The story of the first NFC hardened USB stick EviKey & EviDisk unlockable contactless
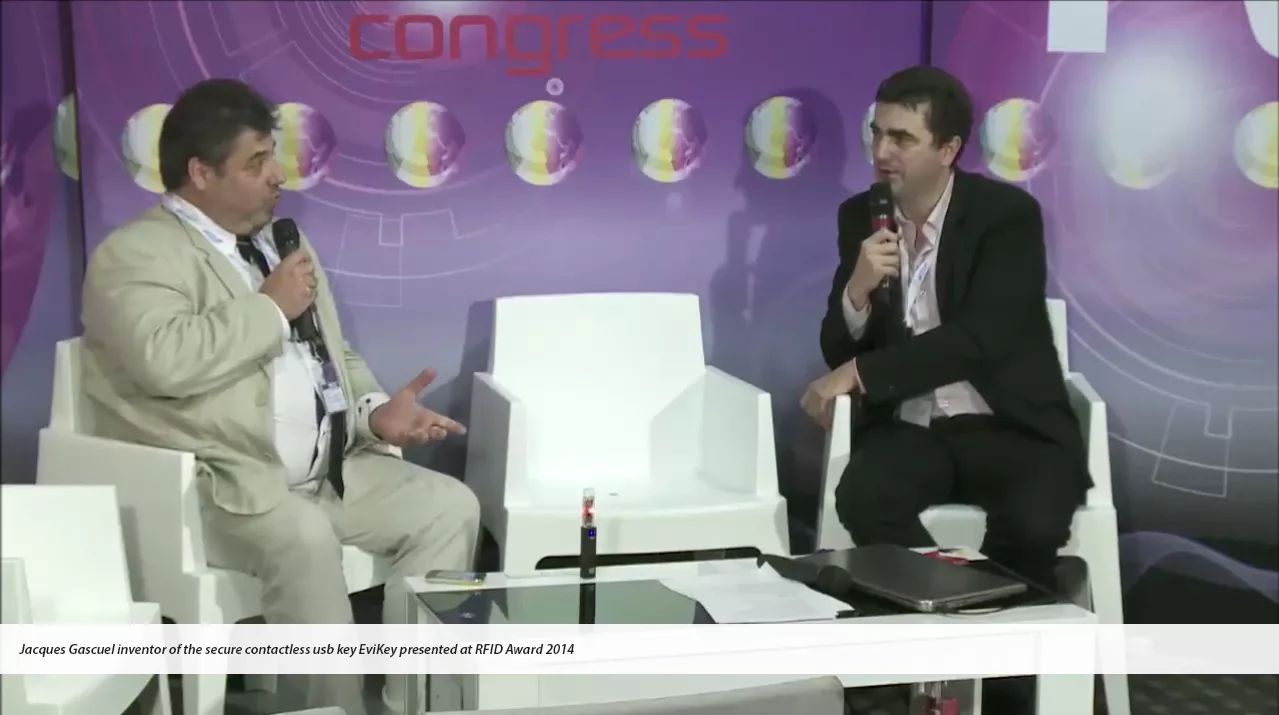
The story of the first NFC hardened USB stick EviKey that can be unlocked without contact and invisible computer systems begins with inventor Jacques Gascuel.
EviKey is a contactless USB stick which works via an NFC phone. It already has the principle of EviCypher technology. Indeed, it already carries a multi-criterion automated authentication system. It is the first physical multi-factor authentication (MFA) system that can be administered by an unfalsifiable black box.
Let’s start the story of the first contactless unlockable hardened USB stick created by the inventor, Jacques Gascuel [1]. He has implemented technology from his patented inventions internationally. For almost 10 years, he has been deeply convinced that the greatest risk will come from the hyperconnection of access controls and their centralization, under the guise of the public interest. That this risk will be all the greater when the burden of proof is reversed, so that user will be technically and financially unable to absolve himself of this legal responsibility.
The inventor includes in his reasoning for the design of electronic safes that there is a significant risk if the access control system is visible,such as a lockand/or keyboard and/or a screen and/or via software. That the best security in the world is human thinking, in contrast to other digitized biometric systems that can be corrupted. The password derived from human thought is becoming more and more complex to implement, due to the exponential increase in connected calculators. According to the inventor, it is necessary to design an augmented thought of man to oppose his own supercomputers.
A real challenge that the inventor will take up for several years to design electronic safes nomadic inviolable.
