APT28 spear-phishing France: targeted attacks across Europe
APT28 Spear-Phishing: Russia’s Fancy Bear Targets Europe APT28, also known as Fancy Bear or Sofacy Group, a notorious Russian state-sponsored cyber espionage group, has intensified its spear-phishing campaigns against European entities. These meticulously crafted attacks primarily target government bodies, military organizations, and energy companies, aiming to extract sensitive information and potentially disrupt critical operations. This article delves into the evolving spear-phishing techniques employed by APT28 and provides essential strategies for effective prevention.
Table of Contents : • APT28 spear-phishing France • Historical Context: The Evolution of APT28 • Priority targets for APT28 spear-phishing campaigns • Spear-phishing and electoral destabilization in Europe • APT28 attribution and espionage objectives • Observed campaigns and methods (2022–2025) • Mapping APT28 to the Cyber Kill Chain • Tactics and Infrastructure: Increasing Sophistication • Coordination spear-phishing & disinformation: The two faces of APT28 • Official Report – CERTFR-2025-CTI-006 • Tactical Comparison: APT28 vs APT29 vs APT31 vs APT44 • Timeline of APT28 Spear-Phishing Campaigns • ANSSI’s operational recommendations • Regulatory framework: French response to spear-phishing • Exclusive availability in France via AMG Pro • Sovereign solutions: DataShielder & PassCypher against spear-phishing • Threat coverage table: PassCypher & DataShielder vs APT groups • Towards a European cyber resilience strategy
APT28 spear-phishing France: a persistent pan-European threat
APT28 spear-phishing France now represents a critical digital security challenge on a European scale. Since 2021, several European states, including France, have faced an unprecedented intensification of spear-phishing campaigns conducted by APT28, a state-sponsored cyber-espionage group affiliated with Russia’s GRU. Also known as Fancy Bear, Sednit, or Sofacy, APT28 targets ministries, regional governments, defense industries, strategic research institutions, critical infrastructure, and organizations involved with the Paris 2024 Olympic Games.
In a tense geopolitical context across Europe, APT28’s tactics are evolving toward stealthy, non-persistent attacks using malware like HeadLace and exploiting zero-day vulnerabilities such as CVE-2023-23397 in Microsoft Outlook. This vulnerability, detailed in a CERT-FR alert (CERTFR-2023-ALE-002), allows an attacker to retrieve the Net-NTLMv2 hash, potentially for privilege escalation. It is actively exploited in targeted attacks and requires no user interaction, being triggered by sending a specially crafted email with a malicious UNC link. This trend mirrors tactics used by APT44, explored in this article on QR code phishing, underscoring the need for sovereign hardware-based tools like DataShielder and PassCypher. European CISOs are encouraged to incorporate these attack patterns into their threat maps.
Historical Context: The Evolution of APT28
APT28 (Fancy Bear) has been active since at least 2004, operating as a state-sponsored cyber-espionage group linked to Russia’s GRU. However, its most heavily documented and globally recognized operations emerged from 2014 onward. That year marks a strategic shift, where APT28 adopted more aggressive, high-visibility tactics using advanced spear-phishing techniques and zero-day exploits.
Between 2008 and 2016, the group targeted several major geopolitical institutions, including:
• The Georgian Ministry of Defense (2008)
• NATO, the White House, and EU agencies (2014)
• The U.S. presidential election campaign (2016)
This period also saw extensive exposure of APT28 by cybersecurity firms such as FireEye and CrowdStrike, which highlighted the group’s growing sophistication and its use of malicious Word documents (maldocs), cloud-based command-and-control (C2) relays, and coordinated influence operations.
These earlier campaigns laid the foundation for APT28’s current operations in Europe — especially in France — and illustrate the persistent, evolving nature of the threat.
Priority targets for APT28 spear-phishing campaigns
Target typology in APT28 campaigns
PT28 targets include:
- Sovereign ministries (Defense, Interior, Foreign Affairs)
- Paris 2024 Olympics organizers and IT contractors
- Operators of vital importance (OVIs): energy, transport, telecoms
- Defense industrial and technological base (BITD) companies
- Research institutions (CNRS, INRIA, CEA)
- Local governments with strategic competencies
- Consulting firms active in European or sensitive matters
Spear-phishing and electoral destabilization in Europe
Political and geopolitical context of APT28 campaigns
APT28’s campaigns often precede key elections or diplomatic summits, such as the 2017 French presidential election, the 2019 European elections, or the upcoming Paris 2024 Olympic Games. These are part of a broader hybrid strategy aimed at destabilizing the EU.
Some spear-phishing attacks are synchronized with disinformation operations to amplify internal political and social tensions within targeted nations. This dual tactic aims to undermine public trust in democratic institutions.
