WhatsApp hacking zero-click exploit (CVE-2025-55177) chained with Apple CVE-2025-43300 enables remote code execution via crafted DNG images by abusing linked-device sync and automatic media processing — update WhatsApp and your OS now.
Quick summary
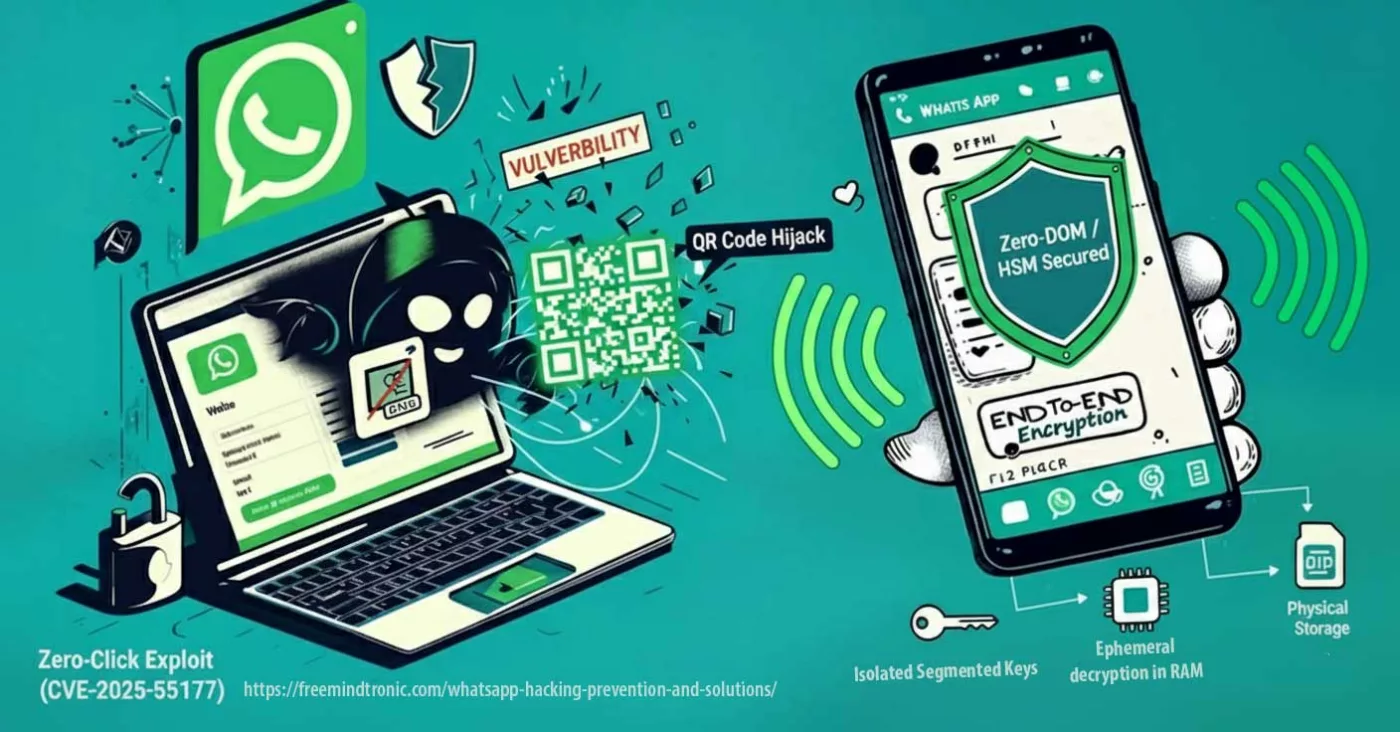
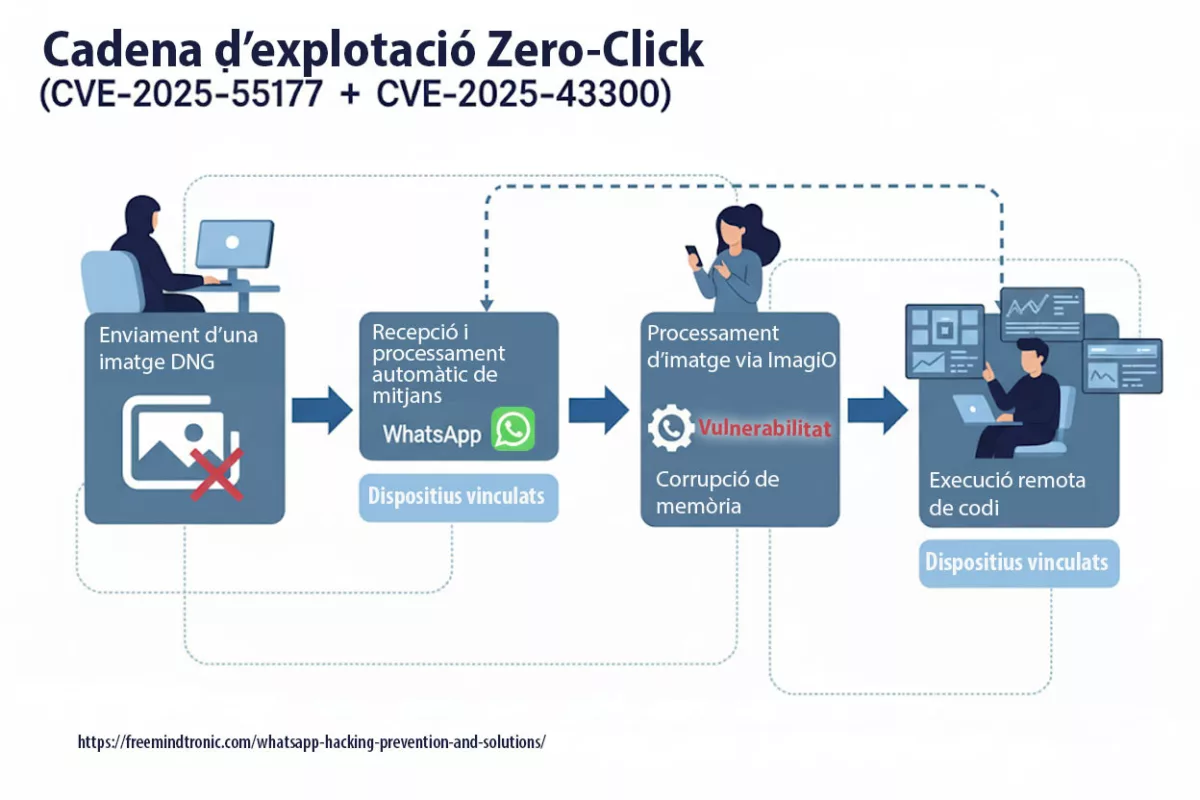
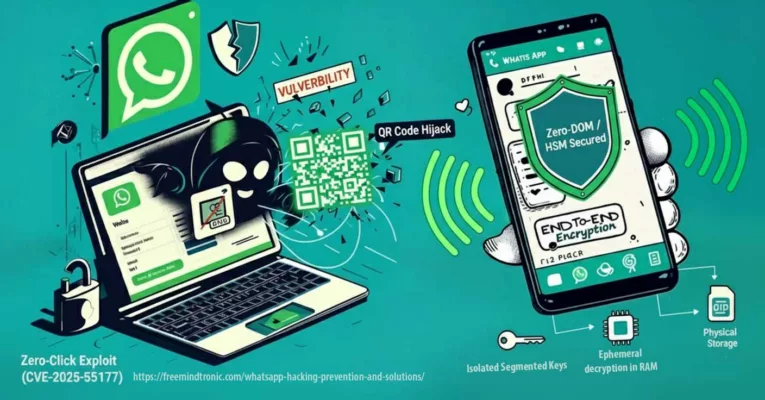
WhatsApp hacking zero-click exploit (CVE-2025-55177, chained with Apple CVE-2025-43300) allows arbitrary code execution from a crafted DNG image — no tap required.
