être un simple outil de service gris. Il devient une menace de retour de flamme. L’arrestation de l’administrateur de Usersbox et la saisie de ses serveurs signalent ce tournant. Elles montrent un centre politique qui tente de reprendre le contrôle. Non seulement sur les données, mais aussi sur le marché noir qui les redistribue.
Le Résumé avancé prépare ainsi la suite de la chronique. Celle-ci détaillera, section par section, les mécanismes techniques et politiques en jeu. Elle reviendra sur le fonctionnement interne du probiv. Elle décrira la séquence exacte autour de Usersbox. Elle analysera surtout la question « pourquoi maintenant ? », avant d’ouvrir sur les architectures souveraines qui empêchent qu’un tel scénario se produise ailleurs.
Les chroniques affichées ci-dessus ↑ appartiennent à la rubrique Sécurité Digitale. Elles prolongent l’analyse des architectures souveraines, des marchés noirs de données et des outils de surveillance. Cette sélection complète la présente chronique consacrée au bot Telegram Usersbox et à l’écosystème probiv russe.
Chronique — Probiv, État et perte de maîtrise
Pour comprendre l’affaire Usersbox, il faut revenir à la structure du probiv. Ce marché noir n’est pas un phénomène marginal. Il résulte d’une centralisation massive des données dans les infrastructures russes. Cette centralisation crée une dépendance forte et des points de rupture. Elle ouvre aussi la porte à des usages clandestins, souvent issus de l’intérieur même des institutions.
Probiv — Modèle économique et mécanique interne
Le probiv repose sur une chaîne simple. D’abord, des bases centralisées contiennent des données très détaillées. Ensuite, des personnes en position d’accès transforment ces droits en marchandise. Enfin, des plateformes assurent l’intermédiation. Ce modèle fonctionne depuis plus d’une décennie. Il se nourrit d’incitations financières et d’un contrôle interne limité.
Les principales sources proviennent des opérateurs télécom, des banques et des administrations locales. Ces services disposent de privilèges étendus. Ils enregistrent identités, adresses, transactions, déplacements ou interactions administratives. Chaque source devient une brique du marché probiv. Chaque brique complète la précédente. L’ensemble forme un miroir social très dense, exploitable par presque n’importe quel acheteur.
Ce fonctionnement crée une asymétrie sévère. Les personnes concernées n’ont aucun moyen de vérifier l’usage de leurs données. Les insiders, eux, disposent d’un levier très rentable. Les canaux Telegram ajoutent une couche de confort. Ils accélèrent la mise en relation entre l’offre clandestine et la demande.
Probiv en chiffres — repères russes
- En mars 2025, le quotidien Izvestia, citant Igor Bederov (société T.Hunter), estime entre 1,2 et 1,5 million le nombre d’utilisateurs actifs de bots Telegram vendant des données personnelles, pour un revenu annuel agrégé d’environ 15 milliards de roubles.
Source : Izvestia (édition anglaise) - En 2024, la Banque de Russie évalue à environ 15 milliards de roubles les montants volés sur le marché financier en un an, principalement via des schémas qui exploitent des données bancaires compromises et revendues sur ces circuits.
Donnée Banque de Russie relayée par TASS - Le 30 novembre 2024, la loi fédérale n° 420-FZ introduit dans le Code pénal un article spécifique sur la « collecte, stockage, utilisation et transmission illégales de données personnelles dans des systèmes informatiques », signalant la volonté du centre politique de judiciariser ce marché.
Texte officiel — site du Kremlin
Ces repères chiffrés replacent Usersbox dans un environnement déjà massif : un marché clandestin évalué à plusieurs dizaines de milliards de roubles, désormais visé explicitement par le législateur russe, tant sur le plan pénal que réglementaire.
Usersbox — Arrestation, mise en scène et signaux faibles
Usersbox s’inscrit dans ce paysage. Il ne crée pas l’écosystème probiv. Il le résume. Ce bot rassemble plusieurs sources dans une seule interface. Il standardise les requêtes. Il fournit des rapports simples et rapides. Son administrateur devient visible, car le service attire une audience large et variée.