Reference: EU DisinfoLab – Russia-backed disinformation narratives
Germany and NATO have also reported a resurgence of APT28 activities, particularly against NATO forces stationed in Poland, Lithuania, and Estonia. This strategic targeting of European institutions is part of a broader effort to weaken collective security in the EU.
APT28 attribution and espionage objectives
- Attribution: Main Intelligence Directorate (GRU), Unit 26165
- Key techniques: Targeted phishing, Outlook vulnerabilities, compromise of routers and peripheral devices
- Objectives: Data exfiltration, strategic surveillance, disruption of critical operations
APT28 also coordinates technical operations with information warfare: fake document distribution, disinformation campaigns, and exploitation of leaks. This “influence” component, though less covered in mainstream reports, significantly amplifies the impact of technical attacks.
Observed campaigns and methods (2022–2025)
| Date | Campaign | Targets | Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| March 2022 | Diplomatic phishing | EU ministries | Theft of confidential data |
| July 2023 | Military campaign | French and German forces | Access to strategic communications |
| Nov. 2024 | HeadLace & CVE exploit | Energy sector | Risk of logistical sabotage |
| April 2025 | Olympics 2024 operation | French local authorities | Compromise of critical systems |
🔗 See also: ENISA Threat Landscape 2024 – Cyberespionage Section
Mapping APT28 to the Cyber Kill Chain
| Kill Chain Step | Example APT28 |
| Reconnaissance | DNS scanning, 2024 Olympic monitoring, WHOIS tracking |
| Weaponization | Doc Word piégé (maldoc), exploit CVE-2023-23397 |
| Delivery | Spear-phishing by email, fake ..fr/.eu domains |
| Exploitation | Macro Execution, Outlook Vulnerability |
| Installation | Malware HeadLace, tunnels cloud (Trello, Dropbox) |
| C2 | GitHub relay, DNS Fast Flux |
| Actions on Obj. | Exfiltration, disinformation coordinated with DCLeaks |
Tactics and Infrastructure: Increasing Sophistication
APT28 Obfuscation and Infrastructure Methods
APT28 campaigns are distinguished by a high degree of stealth:
- Domain spoofing via homographs (e.g. gov-fr[.]net).
- Real-time payload encryption.
- Using legitimate cloud services like GitHub, Dropbox, or Trello as a C2 relay.
- Hosting on anonymized infrastructures (Fast Flux DNS, bulletproof hosting).
- Non-persistent attacks: ephemeral access, rapid exfiltration, immediate wipe. This approach makes detection particularly complex, as it drastically reduces the window of opportunity for forensic analysis, and the attacker’s infrastructure is often destroyed rapidly after compromise.
This mastery of technical obfuscation makes detection particularly complex, even for the most advanced SIEM systems and EDRs.
Coordination spear-phishing & disinformation: The two faces of APT28
APT28 is not limited to digital espionage. This group orchestrates coordinated disinformation campaigns, often leveraging platforms like DCLeaks or Guccifer 2.0, in sync with its spear-phishing operations. These actions aim to weaken the social and political cohesion of targeted countries.
Fake news campaigns exploit leaks to manipulate public opinion, amplify mistrust, and relay biased narratives. These tactics, as detailed in the CERT-EU Threat Landscape Report, highlight the sophisticated efforts deployed to influence perceptions and sow division.
APT28 in figures (source: ENISA, Mandiant, EU DisinfoLab)
- More than 200 campaigns recorded in Europe between 2014 and 2025
- More than 10,000 spear-phishing emails identified
- 65% of campaigns coordinated with influencer operations
- 8 zero-day vulnerabilities exploited since 2021
Weak Signals Before APT28 Attacks
Here are the warning signs identified by the CERTs and CSIRTs:
- Public DNS Recognition Campaigns
- Targeted scans of critical infrastructure
- Fraudulent domain registrations close to official names (e.g., counterfeit .gouv.fr)
- Malicious office files posted on forums or as attachments
Monitoring these indicators enables an active cyber defense posture.
Official Report – CERTFR-2025-CTI-006
Ciblage et compromission d’entités françaises au moyen du mode opératoire d’attaque apt28
Activités associées à APT28 depuis 2021
Published by CERT-FR on April 29, 2025, this report provides an in-depth analysis of APT28 spear-phishing France campaigns and cyber intrusions. Key highlights include:
- Attribution to APT28, affiliated with Russia’s GRU, using stealthy infection chains and phishing tactics;
- Systematic targeting of French government, diplomatic, and research institutions from 2021 to 2024;
- Continued threat amid the ongoing war in Ukraine, extending to Europe, Ukraine, and North America;
- Strong alignment with prior spear-phishing and disinformation tactics analyzed in this article.
