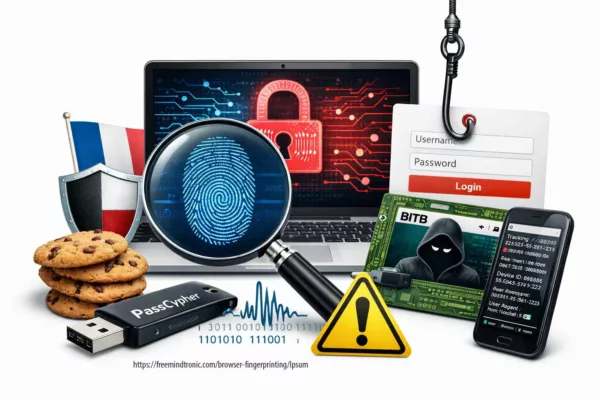
Beware of BitB phishing attacks by iframe!
Phishing by iframe is a malicious technique that inserts a fake web page into a legitimate one, to trick users and steal their personal or financial information. This method often targets cryptocurrency holders, especially BitB users. Learn how to spot and avoid BitB phishing attacks by iframe with Freemindtronic.
BITB Attacks: How to Avoid Phishing by iFrame
We have all seen phishing attacks aren’t uncommon, and they demand urgent attention with fake emails and messages at least once.. However, there’s much more in the cybersecurity landscape than just conventional email practices when it comes to phishing. Enterprises that don’t take the necessary precautions can suffer a death blow from a phishing attack. The top line is affected, but the brand’s image and trust can be obliterated if news of a data breach reaches the public.
The latest form of phishing scam is the browser in the browser attack (BITB) that simulates a browser window within a web browser and steals sensitive user information. A fraudulent pop-up window caters to the user and asks for their credentials to sign into the website in the previous web browser window, leading to identity theft.
This article explains what BITB attacks are and how they work, what the risks and consequences of BITB attacks are, how to prevent and protect yourself from BITB attacks using EviBITB technology, and how to install EviBITB on your web browser.
What are BITB attacks and how do they work?
BITB stands for Browser-In-The-Browser. This phishing technique creates a fake browser window within your web browser using HTML and CSS code. An iFrame of redirection, which is an invisible element that loads content from another URL, is displayed by this fake window. The iFrame of redirection mimics the appearance and functionality of a legitimate site, such as Google, Facebook, or Outlook, and asks you to enter your authentication information.
This fake window shows a legitimate URL in the address bar, as well as the icon and the title of the original site. That is the problem. Most users rely on checking the URL to verify the authenticity of a site. This makes it very difficult to detect the phishing attempt. This attack can affect you even if you use a secure connection (https).
BITB attacks can bypass many security measures that are designed to prevent phishing. That is why they are very dangerous. For example:
- BITB attacks do not involve malicious links or domains. Anti-phishing software may fail to detect them because of that.
- BITB attacks do not intercept your verification codes or tokens. Two-factor authentication may not protect you from them because of that.
- Password managers may autofill your credentials on the fake window. They may not protect you from BITB attacks because of that.
Therefore, BITB attacks can allow hackers to access your accounts, steal your data, or even take over your identity. They pose a serious threat to your online security and privacy because of that.
How do BITB attacks work?
Two features of modern web development enable BITB attacks: single sign-on (SSO) options and iFrames.
Many websites embed SSO options that allow you to sign in using an existing account from another service, such as Google, Facebook, Apple, or Microsoft. This option is convenient because you do not need to create a new account or remember a new password for each website you visit.
iFrames are elements that can load content from another URL within a web page. They are often used for embedding videos, maps, ads, or widgets on websites.
The attackers do the following steps:
- They make a phishing website with SSO options.
- On their phishing website, they embed an iFrame of redirection that leads to their own server with a fake SSO window.
- Using HTML and CSS code, they design their fake SSO window to imitate a browser window inside the browser.
- They make their fake SSO window appear when you click on an SSO option on their phishing website.
- With JavaScript code, they show a legitimate URL in the address bar of their fake SSO window.
- Using OAuth methods, they request you to enter your credentials on their fake SSO window.
- To their server, they send your credentials and then redirect you to the real website.
As you can see, BITB attacks are very deceptive and convincing. They can fool even savvy users who check the URL before entering their credentials.
What are the risks and consequences of BITB attacks?
