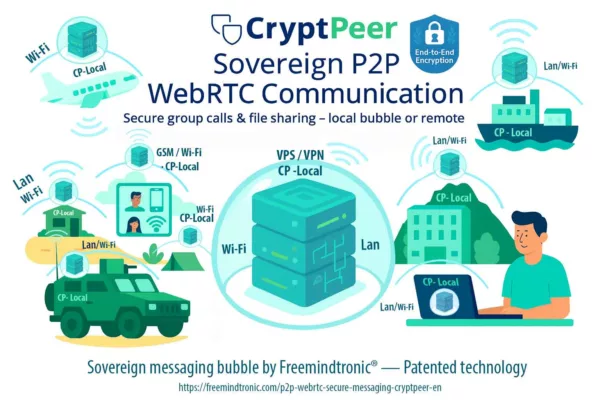
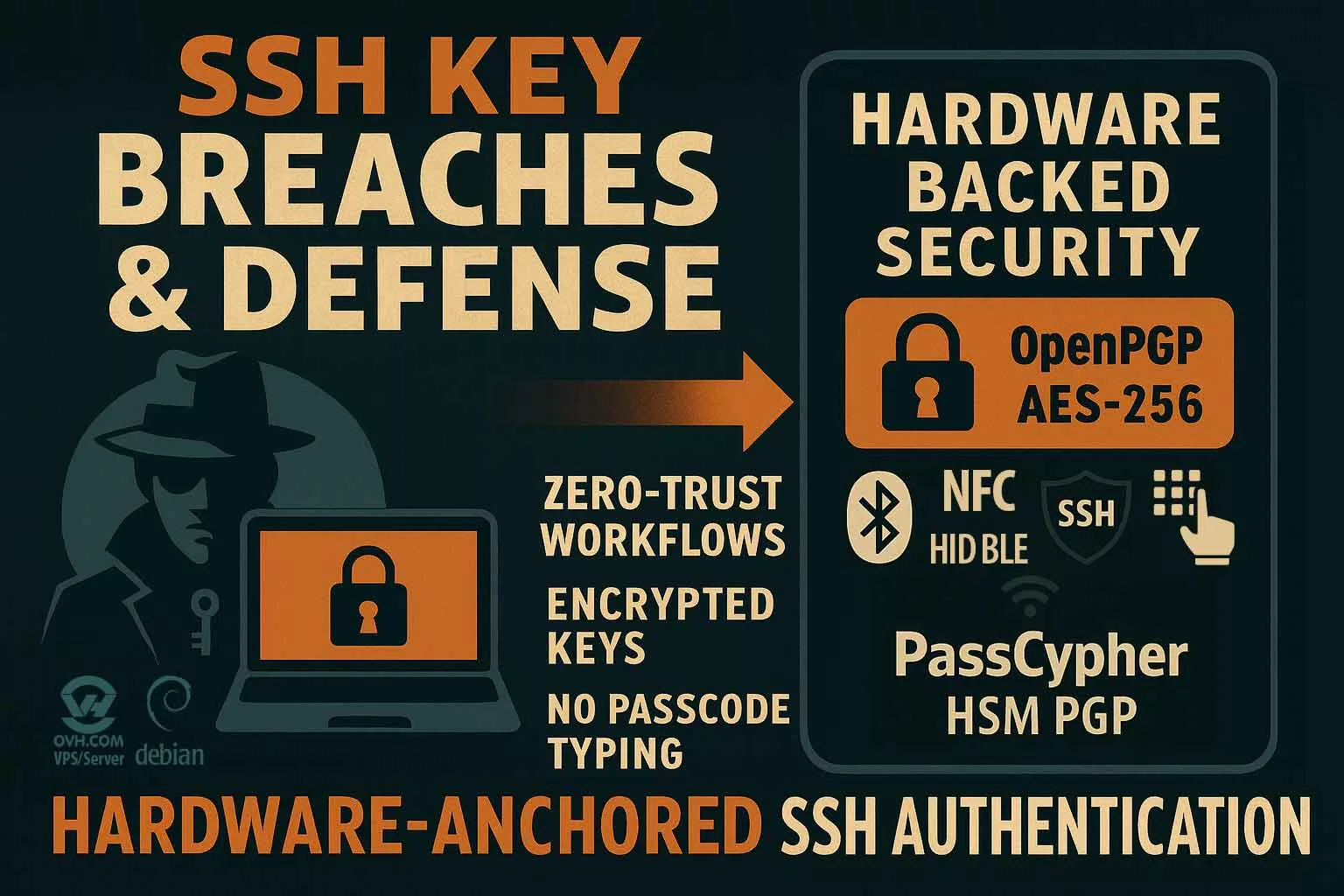
Innovation of rupture is not simply a bold invention—it’s a shift in power, usage, and norms. This article explores two dominant visions of innovation, the role patents play in enabling or constraining breakthroughs, and the systemic resistance that disruptors must navigate. Using Freemindtronic’s sovereign cybersecurity technologies as a real-world case, we analyze how regulatory inertia, industrial dependencies, and biased standards affect the path to adoption. Anchored in field experience and strategic reflection, this narrative offers a vision of innovation that is resilient, disruptive, and sovereign by design.
About the author — Jacques Gascuel is the inventor and founder of Freemindtronic Andorra, where he pioneers disruptive sovereign cybersecurity technologies based on patented architectures. With a legal background and a strategic mindset, he explores how hardware-based security and normative resistance intersect in sovereign contexts. His work focuses on building autonomous systems — offline, OS-independent, and resilient by design — to address the systemic inertia in regulated environments. Through his publications, Jacques bridges field innovation, legal asymmetry, and technological sovereignty, offering a vision of cybersecurity that breaks compliance boundaries without compromising purpose.
Disruptive innovation doesn’t bloom from comfort. It emerges where certainties tremble—when new visions confront the inertia of accepted norms. In today’s strategic landscape, where sovereignty meets cybersecurity and systemic inertia blocks transformation, innovation of rupture becomes more than a buzzword. It’s a tension between evolving what exists and inventing what doesn’t. Many organizations believe innovation must adapt to existing frameworks. Others argue real progress demands defiance—crafting new usage models, new markets, and entirely new expectations. This friction fuels the deeper dilemma: should innovators conform to dominant systems or design alternatives that reshape the rules? In practice, innovation of rupture sits at this crossroads. It alters market structures, redefines user behaviors, and demands new regulatory thinking. But to disrupt effectively, it must challenge more than just technical limitations. It must shake habits, belief systems, and institutional dependencies. This article explores: While patents are commonly viewed as tools for safeguarding innovation, they rarely ensure its success. A patent may shield an idea from duplication, but it does not compel the market to embrace it. This tension is especially true for innovations of rupture, which often disrupt comfortable norms and threaten entrenched interests. Patents are legal instruments designed to grant inventors exclusive rights over their creations. They protect intellectual property, encourage investment, and often strengthen negotiation power. Yet, as powerful as patents are on paper, they do not automatically accelerate adoption. A patented disruptive technology may languish if it collides with regulatory inertia or lacks strategic alignment. 👉 According to the European Patent Office (EPO), over 50% of patents never make it to market. That figure increases when the technology challenges dominant standards or requires user behavior change. When disruption alters usage patterns or demands new norms, patents become part of a broader strategy—not a safety net. For instance, sovereign cybersecurity tools that operate without OS dependency or cloud access may bypass known frameworks entirely. In doing so, they risk clashing with legislation and standards designed around centralized control. 📌 Consider this: a patented sovereign security device offers offline encryption, no RAM exposure, and total independence. But if legal frameworks mandate auditability through centralized servers, the disruptive power becomes paradoxical—it’s secured by law yet suppressed by law. Innovation of rupture thrives only when the patent’s protection aligns with market readiness, user context, and communication strategy. Adoption requires more than exclusivity—it calls for trust, usability, and perceived legitimacy. The patent may block competitors, but only strategic narrative enables traction. As we move forward, it becomes clear that even well-protected inventions need to confront a larger force: systemic resistance driven by lobbying, standards, and industrial dependencies. Even the most visionary innovations are rarely welcomed with open arms. When a technology disrupts existing structures or threatens entrenched powers, it enters an ecosystem where resistance is embedded. Systemic forces—legislative inertia, industrial dependencies, and hidden lobbying—work collectively to defend the status quo. And this resistance doesn’t always wear a uniform. Sometimes it looks like compliance. Other times it’s masked as best practices. Standards are designed to harmonize markets, ensure safety, and guide interoperability. Yet in practice, some norms are shaped by dominant players to protect their advantage. When a disruptive technology operates outside conventional OS frameworks, centralized infrastructure, or cloud ecosystems, it may be deemed non-compliant—not because it is unsafe, but because it is independent. Strategic disobedience then becomes a necessity, not a weakness. The power of lobbying often lies in its subtlety. Through influence on advisory boards, standardization committees, or regulatory language, certain entities steer innovation in directions favorable to existing infrastructures. As reported in the OECD’s regulatory innovation framework, this type of resistance can stall sovereign solutions under the guise of safety, stability, or ecosystem integrity. Large-scale institutions—whether governmental, financial, or industrial—build upon legacy systems that are expensive to replace. Technologies that challenge those infrastructures often face delayed integration, skepticism, or exclusion. Sovereign cybersecurity tools, for instance, may offer superior decentralization, but if the ecosystem demands centralized logging or remote validation, their deployment becomes politically complex. In theory, disruptive innovation sparks transformation. In practice, it challenges conventions head-on. Freemindtronic’s sovereign cybersecurity solutions demonstrate what happens when disruption refuses to conform. Designed to operate fully offline, independent of operating systems or cloud infrastructure, these hybrid HSMs (Hardware Security Modules) embody true innovation of rupture. They don’t just secure — they redefine the terms of security itself. Freemindtronic’s DataShielder NFC HSM devices offer autonomous encryption, air-gapped by design. Credentials and cryptographic operations remain insulated from operating systems, RAM, and clipboard exposure — a direct response to threats like Atomic Stealer (AMOS), which weaponize native OS behaviors. This sovereign architecture decentralizes trust, eliminates third-party dependencies, and removes the attack surface exploited by memory-based malware. In a landscape where cybersecurity often means cloud integration and centralized monitoring, Freemindtronic’s solution is strategically disobedient. Despite its resilience and privacy-by-design principle, this type of sovereign hardware often encounters systemic resistance. Why? Because mainstream standards favor interoperability through centralized systems. Secure messaging protocols, compliance tools, and authentication flows assume OS/cloud integration. A device that deliberately avoids those channels may be seen as “non-compliant” — even when it’s demonstrably more secure. For Freemindtronic, rupture is not a side effect — it’s a strategic direction. By embedding sovereignty at the hardware level, the company redefines what cybersecurity means in hostile environments, mobility constraints, and regulatory asymmetry. Patents protect the technical methods. Field validation confirms operational effectiveness. But the real challenge lies in aligning this innovation with institutions still tethered to centralized control. Innovation of rupture offers strategic independence—but when used maliciously or without accountability, it can destabilize sovereign balance. Technologies designed for autonomy and security may become instruments of opacity, evasion, or even asymmetrical disruption. Furtive devices that bypass OS, cloud, and traceability protocols pose new ethical and political dilemmas. While sovereign tools empower users, they may also obstruct lawful oversight. This paradox reveals the fragility of digital sovereignty: the very features that protect against surveillance can be weaponized against institutions. If rupture becomes uncontrolled stealth, sovereignty turns inward—and may erode from within. State actors must balance innovation support with strategic safeguards. Furtive tech, if exploited by criminal networks or hostile entities, could bypass national defense, disrupt digital infrastructure, or undermine democratic mechanisms. The challenge is to maintain sovereignty without losing visibility. The answer is not to suppress rupture, but to govern its implications. Innovation must remain open—but the usage contexts must be anticipated, the risks modeled, and the countermeasures embedded. Otherwise, strategic disobedience may mutate into strategic evasion. In environments shaped by digital surveillance and institutional control, sovereign technologies must do more than protect — they must resist. Freemindtronic’s HSM architectures do not rely on operating systems, cloud, or centralized protocols. Their independence is not incidental — it is intentional. These devices stand as natural barriers against intrusion, espionage, and normative capture. By operating offline, memory-free, and protocol-neutral, these sovereign systems form natural countermeasures against technical espionage. At the institutional level, they resist interception, logging, and backend exploitation. At the individual level, they preserve digital autonomy, shield private credentials, and deny access vectors that compromise sovereignty. This architecture doesn’t just avoid surveillance — it actively denies the mechanisms that enable it. In doing so, it redefines the notion of defensive security: not as passive protection, but as active strategic disobedience. Sovereign HSMs like those from Freemindtronic don’t block threats — they render them inoperative. The CIA’s 2022 study on cyber deterrence recognizes that disruption of espionage pathways is more effective than traditional deterrence. Similarly, Columbia SIPA’s Cyber Disruptions Dataset catalogs how sovereign tech can neutralize even state-level surveillance strategies. Not all rupture starts by defying the frame. Sometimes, it emerges from strategic differentiation within existing norms. The Boxilumix® technology developed by Asclepios Tech exemplifies this pathway: it doesn’t reject post-harvest treatment—it reimagines it through light modulation, without chemicals. Boxilumix® respects regulatory frameworks yet achieves measurable innovation: longer shelf life, improved appearance, enhanced nutritional value. These advancements address stringent export demands and create value without entering regulatory conflict. Their approach earned high-level validation: Seal of Excellence (European Commission), Booster Agrotech (Business France), and multiple awards for sustainable food innovation. It proves that innovation of rupture can also arise from mastering differentiation, not just rebellion. Whether through institutional challenge or smart alignment, innovation succeeds when it balances context, purpose, and narrative. Asclepios Tech shows that rupture can be elegant, embodied through precision rather than force. Inventing is never enough. For innovation of rupture to matter, it must be adopted—and for adoption to happen, strategy must shape perception. Disruptive technologies don’t just fight technical inertia; they challenge political, cultural, and institutional expectations. Without a compelling narrative, even the most sovereign innovation remains marginal. Innovators often underestimate how tightly trust is bound to context. A sovereign security device may prove resilient in lab conditions, but if users, regulators, or institutions lack visibility into its methods or relevance, adoption slows. Disruption must speak the language of its environment—whether that’s national sovereignty, data protection, or resilience in critical infrastructure. A powerful narrative aligns the innovation with deeper social and institutional needs. It must translate disruption into clarity—not just for engineers, but for decision-makers, legal analysts, and end users. The message must express purpose, urgency, and credible differentiation. Long before markets shift, minds must be convinced. Creating new usage is more strategic than improving old ones. Sovereign cybersecurity tools succeed when they’re not just better, but necessary. Frictionless integration, context-aware functions, and layered utility drive usage organically. Once a tool shapes how people behave, it reshapes how industries and institutions respond. To thrive amid systemic blockers, innovators must anticipate regulatory gaps, industrial dependencies, and political asymmetries. Strategic rupture doesn’t mean isolation—it requires calibrated tension. By preparing answers to compliance queries, forging alternative trust models, and demonstrating social impact, the innovator positions disruption not as rebellion but as solution. Far from being speculative, the concept of innovation of rupture and technological sovereignty is increasingly echoed in global institutional and academic discourse. Recent studies expose how lobbying, standardization politics, and intellectual property systems can hinder strategic adoption. The need for independent frameworks, sovereign infrastructures, and regulatory agility is no longer just theoretical—it’s an emerging priority. The OECD report “Lobbying in the 21st Century” (2021) reveals how influential actors shape regulatory norms to sustain dominant business models. This aligns with our earlier analysis: disruption often faces resistance dressed as “standards.” Transparency International’s statement on OECD lobbying reforms warns of “unregulated influence ecosystems” that may suppress sovereign technologies before public adoption begins. The German institute Fraunhofer ISI defines technological sovereignty as the capacity to “make independent technological choices” in strategically sensitive domains. Their report underscores the role of rupture in escaping dependency traps — especially in digital infrastructure. Dutch research center TNO’s whitepaper details how decentralized, sovereign cybersecurity tools strengthen resilience. Offline hardware models — as exemplified by Freemindtronic — are cited as viable alternatives to cloud-based dependencies. The Stockholm School of Economics provides a detailed thesis on patent limitations: “The Impact of the Patent System on Innovation” by Julian Boulanger explains how patents fail when they lack socio-regulatory traction. Further, Télécom ParisTech’s thesis by Serge Pajak “La propriété intellectuelle et l’innovation” explores how innovation of rupture faces challenges when legal frameworks are not strategically aligned. An EU-wide study by Frontiers in Political Science “Digital Sovereignty and Strategic Autonomy” analyzes conflicts between national interest and imposed technical standards. It confirms what field innovators already know: real sovereignty often requires navigating beneath the surface of compatibility and compliance. The vision behind innovation of rupture is not isolated—it is increasingly echoed across high-level institutions, deeptech policy reports, and academic research. Sovereignty, disobedience by design, and resistance to normative capture are themes gaining traction in both state-level and multilateral contexts. Below is a curated set of official studies, whitepapers, and theses that lend credibility and depth to the disruptive sovereignty framework. The OECD’s report “Lobbying in the 21st Century” highlights how technical standards and regulatory influence are often shaped to favor incumbents. Norms may reflect ecosystem biases, not innovation potential. Transparency International further warns that unregulated influence ecosystems suppress sovereign technologies under the guise of compliance. Fraunhofer Institute’s 2021 paper frames sovereignty as the ability to make independent choices in tech-critical areas. It recognizes rupture as a mechanism to escape dependency traps and enhance strategic autonomy. The Dutch innovation hub TNO lays out clear alternatives to cloud-centric security in its 2024 whitepaper “Cybersecurity and Digital Sovereignty”. It cites air-gapped HSMs as foundational elements of resilience—a core tenet of Freemindtronic’s technology. The DGE’s Deeptech 2025 report defines innovation of rupture as a strategic lever to address industrial sovereignty, cybersecurity, and supply chain independence. It calls for regulatory flexibility and intellectual property reforms to enable adoption. In Springer’s 2024 monograph “Cyber Sovereignty”, researchers analyze how digital sovereignty is used by nations to reassert control in fragmented and unregulated technological ecosystems. It positions rupture as both political and technical strategy. Frontiers in Political Science explores the friction between pan-European norms and national digital autonomy. It validates sovereign hardware and non-cloud infrastructures as legitimate modes of technological independence. Sovereignty doesn’t exclude collaboration. As argued in Intereconomics’ article “Coopetitive Technological Sovereignty”, strategic autonomy may be best achieved by choosing productive interdependence—where innovation remains independent, but dialogue continues. Disruption without sovereignty is often short-lived. True rupture begins when innovation no longer seeks validation from the systems it challenges. As we’ve seen, patents offer protection but not traction, standards can ossify into gatekeeping tools, and market adoption demands a layered strategy. But beyond technique lies posture—a deliberate alignment between vision and action, even when action diverges from dominant models. Strategic disobedience is not recklessness—it’s methodical. It means identifying systemic bottlenecks, assessing normative traps, and crafting technologies that are contextually aware yet structurally independent. Sovereign tools do not just perform—they resist absorption. And for inventors operating at the frontier, that resistance is not a flaw but a function. Technological rupture often unsettles the familiar. It may provoke critique, trigger lobbying pushback, or be framed as “unusual.” But redefinition is born in discomfort. Freemindtronic’s example proves that by designing for autonomy and resilience, innovation can sidestep fragility and embrace sovereignty—not as a theme, but as a framework. This perspective is not closed—it’s open to interpretation, continuation, and even contradiction. Disruptive sovereignty is not a monologue. It’s a strategic invitation to reimagine innovation beyond compatibility, beyond compliance, and beyond control. It calls inventors, policymakers, and tech leaders to embody a form of creation that respects context but isn’t bound by it.Executive Summary
Strategic Reading Guide
Key Strategic Takeaways
Innovation beyond comfort zones
The Patent Paradox: Protection vs Adoption
Protection without traction
Innovation of rupture meets legal friction
Strategic alignment matters
Systemic Resistance: Lobbying, Norms and Market Inertia
Norms as strategic control mechanisms
Lobbying as invisible resistance
Legacy dependencies and institutional inertia
When norms are crafted around centralized control, true sovereignty looks disruptive. And disruption, by design, resists permission.Case Study – Freemindtronic and Sovereign HSM Disruption
Security without OS or cloud dependency
A technology that challenges normative ecosystems
Strategic positioning amid systemic resistance
Freemindtronic’s sovereign HSMs don’t just defend against threats — they reject the frameworks that enable them. That’s where rupture becomes strategy.Risks of Rupture – When Sovereign Technology Challenges Sovereignty Itself
Between emancipation and erosion
National interest and digital asymmetry
Proactive governance over sovereign tools
Without contextual safeguards, innovation of rupture risks becoming a vehicle for sovereignty denial—not reinforcement.Disruptive Counter-Espionage – Sovereignty by Design
Natural sovereignty barriers: institutional and individual
Espionage denial as strategic posture
Global recognition of disruption as countermeasure
Whether institutional or personal, sovereignty begins where espionage ends. Freemindtronic’s rupture model isn’t a shield. It’s a denial of exposure.Innovation Between Differentiation and Disruption
Conforming without compromising innovation
Recognition through integration
Strategic lesson — arbitrating innovation paths
Sometimes, the most strategic disruption is knowing how to differentiate—without leaving the frame entirely.Strategic Adoption: Making Rupture Acceptable
Context drives legitimacy
Storytelling as strategic infrastructure
Usage as a trigger of adoption
Tactical alignment with resistance
Visibility, narrative, and context make rupture acceptable—even when it remains strategically disobedient.Institutional and Academic Validation of Disruptive Sovereignty
OECD – Lobbying and normative bias
Fraunhofer ISI – Technology sovereignty as policy framework
TNO – Autonomy and digital resilience
Academic theses – Patents and resistance strategies
EU studies – Strategic autonomy and sovereignty
From OECD to Fraunhofer, EU institutions to doctoral research, the call for sovereignty in innovation is growing. Freemindtronic’s model is not fringe—it’s frontline.Strategic Validation — When Institutions and Research Confirm the Sovereign Path
OECD – Lobbying and Normative Resistance
Fraunhofer ISI – Defining Technology Sovereignty
TNO – Sovereign Cybersecurity Architectures
France – Deeptech and Sovereign Innovation Strategy
Springer – Cyber Sovereignty and Global Power Shifts
Frontiers – EU and Strategic Autonomy
Academic Theses – Patents and Resistance Mechanics
Towards Coopetitive Sovereignty
From OECD and Fraunhofer to EU bodies and French industrial strategy, your thesis is not just visionary—it’s reflected in the architecture of future innovation governance.Towards Disruptive Sovereignty – A Strategic Perspective
The role of the inventor: method over compliance
Accept discomfort, pursue redefinition
From strategic insight to collective movement
To disrupt meaningfully, innovators must stop asking for permission—and start building what permission never allowed.
Author Archives: FMTAD
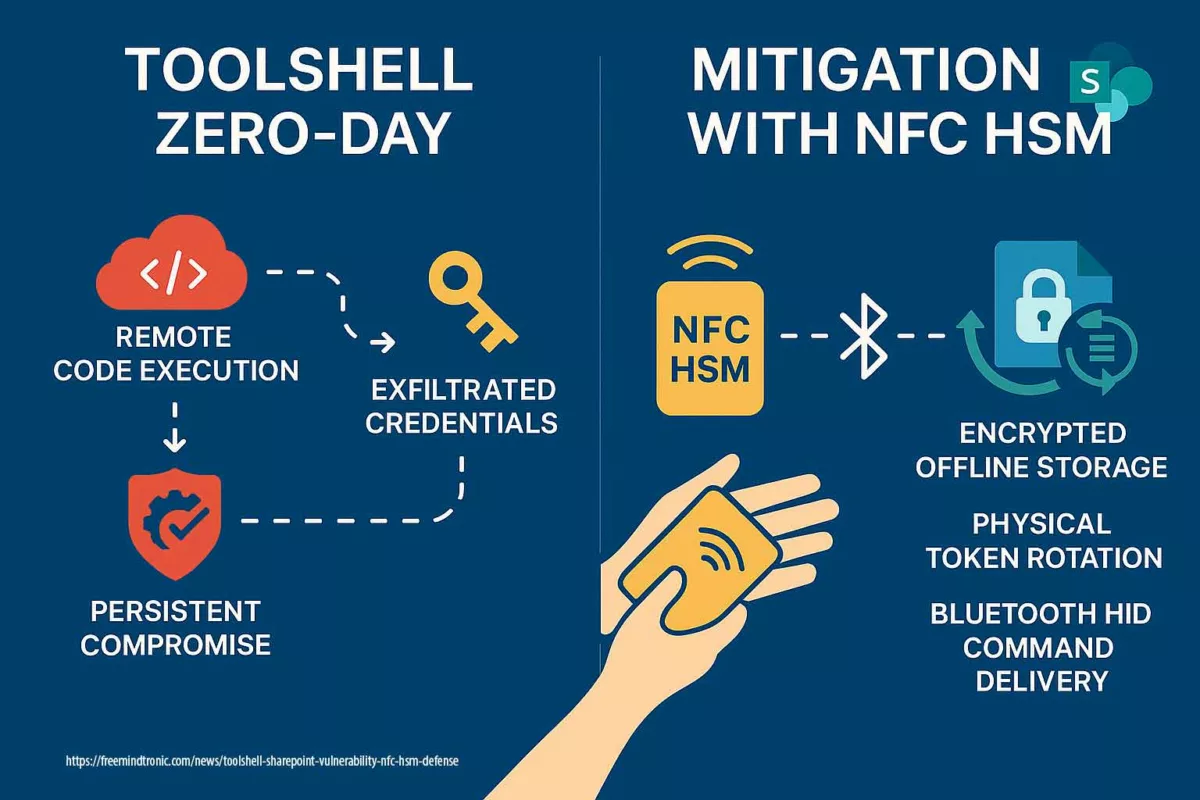
Atomic Stealer AMOS: Redefining Mac Cyber Threats Featured in Freemindtronic’s Digital Security section, this analysis by Jacques Gascuel explores one of the most sophisticated and resilient macOS malware strains to date. Atomic Stealer Amos merges cybercriminal tactics with espionage-grade operations, forming a hybrid threat that challenges traditional defenses. Gascuel dissects its architecture and presents actionable strategies to protect national systems and corporate infrastructures in an increasingly volatile digital landscape.
Explore More in Digital Security
Stay ahead of advanced cyber threats with in-depth articles from Freemindtronic’s Digital Security section. From zero-day exploits to hardware-based countermeasures, discover expert insights and field-tested strategies to protect your data, systems, and infrastructure.
Executive Summary
Atomic Stealer (AMOS) redefined how macOS threats operate. Silent, precise, and persistent, it bypassed traditional Apple defenses and exploited routine user behavior to exfiltrate critical data. This article offers a strategic analysis of AMOS’s evolution, infection techniques, threat infrastructure, and its geopolitical and organizational impact. It also provides concrete defense recommendations, real-world case examples, and a cultural reassessment of how we approach Apple endpoint security.
