Russian cyberattack on Microsoft by Midnight Blizzard (APT29) highlights the strategic risks to digital sovereignty. Discover how the group exploited password spraying, malicious OAuth applications, and legacy exposure — and the sovereign countermeasures offered by DataShielder and PassCypher.
Executive Summary — APT28 spear-phishing in Europe
⚡ Objective
Understand how APT28 spear-phishing campaigns exploit Outlook VBA macro phishing, the NotDoor backdoor, DLL side-loading via OneDrive.exe, and HeadLace loaders to achieve stealth access, data theft, and lateral movement across European infrastructures.
💥 Scope
Targets include French ministries, NATO-linked entities, critical infrastructure operators, research centers, BITD companies, and organizers of the Paris 2024 Olympics. The focus: Outlook-centric intrusion chains and their detection through behavioral monitoring.
🔑 Doctrine
APT28 favors short-lived, stealthy intrusions. Defenders must enforce Outlook hardening, disable macros, monitor anomalous OUTLOOK.EXE child processes and OneDrive.exe DLL loads, and inspect encrypted mail flows (e.g., Proton Mail covert exfiltration). Sovereign encryption HSMs ensure end-to-end protection.
🌍 Strategic Differentiator
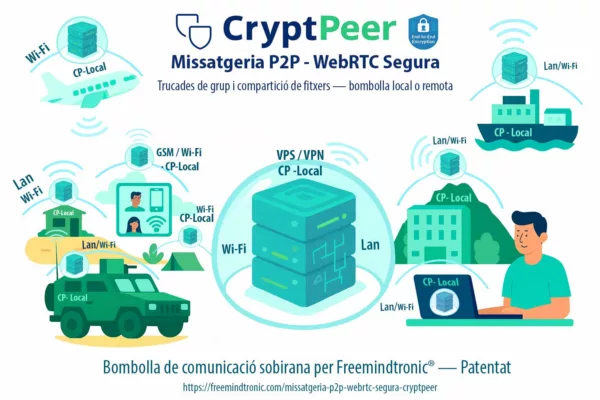
Unlike cloud MFA or purely software-based solutions, DataShielder and PassCypher adopt a zero cloud, zero disk, zero DOM posture: offline encapsulation, volatile-memory decryption only, and offline credential custody.
Result ⮞ resilient spear-phishing defense, neutralization of Outlook backdoor channels, and data sovereignty across the European cyber landscape.
Technical Note
Reading time (summary): ≈ 4 minutes
Reading time (full): ≈ 30 minutes
Level: Cyber threat intelligence / SecOps
Posture: Behavior-first detection, sovereign authentication
Category: Digital Security
Available languages: FR · EN · CAT · ES
Editorial type: Chronicle
About the author: Jacques Gascuel — Inventor of Freemindtronic®, specialist in sovereign HSM architectures, offline key segmentation, and resilient communication security. He develops dual-use encryption technologies (civil/military) officially recognized in Europe, and publishes strategic chronicles on APT cyber-espionage and digital sovereignty.

This chronicle belongs to the Digital Security section and contributes to Freemindtronic’s sovereign operational toolbox (HSM, offline segmentation, resilient communication).
- Executive Summary — APT28 spear-phishing
- APT28 spear-phishing France: a persistent pan-European threat
- Other APT28 campaigns between CVE-2023-23397 and NotDoor
- Historical Context: The Evolution of APT28
- Priority targets for APT28 spear-phishing campaigns
- Spear-phishing and electoral destabilization in Europe
- NotDoor: Outlook backdoor
- APT28 malware matrix
- ANSSI’s operational recommendations
- Regulatory framework: French response
- Sovereign solutions: DataShielder & PassCypher
- Threat coverage: PassCypher & DataShielder
- Towards a European cyber-resilience strategy
- Evolution of APT28 spear-phishing campaigns (2014–2025)
- Sovereign Use Case — Outlook backdoor neutralized
- Official Report — CERTFR-2025-CTI-006
- What We Didn’t Cover — Next chapters
- Weak Signals — Trends to watch
APT28 spear-phishing France: a persistent pan-European threat
APT28 spear-phishing France now represents a critical digital security challenge on a European scale. Since 2021, several European states, including France, have faced an unprecedented intensification of spear-phishing campaigns conducted by APT28, a state-sponsored cyber-espionage group affiliated with Russia’s GRU. Also known as Fancy Bear, Sednit, or Sofacy, APT28 targets ministries, regional governments, defense industries, strategic research institutions, critical infrastructure, and organizations involved with the Paris 2024 Olympic Games. This analysis details an APT28 Outlook backdoor pathway and defensive countermeasures.