In the first phase of his research, he had to answer a first question. Is it possible to create real electronic safes for universal portable use without the use of data encryption? Can we create a universal, hyper-mobile security system that does not use an encryption system but only physical security in the sense of Cybersafety? A system, in fact, that can be used all over the world by people with no particular skill. A solution that is non-intrusive, for everyday use, always secure by default, that does not violate any of the rules of international law, and above all that allows to no longer expose man to the attainment of his physical and/or psychological integrity?
The inventor has entered into a disruptive reasoning of Cybersafety, as opposed to Cybersecurity solutions that refer to digital safes. The inventor believes that Cybersecurity is the physical security of Cybersecurity, which is digital. The inventor, a graduate in industrial electrical engineering, will base his research on the implementation of Cybernetic solutions. How can this physical security approach based on industrial normative elements such as ISA/IEC 62443 mitigate or even prevent an intrusive or non-intrusive cyberattack? The first lead was the implementation of its international patent FullProtect WO/2010/086552, a device to monitor and protect the power and/or environment of an electrical device, equipped with a black box. An invention that allows, in particular, to establish, by physical evidence, the implementation of the criteria MTTF, MTBF, MTTR and establish the TDM index . To learn more about the features and added values of an electronic safe click HERE.
The inventor’s idea is to find a way to prevent, or greatly limit, the possibility of calculating machines. The inventor imagines an autonomous, unconnected electronic safe that uses various physical, analog, logical, digital, use and legal factors that combined make it extremely complicated, computing by the machine. This will require a physical brute force attack on this electronic safe.
The inventor then designed the first MFA Offline Cyber-sterity system to assist man and allow him to defend himself against his own quantum calculators.
We will tell you the story of the birth of the electronic safe of inventor Jacques Gascuel.
The inventor assumes that the only indisputable, and undisputed, way to secure access controls is that they are never connected and totally autonomous, under the control of the man and/or the legal person.
Such an implementation would make a physically remote attack physically impossible. It talks about the principle of the physical electronic safe unconnected MFA, which implies a proximity to open the door of the electronic safe. According to the very principle of an electronic safe, this system must form a block, without any door other than that locked by an access control, via a code defined by the user. The problem of user authentication remained, and thus the use of the code illegally.
This involved designing an unconnected system, capable of providing a set of factors that would establish the near certainty that it is indeed the user and/or a rightful person.
This risk is increased if this access control is connected to a computer system and/or connected to a local server and/or remote with databases. This is a major breach to carry out attacks via the computer systems where it is connected. This risk increases significantly when access control codes are contained in computer systems and/or remote databases. We all know that they are regularly attacked because they are always accessible from a distance.
The birth of the principle of material invisibility as a physical security component of Cybersecurity
The inventor is aware that the impossibility criterion is a bold claim to be implemented in Cybersecurity. However, if it adds physical security, the foundation of Cybersafety, it makes the solution physically invisible, undetectable and untraceable. Making a physically invisible electronic safe of computer systems has become the preferred focus of the inventor’s research and development.
The term impossibility can legitimately be used, within the limits of the state of the art. Similarly, the inventor considers cyber deterrence to be part of the impossibility factor, especially when the brute force attack means implemented are disproportionate to the interest of the attack. The inventor includes the psychological aspect, …. Doubt! Indeed, consider an attacker who has no certainty of finding the coveted data because it is not directly visible, this will generate a doubt strong enough to be a deterrent. According to this approach, the attacker is also not certain whether the time it will take will not exceed the time it would take the owner of this data to make it obsolete, and therefore worthless for the attacker. The inventor therefore includes doubt as a factor of Cyber Dissuasion in the implementation of the Cybersafety of his electronic safe.
The inventor believes that the absolute security of information systems must be two-headed in the sense that Cybersecurity is the digital component of physical security.
Cybersûreté VS Cybersécurité
Cybersecurity is the physical security in contrast to Cybersecurity which is digital security. This is an approach rarely taken into account in information systems engineering that considers it legitimate that Cybersecurity is outside the realm of Cybersecurity. However, experts in these two spheres of safety agree that the complementarity between safety and security is unquestionably complementary in order to prevent the risk of accidents and/or malicious acts.
Even on the margins in the development of specifications or in the offer of Cybersecurity solutions products and services, Cybersecurity is now essential as digital systems are networked. We are in the era of “hyper-connected.” Cybersafety according to the inventor must also be taken into account from the outset in terms of risk management as defined by various ISO/DIS 34001 (SMS), CNPP 1302 [FR], ISO/IEC 27032 (digital security), ISO/IEC 27001 (SMSI), ISO/IEC 29100, CENELEC 50131-1, 50133-1, 50134-1, 50136-1, 50518-1, IEC 60839-11 [series]. A recurring divide on the interpretation of standards, specifically in their translations of English into French; the word “Security” has been translated as “security” instead of “security” in the sense of physical security. This contributes to the marginalization of the consideration of Cybersafety, and consequently, the distinction between digital safe and electronic safe.
