Quantum-Resistant Passwordless Manager 2026 (QRPM) — Best Cybersecurity Solution Finalist by PassCypher sets a new benchmark in sovereign, offline security. Finalist for Best Cybersecurity Solution at Intersec Dubai, it runs entirely in volatile memory—no cloud, no servers—protecting identities and secrets by design. As an offline password manager, PassCypher delivers local cryptology with segmented PGP keys and AES-256-CBC for resilient, air-gapped operations. Unlike a traditional password manager, it enables passwordless proof of possession across browsers and systems with universal interoperability. International recognition is confirmed on the official website: Intersec Awards 2026 finalists list. Freemindtronic Andorra warmly thanks the Intersec Dubai team and its international jury for their recognition.
Fast summary — Sovereign offline Passwordless Ecosystem (QRPM)
Quick read (≈ 4 min): The nomination of Freemindtronic Andorra among the Intersec Awards 2026 finalists in Best Cybersecurity Solution validates a complete sovereign ecosystem built around PassCypher HSM PGP and PassCypher NFC HSM. Engineered from French-origin patents and designed to run entirely in volatile memory (RAM-only), it enables passwordless authentication without FIDO — no transfer, no sync, no persistence. As an offline sovereign password manager, PassCypher delivers segmented PGP + AES-256-CBC for quantum-resistant passwordless security, with embedded translations (14 languages) for air-gapped use. Explore the full architecture in our offline sovereign password manager overview.
⚙ A sovereign model in action
PassCypher HSM PGP and PassCypher NFC HSM operate as true physical trust modules. They execute all critical operations locally — PGP encryption, signature, decryption, and authentication — with no server, no cloud, no third party. This offline passwordless model relies on proof of physical possession and embedded cryptology, breaking with FIDO or centralized SaaS approaches.
Why PassCypher is an offline sovereign password manager
PassCypher HSM PGP and PassCypher NFC HSM act as physical trust modules: all crypto (PGP encryption, signature, decryption, authentication) runs locally, serverless and cloudless. This FIDO-free passwordless model relies on proof of physical possession and embedded cryptology, not centralized identity brokers.
Global reach
This distinction places Freemindtronic Andorra among the world’s top cybersecurity solutions. It reinforces its pioneering role in sovereign offline protection and confirms the relevance of a neutral, independent, and interoperable model — blending French engineering, Andorran innovation, and Emirati recognition at the world’s largest security and digital resilience show.
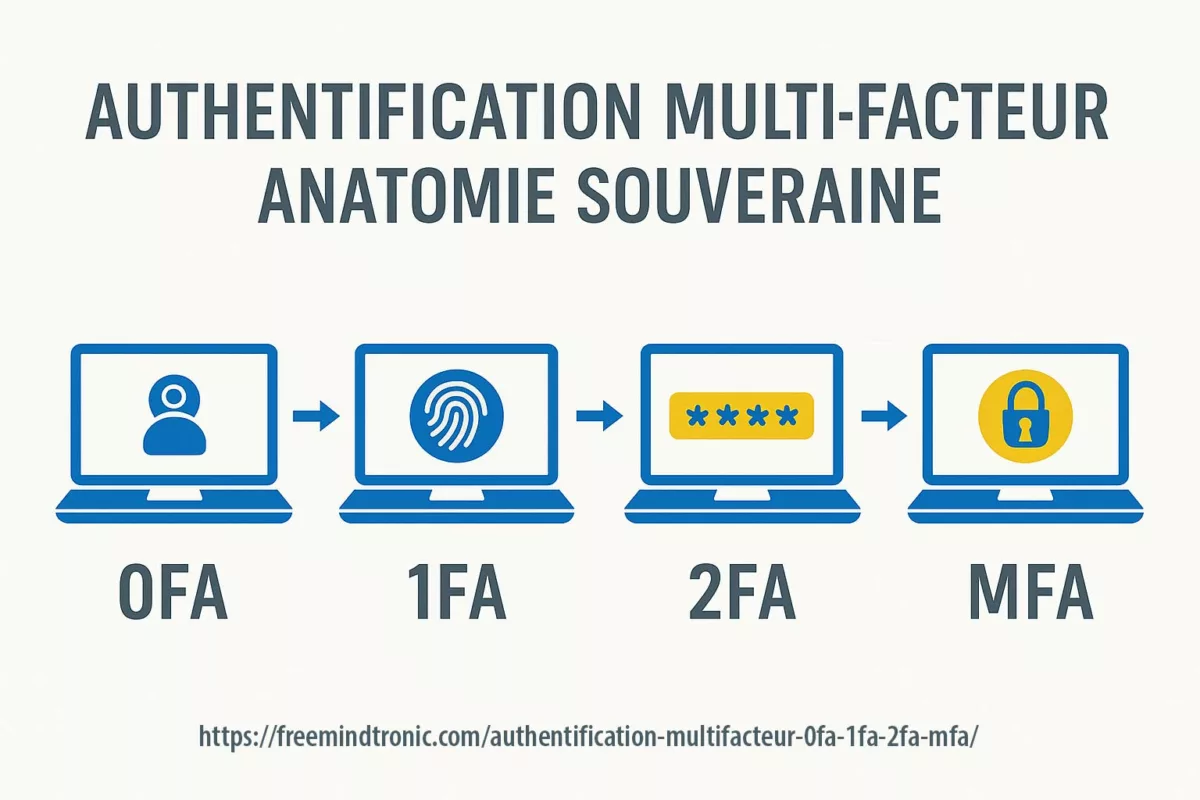
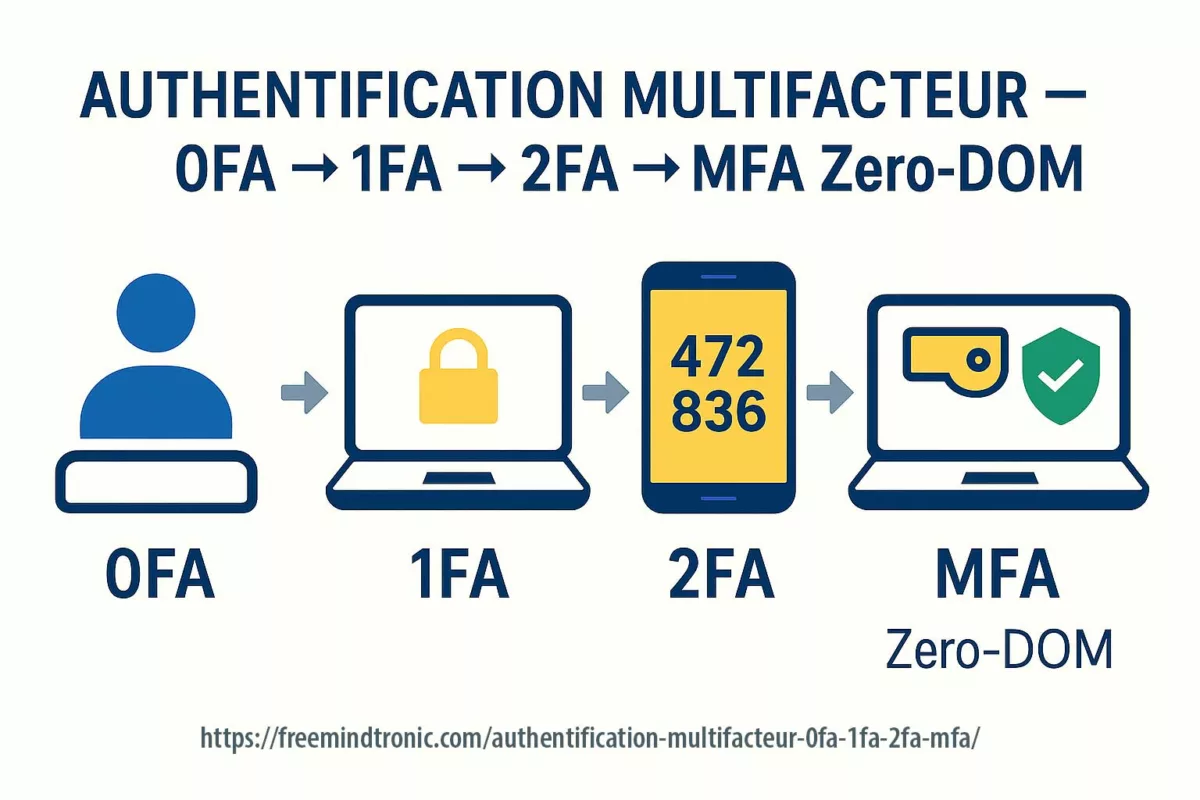
Passwordless authentication without FIDO — sovereign offline model (QRPM)
PassCypher delivers passwordless access without FIDO/WebAuthn or identity federation. Validation happens locally (proof of physical possession), fully offline, with no servers, no cloud, and no persistent stores — a core pillar of the Quantum-Resistant Passwordless Manager 2026 doctrine.
- Proof of possession — NFC/HID or local context; no third-party validators.
- Local cryptology — segmented PGP + AES-256-CBC in RAM-only (ephemeral).
- Universal interoperability — works across browsers/systems without passkeys or sync.
Reading settings
Fast summary reading time: ≈ 4 minutes
Advanced summary reading time: ≈ 6 minutes
Full chronicle reading time: ≈ 35 minutes
Publication date: 2025-10-30
Last update: 2025-10-31
Complexity level: Expert — Cryptology & Sovereignty