In a tense geopolitical context across Europe, APT28’s tactics are evolving toward stealthy, non-persistent attacks using malware like HeadLace and exploiting zero-day vulnerabilities such as CVE-2023-23397 in Microsoft Outlook. This vulnerability, detailed in a CERT-FR alert (CERTFR-2023-ALE-002), allows an attacker to retrieve the Net-NTLMv2 hash, potentially for privilege escalation. It is actively exploited in targeted attacks and requires no user interaction, being triggered by sending a specially crafted email with a malicious UNC link. This trend mirrors tactics used by APT44, explored in this article on QR code phishing, underscoring the need for sovereign hardware-based tools like DataShielder and PassCypher. European CISOs are encouraged to incorporate these attack patterns into their threat maps.
Historical Context: The Evolution of APT28
APT28 (Fancy Bear) has been active since at least 2004, operating as a state-sponsored cyber-espionage group linked to Russia’s GRU. However, its most heavily documented and globally recognized operations emerged from 2014 onward. That year marks a strategic shift, where APT28 adopted more aggressive, high-visibility tactics using advanced spear-phishing techniques and zero-day exploits.
Between 2008 and 2016, the group targeted several major geopolitical institutions, including:
• The Georgian Ministry of Defense (2008)
• NATO, the White House, and EU agencies (2014)
• The U.S. presidential election campaign (2016)
This period also saw extensive exposure of APT28 by cybersecurity firms such as FireEye and CrowdStrike, which highlighted the group’s growing sophistication and its use of malicious Word documents (maldocs), cloud-based command-and-control (C2) relays, and coordinated influence operations.
These earlier campaigns laid the foundation for APT28’s current operations in Europe — especially in France — and illustrate the persistent, evolving nature of the threat.
Priority targets for APT28 spear-phishing campaigns
Target typology in APT28 campaigns
APT28 targets include:
- Sovereign ministries (Defense, Interior, Foreign Affairs)
- Paris 2024 Olympics organizers and IT contractors
- Operators of vital importance (OIVs): energy, transport, telecoms
- Defense industrial and technological base (BITD) companies
- Research institutions (CNRS, INRIA, CEA)
- Local governments with strategic competencies
- Consulting firms active in European or sensitive matters
Historical Context: The Evolution of APT28
APT28 (Fancy Bear) has been active since at least 2004, operating as a state-sponsored cyber-espionage group linked to Russia’s GRU. However, its most heavily documented and globally recognized operations emerged from 2014 onward. That year marks a strategic shift, where APT28 adopted more aggressive, high-visibility tactics using advanced spear-phishing techniques and zero-day exploits.
Between 2008 and 2016, the group targeted several major geopolitical institutions, including:
- The Georgian Ministry of Defense (2008)
- NATO, the White House, and EU agencies (2014)
- The U.S. presidential election campaign (2016)
This period also saw extensive exposure of APT28 by cybersecurity firms such as FireEye and CrowdStrike, which highlighted the group’s growing sophistication and its use of malicious Word documents (maldocs), cloud-based command-and-control (C2) relays, and coordinated influence operations.
These earlier campaigns laid the foundation for APT28’s current operations in Europe — especially in France — and illustrate the persistent, evolving nature of the threat.
Spear-phishing and electoral destabilization in Europe
Political and geopolitical context of APT28 campaigns
APT28’s campaigns often precede key elections or diplomatic summits, such as the 2017 French presidential election, the 2019 European elections, or the upcoming Paris 2024 Olympic Games. These are part of a broader hybrid strategy aimed at destabilizing the EU.
Some spear-phishing attacks are synchronized with disinformation operations to amplify internal political and social tensions within targeted nations. This dual tactic aims to undermine public trust in democratic institutions.
Reference: EU DisinfoLab – Russia-backed disinformation narratives
Germany and NATO have also reported a resurgence of APT28 activities, particularly against NATO forces stationed in Poland, Lithuania, and Estonia. This strategic targeting of European institutions is part of a broader effort to weaken collective security in the EU.