Linked-device synchronization combined with automatic media processing opened the door: a hidden URL is fetched, the image parser corrupts memory, and a crafted payload runs.
Meta reports targeted in-the-wild exploitation against high-risk users. Patched builds landed: iOS ≥2.25.21.73, Business iOS ≥2.25.21.78, Mac ≥2.25.21.78.
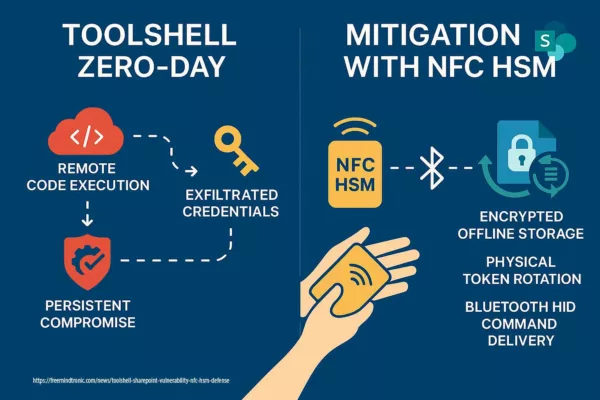
🚨 Bottom line — update now. Treat WhatsApp as a hostile runtime: patch app + OS, temporarily disable Linked Devices & auto-media, and isolate sensitive exchanges under a Zero-DOM posture (HSM/NFC).
Reading parameters
Summary read time: 4 minutes
Estimated full read: 29 minutes
Last updated: 2025-09-30
Complexity: Expert-level
Linguistic note: Sovereign lexicon — high technical density
Technical density: ≈70%
Languages: EN · FR · ES · CAT
Accessibility: Screen-reader optimized — semantic anchors included
Editorial type: Strategic Chronicle (analytical / technical)
About the author: Jacques Gascuel, inventor and founder of Freemindtronic®, specialist in sovereign cybersecurity architectures and creator of NFC & PGP HSM technologies for Zero-DOM protection of secrets.
Key points
- Zero-click RCE via crafted DNG delivered through linked-device sync.
- Chain uses Apple ImageIO bug (CVE-2025-43300) for memory corruption.
- Active, targeted exploitation confirmed for high-risk profiles.
- Patched builds: iOS ≥2.25.21.73 · Business iOS ≥2.25.21.78 · Mac ≥2.25.21.78.
- Sovereign reflex: disable linked sync, preserve logs, adopt hardware Zero-DOM encryption flows (HSM/NFC).
In Sovereign Cybersecurity ↑ This column belongs to the Digital Security section, focused on exploits, systemic vulnerabilities and hardware countermeasures for zero-trust environments.
- Quick summary
- Emergency — zero-click CVE-2025-55177
- The Risks of WhatsApp Hacking
- Techniques used by attackers
- Legitimate tools & misuse
- Freemindtronic sovereign countermeasures
- Recent vulnerabilities
- Advanced phishing campaigns
- Enhancing WhatsApp Security (HSM)
- Preventive Measures
- Best Practices for Messaging App Security
- FAQ — WhatsApp zero-click
- Strategic Outlook
Extended summary
How to Secure WhatsApp from Hacking: Latest Tips for Protecting Messaging Privacy in 2025
WhatsApp hacking is a growing concern as this popular messaging app faces sophisticated threats like phishing scams, spyware, and unauthorized account access. Protecting your data requires understanding the latest WhatsApp vulnerabilities 2025 and adopting secure instant messaging solutions. How can you protect yourself from WhatsApp hacking, and what should you do if it happens? In this article, you’ll learn some tips and tricks to improve your WhatsApp security, as well as innovative encryption technology solutions from Freemindtronic that can significantly enhance your protection.
Key insights include:
- Zero-click RCE via crafted DNG chained with Apple ImageIO bug.
- Linked-device sync can be leveraged as an involuntary fetcher.
- Exploit seen on a limited set of high-risk targets — act as if exposed.
- Zero-DOM posture (HSM/NFC) reduces blast radius even post-compromise.
⧉ When did this vulnerability emerge?