Technical density: ≈ 79%
Languages available: FR · CAT· EN· ES ·AR
Specific focus: Sovereign analysis — Freemindtronic Andorra, Intersec Dubai, offline cybersecurity
Reading order: Summary → Doctrine → Architecture → Impacts → International reach
Accessibility: Screen-reader optimized — anchors & structured tags
Editorial type: Special Awards Feature — Finalist Best Cybersecurity Solution
Stakes level: 8.1 / 10 — international, cryptologic, strategic
About the author: Jacques Gascuel, inventor and founder of Freemindtronic Andorra, expert in HSM architectures, cryptographic sovereignty, and offline security.
Official references and media relays
Sovereign localization (offline)
Both PassCypher HSM PGP and PassCypher NFC HSM are natively translated into 13+ languages, including Arabic. Translations are embedded on-device (no calls to online translation services), ensuring confidentiality and air-gap availability.
☰ Quick navigation
- 🔝 Back to top
- Fast summary — Sovereign offline passwordless ecosystem (QRPM)
- Advanced summary — Doctrine and strategic reach
- Chronicle — Sovereignty validated in Dubai
- Official context — Intersec Awards 2026
- The PassCypher innovation — Sovereignty, security, independence
- An Andorran innovation with European roots
- Historic first — Passwordless finalist in the UAE
- Validated sovereignty — Toward an independent model
- International reach — Sovereign global model
- Consolidated sovereignty — Toward an international standard
- Frequently Asked Questions
⮞ Preamble — International and institutional recognition
Freemindtronic Andorra extends its sincere thanks to the international jury and to Messe Frankfurt Middle East, organizer of the Intersec Awards, for the quality, rigor, and global reach of this competition dedicated to security, sovereignty, and innovation. Awarded in Dubai — at the heart of the United Arab Emirates — this distinction confirms recognition of an Andorran innovation with European roots that stands as a model of sovereign, quantum-resistant, offline passwordless authentication. It also illustrates the shared commitment between Europe and the Arab world to promote digital architectures grounded in trust, neutrality, and technological resilience.
Advanced summary — Doctrine & strategic reach of the sovereign offline ecosystem
Intersec 2026 — PassCypher finalist (Best Cybersecurity Solution)
The Intersec Awards 2026 finalist status in the Best Cybersecurity Solution category sets PassCypher apart not only as a technological breakthrough but as a full-fledged sovereign doctrine for Quantum-Resistant Offline Passwordless Security. This nomination marks a dual historic milestone: it is the first time an Andorran company has been shortlisted as a finalist in an international technology competition in the UAE, and — to the best of our knowledge — the first password manager selected as a UAE finalist in the Best Cybersecurity Solution category. This distinction validates disconnected architectures as credible global alternatives to cloud-centralized models.
Note: the “first password manager” statement is made to the best of our knowledge, based on publicly available information about shortlisted finalists in this category.
↪ Geopolitical and doctrinal reach
This recognition gives Andorra a new role: a laboratory of digital neutrality within the wider European space. Freemindtronic advances a sovereign innovation model — Andorran by neutrality, French by heritage, European by vision. By entering Best Cybersecurity Solution, PassCypher symbolizes a strategic balance between cryptologic independence and normative interoperability.