The implementation of the electronic safe has created technological locks to be lifted
How to design a physically invisible access control, totally autonomous in electrical energy, disconnected from computer systems, disconnected from any type of network? The inventor’s idea is to design a system that is physically isolated from computer systems. It seems impossible to attack what doesn’t physically exist, either remotely or nearby.
How can this approach be implemented?
To implement the theory of invisibility, it was necessary to be able to oppose an intrusive and/or non-intrusive brute force attack. The inventor had to find a way to resist physical attacks, especially on the electronics of access control, without reducing the speed of data transfer on the USB port and SATA. The inventor then devised an electronic system with many countermeasures against physical attacks. It is a system that locks access to the contents of the memories, permanently depending on the level of attack detected. The inventor finds a patented, military-grade resin to coat all the electronics, leaving only the USB or SATA connectors. Hardened to the extreme, close to steel, the electronic safe is now equipped with a shell capable of withstanding various mechanical stresses of several tons, thermal or acidic. Attempting to remove the shell is taking the risk of triggering the countermeasures, but also of irreversibly destroying the memories.
Hardening the electronic safe has spawned other technological locks
The complete coating of the electronic card makes it impossible to repair in case of electrical, thermal, component or assembly defects. This makes it very complex to diagnose the origin of the defect automatically, and be able to access from the outside, without going through the USB and SATA connectors. This is where the Fullprotect invention comes into play, an intelligent asymmetrical circuit breaker with a black box that traces any type of electrical, environmental and/or use event. This electronic safe is then equipped with a system of electric multi-protections by automatic galvanic insulation on the power supply, with electrostatic protection on the exchange of data via the USB port or SATA, making the whole resistant to surges. Another three-point thermal environment self-protection device is capable of self-locking the electronic safe, when the temperature is above 70 degrees.
These electronic devices are coupled with the Cybersafety system, which has several advantages. The controlled galvanic insulation protects electrical hazards and insulates it from computer systems, making the electronic safe undetectable. An intelligent maintenance system is then embedded in the system. Its mission is to prevent the electronic safe from being used in temperatures that could damage the electronics. The same device is also used to detect a thermal brute force attack on three points. This type of physical intrusive brute force attack involves exceeding the thermal resistance by more than 220oC. Such an attack will in fact result in the destruction of electronic components, especially memory, irreversibly. Thanks to the implementation of the Fullprotect invention in these electronic chests, an unfalsifiable black box is present to preserve the various traces of these events and constitute an opposable physical proof.
How do I lift the MFA’s energy autonomy locks?
For the inventor, one last important problem remained to be solved: how, without a source of electrical energy, without using the electrical energy provided by the USB or SATA port, physically administer the access control through the coating and the case?
The solution found by the inventor is THAT of STMicroelectronics’ NFC technology in industrial version, NFC ISO/IEC 15693, which runs without battery, powered via a NFC-enabled Android-enabled computer (Smartphone). In addition, this component incorporates the recovery of energy capable of powering on-board subsystems, including the access control system. These industrial components have many other advantages. They have electronically secure non-volatile memory that can hold stored data for at least 40 years without an electrical source. They also allow 1 million cycles of writing per memory block, without error.
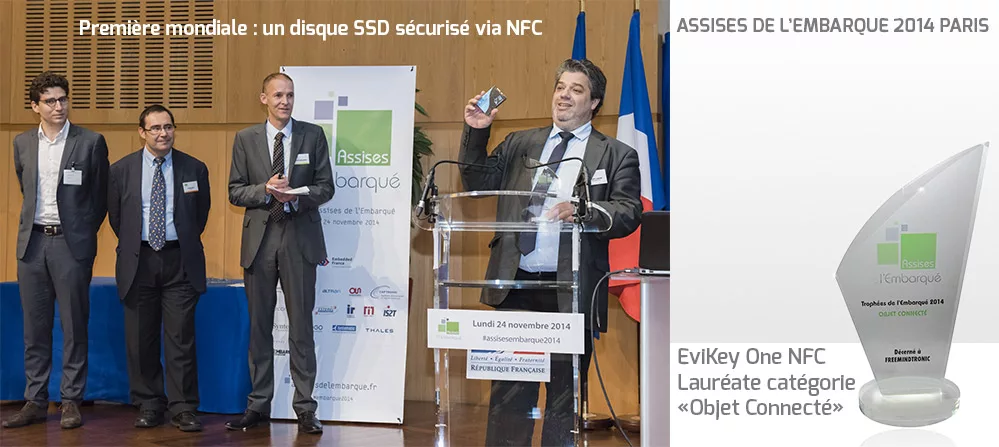
The mobile contactless electronic safes with black box were created under the technological name EviKey One NFC and EviDisk One NFC, under the trademarks of the inventor, EviKey® for the USB stick and EviDisk® for the 2.5-inch 7mm Sata III SSD.
