TETRA Security Vulnerabilities
Tetra is a radio communication standard used by critical sectors worldwide. But it has five security flaws that could expose its encryption and authentication. How can you protect your Tetra system from hackers? Read this article TETRA Security Vulnerabilities to find out the best practices and tips.
TETRA Security Vulnerabilities: How to Protect Critical Infrastructures from Cyberattacks
TETRA (Terrestrial Trunked Radio) is a radio technology that is used worldwide for critical communications and data, especially in the sectors of security, energy, transport and defense. But this technology, which has been kept secret for more than 25 years, hides serious security vulnerabilities, including a backdoor that could allow devastating cyberattacks.
What is TETRA?
TETRA is a European radio standard that was developed in the 1990s to meet the needs of professional mobile services, such as police, firefighters, emergency services, military, prison staff, etc. TETRA allows to transmit data and voice encrypted on frequencies ranging from 380 to 470 MHz, with a range of several kilometers.
TETRA is used by more than 2000 networks in more than 150 countries, according to the TETRA and Critical Communications Association (TCCA), which brings together the manufacturers, operators and users of this technology. Among the main manufacturers of TETRA radios, we find Motorola Solutions, Hytera, Airbus, Sepura and Rohill.
TETRA offers several advantages over other radio technologies, such as:
- better sound quality
- greater transmission capacity
- greater security thanks to encryption
- greater flexibility thanks to the possibility of creating communication groups
- greater interoperability thanks to the compatibility of equipment
Source french: TETRA digital mode & F4HXZ – Blog radioamateur
What are the vulnerabilities of TETRA?
Despite its strengths, TETRA also has weaknesses, which have been revealed by a group of Dutch researchers from Radboud University Nijmegen. These researchers conducted a thorough analysis of the TETRA standard and its encryption algorithms, which were until then kept secret by the manufacturers and authorities.
The researchers discovered two types of major vulnerabilities in TETRA:
- A backdoor in the encryption algorithm TEA1, which is used in radios sold for sensitive equipment, such as pipelines, railways, power grid, public transport or freight trains. This backdoor allows an attacker to decrypt the communications and data transmitted by these radios, and possibly to modify or block them. The backdoor exists since the creation of the algorithm TEA1, in 1998, and cannot be corrected by a simple software update. The researchers managed to extract the secret key of the backdoor by analyzing the binary code of the radios.
- A weakness in the encryption algorithm TEA2, which is used in radios intended for professional mobile services, such as police, firefighters, emergency services, military or prison staff. This weakness allows an attacker to reduce the number of possible keys to test to decrypt the communications and data transmitted by these radios. The researchers estimated that it would take about 10 minutes to find the right key with a standard computer. This weakness was corrected by the manufacturers in 2016, but the radios that have not been updated remain vulnerable.
To find the backdoor in the TEA1 algorithm, the researchers used a technique called “differential analysis”, which consists of comparing the outputs of the algorithm for slightly different inputs. By observing the differences, they were able to identify a part of the code that was not normally used, but that was activated by a special condition. This condition was the presence of a secret key of 64 bits, which was hidden in the binary code of the radios. By analyzing the code, they were able to extract the secret key and test it on encrypted communications with the TEA1 algorithm. They were thus able to confirm that the secret key allowed to decrypt the communications without knowing the normal key of 80 bits. The researchers published their official report and the source code of the TETRA encryption algorithms on their website.
Source: https://cs.ru.nl/~cmeijer/publications/All_cops_are_broadcasting_TETRA_under_scrutiny.pdf
What are the risks for critical infrastructures?
The vulnerabilities identified in TETRA represent a danger for the critical infrastructures that use this technology, because they could be exploited by cybercriminals, terrorists or spies to disrupt or damage these infrastructures.
For example, an attacker could:
- listen to the communications and confidential data of the security or defense services
- impersonate an operator or a manager to give false instructions or orders
- modify or erase data or commands that control vital equipment, such as valves, switches, signals or brakes
- cause failures, accidents, fires or explosions
These scenarios could have dramatic consequences on the security, health, economy or environment of the countries concerned.
How to protect yourself from cyberattacks on TETRA?