RAM-only security for passwordless sovereignty (QRPM)
↪ An offline architecture built on volatile memory
The PassCypher ecosystem rests on a singular principle: all critical operations — storage, derivation, authentication, key management — occur exclusively in volatile memory. No data is written, synchronized, or retained in persistent storage. By design, this approach removes interception, espionage, and post-execution compromise vectors, including under quantum threats.
Segmented PGP + AES-256-CBC powering quantum-resistant passwordless operations
↪ Segmentation and sovereignty of secrets
The system applies dynamic key segmentation that decouples each secret from its usage context. Each PassCypher instance acts like an autonomous micro-HSM: it isolates identities, verifies rights locally, and instantly destroys any data after use. This erase-by-design model contrasts with FIDO and SaaS paradigms, where persistence and delegation form structural vulnerabilities.
↪ A symbolic recognition for sovereign doctrine
Listing Freemindtronic Andorra among the 2026 finalists elevates technological sovereignty as a driver of international innovation. In a landscape dominated by cloud-centric solutions, PassCypher proves that controlled disconnection can become a strategic asset, ensuring regulatory independence, GDPR/NIS2 alignment, and resilience against industrial interdependencies.
⮞ Extended international recognition
The global reach of PassCypher now extends to the defense security domain. The solution will also be showcased by AMG PRO at MILIPOL 2025 — Booth 5T158 — as the official French partner of Freemindtronic Andorra for dual-use civil and military technologies. This presence confirms PassCypher as a reference solution for sovereign cybersecurity tailored to defense, resilience, and critical industries.
⮞ In short
- Architecture: RAM-only volatile memory security with PGP segmented keys + AES-256-CBC.
- Model: passwordless authentication without FIDO, serverless, cloudless, air-gapped.
- Positioning: offline sovereign password manager for regulated, disconnected, and critical contexts.
- Recognition: Intersec 2026 Best Cybersecurity Solution finalist — quantum-resistant passwordless security by design.
The posts shown above ↑ belong to the same editorial section Awards distinctions — Digital Security. They extend the analysis of sovereignty, Andorran neutrality, and offline secrets management, directly connected to PassCypher’s recognition at Intersec Dubai.
Chronicle — Sovereignty validated in Dubai (offline passwordless)
The official selection of Freemindtronic Andorra as an Intersec Awards 2026 Best Cybersecurity Solution finalist marks a dual historic milestone: it is the first time an Andorran company has been shortlisted as a finalist in an international technology competition in the UAE, and — to the best of our knowledge — the first password manager selected as a UAE finalist in the Best Cybersecurity Solution category. This distinction validates disconnected architectures as credible global alternatives to cloud-centralized models.
↪ Sovereign algorithmic resilience (quantum-resistant by design)
Rather than relying on experimental post-quantum schemes, PassCypher delivers structural resilience: dynamic PGP key segmentation combined with AES-256-CBC, executed entirely in volatile memory (RAM-only). Keys are split into independent, ephemeral segments, disrupting exploitation paths—including those aligned with Grover or Shor. It is not PQC, but a quantum-resistant operating model by design.
↪ Innovation meets independence
The nomination validates a doctrine of resilience through disconnection: protect digital secrets with no server, no cloud, no trace. Authentication and secret management remain fully autonomous—passwordless authentication without FIDO, no WebAuthn, no identity brokers—so each user retains physical control over their keys, identities, and trust perimeter.
↪ Intersec Awards 2026 — ecosystem in the spotlight
Curated by Messe Frankfurt Middle East, Intersec highlights security innovations that balance performance, compliance, and independence. The presence of Freemindtronic Andorra underscores the international reach of a sovereign, offline cybersecurity doctrine developed in a neutral country and positioned as a credible alternative to global standards.
⮞ Intersec 2026 highlights
- Event: Intersec Awards 2026 — Conrad Dubai
- Category: Best Cybersecurity Solution
- Finalist: Freemindtronic Andorra — PassCypher ecosystem
- Innovation: Sovereign offline management of digital secrets (RAM-only, air-gapped)
- Origin: French invention patents with international grants
- Architecture: Volatile memory · Key segmentation · No cloud dependency
- Doctrinal value: Technological sovereignty, geopolitical neutrality, cryptologic independence
- Official validation: Official Intersec Awards 2026 finalists
This feature examines the doctrine, technical underpinnings, and strategic scope of this recognition—an institutional validation that proves digital identities can be safeguarded without connectivity.
Key takeaways:
- Sovereign passwordless with 0 cloud / 0 server: proof of physical possession.
- Universal interoperability (web/systems) without protocol dependency.
- Structural resilience via key segmentation + volatile memory (RAM-only).
Held in Dubai, the Intersec Awards have, since 2022, become a global benchmark for security, cybersecurity, and technological resilience. The 5th edition, scheduled for 13 January 2026 at the Conrad Dubai, will honor excellence across 17 categories covering cybersecurity, fire safety, civil defence, and critical infrastructure protection. In the Best Cybersecurity Solution category, only five finalists were shortlisted after a meticulous evaluation process led by an international jury of 23 experts from five countries — the United Arab Emirates, Saudi Arabia, the United Kingdom, Canada, and the United States — representing the world’s highest institutions in safety, civil defence, and cybersecurity.
For context, the previous edition — Intersec Awards 2025 — received over 1,400 international submissions across 15 categories, confirming the global scope and competitiveness of the event. Official source: Intersec 2025 Press Release — Messe Frankfurt Middle East.
⮞ Official Information
Gala attendance: Freemindtronic Andorra will attend the trophy ceremony in Dubai, represented by Thomas MEUNIER.
- Event: Intersec Awards 2026 — 5th Edition
- Venue: Conrad Dubai, United Arab Emirates
- Date: 13 January 2026
- Category: Best Cybersecurity Solution
- Number of Categories: 17
- Jury: Intersec 2026 International Panel (23 Experts)
- Finalists: Official Finalists List
↪ Prestigious International Jury
The Intersec 2026 jury gathered 23 high-level experts representing leading institutions from the UAE, Saudi Arabia, the United Kingdom, Canada, and the United States — highlighting the event’s global credibility and balance between Middle Eastern and Western expertise.