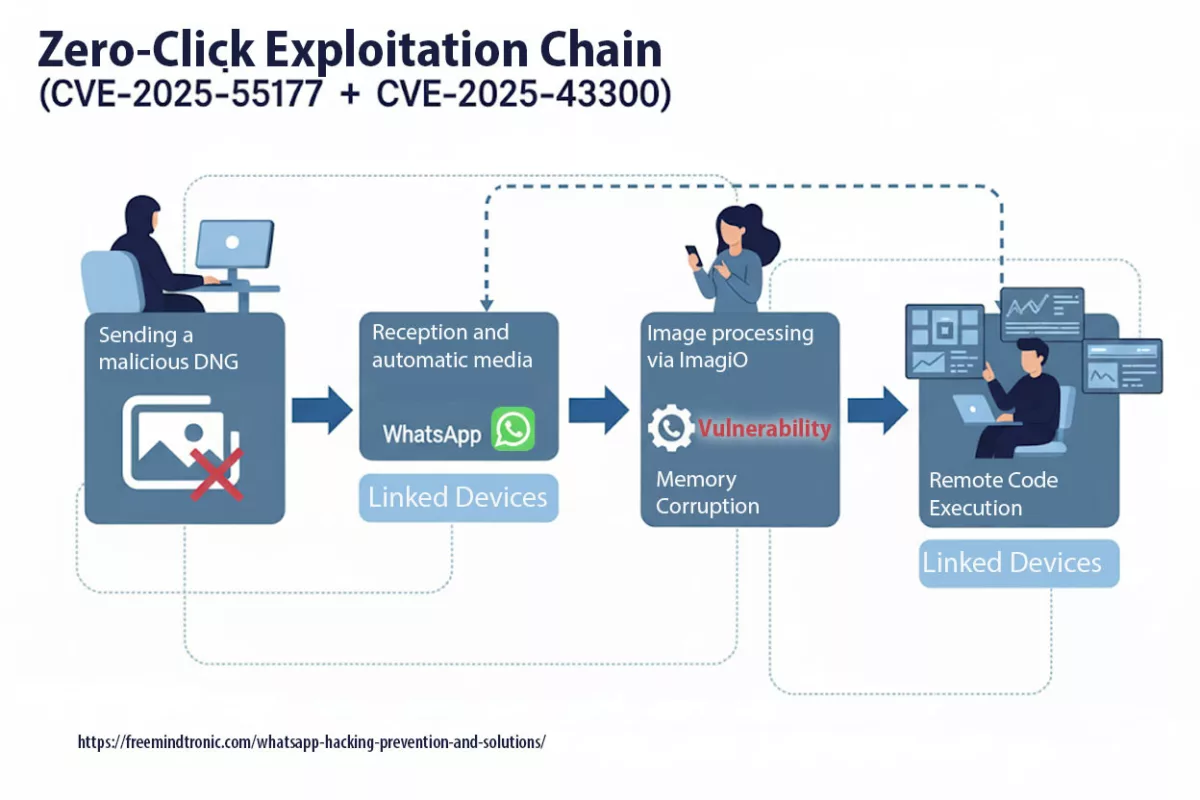
Initial alerts surfaced in May 2025, yet vulnerability CVE-2025-55177 remained exploitable for months due to the absence of a public patch. Experts believe it may have been used long before its institutional recognition, in targeted surveillance campaigns — often without victims ever realizing they had been compromised.
CVE-2025-55177 enabled zero-click remote code execution on iOS and macOS. Its linkage with Apple’s ImageIO flaw (CVE-2025-43300) extended the attack window, especially through automatic media synchronization across devices.
This context reinforces the strategic value of preventive architectures — where secrets are never exposed to the runtime environment and cannot be concatenated without .
⧉ Has it been exploited in the wild?
Yes — Meta confirmed targeted attacks, and the vulnerability is listed in the CISA KEV catalog.
Confirmed exploitations targeted high-risk profiles — including journalists, NGOs, and diplomats — using silent payloads delivered via synced media. No mass-scale abuse has been disclosed, but its inclusion in the Known Exploited Vulnerabilities (KEV) list validates its operational use.
This institutional recognition underscores the relevance of Zero-DOM / HSM technologies, which prevent any secret reconstruction without hardware-level validation — even in cases of DOM compromise or encrypted blob exfiltration.
Emergency: WhatsApp zero-click vulnerability (CVE-2025-55177)
Emergency: WhatsApp zero-click vulnerability (CVE-2025-55177)
An incomplete authorization flaw in linked-device synchronization allowed forced content processing from an arbitrary URL on iOS/macOS, without interaction (zero-click), chained with CVE-2025-43300 (Apple). Update WhatsApp and your OS without delay.
Affected versions
- WhatsApp for iOS: versions before 2.25.21.73
- WhatsApp Business for iOS: versions before 2.25.21.78
- WhatsApp for Mac: versions before 2.25.21.78
Suggested immediate actions
- Update WhatsApp (iOS ≥ 2.25.21.73 · Mac ≥ 2.25.21.78) and apply iOS/iPadOS/macOS updates addressing CVE-2025-43300.
- Temporarily disable Linked Devices and automatic media processing if possible.
- High-sensitivity cases: forensics, preserve logs (timestamps, filenames, URLs), rotate secrets from a clean device.
Forensics & Incident handling (SOC)
- Preserve artifacts: message timestamps, filenames, URLs, device syslogs.
- Capture network traces (pcap) from affected timeframe; note DNS resolutions to unknown hosts.
- Revoke all WhatsApp Web sessions; rotate Apple ID / device tokens from a clean device.
- Reimage only after acquiring images (mobile backups, macOS Time Machine snapshots).
Technical notes (operator-grade)
- Root cause : incomplete authorization côté linked-device sync → déclenchement de traitements depuis URL arbitraire.
- Zero-click : aucune interaction requise ; chaîne observée avec CVE-2025-43300 (Image/DNG → memory corruption).
- Scope : ciblage limité (hauts risques) ; pas de POC public confirmé à ce jour.
• WhatsApp — Security Advisories 2025
• NVD — CVE-2025-55177
• CISA KEV — CVE-2025-55177
• Apple — Security content (CVE-2025-43300)
How to Prevent and Solve WhatsApp Hacking Issues
WhatsApp, with over 2 billion users worldwide, remains a prime target for hackers. Despite its popularity, WhatsApp is not immune to hacking, which can severely compromise the security and privacy of your conversations. Leveraging hardware-based security and encryption tools is essential not only for securing personal chats but also for safeguarding business communication from increasingly sophisticated hacking attempts. So, how can you protect your WhatsApp account from hacking, and what should you do if it gets hacked?
Core hygiene + hardware isolation. Enable 2-step verification, audit Web sessions, restrict permissions, and isolate sensitive exchanges via HSM-backed Zero-DOM flows.
The Risks of WhatsApp Hacking
WhatsApp hacking can have serious consequences for victims. Hackers employ sophisticated WhatsApp hacking techniques to gain unauthorized access to sensitive information stored in messaging apps. This data may include encrypted chats, photos, videos, and personal contacts, underscoring the need for messaging app security and robust encryption technology. They can impersonate the victim, sending fraudulent or malicious messages to contacts. These messages can request money or trick recipients into clicking on infected links. Furthermore, hackers can spread false information or illegal content using the compromised account.