Atomic Stealer AMOS: The Mac Malware That Redefined Cyber Infiltration
Last Updated: 08 july 2025
Version: 1.0
Source: Freemindtronic Andorra
Atomic Stealer – Navigation Guide
- Macs Were Safe. Until They Weren’t.
- Updated Threat Capabilities July 2025
- A Threat Engineered for Human Habits
- Adaptation as a Service
- Two Clicks Away from a Breach
- Institutional Blind Spots
- Detecting the Undetectable
- Malware-as-a-Service, Industrial Grade
- Strategic Exposure: Who’s at Risk
- What Defenders Fear Next
- Threat Actor Attribution: Who’s Really Behind AMOS?
- Indicators of Compromise (IOCs)
- Defenders’ Playbook: Active Protection
- Freemindtronic Solutions to Secure macOS
- What About Passkeys and Private Keys?
- DataShielder: Hardware Immunity Against macOS Infostealers
- PassCypher Protection Against AMOS
- Atomic Stealer Amos and the Future of macOS Security Culture
- Verified Sources
Macs Were Safe. Until They Weren’t.
For more than a decade, macOS held a reputation as a bastion of digital safety. Many believed its architecture inherently protected users from the kind of sophisticated malware seen on Windows. This belief was widespread, deeply rooted—and dangerously wrong.
In April 2023, that myth cracked open.
Security researchers from Malwarebytes and Moonlock spotted a new macOS malware circulating on Telegram. It wasn’t loud. It wasn’t chaotic. It didn’t encrypt files or display ransom notes. Instead, it crept in silently, exfiltrating passwords, session tokens, and cryptocurrency wallets before anyone noticed. They called it Atomic Stealer AMOS for short.
It doesn’t log keystrokes. It doesn’t need to. AMOS exploits macOS-native trust zones like Keychain and iCloud Keychain. Only air-gapped hybrid HSM solutions — like NFC HSM and PGP HSM — fully isolate your secrets from such attacks.

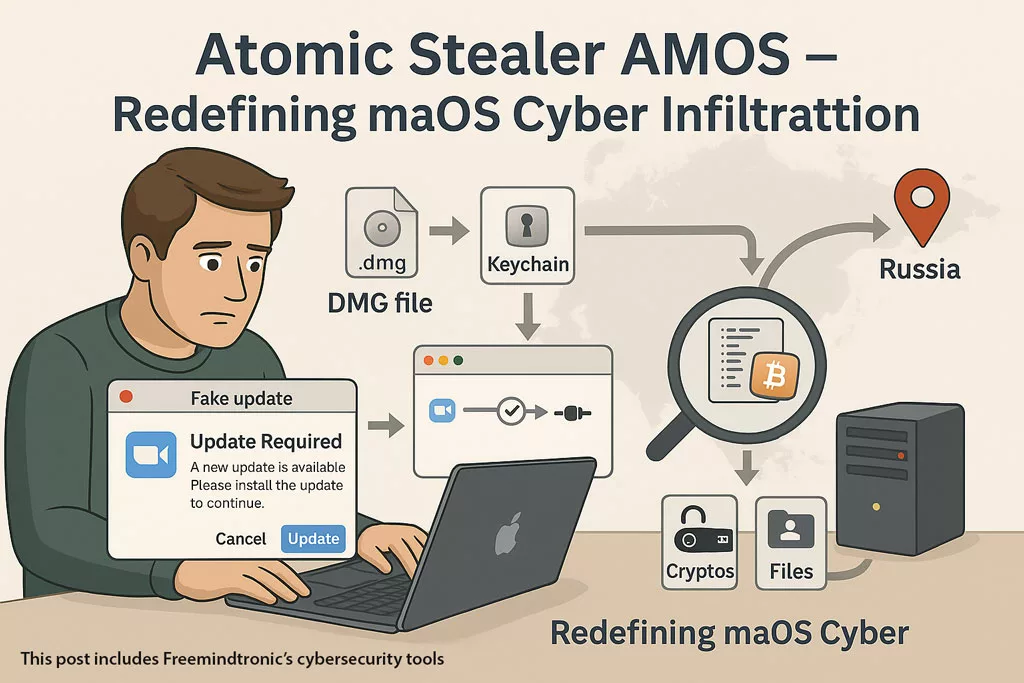
✪ Illustration showing Apple’s ecosystem under scrutiny, symbolizing the covert infiltration methods used by Atomic Stealer AMOS.
By mid-2025, Atomic had breached targets in over 120 countries. It wasn’t a side-story in the malware landscape anymore—it had become a central threat vector, especially for those who had mistakenly assumed their Macs were beyond reach.
In April 2023, that myth cracked open…
They called it Atomic Stealer AMOS for short.
It doesn’t encrypt or disrupt. It quietly exfiltrates credentials, tokens, and crypto wallets—without triggering alerts.
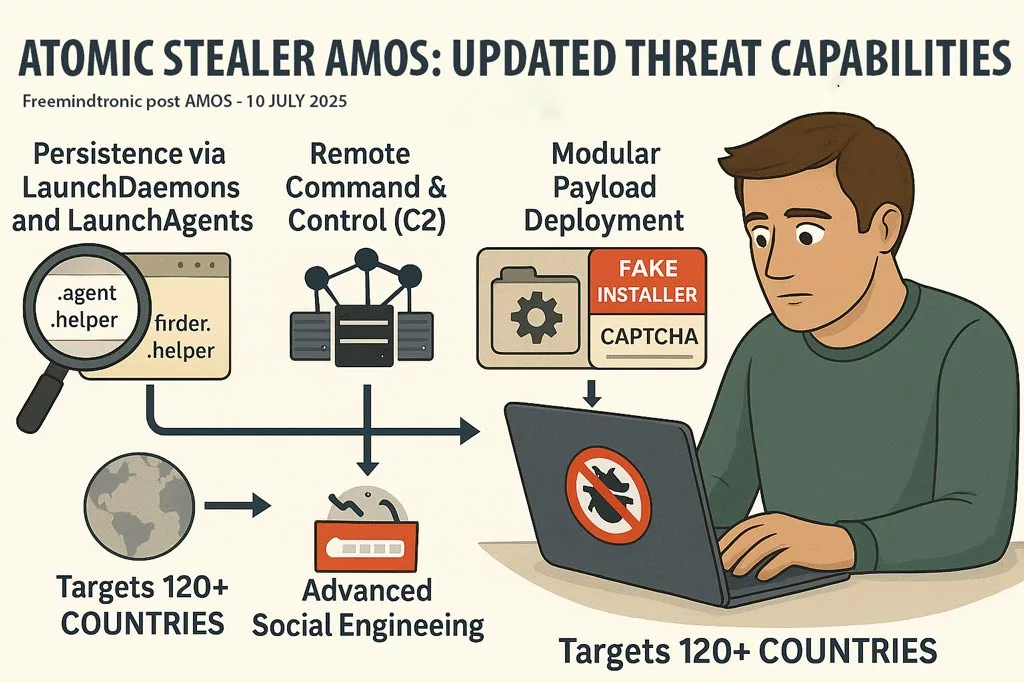
Updated Threat Capabilities July 2025
Since its initial discovery, Atomic Stealer AMOS has evolved dramatically, with a much more aggressive and stealthy feature set now observed in the wild.
- Persistence via macOS LaunchDaemons and LaunchAgents
AMOS now installs hidden.agentand.helperfiles, such ascom.finder.helper.plist, to maintain persistence even after reboot. - Remote Command & Control (C2)
AMOS communicates silently with attacker servers, enabling remote command execution and lateral network movement. - Modular Payload Deployment
Attackers can now inject new components post-infection, adapting the malware’s behavior in real time. - Advanced Social Engineering
Distributed via fake installers, trojanized Homebrew packages, and spoofed CAPTCHA prompts. Even digitally signed apps can be weaponized. - Global Spread
Targets across 120+ countries including the United States, France, Italy, UK, and Canada. Attribution links it to a MaaS operation known as “Poseidon.”
Recommended Defense Enhancements
To defend against this rapidly evolving macOS threat, experts recommend:
- Monitoring for unauthorized
.plistfiles and LaunchAgents - Blocking unexpected outbound traffic to unknown C2 servers
- Avoiding installation of apps from non-official sources—even if signed
- Strengthening your Zero Trust posture with air-gapped tools like SeedNFC HSM and Bluetooth Keyboard Emulator to eliminate clipboard, keychain, and RAM-based exfiltration vectors
Risk Scoring Update for Atomic Stealer AMOS
| Capability | Previous Score | July 2025 Score |
|---|---|---|
| Stealth & Evasion | 8/10 | 9/10 |
| Credential & Crypto Theft | 9/10 | 10/10 |
| Persistent Backdoor | 0/10 | 10/10 |
| Remote Access / C2 | 2/10 | 10/10 |
| Global Reach & Target Scope | 9/10 | 9/10 |
| Overall Threat Level | 7.6 / 10 | 9.6 / 10 |
✪ Illustration showing Atomic Stealer AMOS breaching Apple’s ecosystem, using stealthy exfiltration methods across macOS environments.
New Backdoor: Persistent and Programmable
In early July 2025, Moonlock – MacPaw’s cybersecurity arm – confirmed a significant upgrade: AMOS now installs a hidden backdoor (via .helper/.agent + LaunchDaemon), which survives reboots and enables remote command execution or additional payload delivery — elevating its threat level dramatically
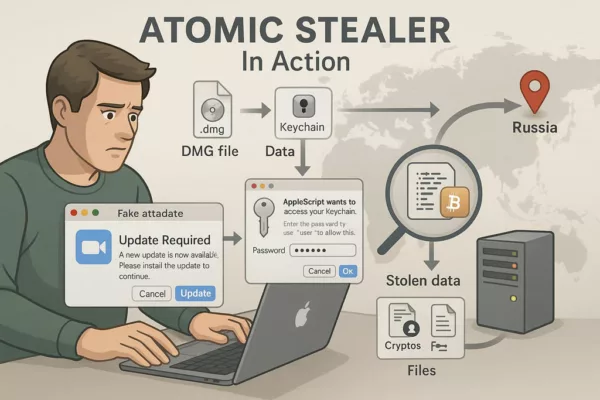
A Threat Engineered for Human Habits
Atomic Stealer AMOS didn’t rely on zero-days or brute force. It exploited something far more predictable: human behavior.
Freelancers seeking cracked design plugins. Employees clicking “update” on fake Zoom prompts. Developers installing browser extensions without scrutiny. These seemingly minor actions triggered full system compromise.
Once deployed, AMOS used AppleScript prompts to request credentials and XOR-encrypted payloads to evade detection. It embedded itself via LaunchAgents and LaunchDaemons, securing persistence across reboots.
✪ A visual breakdown of Atomic Stealer’s infection method on macOS, from fake update to credential theft and data exfiltration.
Its targets were no less subtle:
- Passwords saved in Chrome, Safari, Brave
- Data from over 50 crypto wallets (Ledger, Coinomi, Exodus…)
- Clipboard content—often cryptocurrency transactions
- Browser session tokens, including cloud accounts
SpyCloud Labs – Reverse Engineering AMOS
Atomic didn’t crash systems or encrypt drives. It simply harvested. Quietly. Efficiently. Fatally.
Adaptation as a Service
What makes AMOS so dangerous isn’t just its code—it’s the mindset behind it. This is malware designed to evolve, sold as a service, maintained like a product.
| Date | Evolution Milestone |
|---|---|
| Apr 2023 | First sightings in Telegram forums |
| Sep 2023 | ClearFake phishing campaigns weaponize delivery |
| Dec 2023 | Encrypted payloads bypass antivirus detection |
| Jan 2024 | Fake Google Ads launch massive malvertising wave |
| Jul 2025 | Persistent remote backdoor integrated |

✪ This infographic charts the infection stages of Atomic Stealer AMOS, highlighting key milestones from its emergence via cracked macOS apps to sophisticated phishing and remote access techniques.
Picus Security – MITRE ATT&CK mapping
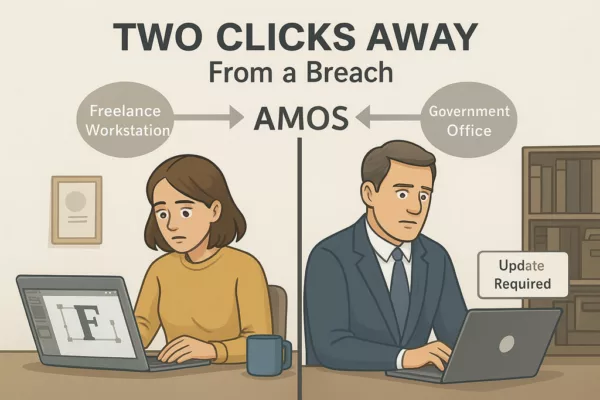
Two Clicks Away from a Breach
To understand AMOS, you don’t need to reverse-engineer its binaries. You just need to watch how people behave.
In a real-world example, a freelance designer downloaded a cracked font plugin to meet a deadline. Within hours, AMOS drained her wallet, accessed her saved credentials, and uploaded client documents to a remote server.
In a separate case, a government office reported unusual login activity. Investigators found a spoofed Slack update triggered the breach. It wasn’t Slack. It was AMOS.
✪ Illustration depicting the dual nature of Atomic Stealer (AMOS) attacks: a freelancer installing a cracked plugin and a government employee clicking a fake Slack update, both leading to data theft and wallet drain.
Institutional Blind Spots
In 2024, Red Canary flagged Atomic Stealer among the top 10 macOS threats five times. A year later, it had infected over 2,800 websites, distributing its payload via fake CAPTCHA overlays—undetectable by most antivirus suites.
Cybersecurity News – 2,800+ infected websites
AMOS breached:
- Judicial systems (document leaks)
- Defense ministries (backdoor surveillance)
- Health agencies (citizen data exfiltration)
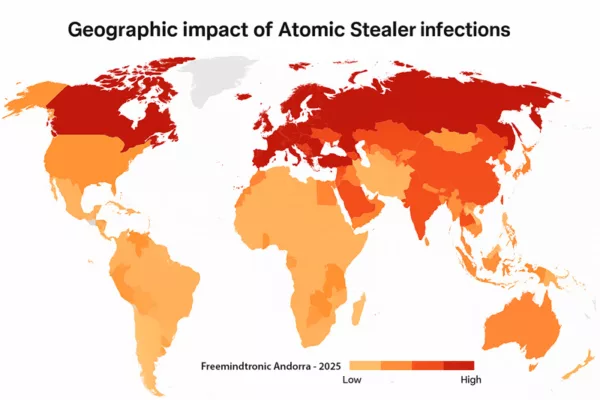
✪ A choropleth heatmap visualizing the global spread of Atomic Stealer AMOS malware, highlighting red zones of high infection (USA, Europe, Russia) and a legend indicating severity levels.
Detecting the Undetectable
AMOS leaves subtle traces:
- Browser redirects
- Unexpected password resets
- .agent or .runner processes
- Apps flickering open
To mitigate:
- Update macOS regularly
- Use Little Snitch or LuLu
- Audit ~/Library/LaunchAgents
- Avoid unverified apps
- Never run copy-paste terminal commands
✪ This infographic checklist outlines 5 key reflexes to detect and neutralize Atomic Stealer (AMOS) infections on macOS systems.
Threat Actor Profile: Who’s Behind AMOS?
While AMOS has not been officially attributed to a specific APT group, indicators suggest it was developed by Russian-speaking actors, based on:
- Forum discussions on Russian-language Telegram groups
- Code strings and comments in Cyrillic
- Infrastructure overlaps with known Eastern European malware groups
These threat actors are not simply financially motivated. The precision, modularity, and persistence of AMOS suggests potential use in state-adjacent cyber operations or intelligence-linked campaigns.
Its evolution also parallels other known cybercrime ecosystems operating in Russia and Belarus, often protected by a “hands-off” doctrine as long as they avoid targeting domestic networks.
Malware-as-a-Service: Industrial Grade
- Custom builds with payload encryption
- Support and distribution via Telegram
- Spread via ClickFix and malvertising
- Blockchain-based hosting using EtherHiding
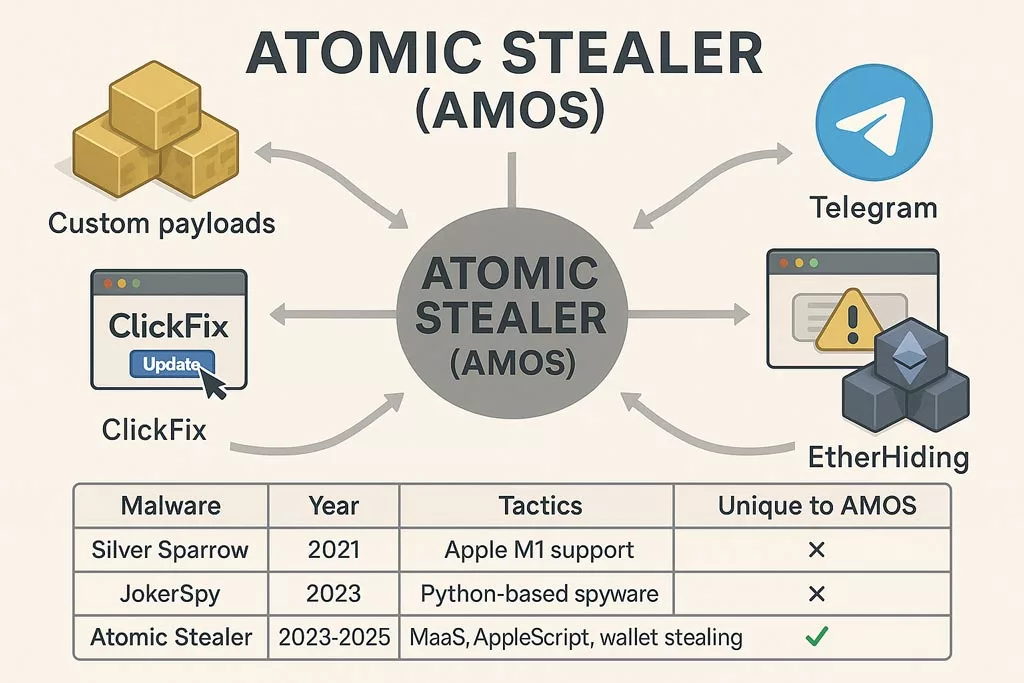
✪ Écosystème MaaS d’Atomic Stealer comparé à Silver Sparrow et JokerSpy, illustrant ses tactiques uniques : chiffrement XOR, exfiltration crypto, AppleScript et diffusion via Telegram.
| Malware Name | Year | Tactics | Unique to AMOS |
|---|---|---|---|
| Silver Sparrow | 2021 | Early Apple M1 compatibility | ✗ |
| JokerSpy | 2023 | Spyware in Python, used C2 servers | ✗ |
| Atomic Stealer | 2023–2025 | MaaS, XOR encryption, AppleScript, wallet exfiltration | ✅ |
AMOS combines multiple threat vectors—social engineering, native scripting abuse, and crypto-focused data harvesting—previously scattered across different strains.
Strategic Exposure: Who’s at Risk
| Group | Severity | Vector |
|---|---|---|
| Casual Users | High | Browser extensions |
| Crypto Traders | Critical | Clipboard/wallet interception |
| Startups | Severe | Slack/Teams compromise |
| Governments | Extreme | Persistent surveillance backdoors |
What Defenders Fear Next
The evolution isn’t over. AMOS may soon integrate:
- Biometric spoofing (macOS Touch ID)
- Lateral movement in creative agencies
- Steganography-based payloads in image files
Security must not follow. It must anticipate.
Strategic Outlook Atomic Stealer AMOS
- GDPR breaches from exfiltrated citizen data (health, justice)
- Legal risks for companies not securing macOS endpoints
- Cross-border incident response complexities due to MaaS
- Urgent need to update risk models to treat Apple devices as critical infrastructure
Threat Actor Attribution: Who’s Really Behind AMOS?
While Atomic Stealer (AMOS) has not been officially attributed to any known APT group, its evolution and operational model suggest the involvement of a Russian-speaking cybercriminal network, possibly APT-adjacent.
The malware’s early presence on Russian-language Telegram groups, combined with:
- Infrastructure linked to Eastern Europe,
- XOR obfuscation and macOS persistence techniques,
- and a sophisticated Malware-as-a-Service support network
…indicate a semi-professionalized developer team with deep technical access.
Whether this actor operates independently or under informal “state-blind tolerance” remains unclear. But the outcome is strategic: AMOS creates viable access for both criminal monetization and state-aligned espionage.
Related reading: APT28’s Campaign in Europe
Indicators of Compromise (IOCs)
Here are notable Indicators of Compromise for Atomic Stealer AMOS:
File Hashes
- fa34b1e87d9bb2f244c349e69f6211f3 – Encrypted loader sample (SHA256)
- 9d52a194e39de66b80ff77f0f8e3fbc4 – macOS .dmg payload (SHA1)
Process Names / Artifacts
- .atomic_agent or .launch_daemon
- /Library/LaunchAgents/com.apple.atomic.*
- /private/tmp/atomic/tmp.log
C2 IPs / Domains (as of Q2 2025)
- 185.112.156.87
- atomicsec[.]ru
- zoom-securecdn[.]net
Behavioral
- Prompt for keychain credentials using AppleScript
- Sudden redirection to fake update screens
- Unusual clipboard content activity (crypto strings)
These IOCs are dynamic. Correlate with updated threat intel feeds.
Defenders’ Playbook: Active Protection
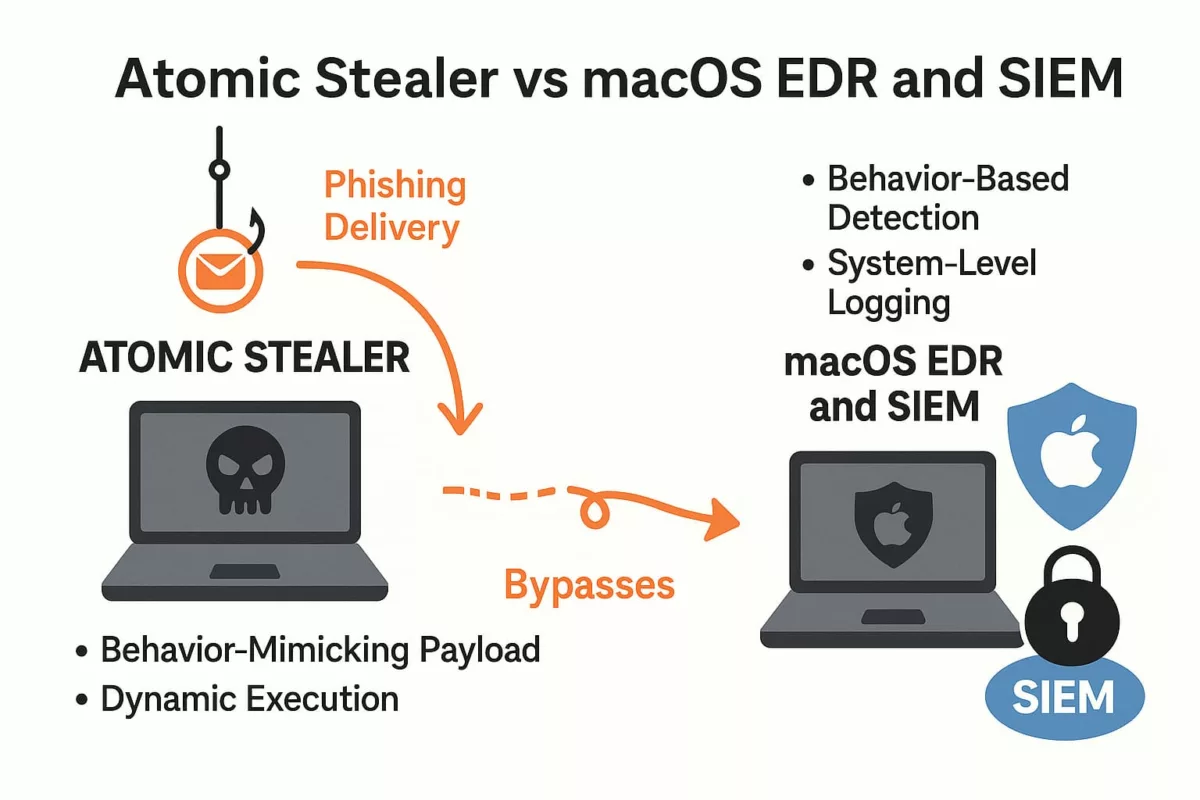
✪ Security teams can proactively counter AMOS using a layered defense model:
SIEM Integration (Ex: Splunk, ELK)
- Monitor execution of osascript and creation of LaunchAgents
- Detect access to ~/Library/Application Support with unknown binaries
- Alert on anomalous clipboard behavior or browser token access
EDR Rules (Ex: CrowdStrike, SentinelOne)
- Block unsigned binaries requesting keychain access
- Alert on XOR-obfuscated payloads in user directories
- Kill child processes of fake Zoom or Slack installers
Sandbox Testing
- Detonate .dmg and .pkg in macOS VM with logging enabled
- Watch for connections to known C2 indicators
- Evaluate memory-only behaviors in unsigned apps
General Hygiene
- Remove unverified extensions and “free” tools
- Train users against fake updates and cracked apps
- Segment Apple devices in network policy to enforce Zero Trust
AMOS is stealthy, but its behaviors are predictable. Behavior-based defenses offer the best chance at containment.
Freemindtronic Solutions to Secure macOS
To counter threats like Atomic Stealer, Freemindtronic provides macOS-compatible hardware and software cybersecurity solutions:
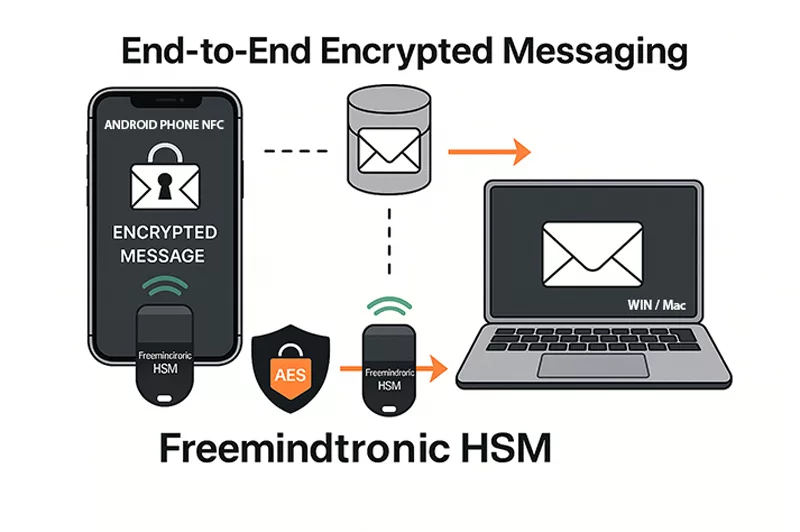
DataShielder: Hardware Immunity Against macOS Infostealers
DataShielder NFC HSM
- Offline AES-256 and RSA 4096 key storage: No exposure to system memory or macOS processes.