L’arrestation d’Igor Morozov le 4 novembre 2025 à Saint‑Pétersbourg intervient dans un contexte nouveau. Les autorités cherchent à reprendre la main. Elles souhaitent marquer une rupture. L’opération s’accompagne de saisies de serveurs et de messages officiels.
Annonce officielle de l’arrestation (4 novembre 2025, Saint‑Pétersbourg)
Le signal vise les utilisateurs, mais aussi les relais internes qui alimentent ces bases clandestines.
Plusieurs signaux faibles apparaissent. D’abord, les services montrent qu’ils peuvent cibler les plateformes très exposées. Ensuite, ils rappellent qu’ils disposent désormais d’un cadre pénal renforcé. Enfin, ils indiquent que certains contenus deviennent trop sensibles. Les requêtes visant des agents, des militaires ou des élites déclenchent ce changement d’arbitrage.
Pourquoi maintenant ? Un changement de rapport de force
La question centrale ne porte pas sur l’existence du probiv. Elle porte sur le calendrier. Pourquoi frapper un bot en 2025 alors que le marché fonctionne depuis des années ? Plusieurs facteurs convergent. Ensemble, ils modifient le rapport de force entre l’État et ce marché noir.
Le premier facteur est juridique. La Russie adopte de nouvelles lois contre la vente illégale de données. Ces textes visent explicitement les plateformes, les bots et les services d’agrégation. Ils permettent des peines lourdes et des opérations ciblées, présentées comme exemplaires.
Le deuxième facteur relève de la sécurité interne. Les plateformes probiv commencent à exposer des personnes particulièrement sensibles. Certains rapports concernent des agents de terrain. D’autres touchent des membres d’administrations locales ou des proches du pouvoir. Cette visibilité crée un risque politique direct.
Le troisième facteur tient à la communication. Les autorités veulent montrer qu’elles protègent les données de la population. Elles organisent des opérations très visibles. Elles construisent un récit de rigueur et de discipline. Dans ce récit, Usersbox devient une affaire emblématique.
Machine d’espionnage ou illusion de contrôle ?
Cette interrogation traverse toute la chronique. Le discours officiel décrit un État parfaitement organisé. Il prétend contrôler chaque base et chaque accès. La réalité montre un modèle différent. Les bases sont vastes. Les accès internes sont nombreux. Les contrôles restent incomplets. Le système produit alors des fuites massives et récurrentes.
Cette situation crée une illusion persistante. L’État croit maîtriser les données grâce à leur centralisation. En pratique, cette centralisation augmente la surface de fuite. Elle rend les abus plus simples. Elle facilite les chaînes clandestines. Le probiv n’est pas une anomalie. Il constitue un produit logique d’une architecture centralisée et mal auditée.
Usersbox agit comme une lentille grossissante. Il révèle les défauts structurels des systèmes d’information russes. Il montre comment un État peut perdre la main malgré des moyens techniques puissants. Il éclaire aussi la manière dont certains services internes peuvent tolérer, voire exploiter, des canaux non officiels tant qu’ils restent utiles et discrets.
Une partie de ces flux alimente une économie grise faite de commissions, de pots-de-vin et de sociétés écrans. L’État peut en tirer un bénéfice indirect, non pas par des recettes fiscales assumées, mais par la capacité de certains réseaux à monétiser l’accès aux bases qu’ils contrôlent ou tolèrent.
OSINT bots — De quoi s’agit-il vraiment ?
Un point mérite d’être clarifié avant d’analyser les risques : qu’appelle-t-on exactement un « bot OSINT » ? Le terme circule beaucoup, mais il regroupe des réalités très différentes selon qu’il s’agit d’un outil civil, d’un service clandestin ou d’un instrument politique.
Un bot OSINT, dans son sens neutre, désigne simplement un programme automatisé. Il répond à une requête en agrégeant des informations accessibles sans intrusion directe dans un système protégé. Cette définition théorique s’applique à des outils légitimes. Ils exploitent des sources ouvertes, des registres publics ou des bases librement consultables.
Dans la pratique, l’expression recouvre aussi des services beaucoup plus ambigus. Certains bots mélangent données publiques, fuites anciennes et informations issues d’insiders. D’autres utilisent des passerelles détournées ou des accès mal contrôlés par des institutions. Dans ce cas, on parle encore de « bot OSINT », mais l’outil devient un point de contact vers des couches opaques ou illégitimes.