- Dubai Civil Defence — Lt. Col. Dr. Essa Al Mutawa, Head of Artificial Intelligence Department
- UL Solutions — Gaith Baqer, Senior Regulatory Engineer
- NFPA — Olga Caldonya, Director of International Development
- IOSH (United Kingdom) — Richard Bate, President-Elect
- WSP Middle East — Rob Davies & Emmanuel Yetch, Executive Directors
- ASIS International — Hamad Al Mulla & Yassine Benaman, Senior Security Leaders
↪ Algorithmic Sovereignty — Quantum-Resistant by Design
Instead of relying on post-quantum experimental algorithms, PassCypher achieves structural quantum resistance through dynamic segmentation of PGP keys protected by AES-256-CBC encryption, executed entirely in volatile memory (RAM-only). Keys are divided into temporary, isolated fragments that self-destruct after use — eliminating exploitation vectors, including theoretical quantum attacks such as Grover and Shor. It is not PQC in the academic sense, but a sovereign, quantum-resistant architecture by design.
↪ PassCypher — HSM Suite Natively Translated into Arabic (Offline)
To the best of our knowledge, PassCypher is the first password manager and HSM suite to offer a fully localized Arabic interface with native RTL (right-to-left) support, operating completely offline. This design bridges European engineering and Arabic linguistic and cultural identity, providing a unique model of digital sovereignty independent of cloud infrastructure or centralized authentication systems.
↪ A Dual Historic Milestone
This nomination represents a dual historic milestone: the first Andorran company ever shortlisted in a UAE-based international technology competition, and — to the best of our knowledge — the first password manager selected as a UAE finalist in the Best Cybersecurity Solution category. This distinction confirms disconnected architectures as credible global alternatives to centralized cloud models.
↪ Euro–Emirati Convergence on Sovereign Security
The 2026 recognition highlights the emergence of a Euro–Emirati dialogue on digital sovereignty and resilience-by-design architectures. PassCypher acts as a bridge between Andorran neutrality, French engineering, British institutional expertise, and transatlantic patent recognition — with technologies patented in the United Kingdom, the United States, and the European Union. This convergence exemplifies how interoperability, trust, and sovereign innovation can coexist within a shared international security vision. With this institutional and technological framework established, the next section explores the sovereign architecture and cryptographic doctrine that earned PassCypher international recognition at Intersec Dubai.
PassCypher innovation — Sovereign offline passwordless: security & independence (QRPM)
In a market dominated by cloud stacks and FIDO passkeys, the PassCypher ecosystem positions itself as a sovereign, disruptive alternative. Developed by Freemindtronic Andorra on French-origin patents, it rests on a cryptographic foundation executed in volatile memory (RAM-only) with AES-256-CBC and PGP key segmentation—an approach aligned with our Quantum-Resistant Passwordless Manager 2026 strategy.
↪ Two pillars of one sovereign ecosystem
- PassCypher HSM PGP: a sovereign secrets and password manager for desktops, fully offline. All crypto runs in RAM for passwordless authentication and air-gapped workflows.
- PassCypher NFC HSM: a portable hardware variant for NFC-enabled Android devices, turning any NFC medium into a physical trust module for universal passwordless authentication.
Interoperable by design, both run with no server, no cloud, no sync and no third-party trust. Secrets, keys, and identities remain local, isolated, and temporary—the core of sovereign cybersecurity.
↪ Sovereign localization — embedded translations (offline)
- 13+ languages natively supported, including Arabic (UI/UX and help).
- Embedded translations: no network calls, no telemetry, no external APIs.
- Full RTL compatibility for Arabic, with consistent typography and safe offline layout.
↪ Sovereign passwordless authentication — without FIDO, without cloud
Unlike FIDO models tied to centralized validators or biometric identity keys, PassCypher operates 100% independently and offline. Authentication relies on proof of physical possession and local cryptologic checks—no external services, no cloud APIs, no persistent cookies. The result: a passwordless password manager compatible with all major operating systems, browsers, and web platforms, plus Android NFC for contactless use—universal interoperability without protocol lock-in.
⮞ Labeled “Quantum-Resistant Offline Passwordless Security”
In the official Intersec process, PassCypher is described as quantum-resistant offline passwordless security. Through AES-256-CBC plus a multi-layer PGP architecture with segmented keys, each fragment is unusable in isolation—disrupting algorithmic exploitation paths (e.g., Grover, Shor). This is not a PQC scheme; it is structural resistance via logical fragmentation and controlled ephemerality.
↪ A model of digital independence and trust
Cloudless cybersecurity can outperform centralized designs when hardware autonomy, local cryptology, and non-persistence are first principles. PassCypher resets digital trust to its foundation—security by design—and proves it across civil, industrial, and defense contexts as an offline sovereign password manager.
With the technical bedrock outlined, the next section turns to the territorial and doctrinal origins that shaped this Best Cybersecurity Solution finalist.
Andorran innovation — European roots of a Sovereign Quantum-Resistant Passwordless Manager
Having outlined the technical bedrock of the PassCypher ecosystem, it’s essential to map its institutional and territorial scope. Beyond engineering, the Intersec 2026 Best Cybersecurity Solution finalist status affirms an Andorran cybersecurity innovation—European in heritage, neutral in governance—now visible on the global stage of sovereign cybersecurity.
↪ Between French roots and Andorran neutrality
Born in Andorra in 2016 and built on French-origin patents granted internationally, PassCypher is designed, developed, and produced in Andorra. Its NFC HSM is manufactured in Andorra and France with Groupe Syselec, a long-standing industrial partner. This dual identity—Franco-Andorran lineage with Andorran sovereign governance—offers a concrete model of European industrial cooperation.
This positioning lets Freemindtronic act as a neutral actor, independent of political blocs yet aligned with a shared vision of trusted innovation.
↪ Why neutrality matters for a sovereign password manager
Andorra’s historic neutrality and geography between France and Spain create ideal conditions for technologies of trust and sovereignty. PassCypher’s offline sovereign password manager approach—RAM-only, cloudless, passwordless—can be adopted under diverse regulatory regimes without foreign infrastructure lock-in.