BITB attacks are a serious threat. They can compromise data and identity for users and businesses. Users who fall victim to BITB attacks face these risks and consequences:
- Their SSO account can be hijacked and all linked services accessed by the attacker.
- Their personal and financial information can be stolen and used for identity theft, fraud or blackmail.
- Their devices can be infected by malware or ransomware and their files damaged or encrypted.
- Their online reputation can be tarnished by spamming or posting malicious content.
Businesses that offer SSO options are also vulnerable to BITB attacks. They can lose trust and loyalty from their customers or employees. Businesses that suffer a data breach due to BITB attacks face these risks and consequences:
- Their customer or employee data can be exposed, exploited or sold by the attacker or the dark web.
- Their brand image and reputation can be damaged by negative publicity and customer complaints.
- Their legal and regulatory compliance can be violated by data protection laws and regulations.
- Their revenue and profitability can be reduced by customer churn, lawsuits and fines.
Recent Examples of BITB Attacks
BITB attacks are not new, but they have become more sophisticated and widespread in recent years. Here are some examples of BITB attacks that targeted governmental entities:
- In February 2020, Zscaler revealed a campaign of phishing BitB targeting users of Steam, a video game digital distribution service. The hackers created fake Counter-Strike: Global Offensive (CS: GO) websites that offered free skins or weapons for the game. These websites displayed a fake pop-up window that asked users to sign in with Steam. If users entered their credentials, they were sent to the hackers who could then access their Steam accounts and steal their items.
- In March 2020, Bitdefender reported a campaign of phishing BitB targeting users of Office 365, a cloud-based suite of productivity applications. The hackers sent emails that pretended to be from Microsoft and asked users to update their Office 365 settings. These emails contained a link that led users to a fake Office 365 website that displayed a fake pop-up window that asked users to sign in with Office 365. If users entered their credentials, they were sent to the hackers who could then access their Office 365 accounts and steal their data.
- In September 2020, Proofpoint uncovered a campaign of phishing BitB targeting users of Okta, a cloud-based identity and access management service. The hackers sent emails that pretended to be from various organizations and asked users to verify their Okta account. These emails contained a link that led users to a fake Okta website that displayed a fake pop-up window that asked users to sign in with Okta. If users entered their credentials, they were sent to the hackers who could then access their Okta account and compromise their other connected applications.
These examples show that BITB attacks can target any SSO provider and any website or web application that uses SSO. They also show that hackers can use various methods to lure users into clicking on malicious links or entering their credentials on fake windows.
What are some statistics on BITB attacks?
BITB attacks use iFrames to deceive users with fake SSO windows. Here are some statistics on BITB attacks:
- According to Statista, the number of unique phishing sites detected worldwide reached 2.11 million in the third quarter of 2020, an increase of 10% from the previous quarter.
- According to The Hacker News, BITB attacks can exploit third-party SSO options embedded on websites such as “Sign in with Google” (or Facebook, Apple, or Microsoft) to create fake browser windows within the browser and spoof legitimate domains.
- According to Zscaler, BITB attacks have been used in the wild at least once before, in February 2020, to target Steam users by means of fake Counter-Strike: Global Offensive (CS: GO) websites.
- According to NetSPI, the volume of successful phishing attacks on organizations worldwide in 2021 was highest in Brazil (25%), followed by India (17%), and Mexico (14%).
- According to DZone, the most targeted industry sectors by phishing attacks as of the third quarter of 2020 were SaaS/Webmail (33%), Financial Institutions (22%), and Payment Services (14%).
How to effectively fight against BITB attacks?
BITB attacks are very hard to detect, but not impossible. There are some signs that can help you spot them and some measures that can help you prevent them. Here are some tips:
- Always check the URL of the site before entering your credentials. Make sure it matches the domain of the site or the SSO provider that you want to use. Do not rely on the URL displayed on the pop-up window, as it can be fake.
- Always check the SSL certificate of the site before entering your credentials. Make sure it is valid and issued by a trusted authority. Do not rely on the padlock icon displayed on the pop-up window, as it can be fake.
- Always use an updated antivirus software and browser extension that can detect and block malicious sites and scripts. They can help you avoid landing on phishing pages or loading fake windows.
- Always use strong and unique passwords for each site or application that you use. Do not reuse the same password for different accounts, as it can increase the risk of compromise if one of them is breached.