- Phishing-resistant authentication: Secure login via NFC, independent from macOS.
- End-to-end encrypted messaging: Works even for email, LinkedIn, and QR-based communications.
- No server, no account, no trace: Total anonymity and data control.
DataShielder HSM PGP
- Hardware-based PGP encryption for files, messages, and emails.
- Zero-trust design: Doesn’t rely on macOS keychain or system libraries.
- Immune to infostealers: Keys never leave the secure hardware environment.
Use Cases for macOS Protection
- Securing Apple Mail, Telegram, Signal messages with AES/PGP
- Protecting crypto assets via encrypted QR exchanges
- Mitigating clipboard attacks with hardware-only storage
- Creating sandboxed key workflows isolated from macOS execution
These tools shift the attack surface away from macOS and into a secure, externalized hardware vault.
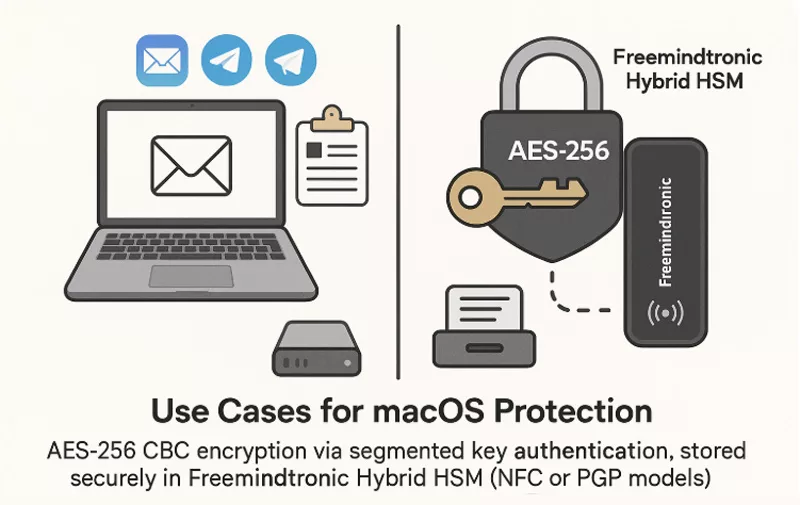
✪ Hybrid HSM from Freemindtronic securely stores AES-256 encryption keys outside macOS, protecting email and messaging apps like Apple Mail, Signal, and Telegram.
SeedNFC HSM Tag
Hardware-Secured Crypto Wallets — Invisible to Atomic Stealer AMOS
Atomic Stealer (AMOS) actively targets cryptocurrency wallets and clipboard content linked to crypto transactions. The SeedNFC HSM 100 Tag, powered by the SeedNFC Android app, offers a 100% externalized and offline vault that supports up to 50 wallets (Bitcoin, Ethereum, and others), created directly on the blockchain.
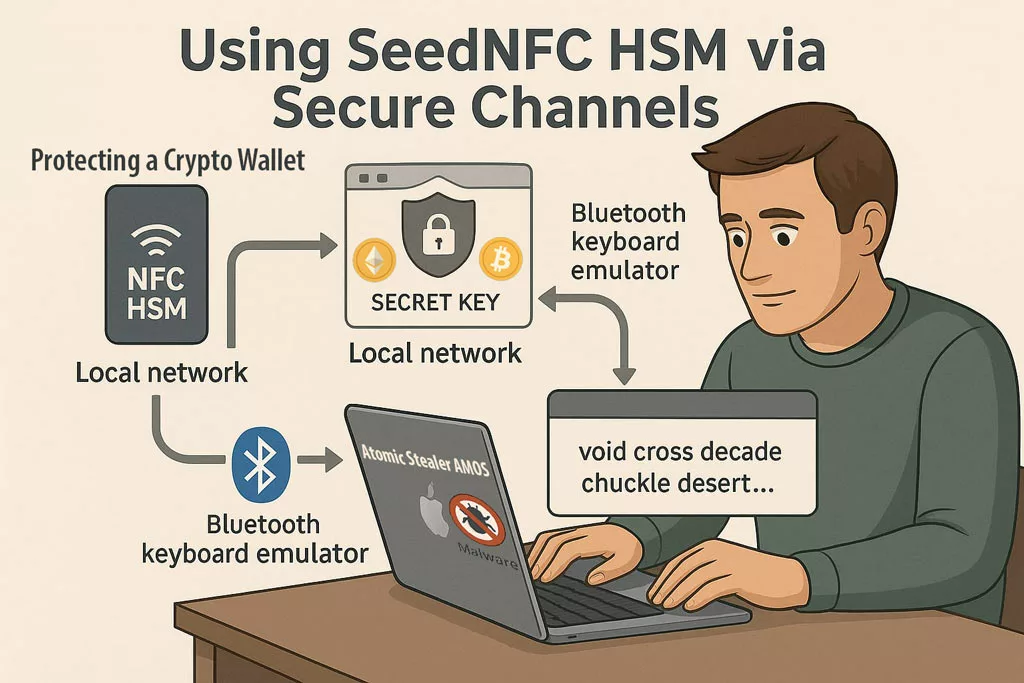
✪ Even if Atomic Stealer compromises the macOS system, SeedNFC HSM keeps crypto secrets unreachable via secure local or Bluetooth emulation channels.
Unlike traditional browser extensions or software wallets:
Private keys are stored fully offline — never touch system memory or the clipboard.
Wallets can be used on macOS and Windows via:
- Web extensions communicating over an encrypted local network,
- Or via Bluetooth keyboard emulation to inject public keys, passwords, or transaction data.
- Wallet sharing is possible via RSA-4096 encrypted QR codes.
-
All functions are triggered via NFC and executed externally to the OS.
This creates a Zero Trust perimeter for digital assets — ideal against crypto-focused malware like AMOS.
Bluetooth Keyboard Emulator
Zero-Exposure Credential Delivery — No Typing, No Trace
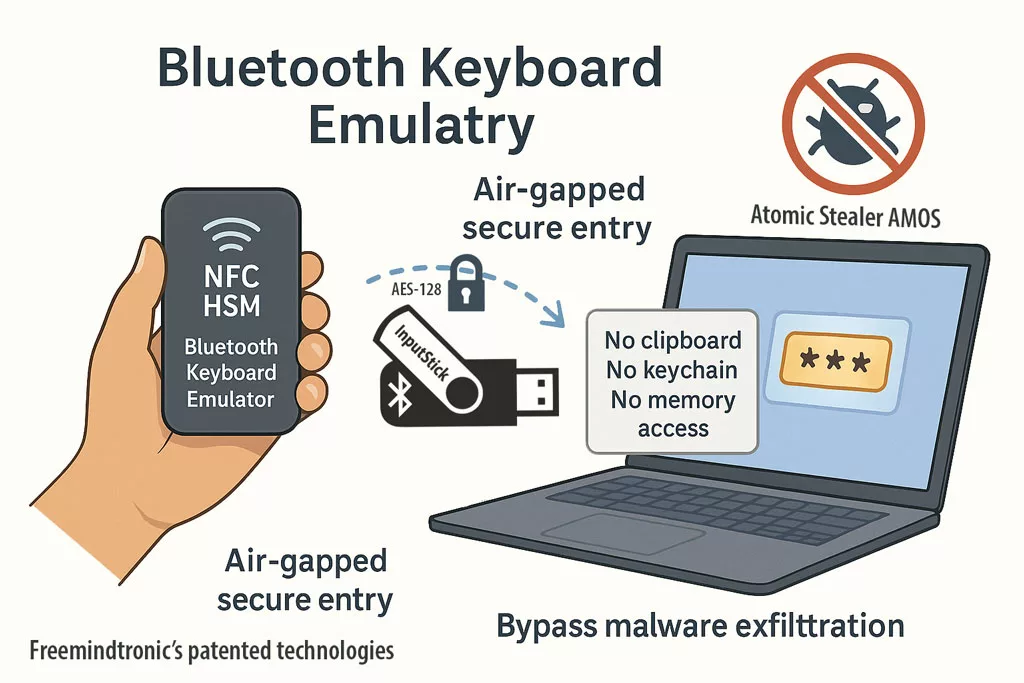
✪ Freemindtronic’s patented NFC HSM delivers secure, air-gapped password entry via Bluetooth keyboard emulation — immune to clipboard sniffers, and memory-based malware like AMOS.
Since AMOS does not embed a keylogger, it relies on clipboard sniffing, browser-stored credentials, and deceptive interface prompts to steal data.
The Bluetooth Keyboard Emulator bypasses these vectors entirely. It allows sensitive information to be typed automatically from a NFC HSM device (such as DataShielder or PassCypher) into virtually any target environment:
- macOS and Windows login screens,
- BIOS, UEFI, and embedded systems,
- Shell terminals or command-line prompts,
- Sandboxed or isolated virtual machines.
This hardware-based method supports the injection of:
- Logins and passwords
- PIN codes and encryption keys (e.g. AES, PGP)
- Seed phrases for crypto wallets
All credentials are delivered via Bluetooth keyboard emulation:
- No clipboard usage
- No typing on the host device
- No exposure to OS memory, browser keychains, or RAM
This creates a physically segmented, air-gapped credential input path — completely outside the malware’s attack surface. Against threats like Atomic Stealer (AMOS), it renders data exfiltration attempts ineffective by design.
Bluetooth keyboard emulation bypasses AMOS exfiltration entirely. Credentials are securely “typed” into systems from NFC HSMs, without touching macOS memory or storage.
What About Passkeys and Private Keys?
While AMOS is not a keylogger, it doesn’t need to be — because it can access your Keychain under the right conditions:
- Use native macOS tools (e.g.,
securityCLI, Keychain API) to extract saved secrets - Retrieve session tokens and autofill credentials
- Exploit unlocked sessions or prompt fatigue to access sensitive data
Passkeys, used for passwordless login via Face ID or Touch ID, are more secure due to Secure Enclave, yet:
- AMOS can hijack authenticated sessions (e.g., cookies, tokens)
- Cached WebAuthn tokens may be abused if the browser remains active
- Keychain-stored credentials may still be exposed in unlocked sessions
Why External Hardware Security Modules (HSMs) Are Critical
Unlike macOS Keychain, Freemindtronic’s NFC HSM and HSM PGP solutions store secrets completely outside the host system, offering true air-gap security and malware immunity.
Key advantages over macOS Keychain:
- No clipboard or RAM exposure
- No reliance on OS trust or session state
- No biometric prompt abuse
- Not exploitable via API or command-line tools
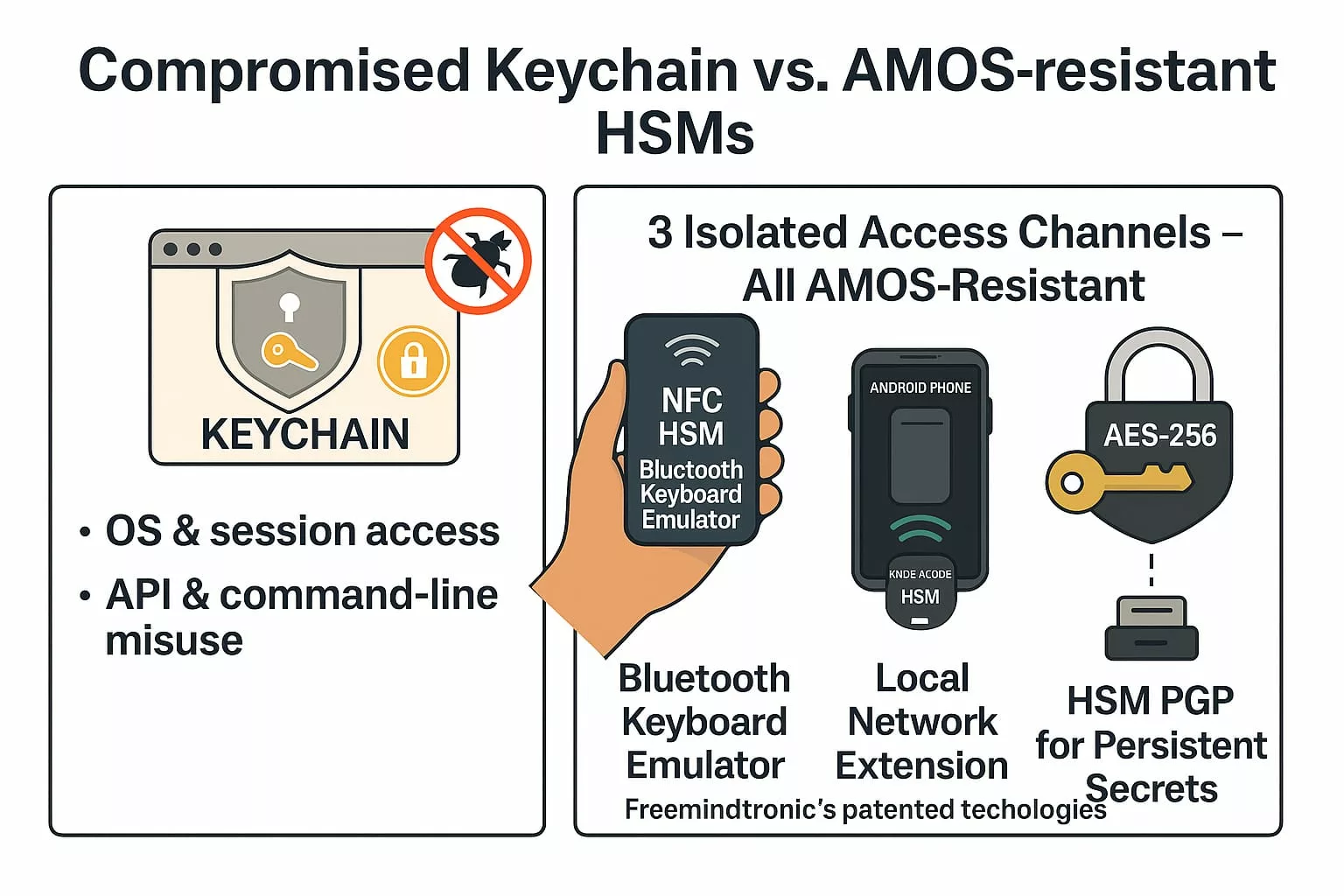
✪ This infographic compares the vulnerabilities of macOS Keychain with the security of Freemindtronic’s NFC HSM technologies, showing how they resist Atomic Stealer AMOS threats.
Three Isolated Access Channels – All AMOS-Resistant
1. Bluetooth Keyboard Emulator (InputStick)
- Sends secrets directly via AES-128 encrypted Bluetooth HID input
- Works offline — ideal for BIOS, command-line, or sandboxed systems
- Not accessible to the OS at any point
2. Local Network Extension (DataShielder / PassCypher)
- Ephemeral symmetric key exchange over LAN
- Segmented key architecture prevents man-in-the-middle injection
- No server, no database, no fingerprint
3. HSM PGP for Persistent Secrets
- Stores secrets encrypted in AES-256 CBC using PGP
- Works with web extensions and desktop apps
- Secrets are decrypted only in volatile memory, never exposed to disk or clipboard
If your credentials live in macOS, they’re fair game. If they live in NFC HSMs or PGP HSMs — with no OS, clipboard, or RAM exposure — they’re not.
PassCypher Protection Against Atomic Stealer AMOS
PassCypher solutions are highly effective in neutralizing AMOS’s data exfiltration techniques:
PassCypher NFC HSM
- Credentials stored offline in an NFC HSM, invisible to macOS and browsers.
- No use of macOS keychain or clipboard, preventing typical AMOS capture vectors.
- One-time password insertion via Bluetooth keyboard emulation, immune to keyloggers.
PassCypher HSM PGP
- Hardware-secured PGP encryption/decryption for emails and messages.
- No token or password exposure to system memory.
- Browser integration with zero data stored locally — mitigates web injection and session hijacking.
Specific Protections
| Attack Vector Used by AMOS | Mitigation via PassCypher |
|---|---|
| Password theft from browsers | No password stored in browser or macOS |
| Clipboard hijacking | No copy-paste use of sensitive info |
| Fake login prompt interception | No interaction with native login systems |
| Keychain compromise | Keychain unused; HSM acts as sole vault |
| Webmail token exfiltration | Tokens injected securely, not stored locally |
These technologies create a zero-trust layer around identity and messaging, nullifying the most common AMOS attack paths.
Atomic Stealer AMOS and the Future of macOS Security Culture

✪ Atomic doesn’t just expose flaws in Apple’s defenses. It dismantles our assumptions.
For years, users relied on brand prestige instead of security awareness. Businesses excluded Apple endpoints from serious defense models. Governments overlooked creative and administrative Macs as threats.
That era is over.
Atomic forces a cultural reset. From now on, macOS security deserves equal investment, equal scrutiny, and equal priority.
It’s not just about antivirus updates. It’s about behavioral change, threat modeling, and zero trust applied consistently—across all platforms.
Atomic Stealer will not be the last macOS malware we face. But if we treat it as a strategic wake-up call, it might be the last we underestimate.
If your credentials live in macOS, they’re fair game. If they live in NFC HSMs with no OS or network dependency, they’re not.
Strategic Note
Atomic Stealer is not a lone threat—it’s a blueprint for hybrid cyber-espionage. Treating it as a one-off incident risks underestimating the evolution of adversarial tooling. Defense today requires proactive anticipation, not reactive response.
APT41 Cyberespionage and Cybercrime represents one of the most strategically advanced and enduring cyber threat actors globally. In this comprehensive report, Jacques Gascuel examines their hybrid operations—combining state-sponsored espionage and cybercriminal campaigns—and outlines proactive defense strategies to mitigate their impact on national security and corporate infrastructures.
APT41 – Navigation Guide:
- History and Evolution
- APT41 – Key Statistics and Impact
- MITRE ATT&CK Matrix Mapping
- Tactics, Techniques and Procedures (TTPs)
- Structure and Operations
- Chrome V8 Exploits
- TOUGHPROGRESS Calendar C2 (May 2025)
- Mitigation and detection strategies
- Malware and tools
- Infrastructure
- Motivations and Targets
- Indicators of Compromise (IOCs)
- Freemindtronic HSM Ecosystem – APT41 Defense Matrix
- Outlook and Next Steps
APT41 (Double Dragon / BARIUM / Wicked Panda) Cyberespionage & Cybercrime Group
Last Updated: April 2025
Version: 1.0
Source: Freemindtronic Andorra
Origins and Rise of the APT41 Cyberespionage and Cybercrime Group
Active since at least 2012, APT41 Cyberespionage and Cybercrime operations are globally recognized for their dual nature: combining state-sponsored espionage with personal enrichment schemes (Google Cloud / Mandiant). The group exploits critical vulnerabilities (Citrix CVE‑2019‑19781, Log4j / Log4Shell – CVE-2021-44228), UEFI bootkits (MoonBounce), and supply chain attacks (Wikipedia – Double Dragon).
APT41 – Key Statistics and Impact
- First Identified: 2012 (active since at least 2010 according to some telemetry).
- Number of Public CVEs Exploited: Over 25, including high-profile vulnerabilities like Citrix ADC (CVE-2019-19781), Log4Shell (CVE-2021-44228), and Chrome V8 (CVE-2025-6554).
- Confirmed APT41 Toolkits: Over 30 identified malware families and variants (e.g., DUSTPAN, ShadowPad, DEAD EYE).
- Known Victim Countries: Over 40 countries spanning 6 continents, including U.S., France, Germany, UK, Taiwan, India, and Japan.
- Targeted Sectors: Government, Telecom, Healthcare, Defense, Tech, Cryptocurrency, and Gaming Industries.
- U.S. DOJ Indictment: 5 named Chinese nationals in 2020 for intrusions spanning over 100 organizations globally.
- Hybrid Attack Model: Unique mix of espionage (state-backed) and cybercrime (personal enrichment) confirmed by Mandiant, FireEye, and the U.S. DOJ.
MITRE ATT&CK Matrix Mapping – APT41 (Enterprise & Defense Combined)
| Tactic | Technique | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Initial Access | T1566.001 | Spearphishing with malicious attachments (ZIP+LNK) |
| Execution | T1059.007 | JavaScript execution via Chrome V8 |
| Persistence | T1542.001 | UEFI bootkit (MoonBounce) |
| Defense Evasion | T1027 | Obfuscated PowerShell scripts, memory-only loaders |
| Credential Access | T1555 | Access to stored credentials, clipboard monitoring |
| Discovery | T1087 | Active Directory enumeration |
| Lateral Movement | T1210 | Exploiting remote services via RDP, WinRM |
| Collection | T1119 | Automated collection via SQLULDR2 |
| Exfiltration | T1048.003 | Exfiltration via cloud services (Google Drive, OneDrive) |
| Command & Control | T1071.003 | Abuse of Google Calendar (TOUGHPROGRESS) |
Tactics, Techniques and Procedures (TTPs)
The APT41 Cyberespionage and Cybercrime campaign has evolved into one of the most widespread and adaptable threats, impacting over 40 countries across critical industries.
- Initial Access: spear‑phishing, pièces jointes LNK/ZIP, exploitation de CVE, failles JavaScript (Chrome V8) via watering-hole, invitations malveillantes via Google Calendar (TOUGHPROGRESS).
- Browser Exploitation: zero-day targeting Chrome V8 engine (e.g., CVE-2025-6554), enabling remote code execution via crafted JavaScript in spear-phishing and watering-hole campaigns.
- Persistence: bootkits UEFI (MoonBounce), loaders en mémoire (DUSTPAN, DEAD EYE).
- Lateral Movement: Cobalt Strike, credential theft, rootkits Winnti.
- C2: abus de Cloudflare Workers, Google Calendar/Drive/Sheets, TLS personnalisé
- TLS fingerprinting: Detect anomalies in self-signed TLS certs and suspicious CA chains (used in APT41’s custom TLS implementation).
- Exfiltration: SQLULDR2, PineGrove via OneDrive.
Global Footprint of APT41 Victimology
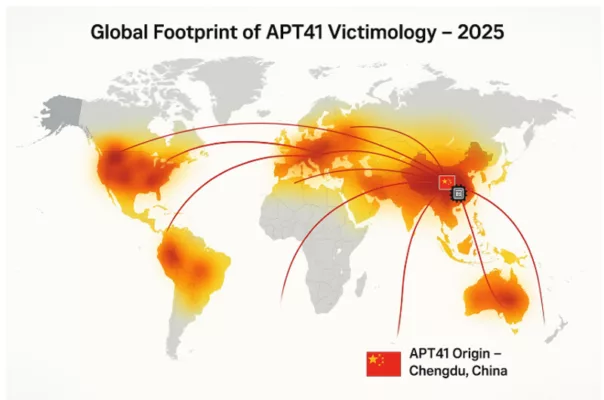
The global heatmap illustrates the spread of APT41 cyberattacks in 2025, with Chengdu, China marked as the origin. Curved arcs highlight targeted regions in North America, Europe, Asia, and beyond. heir targeting spans critical infrastructure, multinational enterprises, and governmental agencies.
APT41 Cyberespionage and Cybercrime – Structure and Operations
The APT41 Cyberespionage and Cybercrime group is believed to operate as a contractor or affiliate of the Chinese Ministry of State Security (MSS), with ties to regional cyber units. Unlike other nation-state groups, APT41 uniquely combines state-sponsored espionage with financially motivated cybercrime — including ransomware deployment, cryptocurrency theft, and illicit access to video game environments for profit. This hybrid approach enables the group to remain operationally flexible while continuing to deliver on geopolitical priorities set by state actors.
Attribution reports from the U.S. Department of Justice (DOJ) [DOJ 2020 Indictment] identify several named operatives associated with APT41, highlighting the structured and persistent nature of their operations. The group has demonstrated high coordination, advanced resource access, and the ability to pivot quickly between long-term intelligence operations and short-term financially motivated campaigns.
APT41 appears to operate with a dual-hat model: actors perform espionage tasks during official working hours and engage in financially driven attacks after hours. Reports suggest the use of a shared malware codebase among regional Chinese APTs, but with distinct infrastructure and tasking for APT41.
Attribution & Legal Action
In September 2020, the U.S. Department of Justice publicly indicted five Chinese nationals affiliated with APT41 for a global hacking campaign. Although not apprehended, these indictments marked a rare instance of legal attribution against Chinese state-linked actors. The group’s infrastructure, tactics, and timing patterns (active during GMT+8 working hours) strongly point to a connection with China’s Ministry of State Security (MSS).
APT41 Cyberespionage and Cybercrime – Chrome V8 Exploits
In early 2025, APT41 was observed exploiting a zero-day vulnerability in the Chrome V8 JavaScript engine, identified as CVE-2025-6554. This flaw allowed remote code execution through malicious JavaScript payloads delivered via watering-hole and spear-phishing campaigns.
This activity demonstrates APT41’s increasing focus on client-side browser exploitation to gain initial access and execute post-exploitation payloads in memory, often chained with credential theft and privilege escalation tools. Their ability to adapt to evolving browser engines like V8 further expands their operational scope in high-value targets.
Freemindtronic’s threat research confirmed active use of this zero-day in targeted attacks on European government agencies and tech enterprises, reinforcing the urgent need for browser-level monitoring and hardened sandboxing strategies.
TOUGHPROGRESS Calendar C2 (May 2025)
In May 2025, Google’s Threat Intelligence Group (GTIG), The Hacker News, and Google Cloud confirmed APT41’s abuse of Google Calendar for command and control (C2). The technique, dubbed TOUGHPROGRESS, involved scheduling encrypted events that served as channels for data exfiltration and command delivery. Google responded by neutralizing the associated Workspace accounts and Calendar instances.
Additionally, Resecurity published a June 2025 report confirming continued deployment of TOUGHPROGRESS on a compromised government platform. Their analysis revealed sophisticated spear-phishing methods using ZIP archives with embedded LNK files and decoy images.
To support detection, SOC Prime released Sigma rules targeting calendar abuse patterns, now incorporated by leading SIEM vendors.
Mitigation and Detection Strategies
- Update Management: proactive patching of CVEs (Citrix, Log4j, Chrome V8), rapid deployment of security fixes.
- UEFI/TPM Protection: enable Secure Boot, verify firmware integrity, use HSMs to isolate cryptographic keys from OS-level access.
- Cloud Surveillance: behavioral monitoring for abuse of Google Calendar, Drive, Sheets, and Cloudflare Workers via SIEM and EDR systems.
- Memory-based Detection: YARA and Sigma rules targeting DUSTPAN, DEAD EYE, and TOUGHPROGRESS malware families.
- Advanced Detection: apply Sigma rules from SOC Prime for identifying C2 anomalies via calendar-based techniques.
- Network Isolation: enforce segmentation and air gaps for sensitive environments; monitor DNS and TLS outbound patterns.
- Browser-level Defense: enable Chrome’s Site Isolation mode, enhance sandboxing, monitor abnormal JavaScript calls to the V8 engine.