Other APT28 campaigns between CVE-2023-23397 and NotDoor
Between the Outlook zero-day CVE-2023-23397 and the emergence of the NotDoor Outlook backdoor, APT28 sustained a steady cadence of precision intrusions. The group leveraged widely deployed enterprise software to deliver APT28 spear-phishing chains at scale, moving from classic maldocs to Outlook-centric compromise and covert exfiltration.
| Vulnerability | Attack type | Target | APT28 usage |
|---|---|---|---|
| CVE-2023-38831 | Malicious ZIP (WinRAR exploit) | Diplomatic & defense sectors | Weaponized archives in targeted phishing; payload staging and credential theft |
| CVE-2021-40444 | ActiveX exploit (MSHTML) | NATO-linked institutions | Malicious Word documents embedding ActiveX to gain initial code execution |
| CVE-2023-23397 | Outlook zero-day | Energy & transport operators | Zero-click NTLM material theft enabling relay and lateral movement |
Takeaway. These campaigns show a tactical progression from maldoc & archive abuse toward Outlook-centric backdoors, culminating with NotDoor’s Outlook VBA macro phishing, DLL side-loading via OneDrive.exe, and Proton Mail covert exfiltration.
NotDoor: a new Outlook backdoor in APT28’s toolchain
OneDrive.exe DLL side-loading and encrypted mail exfiltration. Detections pivot on Outlook child-process chains, macro creation, and anomalous OneDrive module loads.NotDoor represents a tactical leap in APT28 spear-phishing chains: instead of only abusing delivery vectors, the operators weaponize Microsoft Outlook itself. A malicious VBA macro hooks mailbox events, watches for keyword triggers in new mail, and—on match—executes commands, stages files, and exfiltrates data. This Outlook-centric backdoor blends with daily workflows, reduces telemetry noise, and undermines perimeter detections.
How the backdoor operates
- Initial foothold: Outlook VBA macro phishing seeded via targeted messages or trust-store abuse (macro-enabled project in the user profile).
- Mailbox surveillance: event handlers monitor incoming emails for operator tasking (e.g., “Daily Report”, “Timesheet”, summit- or exercise-themed lures).
- Tasking & execution: the macro launches system commands, enumerates files and mailbox items, compresses artifacts, and uploads follow-on payloads.
- Defense evasion: DLL side-loading via OneDrive.exe loads a malicious library behind a trusted Microsoft binary to degrade signature-based controls.
- Covert egress: Proton Mail covert exfiltration camouflages outbound traffic among legitimate encrypted flows.
Where NotDoor fits vs HeadLace & CVE-2023-23397
| Capability | HeadLace | CVE-2023-23397 (Outlook) | NotDoor |
|---|---|---|---|
| Primary role | Loader / C2 staging | Zero-click credential material theft | Outlook-resident backdoor (VBA) |
| Initial trigger | Spear-phishing + droppers | Crafted Outlook item (MAPI reminder) | Mailbox keyword match on new mail |
| Operator actions | Payload delivery, beaconing | NTLM relay → lateral movement | Command exec, file upload, selective exfiltration |
| Key evasions | Cloud relays; short-lived infra | Abuses client processing path | OneDrive.exe DLL side-loading; encrypted mail channel |
| Detections |
|
||
Detection & hunts (behavior-first)
- Macro exposure: disable Outlook VBA by policy; alert on macro project creation/enable in Office trust stores.
- Process chains: flag
OUTLOOK.EXEspawning script interpreters, archivers, or shells; correlate with mailbox event timing. - Side-loading: monitor
OneDrive.exemodule loads from non-system paths; detect unsigned or unexpected DLLs co-located with it. - Mailflow anomalies: DLP/heuristics for sudden encrypted egress to privacy providers from workstation hosts; compressed archives leaving via mail.
- Keyword intel: hunt for mailbox rules/macros using operational terms (e.g., “report”, “invoice”, exercise names, event code-words).
MITRE ATT&CK mapping (core techniques)
- T1204 — User Execution: malicious file/macro (Outlook VBA project)
- T1059 — Command & Scripting Interpreter (cmd/PowerShell/WScript)
- T1574.002 — Hijack Execution Flow: DLL Side-Loading (
OneDrive.exe) - T1041 — Exfiltration Over C2 Channel (encrypted mail channel)
Operational hardening (sovereign posture)
- Harden Outlook (disable macros by default; restrict trusted locations; block unsigned VBA).
- Instrument Outlook/OneDrive behaviors and alert on risky child-process or module-load patterns.