C’est précisément ce que montre le cas russe. Une partie de ces bots sert indirectement les services de l’État. Ils facilitent des vérifications rapides. Ils fluidifient des procédures internes. Ils constituent parfois un canal officieux entre des agents et des accès privilégiés. D’autres bots, en revanche, échappent totalement au contrôle. Ils servent à des enquêtes journalistiques, à des opérations criminelles ou à des usages personnels.
En ce sens, un bot OSINT n’est pas une catégorie stable. C’est un continuum. À une extrémité, des outils légaux et transparents. À l’autre, des interfaces comme Usersbox qui masquent un marché noir complet. Entre les deux, un ensemble d’usages qui se croisent, se superposent et parfois se contredisent.
⮞ Repère essentiel
Dans l’espace russophone, de nombreux bots présentés comme « OSINT » sont en réalité des façades d’accès à des bases internes fuyardes. Ils ne relèvent pas de l’OSINT au sens strict. Ils relèvent d’un modèle hybride où l’automatisation sert de masque à la revente d’informations issues d’insiders.
Risques OSINT — Dépendance aux bots Telegram
Usersbox a aussi une autre conséquence. Il interroge les pratiques de certains analystes OSINT. Beaucoup ont utilisé ce bot. Il offrait un accès rapide à des données très sensibles. Il permettait de documenter des réseaux, des déplacements ou des liens familiaux. Tout cela, en quelques messages sur Telegram.
Cette dépendance pose plusieurs problèmes. D’abord, un problème juridique. Les données proviennent de fuites et d’abus d’accès. Leur statut légal reste très fragile. Ensuite, un problème opérationnel. L’analyste ne maîtrise ni la source exacte, ni les filtres appliqués. Enfin, un problème de sécurité. Utiliser un bot probiv expose la personne qui requête. Les journaux d’usage peuvent être saisis ou analysés.
La frontière entre enquête légitime et exploitation d’un marché noir devient floue. Certains acteurs utilisent ces outils pour documenter des violations graves. D’autres s’en servent pour des motifs plus ambigus, voire opportunistes. Dans tous les cas, la dépendance à une interface opaque fragilise la démarche. Elle place l’enquêteur dans une position d’utilisateur captif.
Ce constat ne concerne pas seulement la Russie. Il touche toute personne tentée par des services similaires. La facilité apparente masque une réalité dure. Le contrôle effectif appartient au fournisseur de bot, ou à ceux qui le surveillent.
⮞ Points d’attention
S’appuyer sur des bots probiv pour l’OSINT expose à trois risques majeurs : insécurité juridique, dépendance technique et possible traçabilité par des services hostiles. La promesse de « données faciles » se paie par une perte nette de souveraineté.
Contre-mesures souveraines — Architectures anti-probiv
L’affaire Usersbox met en lumière un point central. Un probiv ne prospère que si l’architecture l’autorise. Il suppose des bases vastes, centralisées et mal cloisonnées. Il nécessite aussi des accès internes peu surveillés. Réduire ce risque demande plus que des arrestations. Cela impose un changement de conception.
Limiter la centralisation des bases sensibles
Une première piste consiste à limiter la centralisation. Quand toutes les données convergent vers un même point, le gain pour l’attaquant augmente. Il devient rentable d’acheter un accès ou de corrompre un agent. À l’inverse, des bases segmentées réduisent la valeur d’une fuite unique. Elles complexifient les reconstitutions massives et rendent plus difficile la constitution d’un miroir complet de la population.
Maîtriser localement les secrets critiques
Une deuxième piste concerne la maîtrise locale des secrets. Les éléments les plus sensibles ne devraient pas vivre en clair dans des bases interrogeables à distance. Ils devraient être protégés par des modules matériels ou logiques isolés. Leur usage devrait s’effectuer dans des environnements dédiés, hors des systèmes génériques et des applications exposées à Internet.
Tracer et responsabiliser les accès internes
Une troisième piste touche à la journalisation et au contrôle des accès. Chaque consultation de données critiques devrait laisser une trace forte. Cette trace doit être difficile à effacer, y compris pour des administrateurs, et reliée à une identité vérifiable. Cela change les incitations : la fuite devient plus risquée pour l’insider, et l’organisation peut détecter plus tôt des comportements anormaux.