WhatsApp hacking can also impact a victim’s professional life, especially if they use the app for business communication. Hackers can access confidential data like contracts, quotes, or project details. They can also damage the victim’s reputation by sending abusive or defamatory messages to professional contacts.
The Techniques of WhatsApp Hacking
Hackers employ various techniques to compromise WhatsApp accounts, including advanced phishing scams, exploiting vulnerabilities like QR code misuse, and bypassing two-step verification, including:
- Phishing: Hackers send deceptive messages or emails that appear to be from official services like WhatsApp, Google, or Apple. These prompts encourage the victim to click on a link or provide personal information. This link usually leads to a fraudulent site designed to steal the victim’s data.
- Voice Mail Exploitation: Hackers exploit flaws in the WhatsApp authentication process by dialing the victim’s phone number and attempting to access their WhatsApp account. If the victim’s phone is off or in airplane mode, the verification code sent via SMS or call may go to voicemail. Hackers can retrieve it using default or guessed voicemail codes.
- Social Engineering and Hijacking Risks: Recent warnings from law enforcement highlight the increasing use of social engineering to hijack WhatsApp accounts. Attackers often exploit trust by impersonating trusted contacts, requesting verification codes under false pretenses. Police reports have urged users to avoid sharing verification codes even with known contacts, as these are often targeted in coordinated scams.
- QR Code Scanning: This technique takes advantage of WhatsApp Web by scanning a QR code displayed on a computer with the victim’s smartphone. A hacker can then access the WhatsApp account on their own computer.
As these techniques demonstrate, WhatsApp users face an increasing number of sophisticated threats that exploit both technical vulnerabilities and human trust. To counteract these risks, adopting proactive security measures is essential. Below, we outline best practices and tools to help secure your messaging app and protect sensitive data in real time.
Phishing, voicemail PIN abuse, QR/Web session hijack and SIM operations dominate. Adversaries chain social engineering with session theft and media parsing flaws.
Legitimate Monitoring Tools and Their Misuse
While certain monitoring tools are designed for legitimate purposes, such as parental control or employee supervision, they can pose significant privacy risks if misused. Below, we outline some of the most popular tools, their main features, and links to their respective publishers for more details:
Légitimes Monitoring Tools for WhatsApp Surveillance
Certain applications are specifically designed for legitimate use cases, such as parental control or employee monitoring. Below is a list of popular tools, their key features, and links to their respective publishers for further details:
- KidsGuard for WhatsApp
Designed to monitor WhatsApp activity in children, this tool tracks messages, calls, and multimedia files. - FoneMonitor
A straightforward solution for monitoring WhatsApp activities, including conversations and call history. - mSpy
Popular for parental control, mSpy offers detailed tracking of messages, call logs, and media on WhatsApp. - Spyera
Advanced software that allows monitoring of mobile devices, including WhatsApp conversations and voice calls. - Hoverwatch
Enables users to track WhatsApp conversations, calls, and even locate the device. - FlexiSPY
Known for advanced features like call recording and real-time tracking of WhatsApp messages.
Disclaimer: While these tools are designed for legitimate purposes, they can easily be misused for malicious activities. Their use must comply with applicable laws and ensure the consent of all parties involved.
— Steganographic payloads in DNG/RAW sidecars targeting mobile parsers.
— Increased QR-to-Web hijack loops leveraging “trusted” Safe-Link wrappers.
— Brokered zero-day demand focused on media pipelines across messaging apps.
Sovereign response to WhatsApp hacking (zero-click)
While many monitoring tools lack safeguards, Freemindtronic provides hardware measures to contain access and protect personal and professional data.
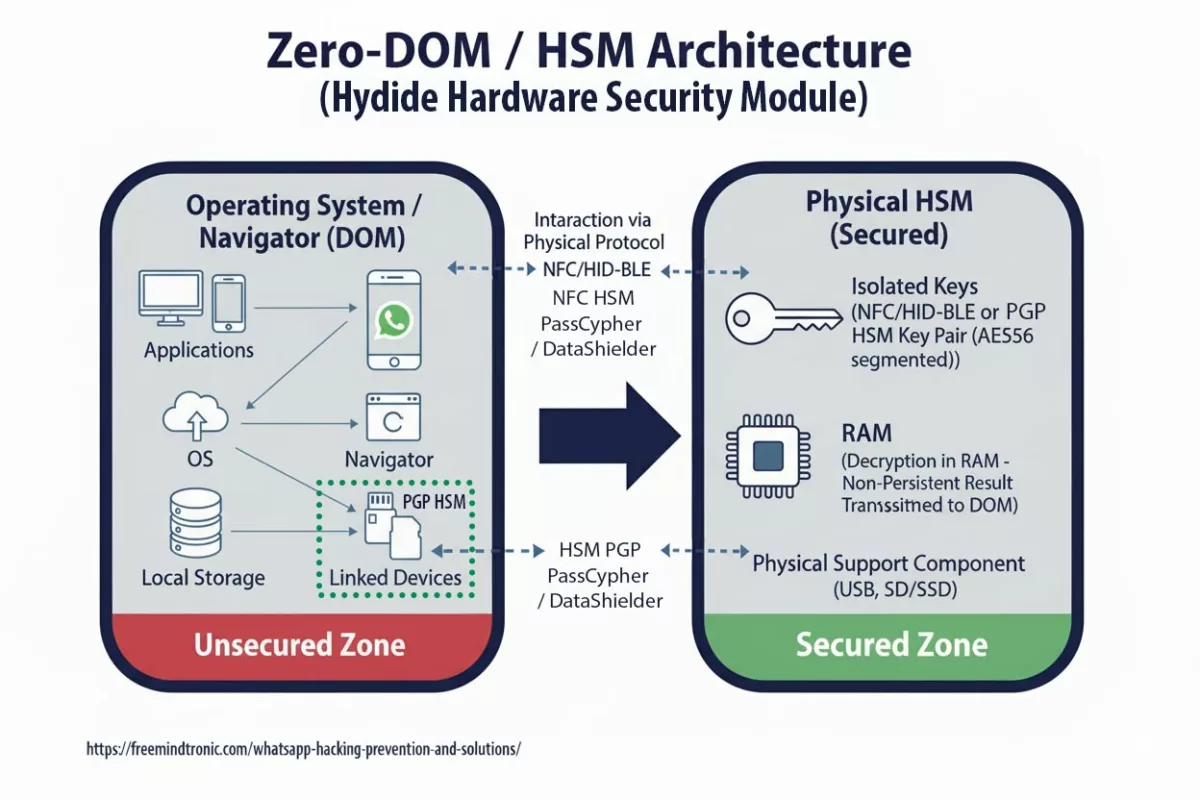
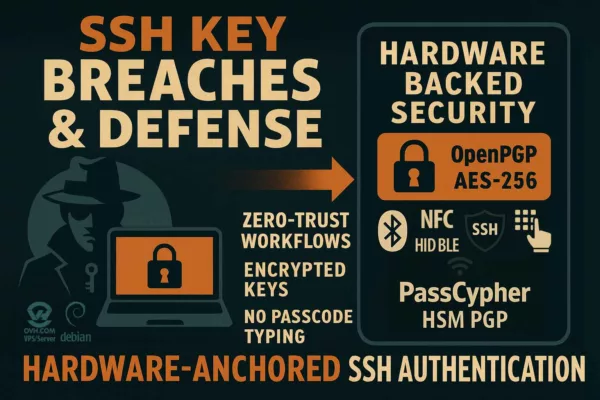
Operational clarification — PassCypher & DataShielder (HSM PGP)
PassCypher and DataShielder rely on autonomous segmented keys: each encrypted container encapsulates 256-bit segments, and the corresponding fragments remain isolated & protected in encrypted local storage and in the HSM device — never transiting or persisting on the host in an exploitable state. Segments may move temporarily — but never in a directly usable form. They are non-exploitable without validated typological concatenation, performed only in host RAM after contextual hardware proof (NFC HSM, storage-backed HSM PGP, and sandbox-URL).