The users of TETRA must be aware of the vulnerabilities of this technology and take measures to protect themselves from potential cyberattacks. Among the recommendations of the researchers, we can mention:
- check if the radios used are affected by the vulnerabilities and ask the manufacturers for correction solutions
- avoid using the algorithm TEA1, which contains the backdoor, and prefer safer algorithms, such as TEA3 or TEA4
- use encryption keys that are long and complex enough, and change them regularly
- set up verification and authentication procedures for communications and data
- monitor the radio traffic and detect anomalies or intrusion attempts
- raise awareness and train staff on cybersecurity and good practices
TETRA digital mode: how to transfer data via TETRA
TETRA (Terrestrial Trunked Radio) is a digital and secure radio communication standard used by emergency services, law enforcement, public transport and industries. TETRA uses a π/4-DQPSK phase modulation and a TDMA time division multiplexing to transmit voice and data on a bandwidth of 25 KHz per transmission channel. Each channel is divided into four timeslots, one of which is reserved for signaling in trunked mode (TMO).
TETRA allows file transfer via radio in two ways: by the packet data service (PDS) or by the circuit data service (CDS).
The PDS uses the IP protocol to transmit data packets on one or more timeslots. It offers a maximum throughput of 28.8 kbit/s per timeslot, or 86.4 kbit/s for three timeslots. The PDS can be used to send small files, such as images, text messages or forms.
The CDS uses the LAPD protocol to transmit data by circuit on a dedicated timeslot. It offers a constant throughput of 4.8 kbit/s per timeslot, or 19.2 kbit/s for four timeslots. The CDS can be used to send large files, such as documents, videos or maps.
The choice of the data service depends on the type of file, the size of the file, the quality of the radio link, the cost and the availability of radio resources. The PDS offers more flexibility and performance, but it requires a good signal quality and it can be more expensive in terms of battery consumption and spectrum occupation. The CDS offers more reliability and simplicity, but it requires a prior allocation of a timeslot and it can be slower and less efficient.
Securing TETRA file transfers with Freemindtronic’s EviCypher technology
However, both data services are subject to the TETRA security vulnerabilities that we have discussed in the previous sections. These vulnerabilities could allow an attacker to intercept, modify or corrupt the files transferred via TETRA, or to prevent their transmission altogether. Therefore, the users of TETRA must ensure the integrity and the confidentiality of the files they send or receive, by using encryption, verification and authentication methods. Freemindtronic’s EviCypher technology can be a valuable solution for encrypting data with post-quantum AES-256 from an NFC HSM with your own randomly generated keys before transferring them via TETRA. This way, even if an attacker corrupts the data transmitted by TETRA, they will not be able to decrypt the data encrypted by a product embedding
How to secure file transfers via TETRA with Freemindtronic’s EviCypher technology
La technologie EviCypher de Freemindtronic peut être une solution précieuse pour chiffrer les données avec AES-256 post-quantique à partir d’un HSM NFC avec vos propres clés générées aléatoirement avant de les transférer via TETRA. Ainsi, même si un attaquant corrompt les données transmises par TETRA, il ne pourra pas décrypter les données cryptées par un produit embarquant la technologie EviCypher NFC HSM technology, such as DataShielder NFC HSM or DataSielder Defense NFC HSM. These products are portable and autonomous devices that allow you to secure the access to computer systems, applications or online services, using the NFC as a means of authentication and encryption.
The management of encryption keys for TETRA
To use encryption on the TETRA network, you need an encryption key, which is a secret code of 80 bits, or 10 bytes. This key must be shared between the radios that want to communicate securely, and must be protected against theft, loss or compromise.
There are several methods to save and enter encryption keys for TETRA, depending on the type of radio and the level of security required. Here are some examples:
- The manual method: it consists of entering the encryption key using the keyboard of the radio, by typing the 10 bytes in hexadecimal form. This method is simple, but impractical and unsafe, because it requires to know the key by heart or to write it down on a support, which increases the risk of disclosure or error. For example, a 80-bit key could be 3A4F9C7B12E8D6F0.
- The automatic method: it consists of using an external device, such as a computer or a smart card, which generates and transfers the encryption key to the radio by a cable or a wireless link. This method is faster and more reliable, but it requires to have a compatible and secure device, and to connect it to the radio at each key change.