⮞ Cas d’usage souverain | Réduire le terrain de jeu du probiv
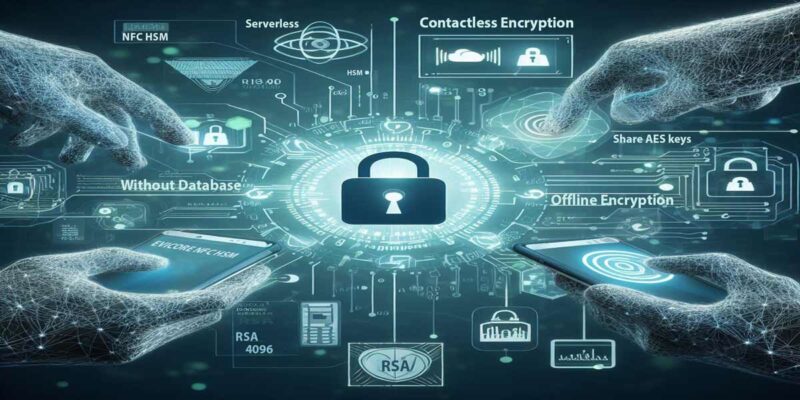
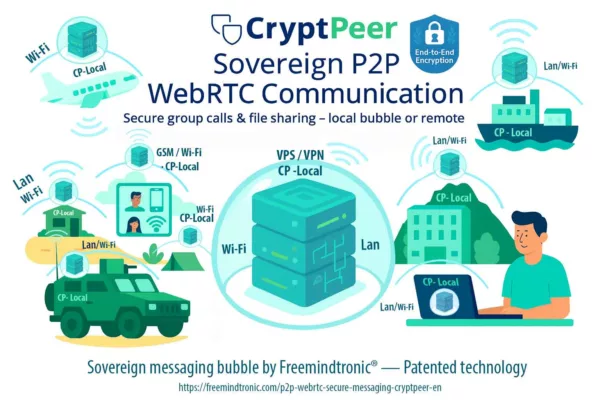
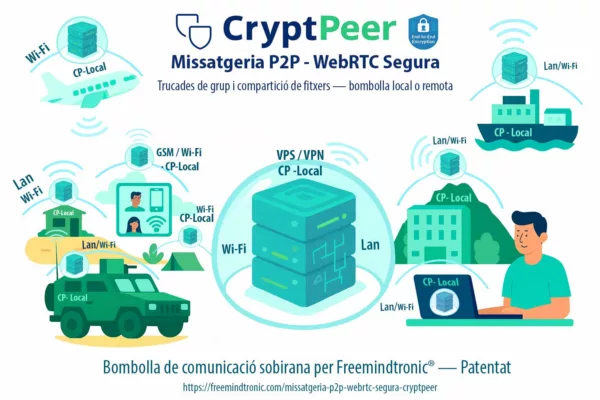
Dans un modèle souverain, les données les plus critiques ne résident jamais dans une base interrogeable par un simple service applicatif. Elles sont chiffrées localement et déchiffrées uniquement dans un environnement sous contrôle direct de l’utilisateur ou de l’organisation. Des solutions comme DataShielder HSM PGP, PassCypher NFC HSM ou CryptPeer.
illustrent cette approche. Elles déplacent la confiance vers le périphérique souverain, le HSM ou le pair, plutôt que vers une base centrale. Dans un tel modèle, un « Usersbox local » ne pourrait jamais agréger une vision complète d’une population.
⮞ Cas d’usage — Chiffrer avant et au-delà de Telegram
Dans le contexte du bot Telegram Usersbox et plus largement des bots probiv russes, cette stratégie de chiffrement par encapsulation montre comment on peut continuer à utiliser Telegram sans alimenter un nouveau Usersbox en données exploitables.