Legitimate access process:
- The HSM validates presence & context (NFC HSM, storage HSM PGP, sandbox-URL, behavioral checks).
- Required segments are released then concatenated in host RAM — only for the exact time needed (container read, secure auto-fill, encrypt/decrypt, PIN or TOTP generation).
- Decryption occurs strictly in volatile memory; no key is written to disk, exposed to the DOM, or persisted in buffers.
- After use, buffers are wiped and the state returns to “locked”: segments remain encapsulated (256-bit) in the HSM and cannot be reused without fresh hardware authorization.
Operational functions
- NFC HSM (mobile): secure auto-fill of WhatsApp login fields when disconnected, with sandbox-URL control and behavioral validation.
- HSM PGP (desktop / extension): isolated containers holding credentials and private OTP/TOTP/HOTP keys; automatic PIN/TOTP generation and integrated Pwned Passwords checks.
- PassCypher: anti-BITB (automatic destruction of malicious iframes) and sandbox control before any secret injection.
- Memory security: concatenation and decryption in host RAM are atomic, ephemeral, and non-exploitable — no persistence, no disk writes, no DOM exposure.
Typological consequence: even with browser-side malicious code (zero-click) or exfiltrated encrypted blobs, attackers cannot reconstruct or exploit secrets without the sovereign hardware proof enforced by the HSM. Note: locally stored segmented keys are never directly exploitable. Reconstruction requires HSM-validated concatenation in a secure host-RAM context.
Why Freemindtronic?
- PassCypher NFC HSM Lite
- Secures WhatsApp access via locally generated OTP/TOTP/HOTP — no cloud dependency.
- Neutralizes phishing and credential theft with non-reusable secrets.
- Contactless, battery-free, and DOM-isolated operation.
- PassCypher HSM PGP
- Advanced password management and PGP encryption with secure HSM storage.
- Isolated, segmented, non-persistent keys; desktop and browser-extension compatible.
- DataShielder NFC HSM Starter Kit
- Real-time encryption of messages/files (AES-256 CBC).
- Secret sharing with typological encapsulation via RSA-4096 generated & stored in the NFC HSM.
- Keys stored locally, inaccessible to remote attackers or malicious scripts.
Protective features
- Anti-phishing / BITB: mitigates Browser-in-the-Browser via automatic destruction of redirection iframes.
- Real-time encryption: protection even if the device is compromised.
- Hardware security: keys remain outside apps, outside the cloud, and outside DOM vectors.
Discover how the DataShielder NFC HSM Starter Kit can secure your communications.
Preventing misuse
- Restrict app permissions to avoid unjustified access.
- Audit installed apps regularly to detect hidden monitoring tools.
- Encrypt upstream with NFC HSM before any cloud backup.
Human error: a persistent vector
Scams asking for the six-digit verification code remain effective; 2SV reduces risk but does not eliminate it.
How DataShielder protects content
- Out-of-WhatsApp encryption: even if the account is compromised, content encrypted by DataShielder/HSM PGP remains inaccessible without the hardware key.
- Local key storage: prevents extraction from the app or the cloud.
- Web integration: HSM PGP enables client-side encryption, usable with WhatsApp Web via Zero-DOM flows (depending on integration).
- Anti-phishing: PassCypher generates dynamic OTPs (TOTP/HOTP) to reduce takeover risk.
In summary
NFC HSM and HSM PGP do more than respond to flaws: they define a new security typology. They are preventive, non-reactive, non-simulable, and non-exploitable without hardware proof. They embody a digital sovereignty architecture where every operation is conditioned, traceable, and non-replayable.
Best Practices for Messaging App Security: Real-Time Encryption and Hardware Solutions
In response to recent warnings, experts and law enforcement stress the importance of enabling two-step verification to add a second layer of security to your WhatsApp account. This simple measure can prevent attackers from hijacking your account even if they gain access to your verification code.
To ensure robust messaging app security, users should adopt preventive measures such as enabling two-step verification, avoiding public Wi-Fi when accessing WhatsApp Web, and securing sensitive communication with advanced encryption tools like DataShielder NFC HSM or DataShielder HSM PGP. These modern instant messaging security solutions provide real-time protection against unauthorized access.
Harden identity (2SV), constrain network exposure, and encrypt outside app memory with NFC/PGP HSM. Treat cloud backups and Web as higher-risk surfaces.
Spyware Pegasus and NSO Group
In December 2024, the U.S. District Court for the Northern District of California (Case No. 19-cv-07123-PJH) ruled that NSO Group violated anti-hacking laws under the Computer Fraud and Abuse Act (CFAA) and California’s Comprehensive Computer Data Access and Fraud Act (CDAFA). The court found NSO liable for its unauthorized use of WhatsApp servers to deploy Pegasus spyware, targeting over 1,400 devices through a WhatsApp vulnerability. While claims of trespass to chattels were dismissed, the lawsuit continues to address other violations. This ruling underscores the growing legal challenges faced by spyware developers and highlights the critical need to keep applications updated to defend against sophisticated attacks. For the official court ruling and details of the case, refer to the backup document.