- Adopt sovereign email encryption HSM: use DataShielder HSM PGP for end-to-end encryption with volatile-memory decryption only; pair with PassCypher HSM PGP for offline OTP/credential custody.
APT28 attribution and espionage objectives
- Attribution: Main Intelligence Directorate (GRU), Unit 26165
- Key techniques: Targeted phishing, Outlook vulnerabilities, compromise of routers and peripheral devices
- Objectives: Data exfiltration, strategic surveillance, disruption of critical operations
APT28 also coordinates technical operations with information warfare: fake document distribution, disinformation campaigns, and exploitation of leaks. This “influence” component, though less covered in mainstream reports, significantly amplifies the impact of technical attacks.
Observed campaigns and methods (2022–2025)
| Date | Campaign | Targets | Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| March 2022 | Diplomatic phishing | EU ministries | Theft of confidential data |
| July 2023 | Military campaign | French and German forces | Access to strategic communications |
| Nov. 2024 | HeadLace & CVE exploit | Energy sector | Risk of logistical sabotage |
| April 2025 | Olympics 2024 operation | French local authorities | Compromise of critical systems |
🔗 See also: ENISA Threat Landscape 2024 – Cyberespionage Section
Mapping APT28 to the Cyber Kill Chain
| Kill Chain Step | Example APT28 |
| Reconnaissance | DNS scanning, 2024 Olympic monitoring, WHOIS tracking |
| Weaponization | Doc Word piégé (maldoc), exploit CVE-2023-23397 |
| Delivery | Spear-phishing by email, fake ..fr/.eu domains |
| Exploitation | Macro Execution, Outlook Vulnerability |
| Installation | Malware HeadLace, tunnels cloud (Trello, Dropbox) |
| C2 | GitHub relay, DNS Fast Flux |
| Actions on Obj. | Exfiltration, disinformation coordinated with DCLeaks |
Tactics and Infrastructure: Increasing Sophistication
APT28 campaigns are distinguished by a high degree of stealth:
- Domain spoofing via homographs (e.g. gov-fr[.]net).
- Real-time payload encryption.
- Using legitimate cloud services like GitHub, Dropbox, or Trello as a C2 relay.
- Hosting on anonymized infrastructures (Fast Flux DNS, bulletproof hosting).
- Non-persistent attacks: ephemeral access, rapid exfiltration, immediate wipe. This approach makes detection particularly complex, as it drastically reduces the window of opportunity for forensic analysis, and the attacker’s infrastructure is often destroyed rapidly after compromise.
This mastery of technical obfuscation makes detection particularly complex, even for the most advanced SIEM systems and EDRs.
Evolution of APT28 spear-phishing campaigns (2014–2025)
This timeline highlights the major APT28 spear-phishing offensives in Europe, from early credential harvesting and the 2017 Macron campaign to Microsoft Outlook exploits in 2020 and large-scale energy sector intrusions culminating in 2025.
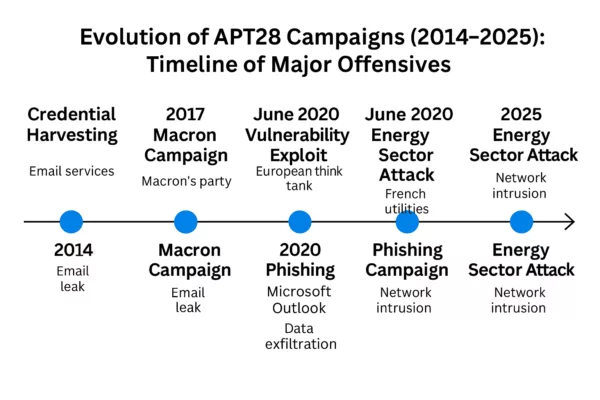
APT28 spear-phishing timeline (2014–2025) — Key campaigns include credential harvesting, the 2017 Macron leak, Outlook phishing exploits in 2020, and critical infrastructure attacks in the European energy sector through 2025.