But, beyond being able to dynamically carry out all types of actions via contactless technology, a new problem has beenborn, the Cybersecurity of the use of electronic safes. Indeed, it is necessary to have an Android/NFC smartphone to use the electronic safe. However, the smartphone is connected to it, thus exposed to the risk of remote attacks and/or proximity on the exchange of data via the NFC signal.
The Evikey NFC solution receives the 2014-2015 “Connected Object” Package with its Physical Cybersafety technology in a USB stick on November 24, 2014 in Paris Bercy. This innovation is twice nominated for the Boarding Assises: “critical on-board system” and “connected object.” This National Trophy recognizes the connected object project that has provided the most innovative service to the general public or professionals.
Paris Bercy 2014 : https://www.entreprises.gouv.fr/numerique/trophees-embarque-2014 (this page has been removed https://www.entreprises.gouv.fr)
The “Assises de l’Embarqué.fr: http://www.assisesdelembarque.fr/trophees-de-lembarque/trophees-de-lembarque-2014
Captronic : https://www.captronic.fr/Les-laureats-des-Trophees-de-l-embarque-2014.html
Electronic Press (http://www.electroniques.biz):
Embedded Trophies 2014: six companies rewarded for their innovations
lembarque.com : Freemindtronic EviKey Evidisk won the 2014 Embedded Technology Awards
The inventor had to find other systems to increase the Cybersecurity and “Cybersecurity” of MFA access control for its mobile electronic safes
The various problems to be solved are known and bring up technological locks. How do I protect the access control of an attack from the smartphone? How to identify the hardware used and authenticate the right or user to unlock the electronic safe, knowing that the smartphone is connected and can be very easily corrupted? How do I detect a brute force attack on the NFC? How can I prevent listening to the NFC signal to pick up the information? How can you physically prevent a malicious person or robot from accessing the electronic safe? How do I prevent a keylogger-type attack? How can I prevent the code from being entered on the smartphone screen? How do I limit the number of code tests, even in unlocked mode? How do I identify the electronic safe in a no-use area? How to give the illusion that the electronic safe is broken? How can the electronic safe be used on a daily basis without the burden of security or even the cause of a loss of productivity? How do you detect the end of the use of the electronic safe without having access to the data flow? How do you systematically lock the electronic safe without taking the risk of damaging the data? How do you give up a passcode that you think is corrupt? How do I create a temporary passcode? How do you put all the information back from the black box to serve as physical evidence? How do you simply plot the geolocation of the use of the passcode and the type of code used? How do I notify the user, even if the electronic system fails, the origin of the malfunction? How do I tell the user how long it will take to use memory without error? How can we ensure that the electronic safe is never obsolescent in time? Finally, could this solution save a life?
The inventor has found an answer to all these and many other questions, thanks to another of his patents, Fullsecure[2] , a stand-alone wireless access control system.
One of the most important challenges remained, the simplicity of use
The inventor’s goal is to offer individual, self-secure, unconnected, obsolescence-free, always accessible, extremely accessible, mobile, very simple to use on a daily basis, for personal and/or professional use, without financial commitment, without a license, multi-station, untraceable and undetectable.
He wanted to offer his owner the least intrusive electronic safe in the world, without drivers and software to install in his computer. An electronic safe compatible with all Windows, Linux, iOS, Raspbian, OS2, Android (OTG) operating systems that use a USB port.
A hardened electronic safe designed to last until the natural end of the components’ life. Multi-protection systems against electrical, electrostatic, thermal, mechanical, immersion in liquid, dust, ultraviolet light, heat source, magnetic field, X-rays.
An electronic safe with a black box that tells the user, in real time, the state of its physical functioning, capable of self-diagnosis and informing the user of the origin of the defect.