- Always use two-factor authentication (2FA) for your accounts, especially those that you use for SSO. 2FA adds an extra layer of security by requiring a second factor (such as a code sent to your phone or email) to verify your identity. Having your username and password is less useful for hackers if they need your device or access to your email account too.
How to prevent and protect yourself from BITB attacks using EviBITB technology?
The best way to prevent and protect yourself from BITB attacks is to use EviBITB technology, a technology that allows you to detect and remove redirection iframes from web pages. EviBITB is integrated for free in the free and paid extensions of Freemindtronic that are compatible with NFC HSM devices that use a smartphone or an NFC HSM device. The latter stores encrypted multiple authentication information (username, password, otp) for secure authentication for any website on the internet or intranet.
EviBITB technology also has a system of automatic backup of the URL of connection to the account using a web browser to connect to an online account on the internet or intranet. This extension is paired with the NFC android phone which is itself paired with an NFC HSM where encrypted detailed authentication information such as username, password, and secret keys OTP (TOP or HOTP) are stored. Thus, before authorizing auto-filling of connection fields or auto-connection to an online account, the phone will check beforehand if the connection URL is compliant (sandbox technique). This system adds to EviBITB protection.(click here to learn more about EviBITB)
By using EviBITB technology, you can enjoy many benefits:
- You can avoid falling victim to BITB attacks that can steal your data or compromise your identity.
- You can reduce the risk of keylogging or malware infections that can capture your keystrokes or spy on your online activity.
- You can save time and hassle by using your smartphone or NFC HSM card as an authentication key instead of creating or remembering passwords for each website you visit.
- You can enjoy a seamless and user-friendly experience by accessing websites with just a tap of your smartphone or NFC HSM card on your computer screen.
- You can protect your privacy by controlling what data you share with each website you visit, such as your name, email, or profile picture.
By using EviBITB technology, you can be sure that the web page you see is the one you want to see, and that you do not give away your data to hackers.
How can EviBITB protect you from BITB attacks?
EviBITB is a technology that enhances your online security. It is implemented in the freemindtronic extensions that allow secure end-to-end autofill and auto-login from an NFC HSM. It also detects and removes phishing iFrames from your web browser.
EviBITB works with an application installed on an NFC Android phone that is paired with an NFC HSM. The application has a sandbox that checks if the origin URLs saved automatically during the first login are compliant. If they are, it transfers encrypted authentication information to the extension.
EviBITB also analyzes the web page source code and detects any possible BITB iFrames. It looks for hidden elements, suspicious URLs, or mismatched styles that indicate a fake browser window.
When EviBITB detects a BITB iFrame, it alerts you by showing a warning window on your computer screen. This window shows you the redirection iFrame URL and asks you to check if you trust this URL before entering any sensitive information.
How EviBITB technology can improve your browsing experience?
EviBITB technology is a security, performance and privacy enhancer. It removes redirection iframes and improves your browsing experience in several ways:
- It speeds up web page loading, by avoiding requests to third-party sites.
- It reduces bandwidth consumption, by saving data transferred to or from iframes.
- It limits exposure to ads and pop-ups, by blocking their sources in iframes.
- It prevents online activity tracking, by deleting cookies and data stored by iframes.
- It enhances readability and usability of web pages, by removing distracting elements from iframes.
- It increases compatibility and accessibility of web pages, by avoiding conflicts or errors caused by iframes.
With EviBITB technology, you can enjoy a faster, smoother and more private browsing experience, without compromising security or convenience.
How to use EviBITB to protect yourself from BITB attacks?
EviBITB is a technology that detects and removes malicious iFrames that expose you to BITB attacks. These attacks simulate a browser window in a web page to prompt you to enter credentials on a fraudulent site.
When EviBITB detects a suspicious iFrame, it shows a warning window that informs you of the risk. This window also gives you five buttons to act on the BITB iFrame:
- Close Warning: this button closes the warning window without acting on the BITB iFrame. You can use it if you trust the iFrame URL or want to ignore it.
- Never Show Warnings On This Site: this button adds the website URL to a list of trusted sites. EviBITB will not alert you of BITB iFrames on these sites. You can use it if you are sure the website is safe and has no malicious iFrames.
- Destroy: this button deletes the BITB iFrame from the web page source code. You can use it if you do not trust the iFrame URL or want to remove it.
- Clean Storage: this button clears the data stored by the BITB iFrame in the browser. You can use it if you have been exposed to phishing by iFrame and want to erase any traces.