- Key Isolation: use hardware HSMs like DataShielder to prevent unauthorized in-memory key access.
- Network TLS profiling: Alert on unknown certificate chains or forged CAs in outbound traffic.
Malware and Tools
- MoonBounce: UEFI bootkit linked to APT41, detailed by Kaspersky/Securelist.
- DUSTPAN / DUSTTRAP: Memory-resident droppers observed in a 2023 campaign.
- DEAD EYE, LOWKEY.PASSIVE: Lightweight in-memory backdoors.
- TOUGHPROGRESS: Abuses Google Calendar for C2, used in a late-2024 government targeting campaign.
- ShadowPad, PineGrove, SQLULDR2: Advanced data exfiltration tools.
- LOWKEY/LOWKEY.PASSIVE: Lightweight passive backdoor used for long-term surveillance.
- Crosswalk: Malware for targeting both Linux and Windows in hybrid cloud environments.
- Winnti Loader: Shared component used to deploy payloads across various Chinese APT groups.
- DodgeBox – Memory-only loader active since 2025 targeting EU energy sector, using PE32 x86 DLL signature evasion.
- Lateral Movement: Cobalt Strike, credential theft, Winnti rootkits, and legacy exploits like PrintNightmare (CVE-2021-34527).
Possible future threats include MoonWalk (UEFI-EV), a suspected evolution of MoonBounce, targeting firmware in critical systems (e.g., Gigabyte and MSI BIOS), as observed in early 2025. Analysts should anticipate deeper firmware-level persistence across high-value targets.
Use of Cloudflare Workers, Google APIs, and short-link redirectors (e.g., reurl.cc) for C2. TLS via stolen or self-signed certificates.
APT41 Cyberespionage and Cybercrime Motivations and Global Targets
APT41 Cyberespionage and Cybercrime campaigns are driven by a unique dual-purpose strategy, combining state-sponsored intelligence gathering with financially motivated cyberattacks. Unlike many APT groups that focus solely on espionage, APT41 leverages its advanced capabilities to infiltrate both government networks and private enterprises for political and economic gain. This hybrid model allows the group to target a wide range of industries and geographies with tailored attack vectors.
- Espionage: Governments (United States, Taiwan, Europe), healthcare, telecom, high-tech sectors.
- Cybercrime: Video game industry, cryptocurrency wallets, ransomware operations.
APT41 Operational Model – Key Phases
This mindmap offers a clear and concise visual synthesis of APT41 Cyberespionage and Cybercrime activities. It highlights the key operational stages used by APT41, from initial access via spearphishing (ZIP/LNK) to data exfiltration through cloud-based Command and Control (C2) infrastructure.
Visual elements illustrate how APT41 combines memory-resident malware, lateral movement, and cloud abuse to achieve both espionage and monetization goals.
Mindmap: APT41 Operational Model – Tracing the full attack lifecycle from compromise to monetization.
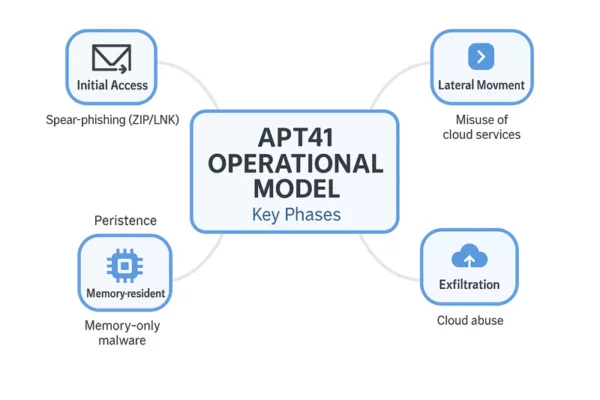
This section summarizes the typical phases of APT41 Cyberespionage and Cybercrime operations, from initial compromise to exfiltration and monetization.
APT41 combines advanced cyberespionage with financially motivated cybercrime in a streamlined operational cycle. Their tactics evolve constantly, but the core lifecycle follows a recognizable pattern, blending stealth, persistence, and monetization.
- Initial Access: Spearphishing campaigns using ZIP+LNK attachments or fake software installers.
- Execution: Fileless malware or memory-only loaders such as DUSTPAN or DodgeBox.
- Persistence: UEFI implants like MoonBounce or potential MoonWalk variants.
- Lateral Movement: Exploitation of remote services (e.g., RDP, PrintNightmare), AD enumeration.
- Exfiltration: Use of SQLULDR2, OneDrive, Google Drive for data exfiltration.
- Command & Control: Cloud-based channels, including Google Calendar events and TLS tunnels.
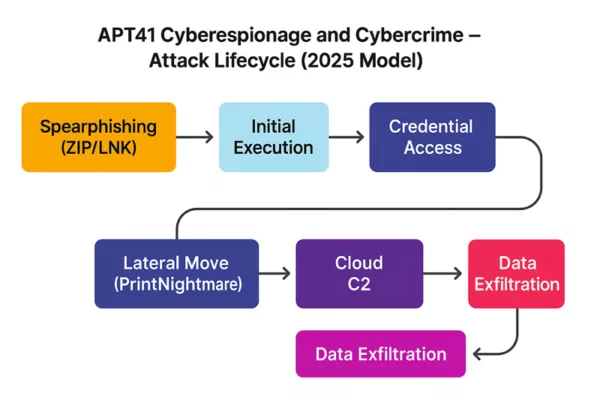
APT41 Cyberespionage and Cybercrime – Attack Lifecycle (2025): From spearphishing to data exfiltration via cloud command-and-control.
Mobile Threat Vectors – Emerging Tactics
APT41 has tested malicious fake installers (.apk/.ipa) targeting mobile platforms, including devices used by diplomatic personnel. These apps are often distributed via private links or QR codes and may allow persistent remote access to mobile infrastructure.
Future Outlook on APT41 Cyberespionage and Cybercrime Operations
APT41 Cyberespionage and Cybercrime exemplifies the hybrid model of modern digital threats, combining stealth operations with financial motives. Its use of stealth technologies—such as UEFI bootkits, memory-only malware, and cloud infrastructure abuse—demands a defense-in-depth approach supported by constantly refreshed threat intelligence. This document will be updated as new discoveries emerge (e.g., MoonWalk, DodgeBox…).
“APT41 represents a quantum leap in hybrid threat models—blurring the lines between state espionage and digital crime syndicates. Understanding their operational asymmetry is key to defending both critical infrastructure and intellectual sovereignty.”
— Jacques Gascuel, Inventor & CEO, Freemindtronic Andorra
APT41 Operational Lifecycle: From Cyberespionage to Cybercrime
APT41 Cyberespionage and Cybercrime operations typically begin with reconnaissance and spear-phishing campaigns, followed by the deployment of malware loaders such as DUSTPAN and memory-only payloads like DEAD EYE. Once initial access is achieved, the group pivots laterally across networks using credential theft and Cobalt Strike, often deploying Winnti rootkits to maintain long-term persistence.
Their hybrid lifecycle blends strategic espionage goals — like exfiltrating data from healthcare or governmental institutions — with opportunistic attacks on cryptocurrency platforms and gaming environments. This dual approach complicates attribution and enhances the group’s financial gain, making APT41 one of the most versatile and dangerous cyber threat actors to date.
Indicators of Compromise (IOCs)
- Malware: MoonBounce, TOUGHPROGRESS, DUSTPAN, ShadowPad, SQLULDR2.
- Infrastructure: Google Calendar URLs, Cloudflare Workers, reurl.cc.
- Signatures: UEFI implants, memory-only malware, abnormal TLS behaviors.
Mitigation and Detection Measures
- Updates: Patch CVEs (Citrix, Log4j), update UEFI firmware.
- UEFI/TPM Protection: Enable Secure Boot, use offline HSMs for key storage.
- Cloud Surveillance: Track anomalies in Google/Cloudflare-based C2 traffic.
- Memory Detection: YARA/Sigma rules for TOUGHPROGRESS and DUSTPAN.
- EDR & Segmentation: Enforce strict network separation.
- Key Isolation: Offline HSM and PGP usage.
APT41 Cyberespionage and Cybercrime – Strategic Summary
APT41 Cyberespionage and Cybercrime operations continue to represent one of the most complex threats in today’s global cyber landscape. Their unique blend of state-aligned intelligence gathering and profit-driven criminal campaigns reflects a dual-purpose doctrine increasingly adopted by advanced persistent threats. From exploiting zero-days in Chrome V8 to abusing Google Workspace and Cloudflare Workers for stealthy C2 operations, APT41 exemplifies the modern hybrid APT. Organizations should adopt proactive defense measures, such as offline HSMs, UEFI security, and TLS fingerprint anomaly detection, to mitigate these risks effectively.
Freemindtronic HSM Ecosystem – APT41 Defense Matrix
The following matrix illustrates how Freemindtronic’s HSM solutions neutralize APT41’s most advanced techniques across both espionage and cybercriminal vectors.
Encrypted QR Code – Human-to-Human Response
To illustrate a real-world countermeasure against APT41 cyberespionage operations, this demo showcases the use of a secure encrypted QR Code that can be scanned with a DataShielder NFC HSM device. It allows analysts or security officers to exchange a confidential message offline, without relying on external servers or networks.
Use case: An APT41 incident response team can securely distribute an encrypted instruction or key via QR Code format — the message remains encrypted until scanned by an authorized device. This ensures end-to-end encryption, offline delivery, and complete data sovereignty.
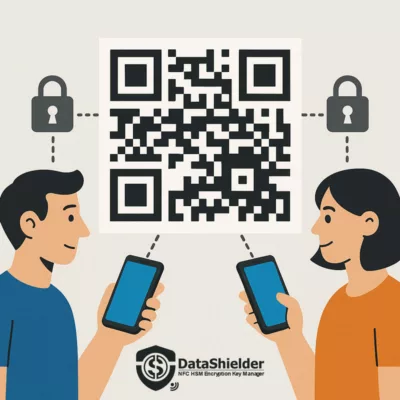

Illustration of a secure QR code-based message exchange to counter APT41 cyberespionage and cybercrime threats.
🔐 Scan this QR code using your DataShielder NFC HSM device to decrypt a secure analyst message related to the APT41 threat.
| Threat / Malware | DataShielder NFC HSM | DataShielder HSM PGP | PassCypher NFC HSM | PassCypher HSM PGP |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Spear‑phishing / Macros | ✘ | ✔ Sandbox |
✘ | ✔ PGP Container |
| MoonBounce (UEFI) | ✔ NFC offline |
✔ OS‑bypass |
✘ | ✔ Secure Boot enforced |
| Cloud C2 | ✔ 100 % offline |
✔ Offline |
✔
Offline |
✔ No external connection |
| TOUGHPROGRESS (Google Abuse) | ✔
No Google API use |
✔ PGP validation |
✔ Encrypted QR only |
✔ Isolated |
| ShadowPad | ✔ No key in RAM |
✔ Offline use |
✔ No clipboard use |
✔ Sandboxed login |
Future Outlook on APT41 Cyberespionage and Cybercrime Operations
APT41 Cyberespionage and Cybercrime exemplifies the hybrid model of modern digital threats, combining stealth operations with financial motives.Its use of stealth technologies—such as UEFI bootkits, memory-only malware, and cloud infrastructure abuse—demands a defense-in-depth approach supported by constantly refreshed threat intelligence. This document will be updated as new discoveries emerge (e.g., MoonWalk, DodgeBox…).
As of mid-2025, security researchers are closely monitoring the evolution of APT41’s toolset and objectives. Several indicators point toward the emergence of MoonWalk—a suspected successor to MoonBounce—designed to target UEFI environments in energy-sector firmware (Gigabyte/MSI BIOS suspected). Meanwhile, campaigns using DodgeBox and QR-distributed fake installers on Android and iOS platforms show a growing interest in covert mobile infiltration. These developments suggest a likely increase in firmware-layer intrusions, mobile surveillance tools, and social engineering payloads targeting diplomatic, industrial, and defense networks.
“APT41 represents a quantum leap in hybrid threat models—blurring the lines between state espionage and digital crime syndicates. Understanding their operational asymmetry is key to defending both critical infrastructure and intellectual sovereignty.”
— Jacques Gascuel, Inventor & CEO, Freemindtronic Andorra
Strategic Recommendations
- Deploy firmware validation routines and Secure Boot enforcement in critical systems
- Proactively monitor TLS traffic for custom fingerprinting or rogue CA chainsde constr
- Implement out-of-band communication tools like encrypted QR codes for human-to-human alerting
- Use memory-scanning EDRs and YARA rules tailored to new loaders like DodgeBox and DUSTPAN
- Monitor mobile ecosystems for signs of unauthorized app distribution or QR-based spearphishing
- Review permissions and logging for Google and Cloudflare API usage in corporate networks
APT41 Cyberespionage and Cybercrime exemplifies the hybrid model of modern digital threats…
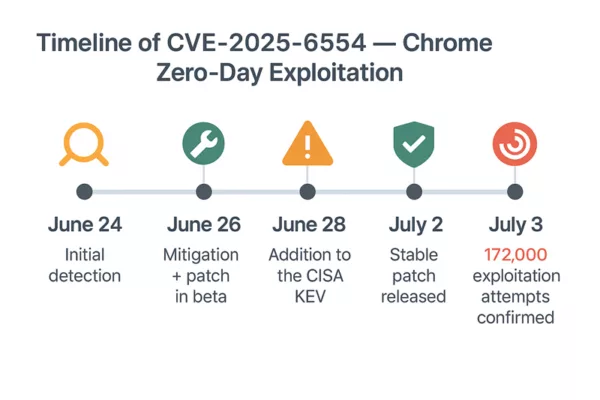
Chrome V8 Zero-Day: CVE-2025-6554 Actively Exploited — A critical type confusion flaw in Chrome’s V8 engine allows remote code execution via a malicious web page. Discovered by Google TAG on June 26, 2025, and patched in Chrome v138, this fourth zero-day exploit of the year highlights the growing risk to browser-based security models. Over 172,000 attacks have been confirmed. Password managers that operate in-browser may be exposed. Hardware-isolated, serverless systems like PassCypher and DataShielder remain unaffected. View official CVE-2025-6554 details
About the Author – Jacques Gascuel is the inventor of patented offline security technologies and founder of Freemindtronic Andorra. He specializes in zero-trust architectures that neutralize zero-day threats by keeping secrets out of reach — even from the browser itself. On June 26, 2025, Google’s Threat Analysis Group (TAG) reported the active exploitation (in-the-wild) of a zero-day flaw targeting Chrome’s V8 JavaScript engine. Identified as CVE-2025-6554, this vulnerability is a type confusion that allows remote code execution through a single malicious web page — with no further user interaction. CVE‑2025‑6554 enables code execution within the V8 JavaScript engine. So far, no sandbox escape has been observed. The compromise is strictly confined to the active browser tab and doesn’t affect other browser processes or the OS — unless a secondary vulnerability is used. This flaw enables arbitrary reads/writes in the memory space of the active process. It provides access to JavaScript objects within the same context and to pointers or structures in the V8 heap/Isolate. However, it does not allow raw RAM dumps or kernel-level access. The V8 JavaScript engine is not exclusive to Chrome. It is also used in Node.js, Electron, Brave, Edge, and others. However, the exploit requires a browser vector, limiting the initial scope. Previous attacks on V8 have been linked to groups like APT41 and Mustang Panda, underlining V8’s strategic interest for espionage campaigns. V8 Attack Structure — This diagram illustrates how a malicious web page exploits the CVE-2025-6554 vulnerability in the V8 JavaScript engine within Chrome, accessing isolated heap memory and JavaScript objects. The sandbox isolates each tab, but when malicious code runs in the same tab as the user, it shares the same logical memory space. Intra-context security depends solely on the quality of the JS engine — now compromised. This is why the PassCypher architecture operates completely outside this paradigm. In the wake of zero-day threats like CVE-2025-6554, architecture matters more than ever. This comparison illustrates how secrets are handled in two fundamentally different security models. In traditional setups, sensitive data — including credentials and access tokens — often reside in the browser’s memory. They are accessible from the JavaScript engine, and therefore vulnerable to contextual attacks like type confusion, injection, or sandbox escape. This model is: Comparison between resilient security design and traditional browser-based architecture vulnerable to zero-day threats like CVE-2025-6554. In contrast, PassCypher and DataShielder are designed around resilient architecture principles. They isolate secrets entirely from the browser, leveraging hardware-based HSMs (Hardware Security Modules) and out-of-band local engines. This model ensures: Classic architecture exposes secrets via browser and JS engine, while PassCypher and DataShielder isolate secrets using HSM and local processing. This architectural shift significantly mitigates risks like browser secret exposure and provides a robust secure JS engine alternative — aligned with future-ready defenses. When secrets are never exposed in the browser, zero-day exploits like CVE-2025-6554 become ineffective. 1. CVE-2025-2783 – Sandbox escape (March 2025) Stay informed on future threats via the Google TAG blog These vulnerabilities were all confirmed as “in-the-wild” exploits by Google TAG and patched through emergency updates. They form the basis of this Chrome Zero-Day alert. CVE‑2025‑6554 marks the fourth zero-day vulnerability fixed in Chrome in 2025, illustrating the increasing frequency of attacks on modern JS engines. Stay informed on future threats via the Google TAG blog While no formal attribution has been published yet, security researchers have observed tactics and targeting patterns consistent with previous APT41 campaigns — particularly in how the group exploits vulnerabilities in JavaScript engines like V8. APT41 (also known as Double Dragon or Barium) has a long history of blending state-sponsored espionage with financially motivated attacks, often leveraging browser-based zero-days before public disclosure. Recent patterns observed in CVE‑2025‑6554 exploitation include: Payload obfuscation using browser-native JavaScript APIs Conditional delivery based on language settings and timezone Initial access tied to compromised SaaS login portals — a known APT41 technique While correlation does not imply causation, the technical and operational overlap strongly suggests APT41’s potential involvement — or the reuse of its TTPs (Tactics, Techniques and Procedures) by another actor. This reinforces the urgency to adopt resilient architectures like PassCypher and DataShielder, which operate completely outside the browser’s trust zone. For high-security environments, it’s possible to manually disable JIT optimization via Exposed: they often use Table comparing security risk levels across different types of password managers, highlighting the resilience of PassCypher and DataShielder. Risk varies depending on architecture: Less exposed, since they operate outside the browser. Still, if auto-fill extensions are used, they may be targeted via V8 attacks. Yes, CVE‑2025‑6554 may compromise password managers — especially those that: Independent threat intelligence teams — including Shadowserver, CERT-EU, and Google TAG — confirmed over 172,000 exploitation attempts related to the Chrome V8 Zero-Day between June 27 and July 2, 2025. These attacks primarily targeted: Because execution occurs within the browser tab’s memory context, attackers could also: The following technical actions will significantly reduce your exposure to Chrome V8 Zero-Day attacks: Update Chrome immediately to version 138.x or higher Restart the browser to apply the patch Disable all non-essential extensions Audit and review permissions of remaining extensions Isolate critical sessions (SSO portals, admin consoles, banking access) Use offline tools such as PassCypher and DataShielder for sensitive operations Notify IT departments and power users Enable SIEM network logging to detect suspicious behavior Disable JavaScript JIT compilation in hardened environments Future-proof defense requires a shift in architecture. To neutralize risks like the Chrome V8 Zero-Day, security must be built into the foundation: PassCypher and DataShielder follow this blueprint. They operate independently of browsers, avoid the V8 engine entirely, and secure all operations through NFC-based hardware modules. This is not about patching faster. It’s about creating systems where nothing sensitive is exposed — even when a zero-day is actively exploited.Executive Summary
Table of Contents
Key insights include:
[TECHNICAL ALERT] Chrome V8 Zero-Day: CVE-2025-6554 Actively Exploited
A critical vulnerability strikes Chrome’s V8 engine again
Technical Details
What CVE‑2025‑6554 Really Enables
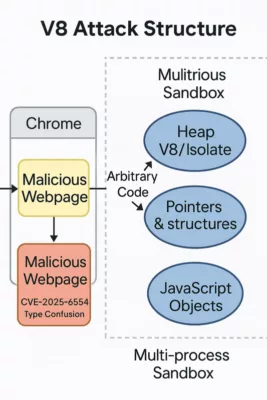
Educational Insight: “Why the V8 Sandbox Doesn’t Fully Protect You”
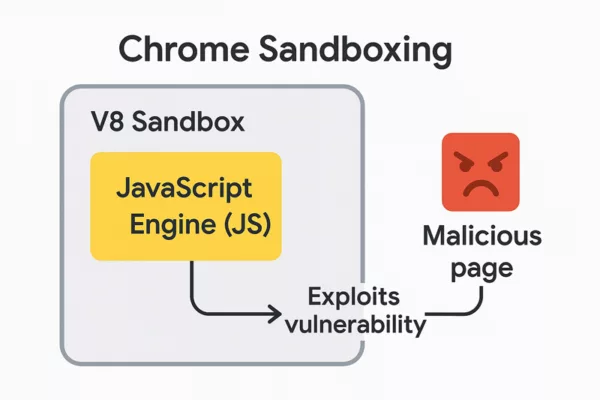
Secure vs Exposed Architectures: Comparative Overview
Classic Browser-Based Architecture
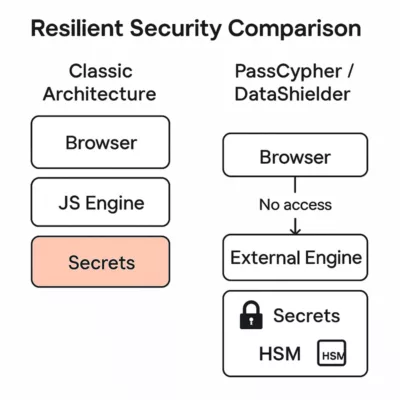
PassCypher / DataShielder: A Resilient Architecture
Other Critical Chrome Zero-Days in 2025
2. CVE-2025-4664 – Type Confusion in V8 (May 2025)
3. CVE-2025-5419 – Heap corruption in WebAssembly (June 2025)
4. CVE-2025-6554 – Type Confusion in V8 (June 2025, Chrome v138)CVE-2025-6554 Incident Timeline:
Possible Link to APT41 Campaigns
Table: Overlap Between APT41 Tactics and CVE-2025-6554 Attack Chain {#apt41-comparison}
Tactic or Indicator
APT41 Known Behavior
Observed in CVE‑2025‑6554?
Exploitation of V8 Engine
✔ (e.g., CVE‑2021‑21166)
✔
SaaS session hijacking
✔
✔
Payload obfuscation via JS API
✔
✔
Timezone or language targeting
✔
✔
Post-exploitation lateral movement
✔ via tools like Cobalt
Unknown
Attribution to Chinese state actors
✔
Under investigation
Disable JIT for Reduced Exposure (Advanced)
chrome://flags/#disable-javascript-jit. This reduces the attack surface at the cost of JavaScript performance.Risks to Traditional Password Managers
1. Integrated browser password managers (Chrome, Edge, Firefox)
localStorage, IndexedDB, or JS APIs to store credentials. → Malicious JS code in the same context may read or inject sensitive data.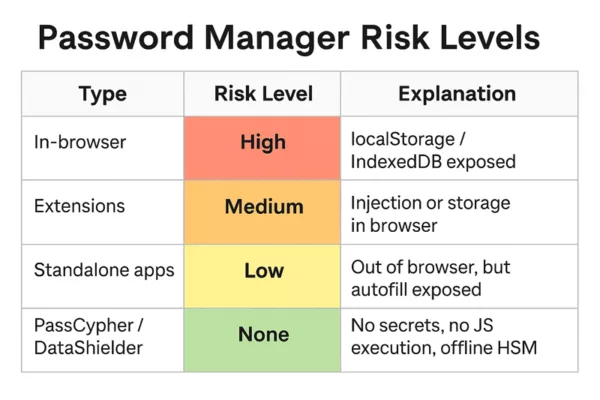
2. Third-party extensions (LastPass, Bitwarden, Dashlane, etc.)
3. Standalone apps (KeePass, 1Password desktop, etc.)
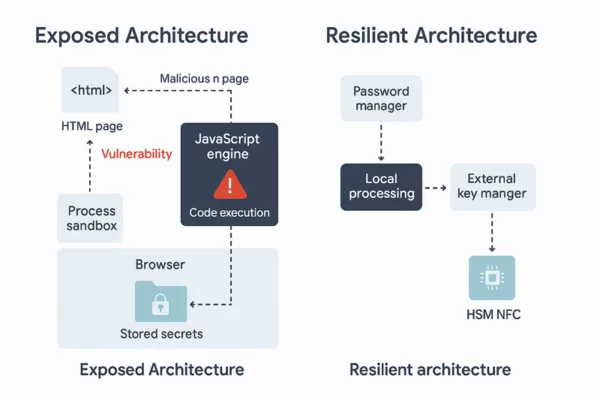
Why PassCypher / DataShielder Stay Outside the Risk Perimeter
Strategic Context, Global Impact, and Timeline
Immediate Operational Checklist
Exposure Risk by User Profile
User Profile
Risk Level
Technical Justification
General Public
Low to Moderate
Exposure limited if browser is up-to-date
Business Users (SaaS)
High
Active extensions, access to privileged services
Admins / DevOps / IT
Critical
Browser-based access to CI/CD, tokens, and admin portals
Building True Resilience: Secure by Design
Strategic Outlook: Security Beyond Patching
A silent cyberweapon undermining digital trust
Two-factor authentication (2FA) was supposed to be the cybersecurity bedrock. Yet, it has a crucial vulnerability: legacy systems that still allow application-specific passwords. Cyber threat actors like UNC6293, tied to the infamous APT29 (Cozy Bear), have seized this flaw to bypass advanced security layers and exfiltrate sensitive data—without triggering alarms.
Understanding How APT29 Exploits App Passwords via Social Engineering
- What makes app passwords a critical weak link.
- How attackers social engineer victims to hand over access.
- Who discovered this exploitation method and its broader geopolitical implications.
This attack vector exemplifies the evolving tactics of Russian state-sponsored actors, echoing campaigns detailed in Freemindtronic’s APT29 spear-phishing analysis.
What Was Discovered—and by Whom?
In May 2024, researchers from Google’s Threat Analysis Group (TAG) and Mandiant jointly published findings revealing that UNC6293, a cluster overlapping with APT29, was leveraging app passwords to gain persistent unauthorized access to Gmail accounts—without defeating 2FA.
Source: https://blog.google/threat-analysis-group/government-backed-attacker-targets-email
Using spear-phishing campaigns impersonating the U.S. State Department, targets—primarily Western academics and think-tank staff—received seemingly legitimate invitations to restricted briefings. The messages included a PDF “technical guide” instructing the recipient to generate and share an application password, presented as a harmless prerequisite to access materials.
Why App Passwords Are a Hidden Threat
App passwords are legacy authentication methods used for third-party email clients (like Thunderbird or Outlook) that do not support modern 2FA. Unfortunately:
- They bypass multi-factor authentication checks entirely.