Encapsulation de chiffrement : un message dans un autre
Dans le modèle probiv russe, Telegram sert souvent de canal entre l’acheteur et les bases fuyardes. Même lorsqu’une messagerie propose déjà un chiffrement intégré, le fournisseur du service et les acteurs qui le surveillent restent en position d’observer les flux ou d’exploiter des implants sur les terminaux. Des solutions comme DataShielder NFC HSM et DataShielder HSM PGP appliquent une approche inverse : le chiffrement est réalisé en amont, localement, dans le HSM, avant même que le message ne soit remis à la messagerie (y compris Telegram ou d’autres services déjà chiffrés). Le texte en clair ne vit jamais dans l’application, ni dans le cloud du fournisseur ; il ne transite que sous forme de bloc chiffré opaque. Lorsque le message est ensuite envoyé par une messagerie chiffrée, celle-ci applique son propre chiffrement par-dessus. On obtient une véritable encapsulation de chiffrement : un message chiffré à l’intérieur d’un autre message chiffré.
Surcouche souveraine : réduire la valeur exploitable
Pour la messagerie, il ne s’agit plus que d’un contenu illisible généré par le HSM. Même en cas de compromission de l’infrastructure ou du client de messagerie, l’attaquant ne récupère qu’un chiffrement dans le chiffrement, inexploitable sans la clé du HSM. Du point de vue de la chronique Usersbox, cette encapsulation change la donne : le canal Telegram reste le même, mais la valeur exploitable pour un probiv s’effondre.
Les données réellement sensibles ne vivent plus en clair ni sur des serveurs russes, ni dans des bases réinterrogeables, ni dans les journaux applicatifs. La messagerie peut continuer à fonctionner, mais elle cesse d’alimenter un stock de PII réutilisable par des bots comme Usersbox. Cette surcouche de chiffrement local illustre la logique souveraine : ne jamais faire confiance par défaut au fournisseur de messagerie, même lorsqu’il promet un chiffrement « de bout en bout », et placer la racine de sécurité dans un HSM contrôlé par l’utilisateur, pas dans une plateforme centralisée.
Signaux faibles — Vers de nouveaux probiv hors Russie
Usersbox disparaît. Le probiv, lui, ne disparaît pas. Il se déplace. Il change de forme. Il migre vers d’autres juridictions et d’autres infrastructures. Certains acteurs vont rechercher des pays plus tolérants. D’autres utiliseront des messageries ou des protocoles différents. Le besoin de ce marché reste intact.
On peut déjà observer plusieurs tendances. D’abord, une montée des services hybrides. Certains mélangent fronts Telegram et sites chiffrés. D’autres s’appuient sur des places de marché fermées. Ensuite, une internationalisation de la demande. Des acheteurs étrangers s’intéressent aux données russes, mais aussi à d’autres ensembles nationaux.
Enfin, une sophistication accrue des schémas d’accès. Des acteurs chercheront à automatiser les interrogations via des outils plus discrets. Ils essayeront de réduire leur propre exposition technique. Le but restera pourtant le même. Reconstituer une vue globale à partir de fuites fragmentées.
Perspective souveraine — Ce que Usersbox annonce pour demain
Usersbox est un cas concret. Il raconte un pays, une architecture et un rapport au pouvoir. Toutefois, son intérêt dépasse largement le cadre russe. Il oblige tous les États à se poser la même question. Que se passerait-il si un bot similaire apparaissait demain, chez eux ?
Un premier enseignement concerne la centralisation des données. Plus un pays concentre les PII dans des silos uniques, plus il crée un risque systémique. Un seul point de défaillance suffit alors à alimenter un probiv national. Les États doivent donc arbitrer entre efficacité administrative et résilience informationnelle.
Un deuxième enseignement touche à la culture de l’accès interne. Les fuites ne viennent pas seulement d’attaques extérieures. Elles proviennent de l’intérieur des institutions. Formation, contrôle, audit et responsabilisation des personnes en accès privilégié restent essentielles. Sans ces garde-fous, toute réforme technique reste partielle.
Un troisième enseignement vise les pratiques OSINT. Il est tentant de s’appuyer sur des outils « magiques ». Ils offrent des raccourcis spectaculaires. Ils masquent cependant des risques lourds. Souveraineté de l’enquête, traçabilité, dépendance à un fournisseur opaque. L’affaire Usersbox rappelle qu’un outil peut se retourner contre ceux qui l’utilisent.
Enfin, un dernier enseignement concerne la conception des systèmes. Un État qui se veut souverain doit prouver cette souveraineté par sa technique. Cela implique des choix clairs. Moins de centralisation. Plus de maîtrise locale. Davantage de chiffrement hors des bases centrales. Plus de modules matériels dédiés pour les secrets les plus sensibles.