The freedom to adapt the level of security of these electronic safes to suit exposure to risk
A system freely set up by the user, via an administrator password, allows you to choose how to unlock the electronic safe. It can also be used in unlocked mode. In the latter case, the user uses his electronic safe in an environment where he feels there is no risk. It uses its EviKey® or EviDisk® as a standard USB stick or SSD.
How do you make Cybersafety non-binding for the user to avoid being tempted or forced to use another unsecured system?
The inventor believes that the use of safety, when it is binding, generates counter-productivity and is naturally circumvented by man. In fact, the inventor has planned different scenarios that allow the man to change the unlock mode very easily. Man is therefore empowered to adapt the level of security of his electronic safe according to his exposure to risks. When the risk is zero, the man must be able to leave the electronic safe always unlocked. This point eliminates the risk of counter-productivity. This mode allows the man to have the comfort of using a standard USB stick or external disk.
A free mode of Cybersafety by use control
The mere fact that the electronic safe is permanently unlocked creates a risk to the use, because the contents of the electronic safe are always exposed, especially when the sensitive data is not encrypted. The inventor therefore took into account this problem of exposure to the risk of connected data via a removable medium. The right balance had to be struck between safety and comfort of use.
A major constraint for the inventor: the inability to access the fully deconstructive data flow of the MFA access control system and the absence of a battery excluding the use of a clock.
The inventor’s idea was the implementation of a timer in correlation with the Cybersafety system and the black box. The user defines a time, in seconds, during which the Cybersafety system counts, via Fullprotect’s electrical analysis device, the data flow. Thus, when the countdown is reached, the electronic vault is auto-locked and the data stream is inactive.
Thanks to this method, the inventor found the right balance in usage. A system that detects when the electronic safe is not used to self-lock. It is the user who defines how long the electronic safe remains unlocked. The user will need to identify himself to unlock the electronic safe.
With this feature, the user can adjust the use of the electronic safe to his environment, while maintaining a level of self-safety over time. A time that is automatically interrupted when the electronic safe is disconnected from the USB or SATA port. In the same way if the power of the USB or SATA port is disabled by the computer system.
Let’s discover the different ways of unlocking these electronic safes designed by the inventor
A mode that requires the entry of a password to unlock the electronicsafe. A proprietary secure keyboard is used with randomly changing keys, which has the effect of combating malware that records key inputs to the Keylogger type keyboard. This system also helps to limit the risk of visual corruption when entering the password (a person looking over your shoulder for example). Indeed, it is very complex to remember the order of keys that change randomly. In addition, this system allows you to participate in the authentication of a person.
Another mode allows you to unlock the electronic safe without the need to enter the password. After recording the identity of their smartphone in the electronic safe (pairing procedure), the user can unlock it by simply presenting his smartphone to the electronic safe, without contact. The user has the ability to register up to three smartphones.
These two modes can be used interchangeably, this has some advantages. Consider two users, one has knowledge of the password and the other does not. But the latter can unlock the electronic safe with his NFC smartphone, without entering the password.
This is a convenience to avoid having to enter a password or to manage two user profiles, one of which uses only the password. However, this comfort does not cover the risk when the smartphone and electronic safe are stolen or lost together. The electronic safe can then be unlocked without the need to enter the password. To cover this risk, the inventor has planned a multi-factor mode that includes three elements: the pairing key, the smartphone’s identity and the password; the concept of a simplified physical blockchain was born.
The safety of using the electronic safe
Let’s imagine a user on the move, which implies that the level of risk is very high. It must be able to choose the highest and, indeed, most restrictive mode of security. The user leaves the comfort of unlocking with his smartphone without a password, to include a multi-factor control chain in case of theft and/or loss of the electronic safe and/or his smartphone. In case of theft or loss of the electronic safe, the malicious person will have to guess the pairing key, the identity of the paired smartphone and the password. Knowing that after 3 unsuccessful tests, the electronic safe is temporarily blocked and that the maximum allowed test is 13 before a permanent blockage.
Cybersafety against the violation of human physical and/or psychological integrity
The inventor asked himself about the risk of an attack on the physical and/or psychological integrity of an electronic safe user in order to obtain the password?
The inventor’s idea was that the electronic safe must have an advanced system of administration and user management, permanent or temporary. The administrator of the electronic safe has the option to assign a specific passcode to the user of the electronic safe, without him being able to know the administrator password.