- Generated passwords can last indefinitely unless manually revoked.
- They create low-visibility, stealth access vectors undetected by most users.
Attackers exploit user unfamiliarity and trust in official-looking procedures to obtain persistent email access, enabling silent observation or data theft over extended periods.
Google strongly advises high-risk users to enroll in the Advanced Protection Program, which disables app passwords entirely.
Mitigation Strategies
Even strong 2FA setups are not enough if legacy methods like app passwords remain active. Here’s how to neutralize this invisible threat:
To protect against such invisible breaches:
- Avoid app passwords—prefer OAuth-based clients or passkeys.
- Never share credentials—even ones labeled as “temporary.”
- Enable account activity monitoring and review app access regularly.
- Opt for physical security keys under Google’s Advanced Protection when handling high-risk communications.
Related Reading from Freemindtronic
This technique directly complements broader tactics used by APT29, including:
- APT29 spear-phishing across Europe
- OAuth token abuse and MFA bypass methods
PassCypher: Hardware-Isolated Sharing for All Credential Types—Without a Backend
In a landscape where attackers exploit trust, identifiers, and server exposure, PassCypher sets a sovereign benchmark in secure credential management. It eliminates traditional weak points—no servers, no databases, no user identifiers—by using patented segmented key containers, enabling fully autonomous and end-to-end secure sharing of any form of identification data.
These containers can encapsulate:
- Login/password pairs (web, VPN, apps)
- 2FA/TOTP secrets
- BitLocker, VeraCrypt, and TrueCrypt recovery keys
- Private SSH keys, OpenPGP identities, or license files
- System secrets or cryptographic material
> All shared containers remain encrypted—even at destination. They are never decrypted or exposed, not even during use.
Browser-Based PassCypher HSM: Segmented Keys for Zero-Trust Distribution
PassCypher HSM creates encrypted containers directly within the browser via JavaScript, using a client-side, patented key segmentation process. Once generated:
- The container can only be accessed using its associated split-key pair;
- Sharing is achieved by exchanging the segmented key pair, not the content;
- The recipient never needs to decrypt the container—usage is performed in-place, fully shielded.
This approach allows compliance with zero-trust governance and offline operational environments, without reliance on cloud infrastructure or middleware.
PassCypher NFC HSM: Air-Gapped, Multi-Mode Secure Sharing
PassCypher’s NFC HSM version adds advanced mobility and decentralized distribution methods, including:
- Secure NFC-to-NFC duplication: total, partial, or unit-based cloning between PassCypher HSMs, each operation protected by cryptographic confirmation;
- Direct QR code export: share encrypted containers instantly via QR, for in-room usage;
- Asymmetric QR transfer (remote): encrypt container delivery using the recipient’s own dedicated RSA 4096 public key, pre-stored in its NFC HSM’s EPROM. No prior connection is needed—authentication and confidentiality are ensured by hardware keys alone.
Each NFC HSM device autonomously generates its own RSA 4096-bit keypair for this purpose, operating entirely offline and without a software agent.
Resilience by Design: No Attack Surface, No Phishing Risk
Because PassCypher avoids:
- Online accounts or identity tracking,
- External database lookups,
- Real-time credential decryption,
…it renders phishing and real-time behavioral override attacks—like those used when APT29 Exploits App Passwords —fundamentally ineffective.
Containers can be shared securely across individuals, air-gapped environments, and even international zones, without exposing content or credentials at any stage. All interactions are governed by asymmetric trust cryptography, offline key exchanges, and quantum-ready encryption algorithms.
> In essence, PassCypher empowers users to delegate access, not vulnerability.
📎 More info:
- PassCypher HSM PGP overview
- PassCypher NFC HSM overview
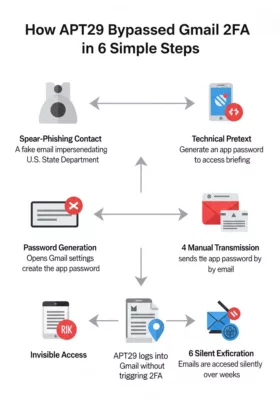
APT29’s attack chain explained in 6 steps — how trust was exploited to bypass Gmail 2FA.
APT29’s attack chain explained in 6 steps — how trust was exploited to bypass Gmail 2FA.
APT29 Attack Flow Using App Passwords
To visualize the manipulation process, here’s a simplified attack chain used by APT29 via UNC6293:
- Reconnaissance Identify high-value targets: academics, journalists, researchers.
- Initial Contact Send authentic-looking spear-phishing emails impersonating government agencies.
- Trust Engineering Engage over several replies, maintain tone of authority and legitimacy.
- Delivery of False Procedure Provide a professional PDF instructing how to generate an app password.
- Credential Submission Convince the target to transmit the app password “for access inclusion.”
- Persistent, Invisible Intrusion Access the mailbox indefinitely without detection.
Threat Evolution Matrix: APT29 Access Techniques
| Campaign | Technique | Target Profile | Access Layer | Visibility | Persistence |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| APT29 OAuth Abuse (2023) | OAuth consent hijack (token abuse) | NGOs, diplomats, M365 admins | Microsoft 365 cloud | Medium (IAM logs) | Weeks to months |
| APT29 UNC6293 (2024–2025) | App password social engineering | Russia analysts, cyber experts | Gmail (legacy auth) | Low (no alerts) | Indefinite |
| APT29 credential phishing (historic) | Fake login portals | Broad civilian targets | Multiple | High (browser warning) | Single session |
This table highlights a shift from technical breaches to human-layer manipulations.
Real-World Mitigation Scenarios
Security advice becomes actionable when grounded in context. Here are practical defense strategies, tailored to real-use environments:
- For researchers receiving invitations to conferences or secure briefings: Avoid app passwords altogether. Demand access via federated identity systems only (e.g., SAML, OAuth). If someone asks for a generated credential—even “just once”—treat it as hostile.
- For cybersecurity teams managing high-risk individuals: Implement rules in Workspace or M365 to disable legacy authentication. Mandate FIDO2 physical keys and enforce real-time log correlation monitoring for unusual delegated access.
- For institutions under threat from espionage: Deploy zero-knowledge solutions like PassCypher HSM, which allow secure credential sharing without revealing the data itself. Instruct all staff to treat any unsolicited “technical procedure” as a potential attack vector.
These don’t just mitigate risk—they disrupt the very tactics APT29 depends on.
At the core of PassCypher lies a different security philosophy—one that rejects reliance and instead builds on cryptographic sovereignty. As its inventor Jacques Gascuel puts it:
Inventor’s Perspective
> “Trust isn’t a feature. It’s a surface of attack.”
As creator of PassCypher, I wanted to reimagine how we share secrets—not by trusting people or platforms, but by removing the need for trust altogether.
When you share a PassCypher container, you’re not giving someone access—you’re handing over an undecipherable, mathematically locked object, usable only under predefined cryptographic conditions. No identity required. No server involved. No vulnerability created. Just a sovereign object, sealed against manipulation.
In an age where attackers win by exploiting human belief, sovereignty begins where trust ends.
— Jacques Gascuel
Final Note: Security as Cognitive Discipline
There is no “end” to cybersecurity—only a shift in posture.
APT29 doesn’t breach your walls. It gets you to open the gate, smile, and even carry their suitcase inside. That’s not code—it’s cognition.
This article is a reminder that cybersecurity lives in awareness, not just hardware or protocols. Each message you receive could be a mirror—reflecting either your vigilance or your blind spot. What you do next shapes the threat.
Furthermore, PassCypher’s ability to render attacks where APT29 Exploits App Passwords ineffective is a major security advantage.
L’arrêt du 18 juin 2025 redéfinit profondément la nature des emails professionnels données personnelles, en affirmant leur accessibilité au titre du RGPD, même après la rupture du contrat. Il s’agit d’une avancée décisive pour l’accès aux preuves en matière prud’homale. Le salarié peut ainsi revendiquer la communication de ses courriels, y compris leurs métadonnées, sauf atteinte justifiée aux droits d’autrui. L’article analyse également la dimension mixte de ces contenus, à la croisée du droit des données et du droit d’auteur.
À propos de l’auteur de ce billet — Jacques Gascuel est le fondateur de Freemindtronic Andorre, où il conçoit des solutions innovantes de sécurité électronique reposant sur des technologies brevetées. Titulaire d’une formation juridique, il s’intéresse aux interactions entre le droit, la cybersécurité matérielle et la protection des données. Ses recherches portent notamment sur les dispositifs de sécurité sans contact, la conformité au RGPD et les cadres juridiques hybrides mêlant propriété intellectuelle, données personnelles et souveraineté numérique. À travers ses publications, il cherche à rendre accessibles les grands enjeux juridiques du numérique, en alliant rigueur conceptuelle et application concrète.
Cass. soc., 18 juin 2025, n° 23-19.022 Un ancien salarié sollicite l’accès à ses données personnelles, incluant ses e-mails professionnels, dans le cadre d’un droit reconnu par l’article 15 du RGPD. L’employeur refuse en invoquant la finalité strictement professionnelle de ces courriels. La chambre sociale de la Cour de cassation rappelle alors qu’un contenu professionnel n’échappe pas par nature au champ du RGPD, dès lors qu’il permet d’identifier une personne physique. Elle impose à l’employeur de transmettre ces données, sauf justification expresse fondée sur un droit supérieur. La motivation de la Haute juridiction s’appuie sur une convergence entre : Longtemps considérés comme de simples outils de travail, les emails professionnels données personnelles relèvent en réalité de régimes hybrides mêlant vie privée, création intellectuelle et subordination juridique. L’arrêt ouvre aussi la voie à une analyse plus fine : celle de la nature “mixte” de certaines communications professionnelles. Un salarié qui rédige un message dans l’exercice de ses fonctions le fait : Il s’agit dès lors d’un contenu potentiellement hybride, au croisement : Ces interrogations ne relèvent pas de la pure spéculation. Elles appellent une vigilance contractuelle accrue et une harmonisation entre droit du travail, RGPD et droit d’auteur. Les données professionnelles ne sont pas exclues du RGPD. La jurisprudence convergente des États membres confirme que le traitement lié à une activité salariée reste encadré par le droit des personnes. Un courriel professionnel, obtenu par le salarié grâce à son droit d’accès au sens de l’article 15 RGPD, peut constituer un mode de preuve recevable en justice, y compris contre l’employeur. Cette recevabilité est conditionnée par les exigences de loyauté et de proportionnalité, principes dégagés par la jurisprudence depuis l’arrêt de principe Nikon (Cass. soc., 2 octobre 2001, n° 99-42.942). Le juge apprécie la régularité de la preuve au regard : L’article 9 du Code de procédure civile permet au juge d’ordonner toute mesure d’instruction utile, notamment la production forcée d’un courriel conservé par l’entreprise, si celui-ci est inaccessible au salarié. Dans la pratique, les courriels pouvant faire l’objet d’une demande d’accès par le salarié sont variés. Voici un tableau synthétique utile à la qualification des situations : Le traitement d’une demande d’accès à des emails professionnels données personnelles impose une méthodologie rigoureuse pour garantir la conformité et la protection des tiers. Pour les professionnels chargés de la conformité, voici un schéma opérationnel pour sécuriser la procédure : Cette jurisprudence contraint les employeurs à revoir leurs pratiques en matière de gestion des emails professionnels données personnelles, y compris après la rupture du contrat. Cette jurisprudence impose ainsi une refonte stratégique de la gouvernance de l’information en milieu professionnel. Le courriel, souvent banalisé, devient un support sensible de droit fondamental, obligeant l’entreprise à conjuguer conformité réglementaire, transparence managériale et maîtrise des risques juridiques. En matière d’innovation, les emails professionnels données personnelles deviennent une source probante pour documenter la contribution technique d’un salarié à une invention brevetable. Bien que l’arrêt ne porte pas directement sur le droit des brevets, il crée un effet de levier important sur la gestion de la preuve de l’invention dans les entreprises technologiques, via le droit d’accès du salarié à ses e-mails professionnels. En effet, une grande partie des échanges liés à la conception, à l’amélioration ou à la stratégie d’exploitation d’un brevet passent par la messagerie professionnelle, qui devient alors un réservoir de preuves de contribution intellectuelle, de date d’antériorité ou de copropriété potentielle. L’accès du salarié à ses courriels peut affecter la preuve de sa contribution à une invention brevetée. Cela concerne particulièrement : La décision du 18 juin 2025 opère bien plus qu’un simple rappel du champ d’application du RGPD. Elle marque une inflexion profonde dans l’équilibre des pouvoirs numériques en entreprise. Par la reconnaissance pleine et entière des emails professionnels données personnelles comme objet d’accès, de preuve et potentiellement d’appropriation partagée, la Cour de cassation transforme l’e-mail en nœud d’intelligibilité du droit du travail numérique. Elle engage une relecture intégrée des droits du salarié : accès, transparence, propriété intellectuelle, loyauté probatoire. Et impose à l’entreprise une gouvernance plus rigoureuse, respectueuse et fondée sur une anticipation contractuelle accrue. À travers cette jurisprudence, la messagerie électronique cesse d’être un simple vecteur logistique : elle devient un espace juridique sensible, révélateur d’une relation de travail désormais soumise à des standards accrus de responsabilité numérique. ⚖️ Synthèse exécutive
Sommaire analytique des points de droit abordés
Points clés à retenir
L’e-mail professionnel comme donnée personnelle : portée, régime hybride et implication de l’arrêt du 18 juin 2025 de la Cour de cassation
Faits, contexte et portée immédiate
Cadre juridique activé par l’arrêt
Le régime des données mixtes : quand le numérique brouille les frontières
Questions clés en droit du travail numérique
Conséquences pratiques : nouvelles obligations des employeurs
Comparaison européenne et diffusion du standard
🇫🇷 France (2025)
🇩🇪 Allemagne (BAG)
🇧🇪 Belgique (APD)
Le salarié peut accéder à ses mails pros même après le départ
Accès aux journaux SMTP permis sous réserve de finalité légitime
L’entreprise doit pouvoir prouver l’intérêt supérieur justifiant la non-communication
Recommandations opérationnelles à intégrer
Pour les DPO :
Pour les RH / directions juridiques :
Pour les salariés :
La preuve électronique et la recevabilité des courriels en justice
Typologie des courriels concernés par le droit d’accès
Catégorie
Exemples typiques
Enjeu principal
Correspondances hiérarchiques
Instructions, félicitations, avertissements
Relations d’autorité, conditions de travail
Directives de management
Injonctions à des pratiques discutables, suivi de performance
Licéité des ordres reçus
Données RH
Convocations à entretien, alertes, sanctions, évaluation
Droit à la preuve en cas de litige disciplinaire
Tensions internes
Désaccords documentés, mails à tonalité hostile, signalements
Harcèlement, discrimination, conflits collectifs
Grille d’analyse DPO : traitement d’une demande d’accès à la messagerie
Étapes
Description
Outils associés
1. Réception de la demande
Identifier le périmètre des données demandées (adresses, périodes, types de fichiers)
Registre RGPD – Formulaire type
2. Vérification de l’identité
S’assurer que la personne est bien le salarié concerné
Système RH, preuve d’identité
3. Extraction ciblée
Exportation des messages envoyés/reçus, pièces jointes, métadonnées
SIEM, outil d’archivage sécurisé
4. Analyse juridique
Identifier d’éventuelles atteintes aux droits des tiers ou au secret des affaires
Intervention du DPO ou service juridique
5. Remise sécurisée
Communication dans un format lisible et sécurisé, avec justification des éventuelles omissions
Délivrance chiffrée, traçabilité
Typologie des courriels concernés par le droit d’accès
Catégorie
Exemples typiques
Enjeux juridiques
Correspondance hiérarchique
Instructions, retours d’évaluation, remerciements ou reproches
Établissement du lien de subordination et des conditions de travail
Directives opérationnelles
Ordres de mission, consignes commerciales, objectifs imposés
Légalité ou loyauté des ordres donnés
Données RH / disciplinaires
Convocations, blâmes, avertissements, entretiens d’évaluation
Droit à la preuve en contentieux prud’homal ou disciplinaire
Tensions internes / alertes
Mails à tonalité conflictuelle, alertes internes, signalements éthiques
Harcèlement, discrimination, procédure d’alerte interne
Grille d’analyse pour le traitement d’une demande d’accès par le DPO
Étape
Objectif opérationnel
Outils ou documents associés
1. Réception et enregistrement
Identifier la demande et le périmètre des données
Formulaire RGPD / CRM dédié / Registre des demandes
2. Vérification d’identité
S’assurer de la qualité du demandeur et éviter les abus
Pièce d’identité, croisement avec fichiers RH
3. Extraction ciblée des données
Cibler uniquement les courriels et métadonnées liées au demandeur
Archivage des mails, moteur de recherche interne, logs
4. Analyse des risques tiers
Repérer les données sensibles de tiers dans les échanges
Analyse manuelle ou automatisée, intervention du service juridique
5. Remise au salarié
Transmettre un export lisible, explicite, dans un format accessible
Formats .eml / .pdf + note explicative éventuelle
Tableau comparatif international (UE / hors UE)
Régime juridique
Reconnaissance de l’e-mail pro comme donnée personnelle ?
Commentaires
🇫🇷 France
✔️ Oui
Affirmé par l’arrêt Cass. soc., 18 juin 2025
🇩🇪 Allemagne (BAG)
✔️ Oui (sous conditions)
Accès possible aux journaux de messagerie pour motifs légitimes
🇪🇸 Espagne (TSJ Madrid)
✔️ Oui
Accès aux messageries refusé si motifs sérieux d’atteinte à autrui
🇨🇦 Canada (LPRPDE)
✔️ Oui
Toute information identifiante = renseignement personnel
🇺🇸 États-Unis
❌ Généralement non
Pas de droit d’accès par défaut, sauf loi sectorielle (ex. santé, finance)
Risques juridiques pour l’employeur en cas de refus injustifié du droit d’accès
Nature du risque
Base juridique
Conséquences possibles
Refus d’accès non motivé
Article 15 RGPD, article 5 §1 RGPD
Plainte CNIL, injonction, amende administrative jusqu’à 4 % du CA mondial
Entrave à un droit fondamental
Article 6 CEDH, article L.1121-1 Code du travail
Nullité de la procédure disciplinaire ou licenciement, dommages-intérêts
Atteinte aux droits d’auteur
Code de la propriété intellectuelle (articles L.111-1 à L.113-9)
Action en contrefaçon ou atteinte à l’intégrité de l’œuvre
Preuve refusée lors d’un contentieux prud’homal
Article 9 CPC
Condamnation de l’employeur pour inégalité des armes ou manquement probatoire
Type de contenu identifié
Risque pour les tiers ?
Action recommandée
Message entre deux salariés nommément cités
Oui (vie privée, secret de correspondance)
Anonymisation ou occultation partielle
Mail collectif sans données sensibles
Non (contenu organisationnel)
Communication intégrale
Pièce jointe contenant une opinion personnelle d’un tiers
Oui (données personnelles tierces)
Extraire uniquement les données du demandeur
Message RH automatisé (ex. alerte badge)
Non (identifiable uniquement par le salarié)
Communication directe sans restriction
Message contenant une plainte d’un tiers
Oui (secret des sources, droit à la confidentialité)
Pondération : vérification du fondement juridique de la restriction
Ce que change fondamentalement cette décision : Effets sur l’entreprise et les droits du salarié
Volet
Avant la décision
Après la décision du 18 juin 2025
Côté salarié
Droit d’accès incertain aux courriels professionnels, surtout après départ.
Droit pleinement reconnu au titre de l’article 15 RGPD, y compris après la rupture du contrat.
Difficulté à constituer une preuve en cas de litige.
Nouveau levier probatoire en cas de harcèlement, discrimination, abus hiérarchique, etc.
Manque de visibilité sur ses propres communications archivées par l’employeur.
Légitimation de la transparence numérique à l’égard de ses propres données et contenus.
Absence de reconnaissance des apports intellectuels aux écrits professionnels.
Ouverture doctrinale à la protection des courriels comme œuvres de l’esprit à part entière.
Côté employeur
Liberté quasi-totale dans la gestion des messageries professionnelles.
Obligation de documenter, encadrer et justifier les traitements et restrictions d’accès.
Refus large d’accès souvent opposé sans justification, en cas de contentieux prud’homal.
Inversion de la charge de la preuve : nécessité de motiver chaque refus et démontrer sa proportionnalité.
Pratiques répandues de coupure immédiate des accès informatiques après rupture.
Nécessité d’établir une procédure encadrée pour garantir l’exercice du droit d’accès en post-contrat.
Contrats parfois muets sur la propriété des contenus numériques créés par les salariés.
Urgence de prévoir des clauses précises de cession ou de partage des droits (RGPD + propriété intellectuelle).
Brevets et e-mails professionnels : un enjeu de traçabilité et de reconnaissance
Risques et opportunités selon les parties
Acteur concerné
Enjeux identifiés
Actions clés à prévoir
Entreprise titulaire du brevet
– Risque de contestation de la titularité par un ancien salarié<br>- Remise en cause d’une invention « missionnelle »
– Clauses précises sur la cession des inventions<br>- Archivage sécurisé des contributions individuelles
Salarié ayant participé
– Possibilité de revendiquer une prime d’invention (art. L.611-7 CPI)<br>- Accès aux preuves de sa contribution
– Exercice du droit d’accès post-départ<br>- Usage des courriels comme éléments probants de création
DPO / service juridique
– Traitement de demandes sensibles pouvant impacter des droits industriels stratégiques
– Procédure renforcée : identification des échanges liés aux secrets techniques ou brevets en cours
Portée systémique de l’arrêt : un changement d’architecture informationnelle
Fondements juridiques à retenir
Bonnes pratiques à recommander
Références complémentaires utiles
Between 2022 and 2025, a sharp rise in military device thefts has exposed sensitive data and compromised national security worldwide. From laptops and USB drives to drones and smartphones, these thefts—often linked to hybrid warfare—reveal how physical assets are used for espionage, sabotage, and cyber infiltration. This article maps confirmed incidents, official warnings from defense leaders, and outlines how even minor breaches can grant access to classified systems. In today’s threat landscape, securing every military device is critical to protecting sovereignty.
The article emphasizes the urgent need for cross-domain defense measures that go beyond encryption, including hardware-level protections, behavioral monitoring, and rapid response protocols. In the new digital battlefield, securing every military device is not optional—it’s a matter of national sovereignty.
About the Author – Jacques Gascuel is the inventor of patented hardware-based security solutions and the founder of Freemindtronic Andorra. With a focus on military-grade data protection, his research spans hybrid warfare, espionage tactics, and counter-intrusion technologies. This article on military device thefts reflects his commitment to developing offline, privacy-by-design tools that secure sensitive assets even beyond cyberspace.
These incidents align with a broader hybrid warfare strategy. They are not isolated cases but rather part of coordinated efforts involving espionage, sabotage, and infiltration. Stolen electronic equipment—laptops, USB drives, mobile phones, SSDs, even SD cards from drones—offers unauthorized access to military or state-level classified networks. Malicious USB devices often serve as physical backdoors into critical infrastructures. Similarly, unidentified drone flyovers over sensitive sites suggest advanced surveillance and tactical scanning operations. As General Philippe Susnjara (DRSD) emphasizes, these threats combine physical theft, cyberattacks, and strategic deception. Their cumulative effect directly undermines sovereignty and national defense. Computerworld Source These incidents align with a broader hybrid warfare strategy. They are not isolated cases but rather part of coordinated efforts involving espionage, sabotage, and infiltration. Stolen electronic equipment—laptops, USB drives, mobile phones, SSDs, even SD cards from drones—offers unauthorized access to military or state-level classified networks. Malicious USB devices often serve as physical backdoors into critical infrastructures. Similarly, unidentified drone flyovers over sensitive sites suggest advanced surveillance and tactical scanning operations. As General Philippe Susnjara (DRSD) emphasizes, these threats combine physical theft, cyberattacks, and strategic deception. Their cumulative effect directly undermines sovereignty and national defense. Computerworld Source A troubling series of incidents—from military bases to defense exhibitions—has led to ministerial alerts. Sébastien Lecornu warns of a sharp increase in thefts affecting both civilian and military personnel. The DRSD highlights that devices often contain strategic data, and their loss could compromise France’s sovereignty. Surveillance drone sightings over sensitive sites and theft of equipment abroad (NATO Paris seminar) point toward sabotage and cross-border vulnerabilities. Still coping with fallout from earlier breaches, like the theft of a contractor laptop holding data on over 207,000 reservists. The case remains a benchmark example of digital fallout from physical theft. Supply-chain attacks demonstrate that not only direct military assets are targeted. Contractors handling sensitive information now represent a serious point of failure. Legislators’ phones and tablets were compromised as part of a state-sponsored campaign of intimidation and influence. These acts blur the lines between cyberespionage and political destabilization. Live conflict context accelerates hybrid operations. Stolen devices are weaponized instantly for signal intelligence (SIGINT). Groups like GRU’s Sandworm exploit battlefield-captured phones. Theft of laptops from SIS headquarters represents one of Africa’s rare public breaches. It reveals structural weaknesses in intelligence security protocols. Drone surveillance and memory card recovery expand the perimeter of military espionage to aerial and autonomous platforms. This represents a shift from physical theft to integrated hybrid reconnaissance. Military electronics are now frontline assets. A stolen laptop, drone SD card, or USB key can become the gateway to classified systems. These devices must be treated as intelligence vectors, not just hardware. The intersection of cyber and physical security demands smarter defense doctrines. Military infrastructure must now integrate AI-enhanced anomaly detection, offline compartmentalization, and self-erasing mechanisms. Resilience is not just about preventing breaches. It’s about ensuring data can’t be exploited even if devices fall into enemy hands. This global mapping of military device thefts reveals more than just negligence—it signals a shift in modern conflict. Where data flows, power follows. And where equipment travels, so do vulnerabilities. To protect sovereignty, nations must harden not just systems, but mindsets. Every stolen smartphone, every breached USB, is a reminder: defense begins with awareness, and ends with action.Executive Summary
Key insights include:
Global Stakes: Hybrid Warfare and Digital Sabotage
Country/Region
Period
Incident Description
Equipment Stolen/Compromised
Context & Modus Operandi
Resolution Status
Source & Verification
France
Spring 2023
Soldiers stole laptops/fixed PCs at Kremlin-Bicêtre
Laptops and desktop computers
Internal military theft, equipment re-sold locally
Resolved
OpexNews
France
Feb 26, 2024
Olympic security plans stolen in RER train
Laptop + USB flash drives
Urban theft in public transit
Resolved
AA.com.tr
France
June 2025
Paris Air Show espionage incident
Laptops, malicious USB sticks
Espionage at a defense exhibition
Partially Resolved
BFMTV
France
May 2023
NATO seminar: German laptop stolen
Military-grade laptop
Theft at high-level event
Unresolved
OpexNews
UK
May 2024
MoD subcontractor cyberattack
Personal data of military staff
Supply-chain breach
Partially Resolved
CSIS
Canada
May 2024
Surveillance of legislators’ devices
Smartphones, tablets
State-level cyberespionage
Ongoing Investigation
CSIS
Belarus → Ukraine
June 2024
Weaponized Excel phishing campaign
Infected XLS files
Digital deception against military targets
Under Analysis
CSIS
USA
2010 (rev. 2024)
Laptop stolen with data on 207,000 reservists
Sensitive PII
Classic case of physical data breach
Still cited
GovInfoSecurity
Gambia
April 2025
Theft at SIS headquarters
Classified military laptops
Compromise of intelligence operations
Under Investigation
Askanigambia
Multi-country
2023–2025
Drone data recovery from crash zones
Micro-SD cards (logs, images, GPS)
Drone espionage and cyber-physical convergence
Detection in progress
60 Minutes / CBS News
Global Stakes: Hybrid Warfare and Digital Sabotage
Inside the Global Shadow War Over Military Devices
🇫🇷 France
🇩🇪 Germany
🇺🇸 United States
🇬🇧 United Kingdom
🇨🇦 Canada
🇺🇦 Ukraine
🇬🇲 Gambia
Multi-region
From Devices to Doctrine: Rethinking Cyber-Physical Defense
Resources & Further Reading
Final Signal: Securing Tomorrow’s Frontlines Today
Incident Summary: A RecordBreaking Breach Unfolds
In June 2025, the digital world entered a new era of vulnerability. A massive breach involving more than 16 billion active credentials was discovered across several darknet marketplaces. This “megaleak” surpasses all previously known data breaches—both in sheer volume and in the freshness and diversity of the stolen data.