Download the official PDF (in French):
View official CERT-FR page – CERTFR-2025-CTI-006.pdf – Full Report
This official warning reinforces the strategic need for sovereign hardware-based solutions like DataShielder and PassCypher to counter APT28 spear-phishing France campaigns effectively.
Tactical Comparison: APT28 vs APT29 vs APT31 vs APT44
While APT44 leverages QR codes to hijack platforms like Signal, APT28 stands out for its “quick strike” attacks, relying on disposable infrastructure.
Unlike APT29 (Cozy Bear), which favors persistent software implants for long-term monitoring, APT28 adopts stealth operations, supported by anonymous cloud relays and targeted social engineering campaigns.
Each of these groups reflects an offensive strategy of Russia or China, oriented against European strategic interests.
| APT Group | Affiliation | Main objective | Key tactics | Infrastructure | Peculiarity |
| APT28 (Fancy Bear) | GRU (Russia) | Espionage, influence | Spear-phishing, zero-day, cloud C2 | Disposable, Fast Flux | Coupled with fake news operations |
| APT29 (Cozy Bear) | SVR (Russia) | Persistent espionage | Software implants, stealthy backdoors | Infrastructure stable | Long-term monitoring |
| APT31 (Zirconium) | MSS (China) | IP Theft, R&D | Email spoofing, maldoc, scan DNS | Chinese Proxy | Recycling of open source tools |
| APT44 (Sandworm) | GRU (Russia) | Sabotage, disruption | QR phishing, attaques supply chain | External Hosting | Use of destructive techniques |
Timeline of APT28 Spear-Phishing Campaigns (2014–2025)
APT28 spear-phishing France is not an isolated threat but part of a broader, long-running offensive against Europe. This timeline traces the evolution of APT28’s major campaigns—from initial credential theft to advanced zero-day exploits and coordinated cyber-influence operations. It highlights the increasing sophistication of Russian GRU-aligned operations targeting national institutions, think tanks, and infrastructure across the continent.
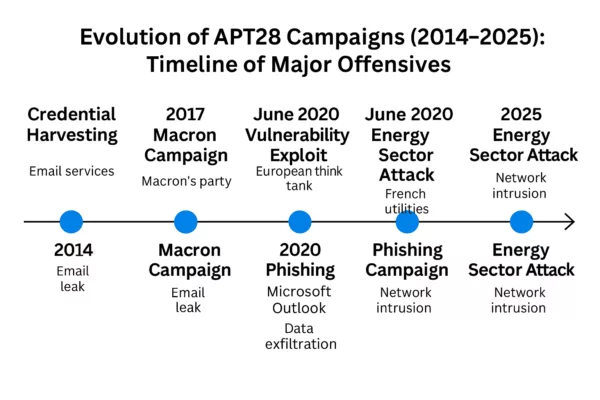
Evolution of APT28 Campaigns (2014–2025): This timeline outlines the key cyberattacks conducted by the Russian GRU-affiliated group APT28, highlighting spear-phishing operations targeting European institutions, critical infrastructure, and high-profile diplomatic events.
ANSSI’s operational recommendations
- Apply security patches (known CVEs) immediately.
- Audit peripheral equipment (routers, appliances).
- Deploy ANSSI-certified EDRs to detect anomalous behavior.
- Train users with realistic spear-phishing scenarios.
- Segment networks and enforce the principle of least privilege.
For detailed guidance, refer to the ANSSI recommendations.
Regulatory framework: French response to spear-phishing
- Military Programming Law (LPM): imposes cybersecurity obligations on OIVs and OESs.
- NIS Directive and French transposition: provides a framework for cybersecurity obligations.
- SGDSN: steers the strategic orientations of national cybersecurity.
- Role of the ANSSI: operational referent, issuer of alerts and recommendations.
- EU-level Initiatives: Complementing national efforts like those led by ANSSI in France, the NIS2 Directive, the successor to NIS, strengthens cybersecurity obligations for a wider range of entities and harmonizes rules across European Union Member States. It also encourages greater cooperation and information sharing between Member States.