- Read More: this button redirects you to a page with more information about EviBITB and its benefits. You can use it if you want to learn more about how EviBITB works and protects you from hackers.
Why you should use EviBITB to secure your online access?
EviBITB is a technology that allows you to use your smartphone or your NFC HSM card as a secure authentication key for any website. With EviBITB, you enjoy many benefits:
- You avoid BITB attacks that can steal your data or impersonate your identity.
- These attacks simulate a browser window in a web page to prompt you to enter your credentials on a fraudulent site.
- You reduce the risk of keylogging or malware infections that can capture your keystrokes or spy on your online activity.
- You save time and hassle by using your smartphone or NFC HSM card as an authentication key instead of creating or remembering passwords for each website you visit.
- You enjoy a seamless and user-friendly experience by accessing websites with just a tap of your smartphone or NFC HSM card on your computer screen.
- You protect your privacy by controlling what data you share with each website you visit, such as your name, email, or profile picture.
By using EviBITB, you can be sure that the web page you see is the one you want to see, and that you do not give away your data to hackers.
How EviBITB can improve your browsing experience?
EviBITB is not only a security tool, but also a performance and privacy enhancer. By removing redirection iframes, EviBITB can improve your browsing experience in several ways:
- It can speed up the loading of web pages, by avoiding unnecessary or malicious requests to third-party sites.
- It can reduce the bandwidth consumption, by saving the data that would otherwise be transferred to or from the iframes.
- It can limit the exposure to ads and pop-ups, by blocking the sources that display them in the iframes.
- It can prevent the tracking of your online activity, by deleting the cookies and other data that the iframes may store in your browser.
- It can enhance the readability and usability of web pages, by removing distracting or irrelevant elements from the iframes.
- It can increase the compatibility and accessibility of web pages, by avoiding potential conflicts or errors caused by the iframes.
By using EviBITB, you can enjoy a faster, smoother and more private browsing experience, without compromising your security or convenience.
How to get started with EviBITB?
Getting started with EviBITB is easy and fast. You just need to follow these steps:
- Download the EviBITB extension for your web browser based on Chromium or Firefox from Freemindtronic’s official website: https://freemindtronic.com/evibitb-stop-bitb-phishing-attacks/
- Install the extension on your web browser and follow the instructions to set it up.
- Get a smartphone or an NFC HSM card compatible with the extension. You can find more information about these devices on Freemindtronic’s website: https://freemindtronic.com/how-does-evibitb-work-detailed-guide/
- Pair your smartphone or NFC HSM card with your computer using Bluetooth or NFC technology.
- Start browsing the web securely with EviBITB. Whenever you visit a website that offers SSO options, you will see a green icon on the address bar indicating that EviBITB is active. You can then tap your smartphone or NFC HSM card on your computer screen to authenticate yourself and access the website.
What are some videos on BITB attacks and EviBITB?
If you want to learn more about BITB attacks and EviBITB technology, you can watch some videos on these topics:
- A video demonstration of a BITB attack by mrd0x:
In conclusion
BITB attacks are a new and sophisticated form of phishing that can steal your credentials by simulating a browser window within your browser. They can bypass many security measures that are designed to prevent phishing and compromise your online security and privacy.
EviBITB is a free technology that detects and removes phishing iFrames from your web browser. It also offers other features to enhance your online security, such as authentication via NFC HSM devices that secure your credentials without typing them on your keyboard.
If you want to benefit from EviBITB technology, you just need to download the extension corresponding to your web browser on Freemindtronic’s official website:
- For Chromium: https://chrome.google.com/webstore/detail/evicypher-webmail-legacy/doenpecmhhichmolaeaefkihggnnmdna?hl=fr
- For Firefox: https://freemindtronic.com/wp-content/uploads/evicypher/evicypher_webmail_&_cloud_1.13.3.xpi
- For Edge: https://microsoftedge.microsoft.com/addons/detail/evicypher-webmail-cloud/ipdnndiijnggdojndnibnalkecegbcob
You will also need a smartphone or an NFC HSM card compatible with the extension. You can find more information about these devices on Freemindtronic’s website.
https://freemindtronic.com/evibitb-stop-bitb-phishing-attacks/ :
Don’t wait any longer and try EviBITB now!
Hashtags: #EviBITB #Phishing #Cybersecurity #NFC #HSM