Unlike historical leaks that often stemmed from isolated serverside intrusions, this attack relied on a silent, distributed compromise executed on a massive scale using highly specialized malware. It reveals a deep transformation of cybercrime, where digital identity becomes a commodity, a weapon, and a tool of foreign interference.
Although the dataset is being presented as a new breach, several cybersecurity analysts have pointed out that it likely includes credentials from older leaks — such as RockYou2021 and earlier credential-stuffing compilations. This raises an important question: are we facing a new mega-leak or an inflation of existing records? Either way, the risk remains real — particularly because infostealers do not care how old a credential is, as long as the session is still valid.
Strategic Keywords: Darknet credentials 2025, global cyberattack, personal data breach, silent credential theft, infostealer logs, digital identity leak, cyber sovereignty breach
Darknet Credentials Breach 2025: A Global Digital Heist
Discover the true scope of the darknet credentials breach that shook the digital world in 2025. This unprecedented leak involved over 16 billion active identifiers and marks a dangerous shift in cybercriminal operations. From stealthy exfiltration to identity abuse and geopolitical espionage, this report unpacks the anatomy of the largest cyber credential heist ever recorded.
16+ Billion
Credentials leaked worldwide, redefining the scale and depth of modern identity theft operations.
Stealthy Exfiltration: How 16 Billion Credentials Were Stolen
The 2025 darknet credentials breach was not a result of serverside intrusions, but of widespread clientside compromise. Sophisticated infostealer malware like LummaC2, Redline, and Titan evolved to bypass traditional antivirus tools and extract session tokens, login credentials, and encrypted vaults with surgical precision.
- Infostealer Payloads: Deployed via cracked software, fake browser updates, and malvertising, exfiltrating data silently to Telegram bots and private C2 servers.
- Cookie Hijacking: Session hijacks from Google, Microsoft, and GitHub accounts allowed direct impersonation—even bypassing MFA.
- Clipboard Scrapers: Targeted password managers, crypto wallets, and 2FA copypaste operations, stealing sensitive content in real time.
- Telegram Exfil Channels: Over 60% of the data was exfiltrated via Telegram bots, enabling realtime credential leaks with minimal traceability.
- OAuth Abuse: Attackers exploited persistent GitHub OAuth tokens to access developer tools, repositories, and secrets without triggering alerts.
- BitB Attacks: Browserinthebrowser phishing pages harvested login credentials using cloned interfaces with perfect mimicry.
Who Was Targeted in the 2025 Breach?
This breach was not random. Behind the 16 billion compromised identifiers lies a calculated selection of highvalue targets spanning continents, sectors, and platforms. A breakdown of exposed credentials shows that this was a datadriven cyber operation designed for maximum strategic disruption.
- Government Entities: Highranking emails, internal portals, and cloud credentials linked to diplomatic and intelligence operations.
- Developers & IT Admins: Credentials linked to GitHub, SSH keys, API tokens, and internal tools—opening attack surfaces for software supply chains.
- Telecom & Infrastructure: VPN, VoIP, and backend access credentials tied to major telecom operators in Europe, the Middle East, and Asia.
- Journalists & Activists: Secure email platforms, PGP key leaks, and social media credentials exposed in authoritarian regions.
- Enterprise Credentials: Active logins to Microsoft 365, Google Workspace, Slack, and Zoom—many with elevated privileges or SSO access.
- Healthcare & Finance: EMR portals, insurance platforms, banking credentials—targeting identity validation and digital fraud channels.
Nature and Origin of Data: A New Class of Digital Assets Compromised
The 2025 megaleak is not just remarkable for its scale, but for the nature and diversity of the compromised data. Unlike past breaches mostly limited to emailpassword pairs or hashed dumps, this leak reveals dynamic, realtime identity layers
The dataset is largely composed of infostealer logs—files generated on compromised endpoints. These contain plaintext credentials, active session cookies, browser autofill data, password vault exports, crypto seed phrases, 2FA backup codes, and even system fingerprints. These logs allow immediate impersonation across services without requiring password resets or MFA tokens.
How Was the Data Acquired?
Most of the data originated from compromised personal and enterprise endpoints, harvested by malware strains such as LummaC2, Raccoon Stealer 2.3, and RedLine. These infostealers are capable of exfiltrating full identity profiles from infected machines in seconds, often without triggering detection systems.
They exploit weak security hygiene such as:
- No hardwarebacked vault protection
- Poor browser security settings Reuse of weak passwords
- Unsafe software downloads (cracks, warez, fake updates)
What Type of Data Was Leaked?
- Plaintext Logins: Emails and passwords for thousands of platforms (Microsoft, Apple, Google, Facebook, TikTok, etc.)
- Session Tokens: Cookies and JWTs enabling instant login without passwords or MFA
- Vault Extracts: Exfiltrated files from KeePass, Bitwarden, 1Password, and Chromiumbased password managers
- Crypto Wallet Seeds: Recovery phrases, keystore files, and hotwallet tokens (MetaMask, Phantom, TrustWallet)
- Browser & Device Fingerprints: IP, location, hardware specs, OS info, browser versions, and language preferences
In response, PassCypher NFC HSM and HSM PGP secure authentication by storing cryptographic keys in tamper-proof hardware that no remote attacker — not even an AI-powered one — can forge, duplicate, or intercept.
Key Sources of Infection
The compromised data points to a global spread of malware through:
- Pirated software and cracked installers
- Fake browser updates or Flash installers
- Email phishing attachments
- Malvertising (malicious ad networks)
- Discord, Telegram, and gaming communities
These infection chains reveal how attackers <strong>exploited trust ecosystems<strong>, disguising malicious payloads within platforms frequented by developers, gamers, and crypto users.
Exfiltration Methods: Silent, Distributed, and Highly Scalable
The exfiltration of over 16 billion credentials in 2025 wasn’t just massive—it was surgically precise. Threat actors orchestrated a globalscale theft using modular infostealers and encrypted communication layers. These methods enabled realtime credential leakage with minimal detection risk.
CommandandControl Channels: Telegram, Discord, and Beyond
The majority of logs were exfiltrated via Telegram bots configured to autoforward stolen data to private channels. These bots used tokenbased authentication and selfdeletion mechanisms, making traditional monitoring tools ineffective.
“`html
Strategic Insight: Over 60% of the logs recovered from darknet forums showed clear Telegramorigin metadata, pointing to widescale use of bot automation.
Discord also played a role, especially in targeting gaming communities and developers. Malicious bots embedded in servers silently captured credentials and pushed them via WebHooks to remote dashboards.
Malware Stealth Techniques: Evasion and Persistence
Infostealers like LummaC2, Redline, and Raccoon 2.3 embedded stealth modules to:
- Disable Windows Defender and bypass AMSI
- Inject payloads into trusted processes (svchost, explorer.exe)
- Encrypt stolen data with custom XOR+Base64 algorithms before exfiltration
The malware lifecycle was shortlived but potent: designed for a singleuse log theft, then selfdeletion. This limited forensics and delayed incident response.
PhishingFree Exfiltration via Fake Updaters
No need for phishing emails. Attackers embedded payloads into fake installers for browsers, media players, and antivirus tools. These were promoted via:
- Malvertising on adult sites and torrent platforms
- SEO poisoning leading users to fake clone sites
- “Browser Update Required” overlays triggering malicious downloads
- Payload Delivery Methods
Cracked software (often bundled with malware via forums and Telegram groups)
Fake installers mimicking Chrome, Brave, and Firefox updates
Weaponized PDFs and Office macros triggering driveby downloads
⚠️ Operational Note: Logs were often exfiltrated to C2 servers registered in rare TLDs (.lol, .cyou, .top), making IP reputationbased blocking inefficient.
Browser Hijacks and AutoFill Abuse
Once inside a system, malware extracted:
- Session tokens from browser cookies (bypassing login screens)
- Autofill form data (names, addresses, phone numbers, card info)
- Saved credentials from Chromium vaults and localStorage APIs
Some payloads injected JavaScript into active browser sessions, capturing credentials before submission, making even secure pages vulnerable.
Victim Profiles: From Diplomats to Developers
This massive breach wasn’t indiscriminate. On the contrary, the leaked credentials reflect a deliberate and **strategic targeting** of users and organizations with highvalue access points. The 16+ billion identifiers mapped out a digital battlefield across continents and sectors.
Governments and Public Institutions
Hundreds of thousands of credentials were traced back to:
- Diplomatic corps and foreign ministry portals
- Intelligencelinked accounts using Microsoft 365 or ProtonMail
- Sensitive platforms used by EU, Gulf, and ASEAN governments
“`html
Strategic Insight: These accounts allowed impersonation at the highest diplomatic levels—without needing to break into state servers.
Developers and System Administrators
Exposed data includes:
- SSH keys, GitHub OAuth tokens, Jenkins login sessions
- Access to devops pipelines, CI/CD dashboards, and production vaults
- API secrets connected to Amazon AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud projects
- These credentials are a launchpad for software supply chain attacks—allowing infiltration far beyond the initial victim.
Enterprises and Cloud SaaS Platforms
Stolen enterprise credentials gave direct access to:
- Microsoft 365 and Google Workspace sessions (many with SSO)
- Zoom, Slack, Atlassian, Salesforce logins
- Admin panels of ecommerce and banking apps
The breach also included access to customer support dashboards, exposing sensitive user communications and KYC documents.
Telecom and Infrastructure Providers
- VPN endpoints and NOC portals in Europe and the Middle East
- Privileged logins to VoIP, fiber provisioning, and 5G orchestration tools
- Backend access to telecom SaaS used by ISPs and mobile operators
Journalists, Activists, and NGOs
Targeted individuals operating in:
- Authoritarian or hybrid regimes (Russia, Iran, China, Belarus, Myanmar)
- Platforms like ProtonMail, Signal, Tutanota, and Mastodon
- Credentials enabling the takeover of anonymous social channels
Healthcare and Financial Systems
- Active sessions to EMR systems, health insurance databases
- Leaked IBANs, SWIFT codes, crypto wallet access
- Identity validation bypasses for fintech services (Stripe, Revolut, Wise)
⚠️ Operational Note: Many stolen credentials had not expired at the time of discovery, allowing active impersonation months after the initial leak.
Up Next: The Cybercrime Ecosystem Monetizing Your Identity
Next, we explore how these stolen credentials are traded, resold, and automated on darknet platforms, turning each login into a revenuegenerating asset for cybercriminals across the globe.
Who Got Hit the Hardest?
By Victim Category (Estimates from 16B credentials sample):
| Victim Category | Share (%) |
|---|---|
| Enterprise SaaS & Cloud Accounts | 32% |
| Developers & IT Admins | 21% |
| Government & Public Sector | 14% |
| Finance & Insurance Platforms | 11% |
| Telecom & Infrastructure | 8% |
| Healthcare Systems | 7% |
| Journalists, Activists & NGOs | 4% |
| Other Personal Accounts | 3% |
By Region (Top 5):
| Region | Share (%) |
|---|---|
| United States | 24% |
| European Union (incl. France, Germany, Italy) | 19% |
| India & Southeast Asia | 15% |
| Middle East (incl. UAE, Israel, KSA) | 13% |
| Russia & Ex-Soviet States | 11% |
Additional Insights: The Scale and Velocity of Credential Leaks
- Infostealer data surge (2024): According to Bitsight and SpyCloud, the volume of logs containing cookies, session tokens, and browser data rose by +34% in underground forums.
- Credential saturation per victim: SpyCloud reports that the average victim had 146 compromised records, spanning multiple platforms—highlighting widespread account reuse and poor credential hygiene.
- Rapid session hijacking: As reported by The Hacker News, 44% of logs now include active Microsoft sessions, with exfiltration typically occurring via Telegram within 24 hours.
💡 These trends reveal how credentials aren’t just stolen—they’re weaponized with growing speed, making the use of reactive defenses increasingly obsolete.
With stolen identities fueling everything from financial fraud to state-sponsored digital espionage, the black market has evolved into a strategic reservoir for hostile influence campaigns. This industrialization of cybercrime now forms the backbone of digital proxy wars — where attribution is murky, and plausible deniability is a feature, not a flaw.
Insight: Targets were not random. The strategic nature of the breach reveals cyber operations tailored to economic influence, software supply chain disruption, and geopolitical destabilization.
Underground Market: The New Gold Rush for Stolen Identities
The massive leak of over 16 billion credentials in 2025 didn’t just disappear into the void—it was monetized, shared, and resold across an increasingly organized underground ecosystem. From Telegram channels to dedicated marketplaces, cybercriminals have professionalized the distribution and monetization of stolen digital identities.
The leaked credentials are not merely dumped for notoriety—they’re sold in targeted bundles by region, sector, or platform, often using subscription-based models. These black-market credentials fuel account takeovers, business email compromises, and deepfake-enabled impersonations.
Key Monetization Channels:
- Telegram bot markets: Instant purchase of fresh logs and access tokens, often automated with search-by-email features.
- Genesis-style marketplaces: Offer full digital fingerprints, session cookies, and device emulations.
- Infostealer-as-a-Service (IaaS): Subscription models where cybercriminals access ready-to-use infection logs in real time.
- Darkweb credential catalogs: Indexed credential collections searchable by domain, country, or company.
Infographic: The black-market ecosystem for stolen digital identities in 2025. From Telegram bots to infostealer-as-a-service (IaaS), this economy fuels cybercrime and espionage.
💡 Strategic Insight: The value of an identity is no longer just tied to username-password pairs. Full access packages with session tokens, fingerprinting data, and behavioral metadata now fetch higher prices and enable stealthier attacks.
Sample Prices (June 2025):
| Item Type | Avg. Price (USD) |
|---|---|
| Gmail account with session cookie | $4.50 |
| Google Workspace admin access | $35–$200 |
| Crypto wallet seed phrase | $20–$500 |
| Full identity kit (passport scan + credentials) | $25–$100 |
| Access to developer tools (GitHub, Jira, etc.) | $8–$60 |
As these stolen credentials are traded and weaponized, their geopolitical consequences begin to surface—especially when the targets include critical sectors and foreign governments.
Credential Pricing Tiers
- Basic Logins: $1–$5 for email/password combos
- Session Cookies: $10–$50 depending on freshness and service
- Enterprise Access: $100–$500+ (especially SSO-enabled)
- Crypto Wallet Seeds: $200–$1,000+ depending on balance
- Developer Tokens & API Keys: $50–$300 depending on scope
Vendors often offer guarantees like “valid login or refund” and accept payments via Monero or USDT.
Market Share of Credential Types (2025)
🔹 35% Session Tokens
🔹 40% Email/Password Combos
🔹 25% Vault & Crypto Credentials
Strategic Insight:
Darknet platforms now operate like ecommerce sites, with search filters by region, platform, and even employer. The industrialization of cybercrime is no longer hypothetical — it’s fully operational.
These marketplaces don’t just sell access — they empower strategic sabotage. In the next section, we examine how hostile states and actors exploited this trove for cyber espionage and digital manipulation.
Geopolitical Exploitation: Cybercrime as a Proxy Tool
Behind the massive leak of over 16 billion credentials in mid-2025 lies more than just a financial motivation — it reveals a darker, more strategic exploitation of stolen identities for geopolitical influence and cyberespionage.
By classifying the data by language, region, platform, and collection date, malicious actors — including nation-state groups — have been able to build curated databases for targeted disinformation campaigns, surveillance, and infiltration of sensitive networks.
These activities blur the line between traditional cybercrime and state-sponsored operations. Initial Access Brokers (IABs), often the first sellers of stolen credentials, may unknowingly serve the interests of geopolitical actors looking for covert entry points into rival nations’ digital infrastructures.
Examples of geopolitical misuse include:
- Hijacking Telegram or WhatsApp groups to spread targeted disinformation during elections;
- Abusing access to GitHub, Notion, or internal platforms to steal trade secrets or diplomatic communications;
- Using compromised LinkedIn accounts to plant narratives, gain trust, or engineer influence within private or public organizations.
With stolen identities fueling everything from financial fraud to state-sponsored digital espionage, the black market has evolved into a strategic reservoir for hostile influence campaigns. This industrialization of cybercrime now forms the backbone of digital proxy wars — where attribution is murky, and plausible deniability is a feature, not a flaw.
These operations rely on the stealth and realism that infostealer data provides. Stolen credentials offer more than access — they offer credible digital identities. This transforms a simple malware victim into a proxy agent of influence.
💡 Strategic Insight
Cybercriminals aligned with geopolitical interests no longer need direct access to weaponized exploits. Instead, credential access allows infiltration with plausible deniability, turning stolen identities into digital mercenaries.
Through this lens, the 2025 mega-leak is not just a cybercrime event — it is a cyber-diplomatic weapon, affecting the very foundations of trust, identity, and sovereignty in cyberspace.
Next: Who is really behind the 2025 credential breach? The next section investigates how behaviorally tailored data sets give adversaries the ability to impersonate, influence, and infiltrate with near-perfect fidelity.
Threat Actor Attribution: Who Engineered the 2025 Mega-Leak?
The forensic evidence left behind by this massive credential breach paints a fragmented picture—but not an anonymous one. While attribution remains inherently complex in cyber operations, several indicators suggest the involvement of well-resourced actors, possibly operating under the protection—or direction—of nation-states.
Malware Signatures and TTPs (Tactics, Techniques, Procedures) identified in the breach align with malware families historically associated with Eastern European cybercriminal ecosystems. The use of Telegram bots, GitHub token abuse, and advanced session hijacking are all markers of actor groups linked to data monetization and hybrid influence operations.
In addition, several C2 domains and payload hashes trace back to infrastructure previously tied to the cybercriminal collective “DC804“, an advanced threat group believed to have links with actors operating from Ukraine and surrounding regions.
💡 Strategic Insight Attribution in cyberspace often relies on patterns, not confessions. In this case, the tooling, language settings, C2 server timings, and monetization channels suggest a fusion of cybercriminal profit motives and geopolitical disruption strategies.
Indicators of Nation-State Involvement
The operational scale of the breach—and its remarkably coordinated exfiltration tactics—raise suspicion that the attackers benefited from infrastructure support, safe havens, or even passive cooperation from government-aligned groups. This includes:
- Regional Target Bias: A disproportionate volume of credentials came from NATO countries and Asian democracies, while data from certain Eastern bloc regions appears underrepresented.
- Language Fingerprints: Several payloads and admin panels were configured in Russian and Ukrainian locales, with Cyrillic-based filename conventions.
- Operational Times: Attack traffic patterns followed Central European and Moscow Time business hours—suggesting actors worked standard office shifts, not criminal ad hoc hours.
- Tool Reuse: Obfuscation layers reused from malware previously attributed to Sandworm and Gamaredon, suggesting potential crossover or tooling leaks.
Attribution Caveat: While these clues are strong, none alone constitute irrefutable proof. The breach may result from a hybrid operation blending financially motivated hackers with state-level beneficiaries or disinformation agendas.
Understanding the threat actors is crucial not just for retaliation, but for anticipating their next moves. The final section delivers actionable insights to help organizations strengthen their cyber posture.
Digital Forensics and Open-Source Intelligence (OSINT)
Independent analysts and cybersecurity firms noted that much of the leaked data first surfaced on Telegram channels used by known ransomware groups. Certain accounts had ties to earlier leaks like “RockYou2024” and “Mother of All Breaches“, indicating an ecosystem where access brokers share, trade, and repurpose stolen credentials.
The GitHub OAuth token abuse, for example, mirrors patterns seen during the SolarWinds follow-on attacks, though no direct link has been established.
Attribution Synthesis:
Behind every leaked credential may lie a chain of actors — from low-level brokers to geopolitical operatives. Understanding this chain is crucial to defend not just individual identities, but the sovereignty of institutions and nations. The final section delivers actionable strategies to mitigate these evolving threats and protect digital assets.
From Espionage to Counter-Espionage: Shifting the Power Balance
With the underground market thriving and nation-states exploiting identity data at scale, the only remaining question is: how can individuals and organizations fight back? In the next section, we explore advanced countermeasures — including hardware-based encryption tools like PassCypher HSM PGP and DataShielder NFC HSM — that offer a radically new approach to protecting digital identity, even when credentials are compromised.
In the wake of the 2025 mega-leak, traditional cybersecurity hygiene practices — like rotating passwords or enabling 2FA — have proven insufficient against the industrialization of credential theft. Cybercriminals no longer need your password. They buy your session.
From Reactive Defense to Proactive Immunity
Infostealers now bypass 2FA by exfiltrating session cookies and device fingerprints, which are then sold in blackmarket ecosystems that emulate your digital identity in real time. The only viable defense lies outside the operating system, in tamper-proof hardware-based authentication.
What Should You Do After the Darknet Credentials Breach?
In response to this unprecedented leak, cybersecurity experts recommend a series of critical actions:
- Immediately change your passwords, especially for email, banking, and social media accounts.
- Enable Two-Factor Authentication (2FA) on all services that support it.
- Check if your email or credentials have been exposed using services like HaveIBeenPwned.
- Use a password manager to generate and store unique, strong passwords for each service.
- Consider switching to Passkeys (FIDO/WebAuthn) for better phishing resistance — though these are not immune to session hijacking.
While these measures are helpful, they remain inherently software-based. Once a device is compromised by an infostealer, even 2FA and passkeys may not be enough.
Ready to reclaim control over your identity?
Discover how PassCypher NFC HSM and PassCypher HSM PGP help you defeat infostealers, session hijacks, and phishing — even when your device is compromised. Offline. Tamper-proof. And yours alone.
PassCypher: The Offline Hardware Identity Shield That Outclasses All Digital Authentication Systems
From password managers to biometric logins and FIDO2 passkeys, most digital authentication systems — even those marketed as “passwordless” — still rely on your operating system, browser, or cloud. This reliance creates an invisible attack surface — always present, and always exploitable.
PassCypher removes the need for trust in software or connected devices altogether. It’s not just another password replacement — it’s a paradigm shift in identity sovereignty.
Developed by Freemindtronic Andorra, the PassCypher suite — combining NFC HSM and HSM PGP — delivers a new security model that goes beyond password managers, passkeys, biometrics, or FIDO tokens.
Unlike traditional solutions, PassCypher never stores secrets on your phone, browser, cloud, or system memory. No master password. No trusted device. No syncing.
Only physical presence and cryptographic segmentation grant access — making phishing, malware, session hijacking, and deepfake impersonation technically impossible.
Passkeys vs PassCypher – When Zero Trust Becomes Zero Exposure
Beyond Trust: A security model where secrets are never exposed — not even after a breach.
What Top Experts Say About Passkeys — and What They Can’t Prevent
Despite their cryptographic rigor, passkeys still depend on trust in the local execution environment. As shown in Trail of Bits’ 2025 analysis and their 2023 investigation, authenticators embedded in browsers or OS-managed enclaves remain exposed to local code injection or manipulation.
- 🕷️ Browser-based malware can trick users into authenticating malicious domains.
- 💥 Counterfeit authenticators may leak private keys if firmware is compromised.
- 🎯 Recovery mechanisms in cloud-based passkey backups widen the attack surface.
PassCypher eliminates all these risks by removing browsers, operating systems, and the cloud from the authentication equation entirely. It stores segmented AES-256 keys in offline, air-gapped tamper-proof hardware. No shared memory. No fallback logic. Nothing exposed to runtime attacks. Not even trust in the hardware manufacturer is required — because the secrets never leave the NFC HSM or HSM PGP container.
🔐 While passkeys resist phishing, PassCypher makes it technically impossible by eliminating every single exposure vector — including those acknowledged by the FIDO/WebAuthn technical literature.
📌 As Trail of Bits concludes, “Passkeys are not silver bullets.” That’s why PassCypher exists.
Digital Authentication vs PassCypher: What Really Keeps You Safe?
Passkeys (FIDO2/WebAuthn) replace passwords with cryptographic key pairs. This reduces phishing attacks but does not eliminate malware threats. In most deployments, the private key is stored inside the OS or a browser-managed enclave — potentially accessible by advanced malware, as highlighted by Trail of Bits (2025).
In addition, studies such as Specops (2024) and MDPI (2023) emphasize the vulnerabilities of passkeys in case of local malware, session hijacking, or cloud sync compromise.
PassCypher takes a radically different approach: keys are generated and stored entirely offline, in a tamper-proof, air-gapped NFC HSM or encrypted local container (PGP). The secret never appears in memory, isn’t accessible by any process, and remains invisible — even to an infected system.
| Feature | PassCypher HSM PGP (Browser Plugin) | PassCypher NFC HSM (Lite or Master) |
|---|---|---|
| Storage | AES-256 encrypted local vault | Hardware-encrypted memory (AES-256 + segmented key) |
| Session Protection | Browser sandboxing & anti-BITB | Offline key access via secure NFC or QR scan |
| Phishing Defense | Domain & URL validation | No online input or login required |
| Compromise Immunity | Immune to clipboard/infostealer malware | OS-isolated, no USB interface |
| Integration | Webmail, Web login, PGP support | Android NFC + Freemindtronic app |
Takeaway: Unlike passkeys and other passwordless systems, PassCypher doesn’t just improve convenience — it physically separates secrets from any exploitable digital environment. Whether browser plugin (PGP) or NFC hardware module, the data remains encrypted, segmented, and unreachable — even by advanced malware or AI-powered impersonators.
Structural Immunity: Up to 97% of Credential Attack Vectors Neutralized
According to public breach analyses and malware telemetry, over 95% of identity-based cyberattacks exploit a narrow set of vectors: phishing (including BITB), session hijacking, OS-level malware, token reuse, and cloud-synced credential leaks.