APT28 malware matrix (Outlook-centric chains)
This matrix summarizes the Outlook-focused toolchain observed in APT28 spear-phishing campaigns, highlighting purpose, triggers, evasions, and succinct detections to operationalize hunts.
| Tool / Vector | Purpose | Initial trigger | Key evasions | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CVE-2023-23397 (Outlook) | Zero-touch credential material theft | Crafted Outlook item (MAPI reminder) | Abuses client processing path; no user click | Enables NTLM relay & lateral movement |
| Detections | Outlook items with reminder props to UNC; anomalous NTLM right after item processing; spikes in external SMB/NTLM auth. | |||
| HeadLace | Loader / staging / C2 | Document lure or dropper delivered via spear-phishing | Cloud relays; short-lived infrastructure | Used for quick-strike access and payload delivery |
| Detections | Unusual OUTLOOK.EXE or user apps spawning LOLBins; beaconing to GitHub/Trello; transient staging dirs; signed-binary proxy exec. |
|||
| NotDoor (Outlook VBA) | Outlook-resident backdoor | Mailbox keyword match on new mail | OneDrive.exe DLL side-loading; encrypted mail channel | Command exec, file upload, selective exfiltration |
| Detections | Outlook macro enable/create events; OUTLOOK.EXE spawning cmd/powershell/wscript; OneDrive.exe loading DLLs from user-writable paths; encrypted egress to privacy providers (e.g., Proton Mail). |
|||
Official report — CERTFR-2025-CTI-006
Title: Targeting and compromise of French entities using APT28 tradecraft
Publisher: CERT-FR (ANSSI) — 29 April 2025
- Scope: Analysis of APT28 campaigns against French government, diplomatic and research bodies (2021–2024), with spillover to wider Europe.
- Attribution: APT28 (Fancy Bear / Sofacy), linked to Russia’s GRU Unit 26165.
- Key TTPs: Targeted spear-phishing, Outlook abuse (incl. CVE-2023-23397), short-dwell intrusions, cloud C2 relays, coordinated information ops.
- Operational risks: Credential theft → lateral movement; data exfiltration; disruption potential for critical operators.
- Defensive priorities: Patch hygiene; macro hardening; behavior monitoring for
OUTLOOK.EXE/OneDrive.exe; DLP on encrypted egress; ATT&CK mapping for hunts (T1204, T1059, T1574.002, T1041).
Links — Official page: CERTFR-2025-CTI-006 · Full PDF: download
Takeaway — The report corroborates the shift of APT28 spear-phishing toward Outlook-centric chains and reinforces the need for behavior-first detection and sovereign encryption/HSM controls.
ANSSI’s operational recommendations
OUTLOOK.EXE/OneDrive.exe, DLP on encrypted egress, and sovereign HSMs for sensitive exchanges and credentials.- Apply security patches (known CVEs) immediately.
- Audit peripheral equipment (routers, appliances).
- Deploy ANSSI-certified EDRs to detect anomalous behavior.
- Train users with realistic spear-phishing scenarios.
- Segment networks and enforce the principle of least privilege.
- Disable Outlook VBA macros by default via group policy; restrict Office trusted locations; block unsigned macros.
- Instrument Outlook & OneDrive process behavior: alert on
OUTLOOK.EXEspawning script interpreters and onOneDrive.exeloading DLLs from non-system paths. - Mailflow controls: DLP/heuristics for unexpected encrypted egress to privacy providers (e.g., Proton Mail) from workstation hosts.
- Sovereign channeling for sensitive comms: use DataShielder HSM PGP to end-to-end encrypt messages with volatile-memory decryption only; pair with PassCypher HSM PGP for offline OTP/credential custody.
- Threat hunting: search for anomalous Outlook rules/macros, compressed archives in sent items, and keyword-based mailbox automations.
- Map NotDoor hunts to MITRE ATT&CK: T1204 (User Execution: Malicious File/Macro), T1059 (Command and Scripting Interpreter), T1574.002 (Hijack Execution Flow: DLL Side-Loading), T1041 (Exfiltration Over C2 Channel).
For detailed guidance, refer to the ANSSI recommendations.
Regulatory framework: French response to spear-phishing
- Military Programming Law (LPM): imposes cybersecurity obligations on OIVs and OESs.
- NIS Directive and French transposition: provides a framework for cybersecurity obligations.
- SGDSN: steers the strategic orientations of national cybersecurity.
- Role of the ANSSI: operational referent, issuer of alerts and recommendations.
- EU-level Initiatives: Complementing national efforts like those led by ANSSI in France, the NIS2 Directive, the successor to NIS, strengthens cybersecurity obligations for a wider range of entities and harmonizes rules across European Union Member States. It also encourages greater cooperation and information sharing between Member States.