↪ Recognition with symbolic and strategic scope
Selection at the Intersec Awards 2026 signals an independent European approach succeeding in a demanding international arena, the United Arab Emirates—a global hub for security innovation. It shows that neutral European territories such as Andorra can balance dominant tech blocs while advancing quantum-resistant passwordless security.
↪ A bridge between two visions of sovereignty
Europe advances digital sovereignty via GDPR, NIS2, and DORA; the UAE pursues state-grade cybersecurity centered on resilience and autonomy. Recognition in Dubai links these visions, proving that neutral sovereign innovation can bridge European compliance and Emirati strategic needs through cloudless, interoperable architectures.
↪ Andorran doctrine of digital sovereignty
Freemindtronic Andorra embodies neutral digital sovereignty: innovation first, regulatory independence, and universal interoperability. This doctrine underpins PassCypher’s adoption across public and private sectors as a passwordless password manager that operates offline by design.
⮞ Transition
This institutional recognition sets up the next chapter: the historic first of a passwordless password manager shortlisted in a UAE technology competition—anchoring PassCypher in the history of major international cybersecurity awards.
Historic first — Passwordless finalist in the UAE (offline, sovereign)
PassCypher NFC HSM & HSM PGP, developed by Freemindtronic Andorra, is to our knowledge the first password manager—across all types (cloud, SaaS, biometric, open-source, sovereign, offline)—to be shortlisted as a finalist in a UAE technology competition.Best Quantum-Resistant Passwordless Manager 2026 — positioning & use cases
Recognized at Intersec Dubai, PassCypher positions as the best quantum-resistant passwordless manager 2026 for organizations needing sovereign, cloudless operations. The stack combines offline validation (proof of possession) with RAM-only cryptology and segmented keys. For market context, see our best password manager 2026 snapshot.
- Regulated & air-gapped environments (defense, energy, healthcare, finance, diplomacy).
- Zero cloud rollouts where data residency and minimization are mandatory.
- Interoperability across browsers/systems without FIDO/WebAuthn dependencies.
In summary:
To the best of our knowledge, no cloud, SaaS, biometric, open-source or sovereign solution in this category had reached finalist status in the UAE before PassCypher. This recognition strengthens Andorra’s stance in the UAE cybersecurity ecosystem and underscores the relevance of a passwordless password manager built for sovereign, offline use.
Doctrinal typology — What this sovereign offline manager is not
Before detailing validated sovereignty, it helps to situate PassCypher by contrast. The matrix below clarifies the doctrinal break.
| Model | Applies to PassCypher? | Why |
|---|---|---|
| Cloud manager | ❌ | No transfer, no sync; offline sovereign password manager. |
| FIDO / Passkeys | ❌ | Local proof of possession; no identity federation. |
| Open-source | ❌ | Patented architecture; sovereign doctrine and QA chain. |
| SaaS / SSO | ❌ | No backend, no delegation; cloudless by design. |
| Local vault | ❌ | No persistence; RAM-only ephemeral memory. |
| Network Zero Trust | ✔️ Complementary | Zero-DOM doctrine: off-network, segmented identities. |
This framing highlights PassCypher as offline, sovereign, universally interoperable—not a conventional password manager tied to cloud or FIDO, but a quantum-resistant passwordless manager 2026 architecture.
Validated sovereignty — Toward an independent model for Quantum-Resistant Passwordless Security
Recognition of Freemindtronic Andorra at Intersec confirms more than a product win: it validates a sovereign offline architecture designed for independence.
↪ Institutional validation of the sovereign doctrine
Shortlisting in Best Cybersecurity Solution endorses a philosophy of disconnected, self-contained security: protect digital secrets without cloud, dependency, or delegation, while aligning with global frameworks (GDPR/NIS2/ISO-27001).
↪ A response to systemic dependencies
Where most solutions assume permanent connectivity, PassCypher’s volatile-memory operations and data non-persistence remove centralization risks. Trust shifts from “trust a provider” to “depend on none.”
↪ Toward a global standard
By combining sovereignty, universal compatibility, and segmented cryptographic resilience, PassCypher outlines a path to an international norm for quantum-resistant passwordless security across defense, energy, health, finance, and diplomacy.
Through Dubai’s recognition, Intersec signals a new paradigm for digital security—where an offline sovereign password manager can serve as a Best Cybersecurity Solution reference.
⮞ Transition — Toward doctrinal consolidation
The next section details the cryptologic foundations and architectures behind this model—volatile memory, dynamic segmentation, and quantum-resilient design—linking doctrine to deployable practice.
International reach — Toward a global model for sovereign offline passwordless
What began as a finalist nod now signals the international confirmation of a neutral European doctrine born in Andorra: a quantum-resistant passwordless manager 2026 approach that redefines how digital security can be designed, governed, and certified as offline, sovereign, and interoperable.
↪ Recognition that transcends borders
The distinction at the Intersec Awards 2026 in Dubai arrives as digital sovereignty becomes a global priority. As a Best Cybersecurity Solution finalist, Freemindtronic Andorra positions PassCypher as a transcontinental reference between Europe and the Middle East—bridging European trust-and-compliance traditions with Emirati resilience and operational neutrality. Between these poles, PassCypher acts as a secure interoperability bridge.
↪ A global showcase for disconnected cybersecurity
Joining the select circle of vendors delivering trusted offline cybersecurity, Freemindtronic Andorra addresses government, industrial, and defense sectors seeking cloud-independent protection. The outcome: a concrete path where data protection, geopolitical neutrality, and technical interoperability coexist—strengthening Europe’s capacity for digital resilience.
↪ A step toward a sovereign global standard
With data volatility (RAM-only) and non-centralization as defaults, PassCypher outlines a universal sovereign standard for identity and secrets management. Trans-regional bodies—European, Arab, Asian—can align around a model that reconciles technical security and regulatory independence. Intersec’s recognition acts as a norm-convergence accelerator between national doctrines and emerging international standards.
↪ From distinction to diffusion
Beyond institutions, momentum translates into industrial cooperation and trusted partnerships among states, companies, and research hubs. Appearances at reference events such as MILIPOL 2025 and Intersec Dubai reinforce the dual focus—civil and military—and rising demand for an offline sovereign password manager that remains passwordless without FIDO.
↪ A European trajectory with global scope
Andorra’s recognition via Freemindtronic shows how a neutral micro-state can influence global security balances. As alliances polarize, neutral sovereign innovation offers a unifying alternative: a quantum-resistant passwordless doctrine that elevates independence without sacrificing interoperability.