La question n’est donc pas de savoir si un nouveau Usersbox apparaîtra ailleurs. La question clé devient plutôt : nos architectures actuelles rendent-elles ce scénario possible, ou le rendent-elles structurellement impossible ? La réponse, pour chaque pays, dira beaucoup plus sur sa souveraineté réelle que n’importe quel discours.
FAQ - Questions fréquentes sur le bot Telegram Usersbox et le probiv russe
Comprendre la place réelle du bot Telegram Usersbox dans l’écosystème probiv
Tout d’abord, il faut rappeler que le bot Telegram Usersbox n’était pas un cas isolé. Il s’inscrivait dans un écosystème déjà ancien de services probiv russes, tous dédiés au marché noir de données personnelles et à la monétisation des données personnelles russes.
En réalité, Usersbox se distinguait surtout par sa visibilité, par son intégration directe dans Telegram et par le moment politique choisi pour l’opération contre lui. Autrement dit, il a servi de vitrine emblématique d’un phénomène plus large, plutôt que d’exception dans l’univers des bots semi-clandestins utilisés pour de l’OSINT gris, pour l’accès illégal aux PII russes et pour alimenter le probiv russe à grande échelle.
Probiv russe et marchés gris de données dans le reste du monde
À première vue, le terme probiv est effectivement spécifique à l’espace russophone. Il renvoie à la vente de « vérifications » à la demande, souvent via des bots Telegram, sur la base de données issues d’opérateurs, de banques ou d’administrations publiques russes.
Cependant, si l’on élargit la perspective, la logique sous-jacente n’est pas propre à la Russie. Partout où l’on trouve des bases de données centralisées, des insiders mal contrôlés et une forte valeur attachée aux données personnelles, on voit apparaître des formes locales de marché gris de données. Ainsi, le probiv russe devient un cas d’école pour analyser les risques structurels de tout État qui centralise trop ses PII sans mettre en place de véritables architectures souveraines de protection des données et sans doctrine claire de souveraineté des données.
Entre OSINT, marché noir de données et zone grise juridique
À première vue, Usersbox était souvent présenté comme un « bot OSINT » pratique pour les enquêtes Telegram. Pourtant, la réalité est beaucoup plus nuancée. L’OSINT repose, par définition, sur des sources ouvertes et légales. Or, le bot Telegram Usersbox s’appuyait en grande partie sur des données issues de fuites internes et de bases réinterrogeables alimentées par des insiders corrompus.
En pratique, cela signifie que certains analystes OSINT ont utilisé un outil qui mélangeait données publiques, données compromises et informations issues du marché noir probiv russe. La frontière entre OSINT légitime et exploitation d’un canal illégal de données personnelles russes devenait donc floue, avec à la clé des risques juridiques, techniques et éthiques importants pour les enquêtes menées via Telegram, notamment lorsqu’elles touchent à la souveraineté numérique ou à la sécurité d’un État.
Vers un OSINT souverain sans dépendance aux bots probiv
Bien sûr. D’un point de vue méthodologique, l’OSINT souverain s’appuie d’abord sur des sources ouvertes, légales et traçables : registres publics, décisions de justice, documents administratifs, réseaux sociaux publics, presse, bases de données ouvertes et archives en ligne.
Les bots probiv sur Telegram, comme Usersbox, proposent un raccourci spectaculaire, en donnant l’illusion d’un accès « magique » aux données personnelles russes. Toutefois, ce raccourci repose sur des données obtenues illégalement, ce qui fragilise la robustesse de l’enquête et la sécurité de l’analyste. En adoptant une approche OSINT souveraine, il est donc préférable de privilégier des outils maîtrisés localement, de comprendre la provenance exacte des données et d’éviter de dépendre d’un bot Telegram dont la logique interne reste totalement opaque et potentiellement surveillée.
Les risques juridiques, techniques et stratégiques d’un OSINT appuyé sur Usersbox
Tout d’abord, le premier risque concerne le cadre juridique. Les données proposées par un bot probiv comme Usersbox proviennent de fuites, d’abus d’accès ou de reventes illégales de données personnelles. Les exploiter expose l’utilisateur à des zones grises, voire à des infractions directes selon les législations nationales en matière de protection des données.