Sovereign solutions: DataShielder & PassCypher against spear-phishing
Sovereign solutions: DataShielder & PassCypher against spear-phishing
DataShielder NFC HSM: An alternative to traditional MFA authentication
Most of APT28’s spear-phishing publications recommend multi-factor authentication. However, this MFA typically relies on vulnerable channels: interceptable SMS, exposed cloud applications, or spoofed emails. DataShielder NFC HSM introduces a major conceptual breakthrough:
These controls provide a sovereign email encryption HSM approach for sensitive exchanges.
| Criterion | Classic MFA | DataShielder NFC HSM |
| Channel used | Email, SMS, cloud app | Local NFC, without network |
| Dependency on the host system | Yes (OS, browser, apps) | No (OS independent) |
| Resistance to spear-phishing | Average (Interceptable OTP) | High (non-repeatable hardware key) |
| Access key | Remote server or mobile app | Stored locally in the NFC HSM |
| Offline use | Rarely possible | Yes, 100% offline |
| Cross-authentication | No | Yes, between humans without a trusted third party |
This solution is aligned with a logic of digital sovereignty, in line with the recommendations of the ANSSI.
DataShielder HSM PGP can encrypt all types of emails, including Gmail, Outlook, Yahoo, LinkedIn, Yandex, HCL Domino, and more. It encrypts messages end-to-end and decrypts them only in volatile memory, ensuring maximum privacy without leaving a clear trace.
PassCypher HSM PGP enhances the security of critical passwords and TOTP/HOTP codes through:
- 100% offline operation without database or server
- Secure input field in a dedicated tamper-proof sandbox
- Protection native contre les attaques BITB (Browser-in-the-Browser)
- Automatic sandbox that checks original URLs before execution
- Secure management of logins, passwords, and OTP keys in a siloed environment
En savoir plus : BITB attacks – How to avoid phishing by iframe
These solutions fit perfectly into sovereign cyber defense architectures against APTs.
🇫🇷 Exclusive availability in France via AMG Pro (Regulatory Compliance)
To comply with export control regulations on dual-use items (civil and military), DataShielder NFC HSM products are exclusively distributed in France by AMG PRO.
These products are fully compliant with:
- French Decree No. 2024-1243 of December 7, 2024, governing the importation and distribution of dual-use encryption systems.
- Regulation (EU) 2021/821, establishing a Union regime for the control of exports, transfer, brokering and transit of dual-use items (updated 2024).
Why this matters:
- Ensures legal use of sovereign-grade encryption in France and across the EU.
- Guarantees traceability and legal availability for critical infrastructures, ministries, and enterprises.
- Reinforces the sovereignty and strategic autonomy of European cybersecurity frameworks.
DataShielder NFC HSM: a French-designed and Andorran-manufactured offline encryption and authentication solution, officially recognized under civil/military dual-use classification.
Threat coverage table: PassCypher & DataShielder vs APT groups
Evaluating sovereign cyber defenses against APT threats
Faced with the sophisticated arsenal deployed by APT groups such as APT28, APT29, APT31 or APT44, it is becoming essential to accurately assess the level of protection offered by cybersecurity solutions. The table below compares the tactics used by these groups with the defense capabilities built into PassCypher, HSM, PGP, and DataShielder. This visualization helps CISOs and decision-makers quickly identify the perimeters covered, residual risks, and possible complementarities in a sovereign security architecture.
| Threat Type | APT28 | APT29 | APT31 | APT44 | Couverture PassCypher | DataShielder Coverage |
| Targeted spear-phishing | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ⚠️ | ✅ | ✅ |
| Zero-day Outlook/Microsoft | ✅ | ✅ | ⚠️ | ❌ | ✅ (sandbox indirect) |
✅ (memory encryption) |
| Cloud relay (Trello, GitHub…) | ✅ | ⚠️ | ✅ | ❌ | ✅ (URL detection) |
✅ |
| QR code phishing | ❌ | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
| BITB (Browser-in-the-Browser) | ✅ | ⚠️ | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ✅ |
| Attacks without persistence | ✅ | ❌ | ⚠️ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
| Disinformation / fake news | ✅ | ⚠️ | ❌ | ✅ | ✅ (scission login/data) |
⚠️ (via partitioning) |
| Compromise of peripheral equipment | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ⚠️ | ❌ | ✅ (via HSM) |
| Targeting elections/Olympics | ✅ | ⚠️ | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ✅ |
✅ = Direct protection / ⚠️ = Partial mitigation / ❌ = Not directly covered
Sovereign Use Case — Outlook backdoor neutralized
Context. A regional authority receives a themed spear-phish. A VBA project drops into Outlook. The macro watches for “weekly report”.