The emergency feature called “user password forgetlessness” is born, which allows a user to delete their password. This emergency system can be activated at any time, very quickly, if it feels that its password is corrupt or that it can be corrupted. In fact, only the administrator will be able to recreate a new user password. This is the birth of the physical blockchain simplified by use. A disruptive approach to the use of oblivion in the value chain of Cybersafety as a physical barrier. This protects the physical and/or psychological integrity of the man vis-à-vis an attacker who wishes to obtain the user’s password against his consent.
Imagine an investigative journalist who goes on a mission abroad to interrogate opponents of a dictatorial regime. The information collected by the journalist is digitally housed in the electronic vault. Such information may impair the physical integrity of the interviewees or the journalist. How can the journalist resist a physical and psychological constraint not to give the password to access the electronic safe? The inventor has found a solution! If the user no longer has access to the password because he has voluntarily abandoned it, and this fact is known to the attacker, it will be useless to try to obtain from the user the administrator password that he never knew about. Only the editor (administrator) has the power to unlock the electronic safe. This does not remove the risk that the attacker will remotely pressure the editor to obtain the admin password. However, the objective is achieved, the one where the attacker has no interest in attacking the journalist. And at the same time, the digital data in the electronic safe remains locked in access. The attacker will have to be able to force the electronic safe to access the data it contains.
This case demonstrates the clear role of the importance of cybersecurity vis-à-vis Cybersecurity, the first flaw of which would be humans. On closer inspection, the inventor’s innovations put man at the center of his own enhanced security in the face of malicious attacks by man or his machines.
Cybersafety by physical silos
The inventor performed a physical silo of the rights holders, i.e., an administrator profile and user profiles, indeterminate or limited-time. There is talk of an additional factor to unlock the electronic safe, so as to block any attempt to pair the electronic safe with another smartphone. The power of Cybersafety makes it physically impossible to simply connect with the electronic safe without the pairing key. Even if the pairing key is corrupted, you also need to know the administrator and/or user password to unlock the electronic safe.
The traceability of events by unfalsifiable embedded black box, accessible without contact via the smartphone
The inventor took into account the burden of physical proof in the legal sense of the term, capable of opposing other forms of evidence constituted in a numerical way; which can be manipulated. This is one of the aspects claimed in the internationally extended Fullprotect patent.
Thus, the inventor has integrated in his electronic safe a black box that traces all types of events, which depending on their importance are recorded, such as an attempt to attack physical or digital brute force.
Such a recording in the black box of the electronic safe is not without consequences in the implementation of countermeasures imagined by the inventor whose secrets he does not reveal.
The most extreme consequence is to render the electronic safe irreversibly unusable.
Intrusive and non-intrusive brute force countermeasures
The inventor considered several aspects of brute force attack targeting cyber safety.
Dismissing non-intrusive brute force attacks was quick. It was more complex for the physical attacks of the man of the trade, the electronics engineer.
With regard to non-intrusive attack, the inventor excluded the use of encryption systems in the implementation of Cybersafety, rendering it unnecessary to use thermal, magnetic, electrical, electromagnetic or radio frequency analysis to try to guess the encryption system used. Indeed, the security system is completely independent of the digital support of the electronic vault where digital data is stored. This system is completely autonomous in electrical energy, without battery, and has only one input and exit, the industrial NFC system. This excludes all these forms of brute force attacks.
Remains the physical brute force attack that involves being in contact with the electronics of the electronic safe. An extremely strong resin and very sticky to the components makes it very dangerous to remove the resin without irreversibly damaging the electronic system, especially the memory. Traps have been built to detect intrusions and cause the electronic safe to be permanently locked through the black box.
The digital brute force attack remained to unlock or activate denial of services. The inventor also predicted these cases of species.
All these attempts are managed and activate countermeasures that block this type of attempt.
In the case of a robotic attack the attacker must create algorithms that take into account random physical variables related to physical elements specific to the electronic components used. This makes it almost impossible to create an algorithm capable of guessing these time factors, some of which are variables derived from random physical elements that depend on various thermal, electrical and usage factors.
To maintain a known use of the public, the inventor uses a system used for bank cards or SIM cards of phones.
In this case, three tests (PIN and/or mobile) are authorized to unlock the electronic safe.
After 3 unsuccessful attempts, access is blocked for 15 minutes. The event is recorded in the black box that activates the light signaling of the electronic safe (two green and blue LEDs flash alternately).
The inventor added the requirement to leave the electronic safe connected to the USB or SATA port during the locking period. Any disconnection involves reseating the countdown. This forces the attacker to leave the robot connected to the key. The Cybersafety system has a very precise electrical analysis system; any positive or negative change results in the meter being reset.