Landmark Legal Decision: NSO Group Held Liable for WhatsApp Hacking
This historic decision by the U.S. District Court for the Northern District of California (Case No. 19-cv-07123-PJH) held NSO Group accountable for hacking and breach of contract in its unauthorized use of WhatsApp’s servers to install Pegasus spyware. The court found that NSO violated the Computer Fraud and Abuse Act (CFAA) and California’s Comprehensive Computer Data Access and Fraud Act (CDAFA). However, claims of trespass to chattels were dismissed. The case now proceeds to determine damages.
Will Cathcart, head of WhatsApp, called the verdict a “victory for privacy,” emphasizing that companies deploying spyware cannot hide behind claims of immunity.
“We have spent five years pursuing this case because we firmly believe that spyware companies cannot evade accountability for their illegal actions,” Cathcart said.
Cybersecurity experts also hailed the ruling as a major milestone in holding the spyware industry accountable. John Scott-Railton of Citizen Lab described it as a “historic decision” with far-reaching implications for the spyware market.
The court underscored that spyware companies cannot claim sovereign immunity when acting outside government employment or deploying hacking tools for commercial profit.
For the official court ruling, refer to the backup document. For a deeper understanding of Pegasus and its broader impact, read our detailed analysis on Pegasus.
Advanced Phishing Campaigns in WhatsApp Hacking: How Users Can Protect Their Data in 2025
In January 2025, it was revealed that the Russian hacking group Star Blizzard launched phishing campaigns targeting WhatsApp accounts of global officials. These attacks demonstrate how sophisticated tactics exploit trust in communication platforms. By employing multi-layered deception techniques, the group accessed sensitive data, underscoring the urgent need for advanced encryption and hardware-based security. These operations highlight vulnerabilities still present in widely-used messaging apps like WhatsApp and the importance of proactive protection measures.
In late 2024, Microsoft uncovered another campaign conducted by Star Blizzard, showcasing evolving techniques used in WhatsApp hacking. The campaign relied on social engineering tactics to compromise user accounts:
- Initial Email Deception: Victims received emails falsely claiming to originate from U.S. officials. These emails included QR codes allegedly leading to WhatsApp groups supporting **Ukrainian NGOs**. However, the QR codes were deliberately broken, prompting victims to reply for assistance.
- Follow-Up Email with Malicious Link: A second email was sent, containing a shortened link in a **Safe Links format**. Clicking this link redirected victims to a phishing page, where they were prompted to scan another QR code.
- WhatsApp Account Takeover: Scanning the QR code granted attackers unauthorized access to victims’ WhatsApp accounts via **WhatsApp Web**, allowing attackers to exfiltrate sensitive messages and gain unauthorized access to private data.
These campaigns highlight how attackers adapt their strategies, exploiting both technological vulnerabilities and human trust. Vigilance is critical, particularly when dealing with QR codes and email links.
For more details on these campaigns, you can refer to Microsoft’s detailed analysis here.
Why These Threats Matter
The Star Blizzard phishing attack illustrates how attackers use multi-layered deception techniques to compromise WhatsApp accounts. By combining email phishing, QR code misuse, and social engineering, this campaign exploited user trust in established formats like Safe Links.
The Star Blizzard attacks illustrate that even high-ranking officials are not immune to WhatsApp hacking. These campaigns underline the importance of adopting hardware-based security measures to combat WhatsApp hacking risks. Such as hardware-based encryption tools and two-step verification, to safeguard sensitive communications.
This attack also highlights the limitations of current messaging platform security. Even though WhatsApp has strong encryption protocols, attackers continue to find ways to bypass user protections through external vectors like phishing and QR codes.
Combatting WhatsApp Hacking with Freemindtronic’s Advanced Security Solutions
The advanced encryption tools provided by Freemindtronic, such as DataShielder NFC HSM and EviCrypt, offer unparalleled protection against sophisticated attacks like those conducted by Star Blizzard. By encrypting messages in real-time and securing encryption keys locally, these solutions minimize the risk of unauthorized access, even in high-profile cases.
With the ever-evolving landscape of cybersecurity threats, Freemindtronic’s solutions stand out as powerful tools to combat WhatsApp hacking. From real-time encryption to hardware-based security modules, these innovations offer users a robust way to protect sensitive information and ensure messaging privacy.
To effectively secure your communication on WhatsApp, hardware-based security for messaging and advanced encryption technologies offer unparalleled protection. Freemindtronic’s solutions integrate seamlessly into your messaging habits, providing real-time encryption for sensitive data.:
- DataShielder NFC HSM Auth and M-Auth:
These advanced hardware security modules encrypt sensitive communications in real time, ensuring your messages and files remain secure even if your account is compromised. The physical origin trust criteria used by these devices ensures that encryption keys cannot be accessed remotely by attackers. - DataShielder HSM PGP:
This solution enables PGP encryption, protecting messages with robust cryptographic algorithms stored securely on the HSM. It provides an additional layer of defense for WhatsApp messages and other instant messaging platforms, such as Telegram or Signal.
By integrating Freemindtronic’s encryption technology into your communication habits, you can ensure robust protection for encrypted communication tools. These tools prevent attackers from accessing sensitive data, even during phishing scams or WhatsApp Web exploitation.
Fake Verified Accounts on WhatsApp
In October 2024, cybercriminals created fake verified accounts pretending to represent WhatsApp’s support team. These fraudulent accounts contacted users under the guise of offering assistance but instead aimed to steal personal information or install malicious software.
To stay safe:
- Be cautious of accounts claiming to be verified without clear evidence.
- Never share sensitive information with unverified sources.
- Contact official WhatsApp support directly if you have concerns.
Isolate secrets outside the DOM: DataShielder NFC HSM and PassCypher HSM PGP provide physical validation (NFC/HID-BLE), ephemeral decryption in RAM, and non-persistence — mitigating the impact of zero-click exploits.