PassCypher neutralizes these threats by architectural design. Instead of patching surface-level symptoms, it eliminates structural exposure entirely:
- 🔐 AES-256 CBC segmented keys — never stored in RAM, browser memory, or synced to the cloud
- 📴 Offline-by-default storage — in local encrypted vaults (HSM PGP) or air-gapped NFC hardware (NFC HSM)
- 📲 Activated only by physical presence — via secure NFC scan or QR code, no trusted device dependency
🧩 PassCypher isn’t just for usernames and passwords. It safeguards:
- 🗝️ SSH private keys with passphrases
- 🔑 TOTP/HOTP secrets with auto-submitted PINs
- 📦 PGP signing and encryption keys
- 🧱 Full-disk encryption keys (BitLocker, VeraCrypt, TrueCrypt)
Multiple independent studies — from
Trail of Bits, Specops, and MDPI — confirm that offline, hardware-rooted and segmented identity models can prevent up to 97% of credential exploitation paths, far beyond the 50–60% blocked by cloud-dependent passkey systems.
This isn’t just breach mitigation — it’s breach immunity. Even advanced AI-powered impersonation or deepfake-based attacks can’t decrypt what’s never exposed. With PassCypher, identity protection becomes a matter of physics, not policy.
🛡️ Active BITB Protection — Defusing a Common Entry Point in Credential Breaches
One of the most exploited attack vectors behind large-scale credential leaks — such as the 2025 Darknet dump of over 16 billion valid identities — is the Browser-in-the-Browser (BITB) phishing technique. It creates fake login popups that are visually identical to real providers (Google, Microsoft, etc.), tricking users into entering valid credentials or initiating trusted sessions.
PassCypher HSM PGP goes beyond simple login isolation. Its embedded BITB defense mechanism automatically destroys iframe-based redirections and, in semi-automatic mode, flags suspicious redirect URLs before they reach the user’s screen — even after authentication. This makes it a rare solution capable of disrupting phishing operations even after login has occurred.
In a world where deepfakes and session hijacks are automated, real-time sanitization of the browser environment isn’t a luxury — it’s a necessity.
📚 Want to See PassCypher in Action?
Curious about how PassCypher actually works? These in-depth guides walk you through the full architecture, usage, and security model:
- How PassCypher HSM PGP Works – Full Tutorial
- PassCypher NFC HSM – Secure, Convenient Hardware Password Manager
Learn how air-gapped key storage, NFC hardware, and PGP plugins create a tamper-proof authentication flow — even on compromised devices.
Security Without Exposure — Not Even After Intrusion
Secrets remain continuously encrypted using AES-256 CBC with segmented keys. No software, hardware, or network-level incident can expose them — because decryption requires multiple simultaneous trust conditions: native 2FA, origin validation, and active anti-BITB protection.
This isn’t reactive security through erasure. It’s proactive immunity through structural inaccessibility — enforced at every single access attempt.Deepfake-Proof Identity: Why Hardware Authentication Is Immune to AI Impersonation
As AI-generated deepfakes evolve to mimic voices, faces, and even behavioral biometrics, traditional identity verification methods — including facial recognition, fingerprint scans, and voice authentication — are becoming dangerously unreliable. Identity is no longer about who you are. It’s about what you control offline.
AI Can Fake You — But Not Your NFC HSM
Today, attackers can execute biometric spoofing attacks using just a smartphone and generative AI tools.
In contrast, PassCypher NFC HSM and PassCypher HSM PGP store secure hardware keys that no remote attacker — not even one powered by AI — can forge, duplicate, or intercept.
Segmentation: The Ultimate Trust Factor
The PassCypher suite introduces segmented key authentication, meaning your identity is only accessible if you physically possess a specific hardware module and successfully authenticate locally via PIN, ID Phone, or a combination. No AI can simulate this chain of trust.
Zero Biometrics, Zero Risk
- No facial data stored or processed
- No fingerprint scans to forge or replay
- No voiceprint to capture or spoof
- Only encrypted secrets stored offline and validated via segmented trust
Hardware Beats AI
When authentication relies on possession, segmentation, and local control, AI impersonation becomes irrelevant. PassCypher doesn’t care what you look or sound like. It only reacts to what you hold — and what you’ve physically secured.
This model ensures that no biometric, behavioral, or system-level data can be faked, phished, or leaked. It’s a trustless-by-design authentication that doesn’t rely on third parties, devices, or assumptions — just physical cryptographic proof.
Resilient Identity: From AI-Resistant Profiles to Hardware-Backed Sovereignty
As generative AI evolves, the line between real and synthetic identities continues to blur. In this age of digital impersonation, resilient identity isn’t just about proving who you are — it’s about proving who you are not.
Why Traditional Identity Checks Fail
- Biometric spoofing: Deepfake engines now bypass facial and voice recognition systems.
- Document forgery: AI-powered scripts auto-generate fake ID cards, passports, and licenses.
- Credential stuffing: Even MFA can be bypassed using session tokens stolen by infostealers.
PassCypher NFC HSM: Enforcing Digital Authenticity at the Hardware Layer
PassCypher NFC HSM devices (Lite or Master editions) enforce identity verification using tamper-proof, air-gapped NFC modules. Each action — login, message decryption, or key sharing — requires physical presence and device trust pairing. In contrast to centralized identity providers, PassCypher works offline, eliminates impersonation risks, and gives users full control of authentication without disclosing biometric or personal data.
Strategic Takeaway
Resilient identity isn’t verified in the cloud — it’s sealed in hardware you control. As threat actors use AI to clone users, organizations must adopt cryptographic proof-of-personhood that cannot be simulated, spoofed, or replicated.
The Future of Authentication: Biometrics, AI and Their Limitations
As threats grow more sophisticated, the push toward biometric and AI-assisted identity verification systems is accelerating. From fingerprint readers to facial recognition and voice authentication, the world is transitioning toward “who you are” rather than “what you know.” But while biometrics offer convenience, they are not immune to compromise.
AI Can Fake You
Deepfake technologies now allow attackers to replicate biometric features using stolen media — including voice samples, images, and videos. In some cases, AI-generated fingerprints have been used to bypass sensor-based authentication systems. AI is no longer just a tool for defense. It’s a weapon in the arsenal of identity theft.
Biometrics = Permanent Risk
Unlike passwords, you can’t change your fingerprint or retina scan after a data breach. If a biometric identifier is stolen, it’s compromised forever — and the attacker can reuse it globally. That makes biometrics **inherently non-revocable**, raising legal and operational risks for long-term security strategies.
Offline Hardware vs. AI-Based Spoofing
PassCypher NFC HSM offers a radically different model: it keeps authentication completely offline and shields your identity from any AI-based spoofing attempt.
- It stores all cryptographic keys offline.
- It performs authentication locally via NFC or QR code.
- It avoids storing, transmitting, or requiring any biometric data — ever.
>Strategic Insight: The future of secure identity is not more AI — it’s less exposure. Air-gapped hardware offers what AI cannot: trust-by-design, not trust-by-illusion.
💡 For journalists, executives, developers and activists, staying under the radar may mean staying out of the biometric web entirely.
Credential leaks don’t just enable fraud — they serve as a gateway for **corporate espionage**. Stolen sessions from executives, developers, or sysadmins can offer deep access to intellectual property, internal tools, and strategic documents.Today’s digital identity is not just personal — it’s **privileged**.
Session Hijack = Invisible Espionage
A hijacked session token grants immediate access to internal dashboards, file repositories, and business communications — **without triggering login alerts**.
This makes session theft the preferred tactic for stealthy reconnaissance and sabotage.
</ux_text]
From Source Code to Insider IP Theft
When credentials from platforms like GitHub, Jira, Confluence or Slack are leaked, attackers can:
- Read source code and introduce backdoors
- Monitor R&D pipelines in stealth mode
- Access procurement and negotiation files
- Sabotage infrastructure (e.g., deleting repositories or staging ransomware)
Case in Point: Silent Access, Maximum Damage
In 2024, multiple leaks led to exfiltration of sensitive data from aerospace, energy, and pharmaceutical sectors — not via malware, but through legitimate session reuse by unauthorized actors. By the time anomalies were noticed, the attackers had already left.
> Strategic Insight: The greatest threat is not breach but invisibility. Session hijacks allow adversaries to operate as if they were insiders — with zero friction.
Advanced persistent threats don’t hack your system. They **borrow your login** — and act as if they built it.
The 2025 identity leak doesn’t just raise cybersecurity concerns — it triggers **legal and compliance minefields**. Organizations impacted by session hijacks and credential resale now face scrutiny under global data protection frameworks.
GDPR, NIS2, and Beyond
Stolen sessions qualify as **personal data breaches**. Under laws like:
- GDPR (EU): Companies must report identity-based breaches within 72 hours.
- NIS2 (EU): Operators of essential services face stricter security obligations.
- CCPA (California): Failure to secure digital identity data can trigger lawsuits.
Failure to comply may result in **multi-million euro penalties** and mandatory audits.
Employer Liability: A Growing Vector
When attackers hijack an employee’s session to commit fraud or espionage, they shift the legal burden onto the company — forcing it to assume responsibility for:
- Failure to implement sufficient identity protection
- Negligence in breach containment
- Insufficient logging and detection
This risk is especially high for sectors with high-value intellectual property (finance, pharma, aerospace).
Compliance Requires More Than Policy
Legal experts now recommend:
- Hardware-based identity proofing for high-privilege roles
- Real-time session traceability with hardware tokens
- Decentralized identity management — to reduce cloud trust exposure
Strategic Insight: Laws were built around passwords and systems. The future of compliance is built around sessions and people.
The next compliance wave isn’t about passwords. It’s about proving you can detect, revoke, and replace stolen digital identities.
Final Strategic Insight – A New Identity Paradigm
The Fortinet mega-leak is not just another breach — it’s a **paradigm shift in the mechanics of digital trust**. We no longer face isolated password leaks. We face the full industrialization of identity emulation, driven by real-time session resale, hardware fingerprinting, and AI-powered impersonation. This demands a new model.
Decentralization + Hardware + Anonymity
The future of identity protection starts when users reclaim control. We must move identity offline, anchor it in tamper-proof hardware, and decentralize it entirely. In this model, users don’t just get “authenticated” — they carry their own cryptographic shield by default. This model:
- Rejects dependence on cloud trust or biometric central servers
- Prevents identity theft at the root: session-level interception
- Empowers sovereign control of credentials and private keys
From Defense to Deterrence
Legacy MFA and password managers cannot scale against AI-enhanced identity fraud. Instead, a shift is needed:
- From credential storage to session immunity
- From cloud-based authentication to air-gapped, tamper-proof hardware
- From password rotation to identity isolation by design
Users must adopt hardware-segmented identity as the only viable long-term strategy — one they control directly, one that remains invisible to malware, and one that even AI cannot forge.
Rebuilding Digital Trust in the Age of AI-Driven Identity Fraud
The leak of over 16 billion valid credentials doesn’t just reveal the failure of perimeter defenses — it confirms something deeper: the collapse of implicit digital trust.
Today, cybercriminals exploit generative AI to synthesize voices, faces, and deepfake videos in real time, using nothing more than data stolen from infostealer logs. In this new reality, a password no longer proves identity. A token means little. Even a voice over the phone could be fake.
To counter this, we must shift the burden of proof back to the individual. Only the user — physically present, cryptographically segmented, and offline — can serve as the unforgeable anchor of trust.
Solutions like PassCypher HSM PGP and PassCypher NFC HSM already operate on this principle. They transform users from the weakest link into the root of trust, removing the need to delegate authentication to vulnerable digital infrastructure.
But technology alone isn’t enough. This transformation begins by radically shifting our mindset: we must stop hosting identity in the cloud, syncing it across devices, or delegating it to third parties — and instead, start making it personal, portable, and verifiable by design.
Until we embrace this model, even the most complex credentials remain exploitable.
Now is not the time to apply security patches. Now is the time to reinvent authentication from the ground up.
Executive Summary
Update 22 july In 2025 : WeTransfer attempted to include a clause in its Terms of Service allowing the use of uploaded user files for AI model training. Withdrawn after public backlash, this clause unveiled a deeper dynamic: file transfers are becoming mechanisms of cognitive capture. Centralized platforms increasingly exploit transmitted content as algorithmic fuel—without informed consent.
Strategic Navigation Index
- Executive Summary
- Clause 6.3 – Legalized Appropriation
- CGU Comparison
- Geopolitical Reactions
- Sovereignty Acceleration – July 2025
- Global File Transfer Landscape
- Timeline of Algorithmic Drift
- Legal Semantics of ToS
- Sensitive File Typologies
- Cognitive AI Capture Statistics
- Algorithmic Contamination Cycle
- Sovereign Countermeasures
Key insights include:
Digital file transfers are no longer neutral mechanisms; they are increasingly transformed into algorithmic extraction vectors. Terms of Service, often written in opaque legalese, have evolved into covert infrastructures for AI training—turning user data into raw cognitive matter. Meanwhile, regulatory efforts struggle to keep pace, continually outflanked by the extraterritorial reach of foreign jurisdictions. In response, the European Union’s recent strategic initiatives—such as EuroStack and the proposed Buy European Act—signal a profound realignment of digital sovereignty. Yet, platform behavior diverges ever more from user expectations, and it becomes clear that only technical measures such as local encryption and isolated key custody can offer meaningful resistance to these systemic risks.
About the Author – Jacques Gascuel is the founder of Freemindtronic Andorra and inventor of patented sovereign technologies for serverless encryption. He operates in critical environments requiring offline, tamper-proof, auditable communications.
Clause 6.3 – Legalized Appropriation
WeTransfer’s 2025 attempt to impose a perpetual, transferable, sublicensable license on uploaded user files for AI purposes exposed the unchecked power platforms hold over digital content.
This move marked a watershed in the perception of user agreements. While the retraction of the clause followed intense public backlash, it revealed a broader strategy among digital service providers to legalize the repurposing of cognitive material for machine learning. Clause 6.3 was not a simple legal footnote—it was a blueprint for algorithmic appropriation masked under standard contract language.
“Worldwide, perpetual, transferable, sublicensable license for AI training and development.” – Extract from Clause 6.3 (Withdrawn)
Such phrasing illustrates the shift from service facilitation to cognitive extraction. By embedding rights for AI development, WeTransfer aligned with a growing trend in the tech industry: treating data not as a user right, but as a training resource. The episode served as a warning and highlighted the necessity for robust countermeasures, transparency standards, and sovereign alternatives that place user control above algorithmic interests.
CGU Comparison
A focused comparison of leading platforms reveals the systemic ambiguity and power imbalance in Terms of Service related to AI usage and data rights.
| Platform | Explicit AI Usage | Transferable License | Opt-Out Available |
|---|---|---|---|
| WeTransfer | Yes (Withdrawn) | Yes, perpetual | No |
| Dropbox | Yes via third parties | Yes, partial | Unclear |
| Google Drive | Algorithmic processing | Yes, functional | No |
Geopolitical Reactions
Sovereign concerns over AI data capture have sparked divergent responses across jurisdictions, highlighting gaps in enforcement and regulatory intent.
- European Union: AI Act passed in 2024, but lacks enforceable civil liability for AI misuse. Push toward EuroStack, Buy European Act, NIS2, and LPM reforms intensifies strategic sovereignty.
- United States: Pro-innovation stance. No federal constraints. Stargate program funds $500B in AI R&D. Cloud Act remains globally enforceable.
- UNESCO / United Nations: Ethical recommendations since 2021, yet no binding international legal framework.
Case Study: Microsoft under French Senate Scrutiny
On June 10, 2025, before the French Senate Commission (led by Simon Uzenat), Anton Carniaux (Director of Public and Legal Affairs, Microsoft France) testified under oath that Microsoft cannot guarantee French data hosted in the EU would be shielded from U.S. intelligence requests.
Pierre Lagarde (Microsoft Public Sector CTO) confirmed that since January 2025, while data is physically retained in the EU, the U.S. Cloud Act supersedes local encryption or contractual frameworks.
– Microsoft admits no guarantee data stays out of U.S. reach
– Cloud Act overrides encryption and contracts
– Transparency reports omit classified requests
Sovereignty Acceleration – July 2025
July 2025 brought a turning point in European digital sovereignty, with official declarations, industrial strategies, and new pressure on U.S. hyperscalers’ extraterritorial influence.
European Union Strategic Shift
- July 21 – Financial Times: EU proposes “Buy European Act” and EuroStack (€300B)
- New Tech Sovereignty Commissioner appointed; exclusion proposed for Amazon, Google, Microsoft from critical infrastructure contracts
Microsoft Senate Testimony (June 10 & July 21, 2025)
- Anton Carniaux, Microsoft France, acknowledges inability to block U.S. Cloud Act data access—even within EU
- Brussels Signal: France accused of “digital suicide” by outsourcing sensitive infrastructure to U.S. clouds
Microsoft Sovereign Cloud Response
- June 16 – Launch of “Microsoft Sovereign Public Cloud” with local controls, Bleu (Orange-Capgemini)
- KuppingerCole: positive move, but concerns over proprietary dependencies remain
– Cloud Act still overrides EU contractual frameworks
– Transparency reports exclude classified requests
– Strategic divergence between EU policy and U.S. platforms deepens
Global File Transfer Landscape
Comparison of major file transfer services reveals systemic vulnerabilities—ranging from unclear AI clauses to lack of encryption and non-European server locations.
| Service | Country | AI Clause / Risk | Reference / Link |
|---|---|---|---|
| TransferNow | 🇫🇷 France | Indirect algorithmic processing authorized | Terms PDF |
| Smash | 🇫🇷 France | Amazon S3 storage, potential AI processing | Official site |
| SwissTransfer | 🇨🇭 Switzerland | No AI, servers located in CH | Official site |
| Filemail | 🇳🇴 Norway | AI in Pro version, automated tracking | ToS |
| pCloud | 🇨🇭 Switzerland | Optional client-side encryption | Terms |
| Icedrive | 🇬🇧 UK | AI in enterprise version | GDPR |
| TeraBox | 🇯🇵 Japan | Native AI, tracking, advertising | Help Center |
| Zoho WorkDrive | 🇮🇳 India | OCR AI, auto-analysis | Under review |
| Send Anywhere | 🇰🇷 South Korea | Unclear risks, AI suggestions | Pending |
| BlueFiles | 🇫🇷 France | ANSSI-certified sovereignty | Pending |
Timeline of Algorithmic Drift
Tracing the evolution of AI file transfer extraction practices through key milestones, from early user content harvesting to the institutionalization of algorithmic appropriation.
The rise of AI file transfer extraction has not occurred overnight. It reflects a decade-long erosion of the boundary between user ownership and platform processing rights. In 2011, Facebook quietly began training algorithms on user-generated content without explicit consent, under the guise of service improvement. This pattern intensified in 2023 when Zoom inserted controversial clauses enabling the use of video streams for generative AI development.
By 2024, a wave of subtle yet systemic changes reshaped the Terms of Service of major cloud providers—embedding AI training clauses into legal fine print. These changes culminated in the 2025 WeTransfer debacle, where the overt Clause 6.3 aimed to codify perpetual AI training rights over all uploaded data, effectively legalizing cognitive content extraction at scale.
This drift illustrates a deeper structural shift: platforms no longer see uploaded files as inert data but as dynamic cognitive capital to be mined, modeled, and monetized. The user’s agency vanishes behind opaque contracts, while algorithmic models extract knowledge that cannot be retracted or traced.
Legal Semantics of ToS
Decoding how the legal language in Terms of Service enables hidden forms of AI file transfer extraction, revealing structural loopholes and algorithmic license laundering.
The Terms of Service (ToS) of digital platforms have become vehicles of silent appropriation. Their language—crafted for maximal legal elasticity—shields platforms from scrutiny while unlocking unprecedented access to user content. Phrases like “improving services” or “enhancing performance” conceal layers of cognitive harvesting by AI systems.
When a clause refers to a “perpetual, worldwide license,” it often translates to long-term rights of exploitation regardless of jurisdiction. The term “sublicensable” allows redistribution to third-party entities, including opaque AI training consortia. Meanwhile, catch-all terms like “content you provide” encompass everything from raw files to metadata, thus legalizing broad extraction pipelines.
This semantic engineering forms the linguistic backbone of AI file transfer extraction. It bypasses informed consent, turning each uploaded document into a potential data vector—where legality is retrofitted to platform ambitions. The visible contract diverges sharply from the underlying operational reality, revealing a growing rift between user expectations and AI data regimes.
Sensitive File Typologies
AI file transfer extraction does not treat all data equally. Administrative, biometric, professional, and judicial files are disproportionately targeted—each representing unique vectors of algorithmic appropriation.
Not all files carry the same cognitive weight. In the context of AI file transfer extraction, typology dictates vulnerability. Administrative files—containing national ID scans, tax records, or electoral data—offer structured, standardized templates ideal for training entity recognition systems. Similarly, biometric files such as passport scans or fingerprint data are exploited for facial recognition model reinforcement and biometric signature prediction.
Meanwhile, professional and contractual documents often include internal memos, business strategies, and technical schematics—unintentionally fueling AI agents trained on corporate decision-making and supply chain optimization. Judicial documents, ranging from affidavits to forensic reports, present a rare density of factual, narrative, and procedural data—perfectly suited for training legal decision engines.
Concretely, a leaked internal arbitration file from a multinational energy firm was reportedly used in 2024 to refine conflict resolution modules in a closed-source LLM deployed by a U.S. defense contractor. Elsewhere, a biometric file exfiltrated from a compromised passport office—later found in a 2025 training dataset for a commercial facial recognition suite—highlights the unintended consequences of lax file transfer governance.
– Pattern: Judicial files disproportionately present in anonymized training datasets
– Trend: Rising correlation between enterprise document formats and AI-captured syntax
– Vector: Embedded metadata used to refine prompt injection vulnerabilities
– Deploy DataShielder NFC HSM to localize file access with zero exposure
– Use PassCypher for contractual document integrity via hash verification
– Strip metadata before file transfers using sovereign scrubbers
Cognitive AI Capture Statistics
AI file capture now represents over 24% of datasets used for commercial model training. Sensitive sectors such as energy, healthcare, and legal services are disproportionately impacted.
According to the 2025 AI Dataset Integrity Consortium, approximately 1.4 billion documents extracted via public and semi-private channels were incorporated into model pretraining pipelines since 2023. Within these, legal records account for 16%, while biometric files comprise 11%. The healthcare sector—long presumed protected under HIPAA and GDPR—contributes nearly 19% of identifiable documents, largely through indirect metadata trails.
In practical terms, models trained on these datasets demonstrate elevated performance in tasks related to compliance prediction, medical diagnostics, and even behavioral inference. The economic value of such datasets is surging, with a recent valuation by QuantMinds placing them at €37.5 billion for 2025 alone.
Sector-specific analysis reveals that critical infrastructure sectors are not only data-rich but also structurally exposed: shared drives, collaborative platforms, and cross-border storage routes remain the most exploited vectors. As AI accelerates, the strategic imperative to regulate file-level provenance becomes a national security concern.
Algorithmic Contamination Cycle
Once ingested, contaminated files do not remain passive. They recursively alter the behavior of downstream AI models—embedding compromised logic into subsequent algorithmic layers.
The act of file ingestion by AI systems is not a neutral event. When a compromised or biased file enters a training dataset, it triggers a cascade: extracted knowledge reshapes not just that model’s predictions, but also its influence over future derivative models. This recursive pollution—a phenomenon we term the algorithmic contamination cycle—is now structurally embedded into most large-scale model pipelines.
Consider the case of predictive compliance engines used in fintech. A single misinterpreted regulatory memo, once embedded in pretraining, can result in systematic overflagging or underreporting—errors that multiply across integrations. The contamination spreads from LLMs to API endpoints, to user interfaces, and eventually to institutional decision-making.
Worse, this cycle resists remediation. Once a file has altered a model’s parameters, its influence is not easily extractable. Re-training or purging data offers no guarantee of cognitive rollback. Instead, AI architectures become epistemologically infected—reproducing the contamination across updates, patches, and forked deployments.
– Vector: Unmonitored AI pipelines reusing contaminated weights
– Pattern: Cascade of anomalies across decision support systems
– Risk: Institutional reliance on non-auditable model layers
– Isolate model training from operational environments
– Employ auditable training datasets using Freemindtronic-sealed archives
– Prevent contamination via air-gapped update mechanisms
Sovereign Countermeasures
From Legal Clauses to Operational Realities
Most mitigation attempts against cognitive AI capture remain declarative: consent forms, platform pledges, or regional hosting promises. These approaches fail under adversarial scrutiny. In contrast, Freemindtronic’s sovereign architecture introduces operational irreversibility: the data is cryptographically sealed, physically isolated, and strategically fragmented across user-controlled environments.
Discrepancies Between Clauses and Actual Exploitation
Recent examples underscore this fragility. In 2025, WeTransfer attempted to introduce a clause enabling AI training on uploaded files. Though officially retracted, the very proposal confirmed how CGUs can be weaponized as silent appropriation instruments. Similarly, SoundCloud’s terms in early 2024 briefly allowed uploaded content to be used for AI development, before the platform clarified its scope under pressure from the creator community.
Timeline: The WeTransfer Clause 6.3 Incident
- June 2025: WeTransfer updates Clause 6.3 to include rights “including to improve performance of machine learning models” — set to take effect on August 8, 2025.
- July 14, 2025: The clause is flagged publicly on Reddit (source), triggering concern across creative communities.
- July 15, 2025: WeTransfer issues a public clarification that it “does not and will not use files for AI training” (official statement).
- July 16, 2025: Revised ToS removes the AI clause entirely (coverage).
First alarm was raised by professionals in Reddit’s r/editors thread, quickly echoed by Ashley Lynch and other creatives on X and LinkedIn. This incident highlights the time-lag between clause deployment and retraction, and the necessity for vigilant watchdog networks.
Such episodes highlight a critical dynamic: CGUs operate in the realm of legal possibility, but their enforcement—or the lack thereof—remains opaque. Unless independently audited, there is no verifiable mechanism proving that a clause is not operationalized. As whistleblowers and open-source investigators gain traction, platforms are pressured to retract or justify vague clauses. However, between declared terms and algorithmic pipelines, a sovereignty vacuum persists.
Devices such as DataShielder NFC HSM render files unreadable unless decrypted via local authentication, without server mediation or telemetry leakage. Meanwhile, PassCypher validates document provenance and integrity offline, resisting both exfiltration and prompt injection risks.
These tools do not simply protect—they prevent transformation. Without access to raw cleartext or embedded metadata, AI systems cannot reconfigure input into modelable vectors. The result is strategic opacity: a file exists, but remains invisible to cognitive systems. Sovereignty is no longer abstract; it becomes executable.