⮞ Transition — Toward final consolidation
This international reach is not honorary: it is a global validation of an independent, resilient, sovereign model. The next section consolidates PassCypher’s doctrine and its role in shaping a global standard for digital trust.
Consolidated sovereignty — Toward an international standard for sovereign passwordless trust
In conclusion, the Intersec Awards 2026 finalist status for PassCypher is more than honorary: it signals the global validation of a sovereign cybersecurity model built on controlled disconnection, RAM-only (volatile) operations, and segmented cryptology. This trajectory aligns naturally with diverse regulatory environments — from EU frameworks (GDPR, NIS2, DORA) to UAE references (PDPL, DESC, IAS) — and favors the sovereign ownership of secrets at the heart of a quantum-resistant passwordless manager 2026 approach.
↪ Global regulatory compatibility by design
The offline sovereign password manager model (no cloud, no servers, proof of possession) supports key compliance objectives across major jurisdictions by minimizing data movement and persistence:
- United Kingdom: UK GDPR, Data Protection Act 2018, and NCSC CAF control themes (asset management, identity & access, data security).
- United States: alignment with control families in NIST SP 800-53 / SP 800-171 and Zero Trust (SP 800-207); supports privacy/security safeguards relevant to sectoral laws such as HIPAA and GLBA (data minimization, access control, auditability).
- China: principles of the Cybersecurity Law, Data Security Law, and PIPL (data localization & purpose limitation aided by local, ephemeral processing).
- Japan: APPI requirements (purpose specification, minimization, breach mitigation) supported by volatile-memory operation and no persistent stores.
- South Korea: PIPA safeguards (consent, minimization, technical/managerial protection) helped by air-gapped usage and local validation.
- India: DPDP Act 2023 (lawful processing, data minimization, security by design) addressed through FIDO-free passwordless and on-device cryptology.
Note:
PassCypher does not claim automatic certification; it enables organizations to meet mandated outcomes (segregation of duties, least privilege, breach impact reduction) by keeping secrets local, isolated, and ephemeral.
↪ Consolidating a universal doctrine
The doctrine of sovereign cybersecurity has moved from manifesto to practice. PassCypher HSM PGP and PassCypher NFC HSM show that cryptographic autonomy, global interoperability, and resilience to emerging threats can coexist in an offline sovereign password manager. Cross-regional interest — Europe, the GCC, the UK, the US, and Asia — confirms a simple premise: trusted cybersecurity requires digital sovereignty. The offline, volatile architecture underpins passwordless authentication without FIDO and independent secrets management at enterprise and state scale.
↪ Multilingual by design (embedded, offline)
To support global deployments and air-gapped operations, PassCypher ships with 13+ embedded languages (including Arabic, English, French, Spanish, Catalan, Japanese, Korean, Chinese Simplified, Hindi, Italian, Portuguese, Romanian, Russian, Ukrainian). UI and help content are fully offline (no external translation APIs), preserving confidentiality and availability.
↪ A catalyst for international standardization
Recognition in Dubai acts as a standardization accelerator. It opens the way to shared criteria where disconnected security and segmented identity protection are certifiable properties. In this view, PassCypher operates as a functional prototype for a future international digital-trust standard, informing dialogues between regulators and standards bodies across the EU, the UK, the Middle East, the US and Asia, encouraging convergence between compliance and sovereign-by-design architectures.
↪ Andorran sovereignty as a lever for global balance
Andorra’s neutrality and regulatory agility offer an ideal laboratory for sovereign innovation. The success of Freemindtronic Andorra shows that a nation outside the EU, yet closely aligned with its economic and legal sphere, can act as a balancing force between major technology blocs. The distinction in Dubai highlights a new center of gravity for global digital sovereignty, supported by Andorran leadership and French industrial partnerships — relevant to ministries, regulators, and critical industries across the UAE and beyond.
↪ A shared horizon: trust, neutrality, independence
This doctrine reframes the cybersecurity triad:
- trust — local verification and proof of possession;
- neutrality — no intermediaries, no vendor lock-in;
- independence — removal of cloud/server dependencies.
The outcome is an open, interoperable, sovereign model — a practical answer for governments and enterprises seeking to protect digital secrets without sacrificing user freedom or national sovereignty.
“PassCypher is not a password manager. It is a sovereign, resilient, autonomous cryptographic state, recognized as an Intersec Awards 2026 finalist.” — Freemindtronic Andorra, Dubai · 13 January 2026
⮞ Weak signals identified
- Pattern: Rising demand for cloudless passwordless in critical infrastructure.
- Vector: GDPR/NIS2/DORA convergence with off-network sovereign doctrines; UAE PDPL/DESC/IAS imperatives; growing UK/US/Asia regulatory emphasis on data minimization and zero trust.
- Trend: Defense & public-sector forums (e.g., Milipol November 2025, GCC security events) exploring RAM-only architectures.
⮞ Sovereign use case | Resilience with Freemindtronic
In this context, PassCypher HSM PGP and PassCypher NFC HSM neutralize:
- Local validation by proof of possession (NFC/HID), no servers or cloud.
- Ephemeral decryption in volatile memory (RAM-only), zero persistence.
- Dynamic PGP segmentation with contextual isolation of secrets.
FAQ — Quantum-Resistant Passwordless Manager & sovereign cybersecurity
Quick take
Yes. PassCypher validates access by proof of possession with no server, no cloud, and no WebAuthn.
Why it matters
Because everything runs in volatile memory (RAM-only), it stays offline, universal, interoperable across browsers and systems. This directly serves queries like passwordless authentication without FIDO and offline sovereign password manager inside our Quantum-Resistant Passwordless Manager 2026 positioning.
In one sentence
FIDO relies on WebAuthn and identity federation; PassCypher is FIDO-free, serverless, cloudless, using segmented PGP + AES-256-CBC entirely in RAM.
Context & resources
Federation centralises trust and increases the attack surface. PassCypher replaces it with local cryptology and ephemeral material (derive → use → destroy). See:
WebAuthn API hijacking,
DOM extension clickjacking (DEF CON 33).
Targets: quantum-resistant passwordless security, passwordless password manager 2026.