Recent WhatsApp Vulnerabilities
In addition to these techniques, new vulnerabilities have emerged that pose significant risks to WhatsApp users:
- Remote Code Execution Vulnerabilities: In late 2023, two critical remote code execution (RCE) vulnerabilities were discovered in WhatsApp. These vulnerabilities, identified as CVE-2023-5668 and CVE-2023-38831, allowed attackers to execute arbitrary code on a victim’s device through specially crafted video files or other exploitative methods. Although WhatsApp has since patched these vulnerabilities, they underscore the importance of keeping the app updated to avoid potential exploitation.
- Xenomorph Malware: The Xenomorph Android malware has evolved into a significant threat to Android users, including those using WhatsApp. This malware disguises itself as legitimate apps and can bypass multi-factor authentication to steal credentials and take over user accounts. Its capabilities include stealing data from both banking apps and cryptocurrency wallets, potentially targeting WhatsApp accounts as well.
- Dark Web Exploits: The demand for zero-day vulnerabilities, especially for apps like WhatsApp, has surged. These vulnerabilities are being sold for millions of dollars on the dark web, highlighting their value to hackers. Such exploits could allow attackers to bypass security measures and gain unauthorized access to user data. It is crucial to stay informed about the latest patches and updates released by WhatsApp to mitigate these risks.
These WhatsApp hacking vulnerabilities underline the need for advanced security features, like hardware encryption, to protect business communication.
RCE chains reappear cyclically across media handlers and Web flows. Patch cadence and operational isolation are decisive.
WhatsApp Phishing Scams
In November 2024, authorities reported a surge in phishing scams targeting WhatsApp users. Cybercriminals impersonated trusted contacts, requesting verification codes or money transfers through platforms like Bizum. These scams rely on exploiting users’ trust to hijack accounts or steal funds.
To protect yourself:
- Never share verification codes with anyone.
- Always verify the authenticity of requests for help.
- Enable two-step verification in WhatsApp’s settings.
For further details, see the Cadena SER article here.
New Vulnerability Found in WhatsApp’s “View Once” Feature
WhatsApp’s “View Once” feature, designed to enhance privacy by making media disappear after just one view, has recently revealed a serious security vulnerability. Discovered by Zengo X, this flaw lets attackers bypass the feature, especially on web and desktop versions.
Vulnerability Details
While mobile devices effectively prevent screenshots and saving media, the protection doesn’t extend as well to non-mobile platforms. Zengo X researchers found that browser extensions, like those available for Chrome, can easily modify WhatsApp’s code. They disable the “View Once” flag, turning temporary messages into permanent ones. This allows attackers to save, forward, and view messages repeatedly.
Moreover, messages marked as “View Once” are sent to all devices linked to the recipient. This includes those that shouldn’t handle this feature, such as web and desktop platforms. Attackers can exploit this loophole and save media on these platforms. Additionally, these messages remain stored on WhatsApp servers for up to two weeks, increasing the risk of potential abuse.
Meta’s Response
Meta, the parent company of WhatsApp, has responded after Zengo X responsibly disclosed the flaw. Meta confirmed they are currently rolling out patches, focusing on securing web versions of WhatsApp. However, this interim measure isn’t the final fix. A more comprehensive update is expected to address the vulnerability fully.
Meta’s bug bounty program played a critical role in identifying this issue. They are working towards a full patch and encourage users to remain cautious. Specifically, Meta suggests sharing sensitive media only with trusted contacts during this period.
Ongoing Concerns
While Meta is working on a complete fix, users should remain aware of the limitations in the current “View Once” feature. The vulnerability allows attackers not only to bypass the feature but also to access low-quality media previews without downloading the entire message. Attackers can also manipulate the system by changing the “view once” flag to “false,” making the message permanent.
Security experts, like Tal Be’ery of Zengo X, have emphasized that this flaw creates a “false sense of privacy”. Users think their messages are secure when, in reality, they are vulnerable on certain platforms.
Recommendations
Until a final patch is released, users should exercise caution when using the “View Once” feature. Sharing sensitive information via WhatsApp Web or desktop versions is risky due to phishing attacks and exploitable vulnerabilities. Using secure instant messaging solutions, like those integrating hardware encryption, ensures your communication remains private.
For more in-depth details, you can read the full technical report by Zengo X here.
More Recent WhatsApp Vulnerabilities
WhatsApp has recently addressed several other serious security vulnerabilities that could put users at risk. While updates have been rolled out, these issues demonstrate why keeping WhatsApp updated is crucial.
Remote Code Execution Vulnerabilities (CVE-2022-36934 & CVE-2022-27492)
WhatsApp fixed two critical remote code execution (RCE) vulnerabilities in 2024. The first, identified as CVE-2022-36934, affected the Video Call Handler. Attackers could exploit this flaw by initiating a video call, leading to an integer overflow that let them take control of the device. The second, CVE-2022-27492, was found in the Video File Handler. It allowed attackers to execute malicious code when users opened a specially crafted video file.
These flaws impacted both iOS and Android users with WhatsApp versions prior to 2.22.16.12 for Android and 2.22.15.9 for iOS. Users are strongly advised to update their apps to protect against such risks.
Enhancing WhatsApp Security
To combat the increasing risks of hacking, WhatsApp introduced several new security features. These enhancements provide significantly stronger protection against unauthorized access and malware attacks.
Account Protect adds an extra layer of security when transferring your WhatsApp account to a new device. This feature requires confirmation from your old device, making it much harder for unauthorized users to take over your account.
Device Verification is another critical update. It prevents advanced malware attacks that attempt to hijack your WhatsApp account. By introducing automated security tokens, WhatsApp ensures that your account remains protected, even if your device is compromised.
Additionally, Automatic Security Codes streamline the verification of secure connections. WhatsApp has introduced a feature called Key Transparency, which automates this process. This ensures your conversations are secure without requiring manual intervention, offering further protection against WhatsApp hacking.
To learn more about these new security features, check out WhatsApp’s official blog post.
Mark Zuckerberg’s Security Recommendations
In addition to WhatsApp’s built-in security features, recommendations from key figures like Mark Zuckerberg highlight how users can take additional steps to enhance their messaging privacy. These measures complement advanced encryption tools by addressing common vulnerabilities users face daily.
In January 2025, Mark Zuckerberg emphasized the importance of using disappearing messages to enhance WhatsApp security. This feature allows users to set a time limit for messages to automatically delete, reducing risks if a device is compromised.
To enable this feature, go to WhatsApp’s privacy settings. You can find more information in the Presse-Citron article here.
By combining disappearing messages with tools like hardware-based encryption, users can build a multi-layered security strategy to protect personal and professional communication.