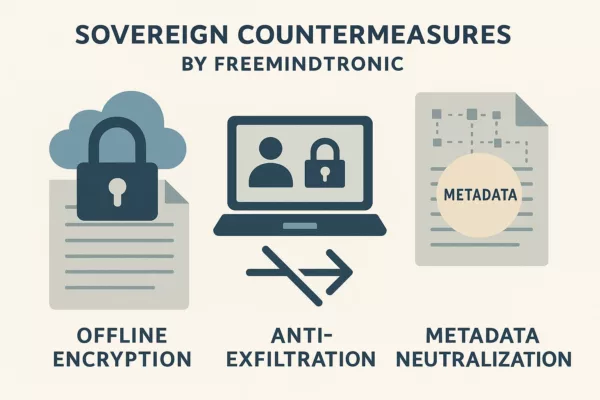
🔗 Related to:
– Chronicle: The Rise of AI-Assisted Phishing
– Note: Exploiting Offline NFC Vaults for Counter-AI Defense
– Publication: Securing Supply Chains Through Sovereign Cryptography
⮞ Sovereign Use Case | Resilience with Freemindtronic
In a cross-border legal proceeding involving sensitive EU arbitration documents, Freemindtronic’s DataShielder NFC HSM was deployed to encrypt and locally isolate the files. This measure thwarted exfiltration attempts even amid partial system compromise—demonstrating operational sovereignty and algorithmic resistance in practice.
⛏ What We Didn’t Cover
While this Chronicle dissected the structural vectors and sovereign responses to AI file transfer extraction, adjacent vectors such as voiceprint leakage, encrypted traffic telemetry, and generative prompt recycling remain underexplored. These domains will be treated in future briefings.
🔎 Weak Signals:
– Multiple platforms (e.g., SoundCloud, WeTransfer) have introduced and then revised AI-related clauses in their Terms of Service following public pressure.
– The absence of independent audits or technical proofs prevents any reliable verification of actual AI clause enforcement.
– Whistleblowers, investigative journalists, and open-source monitors remain the only safeguards against undeclared algorithmic data harvesting.
– This reinforces the necessity of sovereign technical countermeasures over declarative trust models.
La Llei andorrana sobre el doble ús s’inscriu en una reforma estratègica del control de les exportacions. Davant les noves amenaces híbrides, es crea una base jurídica centrada en el dret duaner, la sobirania tecnològica i l’alineament parcial amb la UE. Identificació EORI, compliment UE i regulació criptogràfica esdevenen pilars d’aquesta seguretat reglamentària, convertint aquesta anàlisi en una referència en català per al control estratègic de la tecnologia.
El control de les exportacions de béns de doble ús esdevé un pilar de la sobirania tecnològica andorrana. Davant la complexitat creixent de les cadenes de valor, la criptologia exportada i les regulacions extraterritorials, Andorra anticipa aquests desafiaments mitjançant una reforma estratègica del seu marc duaner i reglamentari. Aquesta anàlisi jurídica especialitzada explora: ✔ Com Andorra articula el compliment UE i al mateix temps la autonomia sobirana a través de la Llei 10/2025.
Sobre l’autor — Inventor de tecnologies de doble ús i fundador de Freemindtronic Andorra, Jacques Gascuel desenvolupa solucions de protecció de dades i contraespionatge amb vocació civil i militar. Analitza aquí els aspectes estratègics de la llei andorrana sobre el doble ús des d’una perspectiva «privacy by design» conforme a les exigències reglamentàries internacionals.
El Consell General d’Andorra va aprovar la Llei 10/2025 el 13 de maig de 2025, publicada posteriorment al BOPA núm. 68 del 4 de juny de 2025. Aquesta llei suposa un punt d’inflexió clau en l’evolució del dret duaner andorrà, ja que busca l’alineació de la legislació nacional amb el Codi Duaner de la Unió Europea, segons estableix el Reglament (UE) núm. 952/2013 de 9 d’octubre de 2013 (EUR-Lex – CELEX:32013R0952). En substitució de la Llei 17/2020, aquesta reforma introdueix una arquitectura moderna per a la regulació duanera. Consta de 296 articles repartits en nou títols. Concretament, facilita els tràmits duaners, impulsa la digitalització de les operacions i, sobretot, estableix un marc jurídic sòlid per al control dels fluxos sensibles, especialment pel que fa als béns de doble ús. Per a més informació oficial, els textos són consultables aquí: Així, aquesta nova legislació posiciona Andorra en una lògica de compliment reforçat i integració reguladora progressiva amb la Unió Europea. Abans d’abordar les disposicions específiques de la Llei andorrana de doble ús, és útil revisar els punts estructurants del nou Codi de Duana, que reforcen l’eficiència i la transparència del sistema duaner andorrà. El Codi redefineix conceptes clau per millorar la seguretat jurídica: Continuem l’anàlisi de la Llei andorrana de doble ús examinant ara l’estructura financera i procedimental que regula els fluxos duaners. Aquest pilar normatiu, lluny de ser secundari, assegura la seguretat dels ingressos públics i aporta previsibilitat i fiabilitat als operadors econòmics. Aquesta part del nou Codi estableix un triplet coherent: gestió del deute duaner, implementació de garanties i disseny d’autoritzacions administratives. Aquests elements asseguren una governança rigorosa dels fluxos comercials de risc, especialment els relacionats amb tecnologies sensibles. La Llei 10/2025 introdueix un mecanisme coherent de càlcul, pagament i reemborsament dels drets de duana. A més, estableix normes precises sobre el deute duaner i exigeix, en determinats casos, garanties financeres dels operadors. Aquesta estructuració pretén establir una logística més fluïda tot mantenint un alt nivell de supervisió. La nova llei estableix un sistema estructurat per a les sol·licituds, tramitació i emissió d’autoritzacions duaneres, fonamental per garantir la seguretat jurídica dels operadors econòmics. L’administració duanera pot atorgar autoritzacions generals o específiques segons el tipus d’operació i el nivell de risc associat. Un registre digital centralitzat recull totes les autoritzacions emeses, assegurant-ne la traçabilitat i verificabilitat. El codi imposa un termini màxim de resposta per evitar bloquejos administratius. Ara entrem al nucli del dispositiu legal relatiu als béns de doble ús, un aspecte sensible de la Llei 10/2025. Text de referència: Reglament (UE) 2021/821 Aquesta disposició va entrar en vigor immediatament després de la publicació de la llei, el 5 de juny de 2025, segons la seva disposició final. El Decret 207/2025, publicat el 12 de juny de 2025, especifica els tràmits associats a l’autorització. Text oficial: BOPA Andorra – GR_2025_06_11_13_27_27 Aquest text preveu que: Abans fins i tot de l’entrada en vigor de la Llei andorrana de doble ús, Freemindtronic ja havia iniciat, des de 2021, una acció exemplar. Avançant-se a les obligacions reguladores, l’empresa va estructurar els seus fluxos comercials sensibles dins un marc ètic i jurídic rigorós. Freemindtronic va proposar una Carta Ètica, acompanyada d’una documentació formalitzada des de 2022, per regular l’ús i exportació de les seves tecnologies criptogràfiques sensibles. Mesures concretes: Per garantir una conformitat jurídica total en l’exportació de tecnologies sensibles, Freemindtronic també s’ha recolzat en els requisits francesos pel que fa al control dels mitjans de criptologia. Els expedients s’han d’enviar a: El formulari principal, Annexe I, és disponible aquí: formulari PDF. Aquest document inclou: Gràcies a aquest rigor, Freemindtronic ha pogut exportar legalment els mòduls DataShielder NFC HSM Defense, amb la validació del seu soci exclusiu AMG Pro. Mentre l’aplicació de la Llei andorrana sobre els béns de doble ús tot just comenca, els actors públics i privats poden tenir un paper estratègic en la difusió de bones pràctiques. Aquesta dinàmica representa una gran oportunitat per estructurar un ecosistema virtuós d’acompanyament normatiu i de sensibilització dels operadors econòmics. En particular, Andorra disposa d’un potencial de co-construcció entre institucions i empreses innovadores, amb respecte a les seves prerrogatives respectives. En aquest context, esdevé pertinent desenvolupar eines d’ajuda per a la comprensió de la regulació i oferir informació clara i estructurada als professionals implicats. La regulació andorrana sobre els béns de doble ús, tot i estar publicada al BOPA, pateix actualment una manca de documentació aplicada. Encara no s’han publicat punts d’informació especialitzats, tutorials administratius o guies de conformitat per part de les institucions públiques. Basant-se en la seva experiència reguladora, Freemindtronic ha iniciat la redacció d’una guia pràctica de conformitat, co-marcable amb entitats com la Duana Andorrana (enllaç oficial). Aquesta iniciativa té per objectiu: Paral·lelament, Freemindtronic ha publicat diversos recursos accessibles en línia sobre la regulació internacional dels productes de doble ús, en particular: Aquests recursos es presenten com a complements informatius fiables als textos oficials i contribueixen a la implementació de la Llei andorrana sobre els béns de doble ús. El règim andorrà de control de les exportacions de doble ús forma part d’un marc regulador global, on cada jurisdicció imposa estàndards específics per a la regulació i el seguiment dels fluxos comercials sensibles. A causa del seu acord duaner amb la Unió Europea, Andorra es beneficia de peculiaritats que influeixen en el seu enfocament de les exportacions i les exempcions aplicables. No obstant això, la normativa vigent a les grans potències econòmiques – la Unió Europea, els Estats Units, el Regne Unit, Suïssa, els països de la Commonwealth – influeix en les obligacions dels exportadors andorrans. Aquesta dinàmica es reflecteix en: Per tal de comparar aquestes regulacions i avaluar el seu impacte en el comerç intracomunitari, a la taula següent es presenta un resum de la normativa internacional, les seves dates d’entrada en vigor i les seves implicacions per a Andorra. Marc normatiu de les principals jurisdiccions Efecte extraterritorial i singularitat andorrana L’ efecte extraterritorial de la normativa nord-americana (AEOI) i europea (Reglament UE 2021/821) afecta la gestió de les exportacions d’Andorra. No obstant això, gràcies a l’Acord Duaner de 1990, Andorra es beneficia d’una unió duanera parcial amb la UE, que permet la lliure circulació de productes industrials (capítols 25 a 97 de l’aranzel duaner) un cop introduïts a la cadena europea, sense tràmits addicionals. Així, una anàlisi en profunditat suggereix que és possible exportar productes de doble ús d’Andorra a la Unió Europea sense autorització prèvia, subjecte a les condicions següents: Aquesta peculiaritat normativa diferencia Andorra dels Estats membres de la UE, que han d’aplicar estrictes règims de control de les exportacions. No obstant això, encara cal una major vigilància, especialment pel que fa als desenvolupaments legislatius internacionals que podrien reforçar els requisits duaners. La promulgació de la Llei andorrana sobre els béns de doble ús (Llei 10/2025) marca una evolució significativa dins de l’arquitectura normativa del país, en establir les primeres bases per a un control d’exportació reglamentat. Aquesta secció analitza l’abast material, els actors institucionals implicats i els efectes concrets per als operadors econòmics, en un context d’integració progressiva al marc europeu. El Reglament (UE) 2021/821 permet, en general, la lliure circulació dels béns de doble ús dins del mercat interior de la UE, excepte per a productes especialment sensibles inclosos a l’Annex IV. Això implica que, un cop un bé forma part de l’àmbit de la UE, la seva reexportació cap a un altre Estat membre no requereix autorització addicional, llevat de casos particulars. L’Acord del 1990 estableix una unió duanera parcial entre el Principat d’Andorra i la Unió Europea, que cobreix els capítols 25 a 97 del Tarifa Duaner Comuna. Aquest acord permet la lliure circulació de mercaderies, suprimint barreres aranzelàries per als productes concernits. Segons les anàlisis del CEPS, els productes prèviament importats a Andorra des d’un Estat tercer i que disposin d’un número EORI poden circular lliurement per la UE sense formalitats addicionals, excepte els productes del tabac, que resten sotmesos a regulacions específiques. Una conclusió a verificar és si, sobre la base de l’acord duaner i el reglament europeu, esdevé possible exportar béns de doble ús des d’Andorra cap a la UE sense autorització prèvia andorrana, sota certes condicions: Si aquestes condicions es compleixen, representaria una singularitat notable en relació amb les regulacions dels Estats membres de la UE. Recursos oficials: La reforma duanera impulsada per la Llei 10/2025 i el seu decret d’aplicació proporciona als industrials andorrans condicions operatives estratègiques en un entorn altament regulat a escala internacional.. En aquest sentit, diversos dispositius criptogràfics “fabricats a Andorra” de la gamma DataShielder NFC HSM o PGP HSM, malgrat estar classificats dins de la categoria 5, part 2 del Reglament (UE) 2021/821, no estan inclosos a l’Annex IV i per tant es beneficien plenament de l’exempció europea contemplada per aquesta nova normativa andorrana: Impactes concrets: A tall d’il·lustració, es presenten dos models de documents inspirats en les annexes del Decret 207/2025 per facilitar l’adaptació immediata. DESTINATARI: Data, lloc, segell i signatura DESTINATARI: Em comprometo a: Data, lloc, signatura, segell, funció del signant Tot i que Andorra ha reforçat recentment el seu marc legislatiu amb la Llei andorrana sobre els béns de doble ús, en particular a través de l’article 267, paràgraf 3, lletra f de la Llei 10/2025, persisteix una zona grisa preocupant pel que fa a sancions i embargaments. Aquesta llei defineix les condicions d’autorització d’exportació per als béns sensibles criptogràfics, però no preveu cap mecanisme de control a posteriori ni dispositiu repressiu autònom en cas d’incompliment de les seves obligacions. A les jurisdiccions europees i nord-americanes, aquesta mancança donaria lloc a un sistema detallat tant administratiu com penal. Per exemple, el Reglament (UE) 2021/821 estableix procediments clars per a la repressió d’infraccions, mentre que els Estats Units disposen d’un arsenal normatiu sòlid a través de l’EAR i de les sancions de l’OFAC. A Suïssa i a França, l’exportació no autoritzada de tecnologies de doble ús és objecte de sancions severes, inclosa la responsabilitat penal dels directius. A l’inrevés, el marc jurídic exportador andorrà encara presenta mancances estructurals quant a la resposta davant infraccions. Aquesta absència d’un règim sancionador explícit obre un buit normatiu que pot exposar el país a riscos d’abús i posar en qüestió la seva cooperació internacional, especialment en el marc del Reglament europeu esmentat. Davant les mancances detectades en el règim actual, sembla oportú consolidar progressivament una governança nacional andorrana del control d’exportació. Aquesta podria inspirar-se útilment en els dispositius implantats a França i Espanya, sense fer una transposició mecànica, sinó amb respecte per la sobirania jurídica d’Andorra. En aquest context, Andorra podria instaurar un Comitè intergovernamental andorrà del doble ús, integrat per: Aquest comitè tindria el mandat d’elaborar una doctrina sobirana d’exportació, adoptar un decret d’aplicació autònom que defineixi sancions i controls, i coordinar la cooperació amb els socis europeus. Aquesta inspiració té una legitimació especial, ja que els dos estats de referència – França i Espanya – són també coprínceps constitucionals d’Andorra. La seva influència institucional i arrelament històric confereixen a les seves pràctiques un estatus de referència compatible amb l’ordre jurídic andorrà. A la llum de les disposicions introduïdes per la Llei andorrana sobre els béns de doble ús i el seu decret d’aplicació, sembla evident que el legislador andorrà ha fet un pas estructurant cap a una convergència amb els estàndards europeus, tot preservant l’especificitat jurídica del Principat d’Andorra. L’articulació entre el dret intern, el dret de la Unió Europea i els règims extraterritorials internacionals (US EAR, UK, Wassenaar) exigeix a partir d’ara una vigilància constant per part dels operadors econòmics, a fi de garantir la conformitat dinàmica de les seves pràctiques exportadores. En aquest sentit, la trajectòria anticipadora i ètica de Freemindtronic — il·lustrada per actuacions documentades i una doctrina de conformitat consolidada — constitueix un model transferible. Demostra que la iniciativa privada pot contribuir útilment a la construcció d’un règim jurídic coherent, en benefici tant de l’Estat com dels actors industrials. Correspon ara a les autoritats andorranes competents continuar amb l’esforç d’acompanyament normatiu, en particular mitjançant la producció de doctrines administratives, guies oficials i la posada en marxa de formacions i finestretes especialitzades. En paral·lel, les empreses han d’institucionalitzar una vigilància reguladora integrada, articulada amb matrius d’impacte extraterritorial, per fer de la conformitat exportadora un veritable eix estratègic. Així, la implementació efectiva i fluida d’aquest règim es fonamenta en una sinergia entre dret, tecnologia i responsabilitat compartida. Traça els contorns d’un nou pacte normatiu andorrà basat en la transparència, la seguretat jurídica i l’ambició d’un model econòmic obert però rigorosament regulat. La reforma del Codi de Duana mitjançant la Llei 10/2025, del 13 de maig, juntament amb el Reglament d’execució sobre l’exportació de béns de doble ús (Decret 207/2025), ofereix una oportunitat inèdita per al Principat d’Andorra de construir una doctrina pròpia en matèria de control estratègic, alineada però diferenciada dels règims europeus (UE), francès, espanyol i suís. França: el règim francès es fonamenta en el Codi de la defensa, l’ordre del 8 de juliol de 2015 per a les AIMG i l’ordre del 2 de juny de 2014 per a les LEMG, combinats amb decisions puntuals de suspensió de derogacions. Distingix rigorosament entre materials classificats (cat. ML) i béns de doble ús (cat. DU), i imposa procediments complexos i centralitzats, incloses les importacions temporals de materials amb finalitats d’exhibició. Espanya: sota l’empara del Reial decret 679/2014, Espanya també aplica el Reglament (UE) 2021/821, amb una interpretació administrativa sovint conservadora. La classificació en matèria de criptologia o de components electrònics és sistemàtica, i l’exportació cap a països tercers (fora de la UE) està subjecta a un seguiment reforçat. Suïssa: tot i no ser membre de la UE, Suïssa adopta una política d’equivalència basada en la Güterkontrollverordnung (GKV) i l’Ordenança sobre el material de guerra (OMG). L’autoritat SECO supervisa un règim fluid però rigorós, amb èmfasi en la transparència comercial i la conformitat extraterritorial. Unió Europea: el Reglament (UE) 2021/821 (versió consolidada) estableix una base harmonitzada fonamentada en les llistes de control, els criteris de seguretat internacional i l’anàlisi de risc per país. Reptes específics per a Andorra: cap a una doctrina nacional del doble ús La Carta Ètica entre Freemindtronic i el Govern d’Andorra prefigura aquesta doctrina, integrant els principis de transparència, no proliferació, desenvolupament sostenible i sobirania jurídica. Constitueix una base rellevant per estendre la regulació a segments tecnològics emergents, com ara sistemes d’autenticació distribuïda, mitjans criptològics d’ús ciberdefensiu, o tecnologies fonamentades en ADN digital. La UE preveu ampliar l’àmbit d’aplicació del règim de doble ús a tecnologies crítiques com la intel·ligència artificial, la ciberseguretat i la cadena de blocs, en el marc de l’estratègia de seguretat econòmica europea (Comunicació COM(2023) 249 final). Andorra haurà d’anticipar aquests moviments per mantenir l’equivalència reguladora. La dinàmica actual impulsa el país a estructurar una capacitat nacional de doctrina, supervisió i innovació reguladora sobre el doble ús, incloent:
Anàlisi jurídica profunda de la llei andorrana de doble ús Llei 10/2025 del Codi de Duana d’Andorra
✔ Per què el règim EORI i l’acord duaner Andorra–UE ofereixen un avantatge per a les exportacions estratègiques.
✔ Com estructurar una doctrina andorrana del doble ús, en coherència amb el Règim (UE) 2021/821.
✔ Quins són els futurs reptes: IA, ciberseguretat hardware, sobirania de cadenes crítiques.1. Anàlisi estratègica de la Llei andorrana de doble ús: reforma del Codi de Duana 2025
2. Elements estructurants del nou Codi de Duana andorrà
2.1 Ampliació del perímetre duaner
2.2 Precisió terminològica essencial
Terme
Definició (segons la llei)
Estatut duaner
Caràcter comunitari o no d’una mercaderia
Posada en lliure pràctica
Règim que permet l’entrada al mercat andorrà
Representant duaner
Mandatari autoritzat per realitzar els tràmits duaners en nom d’un tercer
2.3 Digitalització dels procediments
3. Sistema andorrà de drets, garanties i autoritzacions: cap a un control eficaç
3.1 Regulació dels deutes duaners i garanties
3.2 Règims econòmics duaners: fluïdesa amb condicions
3.3 Gestió de les autoritzacions duaneres: un gir normatiu
4. Regulació específica de la Llei andorrana de doble ús
4.1 Article 267.3.f: marc jurídic essencial
4.2 Decret d’aplicació 207/2025: modalitats pràctiques
4.3 Freemindtronic: un exemple de conformitat proactiva
4.4 Documentació de conformitat internacional: model francès i procediment ANSSI
5. Cooperació andorrana i recursos pedagògics: una obertura estratègica
5.1 Absència de guies institucionals: un buit a omplir
5.2 Contribució de Freemindtronic: contingut pedagògic, guia pràctica i sensibilització
5.3 Eines digitals disponibles
Alineació del règim andorrà amb la normativa internacional
Jurisdicció
Regulació
Data d’entrada en vigor
Data de curació
Particularitats per a la
Unió Europea
Reglament (UE) 2021/821
9 de setembre de 2021
Des del 2022 amb la guerra d’Ucraïna
Lliure circulació dins de la UE, excepte l’article IV per a determinades mercaderies.
Estats Units (EAR)
15 CFR 730 i següents.
13 de setembre de 1979
2022 – Reforç de les sancions contra Rússia i la Xina
Regla de minimis, extraterritorialitat, sancions de l’OFAC. Oficina d’Indústria i Seguretat
El Regne Unit
Ordre de control d’exportacions 2008
17 de desembre de 2008
2022 – Alineació amb les sancions de la UE i els EUA contra Rússia
Llicència a través de SPIRE, règim nacional post-Brexit. Control d’exportacions del Regne Unit
Suïssa
Ordenança OCB, SR 946.202
1 de juliol de 2012
2023 – Adopció de sancions selectives
Alineació amb la UE, però amb autoritzacions específiques. SECO suïssa
El Marroc
Llei nº 42-18
17 de desembre de 2020
1 de gener de 2025
Llicència obligatòria a partir de l’1 de gener de 2025, amb una fase transitòria de tres mesos.
Ucraïna
Llei d’Ucraïna sobre control d’exportacions
27 de juny de 2012
2022 – Sancions generalitzades contra Rússia
Regulació estricta de les exportacions i control millorat de les mercaderies sensibles.
Israel
Regulacions israelianes de doble ús
2016
2023 – Reforç dels controls militars d’exportació
Estricte control de les exportacions, alineació parcial amb els estàndards de Wassenaar.
Rússia
Regulacions russes sobre exportacions sensibles
2003
2022 – Enduriment de les restriccions a causa de les sancions internacionals
Control estricte de les exportacions estratègiques.
Xina
Regulacions de doble ús de la Xina
2020
2023 – Més dur amb les exportacions de semiconductors i IA
Estricte règim de control i restriccions tecnològiques.
Singapur
Normativa de control d’exportacions
2003
2022 – Augment de les restriccions a les tecnologies estratègiques
Regulació estricta dels articles de doble ús.
Brazil
Normativa brasilera sobre exportacions estratègiques
2011
2024 – Reforç de sancions i controls tecnològics
Control d’exportacions a través del Ministeri de Comerç Exterior.
6. Alineació del règim andorrà amb les regulacions internacionals
6.1 Lliure circulació dins de la UE
6.2 Andorra i la Unió Duanera Parcial
6.3 Implicacions per als béns de doble ús
6.4. Beneficis directes per als industrials andorrans del sector dual i defensa
6.5 Il·lustracions pràctiques: models de conformitat
Model A – Formulari de sol·licitud d’autorització d’exportació de béns de doble ús
Duana Andorrana – Despatx Central de Duana
Av. Fiter i Rossell, núm. 2, bloc A, Escaldes-Engordany, AD700
[ ] Exportació puntual – Data estimada: ____
[ ] Exportació recurrent – Període: del ____ al ____
Nom/Raó social: ____
NRT: ____
Nom/Raó social: ____
Adreça completa: ____
Activitat econòmica relacionada amb els béns: ____
Lloc web: ____
Nom/Raó social: ____
Adreça completa: ____
Activitat: ____
Lloc web: ____
Codi TARIC (10 dígits): ____
Descripció: ____
Quantitat/Unitat: ____
Valor (€): ____
País d’origen: ____
País de procedència: ____
Data del contracte: ____
Codi del règim duaner: ____
Ús final detallat: ____
Documents adjunts: [ ] Declaració de destinació finalModel B – Declaració de destinació final
Duana Andorrana – Despatx Central de Duana
Av. Fiter i Rossell, núm. 2, bloc A, Escaldes-Engordany, AD700
Nom/Raó social: ____
NRT: ____
Nom/Raó social: ____
Adreça completa: ____
Descripció: ____
Quantitat/Unitat: ____
Activitat econòmica del comprador: ____
Ús/destinació dels béns: ____
– Utilitzar els béns exclusivament segons l’ús declarat;
– No reexportar-los sense autorització de les autoritats del país de destinació.6.6. Sancions, embargaments i buit regulador a Andorra
6.7. Cap a una governança andorrana del doble ús: inspiració europea i marc operatiu
El control dels béns de doble ús a França és competència de la Subdirecció de Comerç Internacional de Béns Estratègics (SBDU), vinculada a la Direcció General d’Empreses (DGE). Aquest organisme concedeix autoritzacions d’exportació en coordinació amb la Duana i el Ministeri de les Forces Armades a través del Servei d’Informació i Documentació (SID) per a un seguiment reforçat postexportació.
🔹 SBDU: Autoritat competent en matèria de control i emissió de llicències.
➡ Ministeri d’Economia – Béns de doble ús
🔹 Coordinació amb la Duana: Seguiment dels fluxos comercials sensibles i verificació de conformitat.
➡ Direcció General de Duanes i Drets Indirectes (DGDDI)
🔹 Ministeri de Defensa – SID: Anàlisi de riscos i control estratègic de les exportacions.
➡ Servei d’Informació i Documentació (SID)
🔹 SECOMS: Responsable de l’aplicació de regulacions sobre exportacions i importacions sensibles.
➡ Ministeri d’Indústria, Comerç i Turisme
🔹 JIMDDU: Òrgan intergovernamental competent sobre exportacions estratègiques.
➡ Decret oficial BOE 2023-21672
🔹 Informe semestral sobre exportacions de material de defensa i béns de doble ús:
➡ Estadístiques i dades (2024)
Accions pràctiques a implementar des d’ara
7. Abast normatiu i perspectives d’aplicació
8. Enfocament comparatiu i prospectiu: cap a una doctrina andorrana del doble ús
Comparacions doctrinals i marcs jurídics
Perspectives d’evolució reguladora
Reptes futurs i sobirania tecnològica andorrana
Glossari d’acrònims i termes especialitzats