Ensuite, il existe un risque opérationnel et sécuritaire. L’analyste ne sait pas comment les données sont filtrées, modifiées ou croisées, ni s’il ne s’agit pas de données manipulées. De plus, ses propres requêtes peuvent être journalisées et réexploitées par le fournisseur du bot ou par des services de renseignement qui surveillent ces réseaux Telegram. En somme, utiliser un bot Telegram Usersbox ou un service probiv équivalent revient à accepter une forte dépendance technique, une traçabilité potentielle et une perte de souveraineté de l’enquête OSINT, notamment dans un contexte de confrontation informationnelle.
Prévenir un Usersbox local par le design des architectures souveraines
Pour commencer, un État qui se veut souverain doit agir au niveau de l’architecture de ses systèmes d’information, et pas seulement au niveau des lois répressives. Concrètement, cela implique de limiter la centralisation des PII, de segmenter les bases, de réduire les privilèges internes et de renforcer les contrôles d’accès et la journalisation.
Par ailleurs, il devient indispensable de sortir les secrets critiques des bases interrogeables. Des approches fondées sur le chiffrement local et des HSM souverains, comme DataShielder NFC HSM, DataShielder HSM PGP ou encore des solutions pair à pair comme CryptPeer, permettent de faire vivre les données sensibles hors des silos classiques. De cette manière, même si un bot probiv ou une messagerie comme Telegram sont compromis, la valeur exploitable pour un marché noir de données personnelles s’effondre. C’est précisément ce type d’architecture qui rend structurellement impossible l’apparition d’un « Usersbox local » sur des bases nationales.
Usersbox comme révélateur de la vraie souveraineté numérique d’un État
En apparence, Usersbox n’est qu’un bot de plus sur Telegram. Cependant, si l’on regarde de plus près, il devient le révélateur d’un problème structurel : un État qui centralise massivement ses données, tolère un probiv russe à grande échelle et découvre, trop tard, que son illusion de contrôle se retourne contre lui.
En ce sens, l’affaire du bot Telegram Usersbox oblige chaque pays à se poser une question simple : « nos architectures de données actuelles rendent-elles possible, demain, l’apparition d’un Usersbox local sur notre propre territoire ? ». La réponse à cette question en dit bien plus sur la souveraineté numérique réelle et sur le niveau de protection des données personnelles d’un État que n’importe quel discours sur la cybersécurité, l’OSINT ou la régulation des plateformes comme Telegram.
Ce que nous n’avons pas couvert
Cette chronique se concentre sur quelques axes précis : l’écosystème probiv russe, l’affaire Usersbox, le paradoxe d’un État qui centralise ses données mais en perd la maîtrise, et les réponses architecturales possibles. Elle laisse volontairement de côté plusieurs dimensions qui mériteraient, à elles seules, des analyses dédiées.
- Une cartographie détaillée de l’ensemble des services probiv russes, de leurs liens entre eux et de leurs éventuelles connexions avec des groupes criminels organisés.
- Une étude juridique comparée des cadres de protection des données dans d’autres pays, y compris en Europe, et de la façon dont ils pourraient, ou non, empêcher l’émergence d’un « Usersbox local ».
- Une analyse opérationnelle des techniques avancées de détection des fuites internes, des schémas de corruption et des modèles de supervision temps réel des accès privilégiés.
- Une exploration détaillée des alternatives OSINT souveraines, fondées uniquement sur des sources ouvertes et des outils maîtrisés localement, sans recours à des bots de type probiv.
Ces éléments pourront faire l’objet de futures chroniques, notamment dans la même collection Cyberculture, pour approfondir la part juridique, opérationnelle et prospective de la souveraineté des données à l’échelle d’un État.
Sources officielles et références
- Loi fédérale russe 420-FZ (30 novembre 2024) — Portail officiel Kremlin / pravo.gov.ru
- Banque de Russie – Estimation des pertes dues aux données compromises (2024–2025) — Banque centrale de Russie (cbr.ru)
- Izvestia – Analyse économique du marché probiv par Igor Bederov (T.Hunter) — Izvestia (iz.ru)