Short answer
Yes. Arabic (RTL) and 13+ languages are embedded; translations work fully offline (air-gap), no external API calls.
Languages included
العربية, English, Français, Español, Català, Deutsch, 日本語, 한국어, 简体中文, हिन्दी, Italiano, Português, Română, Русский, Українська — aligned with the long-tail sovereign password manager for multi-region rollouts.
Essentials
No cloud, no servers, no persistence: secrets are created, used, then destroyed in RAM.
Under the hood
The RAM-only password manager pattern plus key segmentation removes common exfiltration paths (databases, sync, extensions). That’s core to our Quantum-Resistant Passwordless Manager 2026 doctrine.
Both roles, one stack
It is an offline sovereign password manager that also enables passwordless access without FIDO.
How it plays together
As a manager, secrets live only in volatile memory. As passwordless, it proves physical possession across browsers/systems. Covers intents: best password manager 2026 offline, cloudless password manager for enterprises.
Operational view
Yes. It is cloudless and serverless by design, compatible with desktop, web, and Android NFC environments.
Risk notes
No identity broker, no SaaS tenant, no extension layer — consistent with Zero Trust (local verification, least privilege). Related reads:
Persistent OAuth / 2FA weaknesses,
APT29 app-password abuse.
What you can expect
PassCypher doesn’t certify you automatically; it enables outcomes (minimisation, least privilege, impact reduction) by keeping secrets local, isolated, ephemeral.
Where it fits
Aligned with policy goals in EU GDPR/NIS2/DORA, UAE PDPL/DESC/IAS, UK (UK GDPR/DPA 2018/NCSC CAF), US (NIST SP 800-53/171, SP 800-207 Zero Trust, sectoral HIPAA/GLBA), CN (CSL/DSL/PIPL principles), JP (APPI), KR (PIPA), IN (DPDP). Supports our secondary intent: Best Cybersecurity Solution finalist (Intersec 2026).
Plain explanation
Here, “quantum-resistant” refers to structural resistance — segmentation and ephemerality in RAM — not to new PQC algorithms.
Design choice
We don’t replace primitives; we limit usefulness and lifetime of material so isolated fragments are worthless. Matches the long-tail quantum-resistant passwordless security.
Snapshot
It avoids the layers under fire: no WebAuthn, no browser extensions, no OAuth persistence, no stored app passwords.