Given the evolving nature of these vulnerabilities, leveraging robust security solutions, such as Freemindtronic’s encryption tools, becomes critical for safeguarding sensitive communications.
Enhancing WhatsApp Security in 2025: DataShielder NFC HSM and Advanced Encryption Tools
For even greater security, especially in scenarios where your credentials might be compromised, integrating advanced hardware security modules (HSM) like DataShielder NFC HSM, DataShielder HSM PGP, or PassCypher NFC HSM can significantly fortify your defenses.
DataShielder NFC HSM securely stores and manages encryption keys on a hardware device, ensuring that even if your credentials are exposed, your encrypted data remains inaccessible. You can explore the DataShielder NFC HSM Starter Kit here.
DataShielder HSM PGP provides robust protection for your WhatsApp messages by using PGP encryption. This ensures that all communications are encrypted with strong cryptographic keys securely stored on the HSM.
PassCypher NFC HSM enhances security by generating one-time passwords (OTP) using TOTP or HOTP methods. Even if your static credentials are compromised, the dynamic passwords generated by PassCypher prevent unauthorized access. This, combined with secure key management, makes it nearly impossible for attackers to access your account. Learn more about PassCypher NFC HSM here.
These technologies add critical layers of defense, ensuring that your WhatsApp communications are protected from even the most sophisticated hacking attempts.
Preventive Measures Against WhatsApp Hacking
WhatsApp hacking can compromise any user, leading to severe consequences for private and professional communications. Implementing effective two-step verification techniques, combined with encryption technology, ensures messaging app security. Therefore, it’s crucial to adopt simple yet effective preventive measures, such as activating two-step verification, using fingerprint or face recognition, and changing your voicemail code regularly. Additionally, incorporating advanced technological solutions like those offered by Freemindtronic, such as EviCrypt, EviFile, DataShielder, and PassCypher, can further enhance your security by encrypting texts and files directly within WhatsApp, using physical origin trust criteria.
By leveraging real-time encryption tools like DataShielder products, users can significantly mitigate threats from advanced cyberattacks such as those conducted by Star Blizzard.
Recent examples of vulnerabilities, such as QR code misuse and phishing scams targeting high-profile officials, demonstrate the critical need to pair preventive practices with robust technological solutions.
Core hygiene + hardware isolation. Enable 2SV, verify unusual requests, audit Web sessions, and encrypt outside app memory with NFC/PGP HSM to contain compromise.
Core Preventive Practices
To effectively secure your WhatsApp account, here are the key steps every user should follow:
- Verify unexpected requests: Even if the message appears from a trusted source, confirm authenticity through another communication channel.
- Enable two-step verification: This remains the most effective way to safeguard your account against hijacking attempts.
- Act swiftly if compromised: Log out all active WhatsApp Web sessions immediately and contact WhatsApp support to recover your account.
Advanced Sovereign Countermeasures
By integrating advanced solutions like PassCypher, which generates one-time passwords, and EviCrypt, which encrypts sensitive data directly on your device, users can ensure real-time protection against even the most sophisticated hacking attempts.
With these robust measures in place, you can greatly reduce the risk of WhatsApp hacking, ensuring that your sensitive data remains secure. By combining two-step verification, real-time encryption, and secure messaging apps, users can mitigate risks and protect their personal and professional communication.
Stay informed and adopt these robust security measures to protect your personal and professional communications. Don’t wait—secure your account today.
This Chronicle focused on mobile/iOS–macOS chains and linked-device sync. Topics like Android media stacks, carrier SS7 exposure and enterprise MDM guardrails will be addressed later.
With DataShielder NFC HSM and PassCypher HSM PGP, secrets never touch the DOM: physical validation (NFC/HID-BLE), ephemeral RAM decryption, no persistence. This materially limits the impact of WhatsApp zero-clicks and web session hijacks.
- Out-of-browser encryption (Zero-DOM) for messages/files.
- Air-gapped key material; no cloud telemetry.
- PGP/OTP workflows that resist phishing and QR-based takeover.
FAQ — WhatsApp zero-click
Yes. The chain abused linked-device sync + automatic media processing to trigger parsing of a crafted DNG (zero-click). Patch WhatsApp and iOS/iPadOS/macOS, then re-enable features only if required. See Emergency — zero-click CVE-2025-55177.
Patched builds: iOS ≥ 2.25.21.73, Business iOS ≥ 2.25.21.78, Mac ≥ 2.25.21.78. Update the OS for Apple CVE-2025-43300 as well. See affected versions.
For high-risk profiles: temporarily disable Linked Devices and avoid Web/Desktop bridges until you’ve patched. If you must use them, isolate secrets with Zero-DOM / HSM workflows.
Treat them as high-sensitivity. Prefer client-side encryption before backup (PGP/HSM), reduce retention, and restrict who can restore. Hardware key isolation (NFC HSM) prevents key exfiltration.
Keep timestamps, filenames, URLs, device syslogs, crash logs (ImageIO), and any network traces in the suspected window. Revoke Web sessions and rotate credentials from a clean device. See “Suggested immediate actions” in Emergency.
This lets you verify if your version includes the latest security patches.
However, Android remains vulnerable to other zero-day vectors — maintain vigilance and apply updates promptly.
It uses isolated keys (e.g. HSM via NFC/HID-BLE) and ephemeral decryption in RAM — ensuring no persistence and resistance to zero-click exploits.
Adopt a Zero-DOM posture: out-of-browser encryption, hardware-stored keys (NFC/HSM), ephemeral decrypt in RAM, and non-persistence. See Freemindtronic sovereign countermeasures.
Strategic Outlook
Zero-clicks won’t slow down. Messaging stacks will keep absorbing browser-grade risk via Web/Desktop bridges and media codecs.
The sustainable path is twofold: shorten patch windows and remove secrets from app memory.
Enterprises should formalize a Zero-DOM doctrine for high-value exchanges, push MDM baselines that restrict WhatsApp Web, and rotate credentials from clean devices after any suspected targeting.
Admin checklist (enterprise / MDM)
- Force app updates ≥ patched builds; block outdated via MDM.
- Temporarily disable WhatsApp Web on managed endpoints with risky profiles.
- Harden media handling (macOS/iOS) and restrict arbitrary URL fetch by companion apps.
- Adopt hardware key isolation for VIPs (NFC HSM / PGP) — Zero-DOM for critical exchanges.
- Run targeted threat hunts: DNG/RAW anomalies, ImageIO crash logs, suspicious WebSockets.