Sovereign solutions: DataShielder & PassCypher against spear-phishing
Sovereign solutions: DataShielder & PassCypher against spear-phishing
DataShielder NFC HSM: An alternative to traditional MFA authentication
Most of APT28’s spear-phishing publications recommend multi-factor authentication. However, this MFA typically relies on vulnerable channels: interceptable SMS, exposed cloud applications, or spoofed emails. DataShielder NFC HSM introduces a major conceptual breakthrough:
| Criterion | Classic MFA | DataShielder NFC HSM |
| Channel used | Email, SMS, cloud app | Local NFC, without network |
| Dependency on the host system | Yes (OS, browser, apps) | No (OS independent) |
| Resistance to spear-phishing | Average (Interceptable OTP) | High (non-repeatable hardware key) |
| Access key | Remote server or mobile app | Stored locally in the NFC HSM |
| Offline use | Rarely possible | Yes, 100% offline |
| Cross-authentication | No | Yes, between humans without a trusted third party |
This solution is aligned with a logic of digital sovereignty, in line with the recommendations of the ANSSI.
DataShielder HSM PGP can encrypt all types of emails, including Gmail, Outlook, Yahoo, LinkedIn, Yandex, HCL Domino, and more. It encrypts messages end-to-end and decrypts them only in volatile memory, ensuring maximum privacy without leaving a clear trace.
PassCypher HSM PGP enhances the security of critical passwords and TOTP/HOTP codes through:
- 100% offline operation without database or server
- Secure input field in a dedicated tamper-proof sandbox
- Protection native contre les attaques BITB (Browser-in-the-Browser)
- Automatic sandbox that checks original URLs before execution
- Secure management of logins, passwords, and OTP keys in a siloed environment
En savoir plus : BITB attacks – How to avoid phishing by iframe
These solutions fit perfectly into sovereign cyber defense architectures against APTs.
🇫🇷 Exclusive availability in France via AMG Pro (Regulatory Compliance)
To comply with export control regulations on dual-use items (civil and military), DataShielder NFC HSM products are exclusively distributed in France by AMG PRO.
These products are fully compliant with:
- French Decree No. 2024-1243 of December 7, 2024, governing the importation and distribution of dual-use encryption systems.
- Regulation (EU) 2021/821, establishing a Union regime for the control of exports, transfer, brokering and transit of dual-use items (updated 2024).
Why this matters:
- Ensures legal use of sovereign-grade encryption in France and across the EU.
- Guarantees traceability and legal availability for critical infrastructures, ministries, and enterprises.
- Reinforces the sovereignty and strategic autonomy of European cybersecurity frameworks.
DataShielder NFC HSM: a French-designed and Andorran-manufactured offline encryption and authentication solution, officially recognized under civil/military dual-use classification.
Threat coverage table: PassCypher & DataShielder vs APT groups
Evaluating sovereign cyber defenses against APT threats
Faced with the sophisticated arsenal deployed by APT groups such as APT28, APT29, APT31 or APT44, it is becoming essential to accurately assess the level of protection offered by cybersecurity solutions. The table below compares the tactics used by these groups with the defense capabilities built into PassCypher, HSM, PGP, and DataShielder. This visualization helps CISOs and decision-makers quickly identify the perimeters covered, residual risks, and possible complementarities in a sovereign security architecture.
| Threat Type | APT28 | APT29 | APT31 | APT44 | Couverture PassCypher | DataShielder Coverage |
| Targeted spear-phishing | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ⚠️ | ✅ | ✅ |
| Zero-day Outlook/Microsoft | ✅ | ✅ | ⚠️ | ❌ | ✅ (sandbox indirect) |
✅ (memory encryption) |
| Cloud relay (Trello, GitHub…) | ✅ | ⚠️ | ✅ | ❌ | ✅ (URL detection) |
✅ |
| QR code phishing | ❌ | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
| BITB (Browser-in-the-Browser) | ✅ | ⚠️ | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ✅ |
| Attacks without persistence | ✅ | ❌ | ⚠️ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
| Disinformation / fake news | ✅ | ⚠️ | ❌ | ✅ | ✅ (scission login/data) |
⚠️ (via partitioning) |
| Compromise of peripheral equipment | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ⚠️ | ❌ | ✅ (via HSM) |
| Targeting elections/Olympics | ✅ | ⚠️ | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ✅ |
✅ = Direct protection / ⚠️ = Partial mitigation / ❌ = Not directly covered
Towards a European cyber resilience strategy
APT28, APT29, APT44: these are all groups that illustrate an offensive escalation in European cyberspace. The response must therefore be strategic and transnational:
- Coordination by ENISA and the European CSIRT Network
- IOC sharing and real-time alerts between Member States
- Regulatory harmonization (NIS2 revision, Cyber Resilience Act)
- Deployment of interoperable sovereign solutions such as DataShielder and PassCypher
See also: Cyber Resilience Act – EU 🔗 See also: APT44 QR Code Phishing – Freemindtronic
CISO Recommendation: Map APT28 tactics in your security strategies. Deploy segmented, offline authentication solutions like DataShielder, combined with encrypted questionnaire tools such as PassCypher to counter spear-phishing attacks.