After these first 15 minutes it is possible to try again. If the entered password is correct, the electronic safe unlocks and the test counter is reset. The event is kept in the black box. If the PIN or mobile is not correct, the electronic safe is blocked again for 30 minutes this time. With each new error, the delay is multiplied by 2.
This implementation, conceived by the inventor, was intended to deter an attacker from generating a denial of services, i.e., to prevent the user of the electronic safe from using it permanently.
Thus, the attacker will have to wait a few months to be able to seize the 13th unsuccessful test, and thus make the electronic safe permanently locked.
Visionary the cyber-safety of these electronic safes in the service of BYOD, CYOD, COPE already compatible before the birth of the RGPD
Meaning BYOD acronyms “Bring Your Personal Device,” CYOD “Choose Your Company-Approved Personal Device,” COPE “your personal device purchased by the company.”
10 years earlier, the visionary inventor took into account the problem of the use of private equipment for professional use, which posed a problem related to the privacy of mobile data of various origins, both private and professional or computer systems.
BYOD, CYOD and COP are not framed in the same way at the legal level, which complicates the implementation of the security charter in a company, especially on mobile data such as USB sticks and external discs connected via a USB port. The latter poses a greater risk due to the memory capacity of several terra Bytes.
The use of data encryption is recognized as the only way to secure the data. But the reality is different in the use and security of passwords, encryption keys and/or decryption.
The inventor knows that in everyday use, the complexity of implementing a trusted encryption system is time-consuming, which reduces productivity. In fact, humans bypass the problem by using the unsecured BYOD to transport sensitive data. Similarly, the password entered to decrypt may be corrupted by various brute force attack and/or espionage.
The inventor wonders how to ensure that the Cybersafety system is able to independently cover all these risks? To solve this problem, first, he splits the types of uses into two: an individual use that he identifies as “Premium” and a collective use that he identifies as “Pro”.
Then he comes to the conclusion that the electronic safe is upstream of the backup of the mobile or fixed data, making it a common core. Thus, the mere fact that the principle of the operation of the electronic safe is closed by default and that a password is required to access the data, whether encrypted or not, constitutes a common physical barrier to all these uses. In fact, it is enough to manage the type of use and their use rights.
The professional version was born, which has a separate administration system for users of the electronic safe and an individual version whose administrator is also the sole user.
In case of loss or theft, the electronic safe is always locked which prevents access to the data it contains whether it is private or professional.
Thus, regardless of the choice of the company, CYOD, BYOD or COPE, the inventor’s electronic safes are legitimately compatible with the rules of law in force, notably with the RGPD and the decree 2018-418 of May 19, 2018 coming into force on January 1, 2019. (See on LinkedIn the article of June 13, 2018 https://www.linkedin.com/pulse/pourquoi-les-coffres-forts-%C3%A9lecttronics-nfc-offline-de-gascuel)
As part of a COPE use, the company has a function that allows it to administer a profile of the use of the electronic safe that is required of the permanent and/or temporary user. The black box traceability, allows the administrator to have a history of use, some of which are geo-located.
A 100% stealth mode can be activated by disabling LEDs. In fact, the locked electronic safe, undetectable computer systems, simulates the symptoms of a USB stick that doesn’t work. Similarly, the extinction of LEDs makes it possible not to visually indicate that readings or writings are carried out with the electronic safe. Conversely, the choice of colors, and/or the extinction of one of the LEDs, makes it possible to identify the electronic safe among others. This mode is also convenient for viewing the use of an electronic safe in a prohibited or authorized area. Let’s take the example of an entire service that uses keys whose LED flashes pink when writing or reading data, if the manager sees a key flashing yellow, he will know that this key is an intruder.
The inventor aware of the problems related to the use of USB sticks and external discs in the company has provided a concrete response with the use of his electronic safes.
It was up to the inventor to lift the last locks! How can we make the connection to electronic safes universal to any type of computer system?
Finally, the inventor had to find a way to be as intrusive as possible, when the electronic vault is connected to a particularly professional computer system that prevents the installation of unauthorized software by the information systems manager.
This problem was naturally solved when the separation of the security system and the non-volatile physical memory where the data is housed was implemented.
Indeed, since the security of the electronic safe is separated from the support, there is no need to secure the USB port or the SATA of the SSD disk, so there is no need to install security software on a computer system. In fact, all computer systems that use a USB or SATA port are immediately compatible with safes. No need for drivers or software to install for these electronic safes. This allows to respect the security constraints imposed by the company, while remaining under the control of the user.