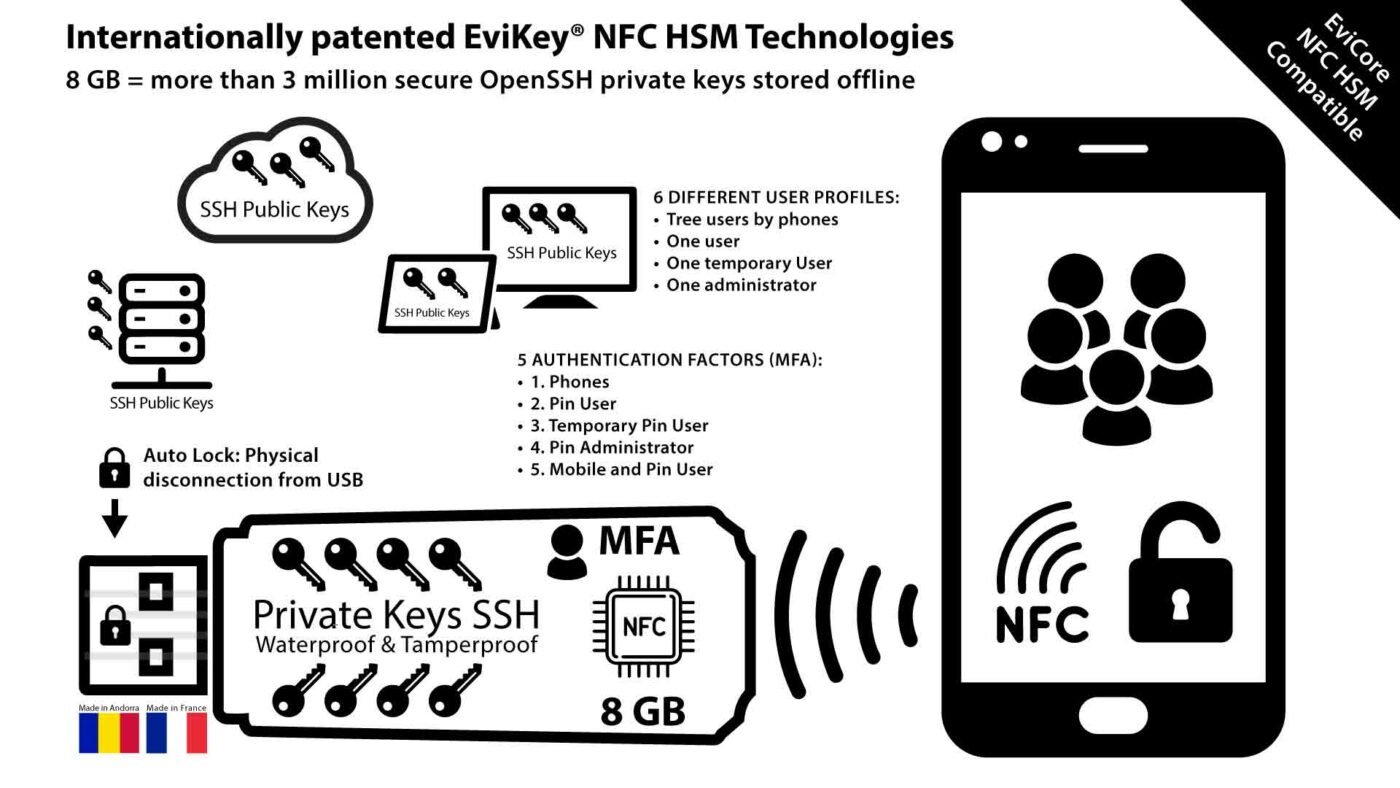
- The EviPass method: it consists of using the EviPass NFC HSM technology which allows to generate, store and manage keys and secrets in a secure and independent NFC HSM device. This method is the most innovative and secure, because it allows to create keys higher than 80 bits randomly in hexadecimal base 16, 58, 64 or 85, to store them in a physical device protected by an access code and a robust AES-256 post-quantum encryption algorithm, and to transfer them by various contactless means, via a computer. This method does not require to know or write down the key, which reduces the risk of disclosure or error. For example, a 10-byte key of 80 bits could be 3F 8A 6B 4C 9D 1E 7F 2A 5B 0C.
The EviPass NFC HSM technology of Freemindtronic allows to create secure gateways between the NFC devices and the computer systems, using advanced encryption protocols, such as AES, RSA or ECC. The EviPass NFC HSM technology is embedded in the PassCyber NFC HSM product, which is a portable and autonomous device that allows to secure the access to computer systems, applications or online or offligne services, using the NFC as a means of authentication.
Conclusion
TETRA is a radio technology that was designed to offer secure and reliable communication to professional mobile services and critical infrastructures. But this technology, which has been kept secret for decades, presents vulnerabilities that could be exploited by cyberattackers to compromise these communications and infrastructures. The users of TETRA must be vigilant and take measures to protect themselves from these threats, by updating their equipment, choosing robust encryption algorithms, using strong keys, verifying and authenticating data and monitoring radio traffic. The EviPass NFC HSM technology of Freemindtronic can be an effective solution to strengthen the security of keys and secrets used for verification and authentication, by storing them in a secure and independent NFC device. The researchers who revealed the vulnerabilities of TETRA hope that their work will contribute to improve the security of communications in critical domains.