- Before: No macro hardening.
OUTLOOK.EXEspawnspowershell.exe;OneDrive.exeside-loads DLL; artifacts exfiltrated via encrypted mail to a privacy provider. - With DataShielder: Sensitive threads are end-to-end encrypted; decryption occurs only in volatile memory; exfiltration yields ciphertext with no reusable keys.
- With PassCypher: Admin/partner credentials and TOTPs are offline, outside browser/DOM; phishing-induced login prompts fail; anti-BITB sandbox blocks spoofed portals and checks original URLs before input.
- Detection: SOC rules flag
OUTLOOK.EXE → powershell.exeandOneDrive.exeloading non-system DLLs. DLP alerts on unexpected encrypted egress volume from workstations. - Outcome: Macro tasking is contained; no cleartext data loss; no credential replay; attacker’s window closes within minutes.
Towards a European cyber resilience strategy
APT28, APT29, APT44: these are all groups that illustrate an offensive escalation in European cyberspace. The response must therefore be strategic and transnational:
- Coordination by ENISA and the European CSIRT Network
- IOC sharing and real-time alerts between Member States
- Regulatory harmonization (NIS2 revision, Cyber Resilience Act)
- Deployment of interoperable sovereign solutions such as DataShielder and PassCypher
See also: Cyber Resilience Act – EU 🔗 See also: APT44 QR Code Phishing – Freemindtronic
CISO Recommendation: Map APT28 tactics in your security strategies. Deploy segmented, offline authentication solutions like DataShielder, combined with encrypted questionnaire tools such as PassCypher to counter spear-phishing attacks.
Related links — Russian APT actors
- APT29 — Spear-phishing in Europe: stealthy Russian espionage
SVR (Russia): low-noise campaigns, cloud relays, and minimal persistence. A natural complement to APT28’s Outlook-centric chains. - APT29 — Exploitation of app passwords
Access techniques bypassing traditional passwords (OAuth/app passwords), relevant to strengthening sovereign email controls. - APT44 — QR-code phishing & blended info-ops
Sandworm/GRU (Russia): mobile-first vectors and influence operations, converging with Outlook-focused tactics.
What We Didn’t Cover — Next chapters
- APT29: OAuth app-based persistence and cloud forensics pitfalls.
- APT31: Credential-phishing against diplomatic targets and router exploitation.
- APT44: Mobile-first QR-phishing and blended info-ops.
- Incident response playbooks: mailbox macro triage, OneDrive side-load scoping, encrypted-egress containment.
Weak Signals — Trends to Watch
- AI-generated lures at scale — Highly tailored spear-phish (meeting minutes, RFPs, summit agendas) produced by LLM pipelines, increasing click-through and bypassing traditional content heuristics.
- Malicious Outlook add-ins / COM supply chain — Pivot from VBA macros to signed-looking add-ins that survive macro hardening and blend with productivity tooling.
- OAuth consent phishing & token replay — App-based persistence without passwords; mailbox rules + Graph API automation to emulate “human” inbox behavior.
- Legacy VPN & SASE bypass — Reuse of stale creds, split-tunnel misconfigs, and coarse geofencing to reach O365/Outlook from “trusted” egress points.
- Encrypted DNS/DoH for staging — Low-signal C2 bootstrap and selector lookups hidden in privacy traffic; harder to baseline on egress.
- Deepfake-assisted vishing — Real-time voice cloning to legitimize urgent mailbox actions (“approve macro”, “send weekly report”).
- QR-code hybrid lures (desktop ↔ mobile) — Convergence with APT44 playbooks; cross-device session hijack and MFA coercion via mobile scanners. See also: APT44 QR code phishing.
- OneDrive.exe side-loading variants — New search-order tricks and user-writable paths; signed-binary proxying to evade EDR trust gates.
- SOHO/edge router staging — Short-lived hops and NAT-ed implants to mask operator infrastructure and rotate origins near targets.
- MFA friction exploits — Push-fatigue + number-matching workarounds; social sequences that time prompts to business rituals (shift changes, on-call handovers).
- ECH/TLS fingerprint hiding — Encrypted Client Hello + JA3 randomization to degrade domain/SNI-based detections on mailbox-adjacent exfiltration.