The inventor, perfectionist, uses the speed of analog electronics systems to secure the operation of Android applications
The inventor designed two separate applications that work in the volatile memory of the NFC smartphone. FullKey NFC for EviKey NFC Pro and EviDisk NFC Pro and FullKey NFC Premium for EviKey NFC Premium and EviDisk NFC Premium. The inventor used the extreme speed of analog systems and radio frequency to exchange passwords to unlock these safes. This is a machine-to-machine (M2M) transfer between the smartphone’s NFC and the electronic safe NFC.
An intelligent physical cyber safety system is implemented at various points in electronic design to combat brute force attacks that seek to copy the weft of a radio wave produced by the NFC signal:
- a steering branch,
- an energy recovery management system,
- A single peer-to-peer NFC hooking system by pairing key,
- self-locking electronic vault memories on data exchange,
- analysis of the electrical energy recovered by the smartphone’s NFC signal,
- management of the speed of data transfer on NFC signal,
This listening is extremely complex to achieve because of the proximity that must exist between the smartphone and the electronic safe and the fact that the exchange of data is impulse and totally random.
Offline e-mail safes
The inventor had an unstoppable idea to fight against listening to the NFC signal! Desynchronization when unlocking the electronic safe. It adds a new variable: the unpredictable! In fact, the user can unlock his electronic safe without needing to be connected to a USB or SATA port. In fact, an attacker cannot use a computer system and/or power source as a cue to perform his listening. This effectively excludes the use of espionage. Indeed, the unlocking can be carried out anywhere, anytime, in any situation (even underwater), it physically stops any attempt to listen to the NFC signal from the inventor’s electronic safe.
Cybersecurity of Fullkey NFC Pro and Premium applications
The inventor has no confidence in the resilience of a brute force attack on applications developed on Android. In fact, it has taken into consideration immediately in its innovations that its applications can be corrupted in seconds by experts. In fact, he designs applications with a relisence criterion equal to ZERO. Thus, if the application is corrupted, no sensitive information can be used to successfully unlock the electronic safe.
The finding of the implementation of Cybersecurity for the benefit of cybersecurity of electronic safes
The mere fact of not being able to connect to the electronic safe without a pairing key is enough to establish that the inventor’s electronic safe meets all the criteria of Cyber safety.
The simple fact of not being able to unlock the electronic safe without a password, and the fact that the passwords are physically in electronics, it is also not possible to establish a connection with the electronic safe.
The inventor goes all the way to the end of the reasoning of cybersafety by black box: an on-board after-sales service and the management of obsolescence
Obviously, no doubt, never has a USB stick or an SSD been able to inform their user in real time of any type of events, including brute force attacks and to self-diagnose the state of operation of the electronic safe as well as the origin of an electronic, environmental, embedded system, use and attack intrusive or non-intrusive brute force.
Of course, all this will be true, until Jacques Gascuel’s patents fall into the public domain.
Finally, the black box allows the manufacturer, as well as the user, to know the origin of the anomalies, but not only. A flash memory usage counter is built in to estimate the risk of writing or reading errors. The aim is for the inventor to give the user the opportunity to have a trusted benchmark on his ability to retain information without error in the electronic safe. Indeed, flash memories have all the natural wear and tear due to writing that includes data erasure. This is an approximation that varies according to the memories used in the manufacture of electronic safes.
About the company
Jacques Gascuel’s patents are managed by Freemindtronic SL in Andorra.
Electronic safes are currently manufactured in France under an exclusive manufacturing and distribution license for France awarded to the SYSELEC Group in Occitanie (France).
These NFC hardened USB stick EviKey ® and NFC hardened SSD EviDisk® electronic safes are available from Freemindtronic partner’s.
You want to know more about how it works, you can view the usage guides
Fullkey Plus Android app from Freemindtronic Andorra: https://youtu.be/ckIc7PwedaE
You can also use secret keepers with EviCypher technology to manage and unlock EviKey USB sticks and EviDisk SSDs. Automatically administer and manage your pairing keys, administrator, user and guest passwords.
[1] Jacques Gascuel owns various patents. The PATENT WO/2010/086552 published internationally since 2010 for the technology called Fullprotect, a monitoring and protection device for power and/or environmental of an electrical device equipped with an unfalsifiable black box device. And the 2017/129887 WO/2017 patent for the technology called Fullsecure, a wireless electronic access control device with multi-factors of authentication.
[2] Patent called Fullsecure NO. WO/2017/129887 published in 2017 for the technology called Fullsecure, a wireless electronic access control device with multi-factors of administrative authentication.