Go deeper
Recommended reading:
WebAuthn API hijacking,
DOM extension clickjacking,
Persistent OAuth flaw (2FA),
APT29 app-passwords.
Reason in brief
For demonstrating that offline, sovereign, passwordless security (RAM-only + segmentation) scales globally — without cloud or federation.
Awards intent capture
This answers searches like best cybersecurity solution 2026 and best password manager 2026 offline, and supports our keyphrase Quantum-Resistant Passwordless Manager 2026 with multilingual reach (incl. Arabic) for Dubai & GCC audiences.
⮞ Go further — PassCypher solutions worldwide
Discover where to evaluate our offline sovereign password manager stack and passwordless authentication without FIDO across EMEA. These links cover hardware options, RAM-only apps, and universal interoperability accessories.
AMG PRO (Paris, France)
KUBB Secure by Bleu Jour (Toulouse, France)
- PassCypher HSM PGP — passwordless manager (RAM-only, offline)
- Crystal PassCypher USB key — secure removable support
- Bluetooth Keyboard Emulator — universal K/M bridge for NFC HSM
- KUBB Secure Mini — fanless NFC HSM for sovereign passwordless
Fullsecure Andorra
- PassCypher HSM PGP — offline secrets manager (volatile memory)
- PassCypher NFC HSM Lite — NFC passwordless authentication
- PassCypher NFC HSM Master — advanced identity & secrets management
- Bluetooth Keyboard Emulator — universal compatibility (air-gapped use)
Tip: for internal linking and search intent capture, reference anchors such as /passcypher/offline-password-manager/ and /passcypher/best-password-manager-2026/ where appropriate.
⮞ Strategic outlook
Recognition of Freemindtronic Andorra at Intersec 2026 underlines that sovereignty is a universal technology value. By enabling cloudless, serverless operations with passwordless authentication without FIDO, the Quantum-Resistant Passwordless Manager 2026 approach advances a pragmatic path toward a global standard for digital trust — born in Andorra, recognized in Dubai, relevant to EMEA, the Americas, and Asia-Pacific.



























































































































































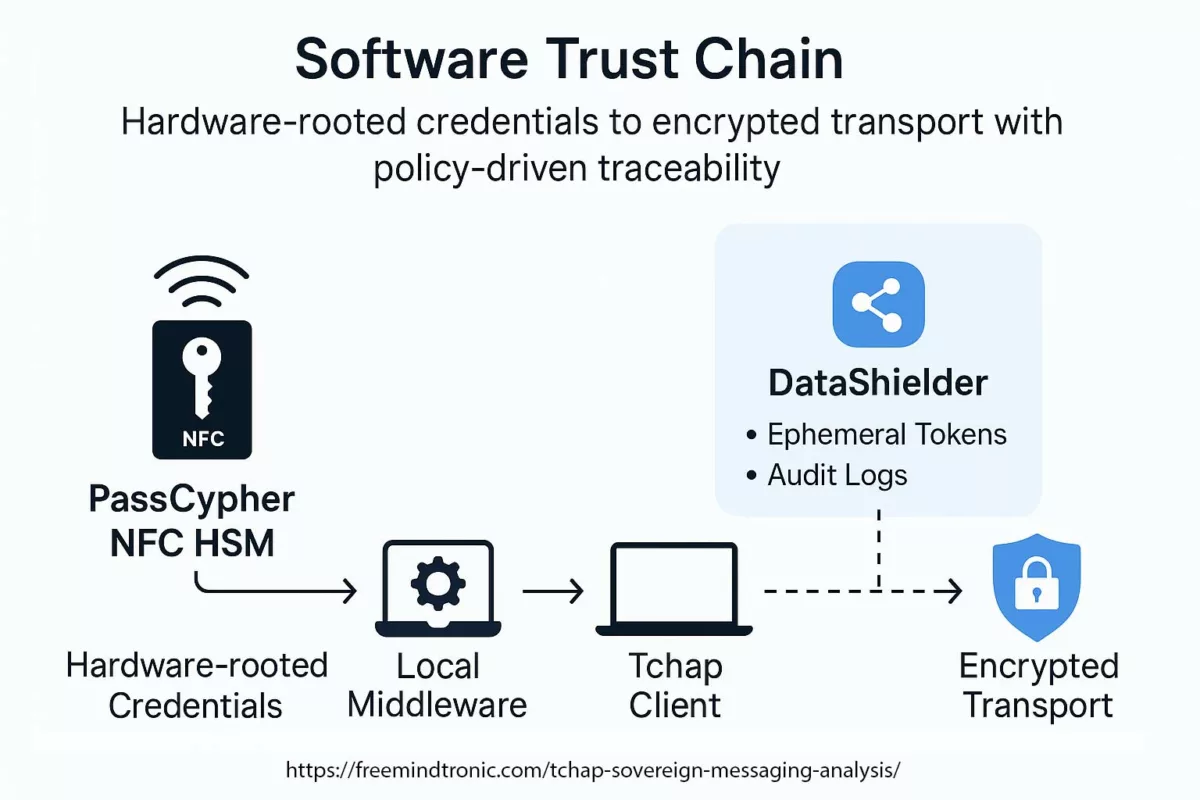
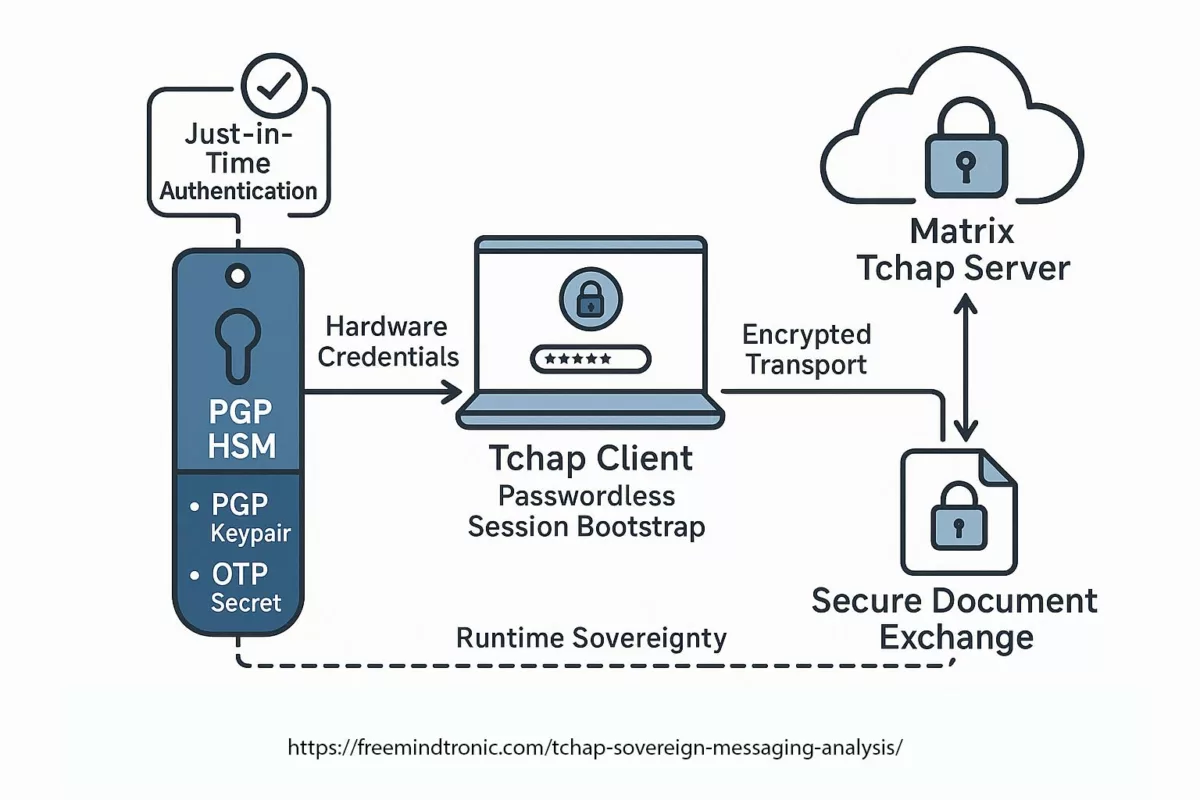
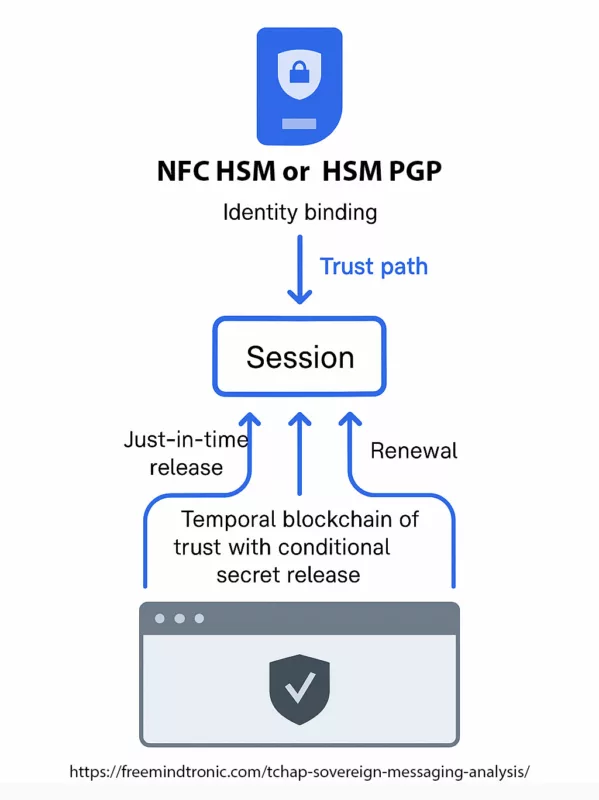
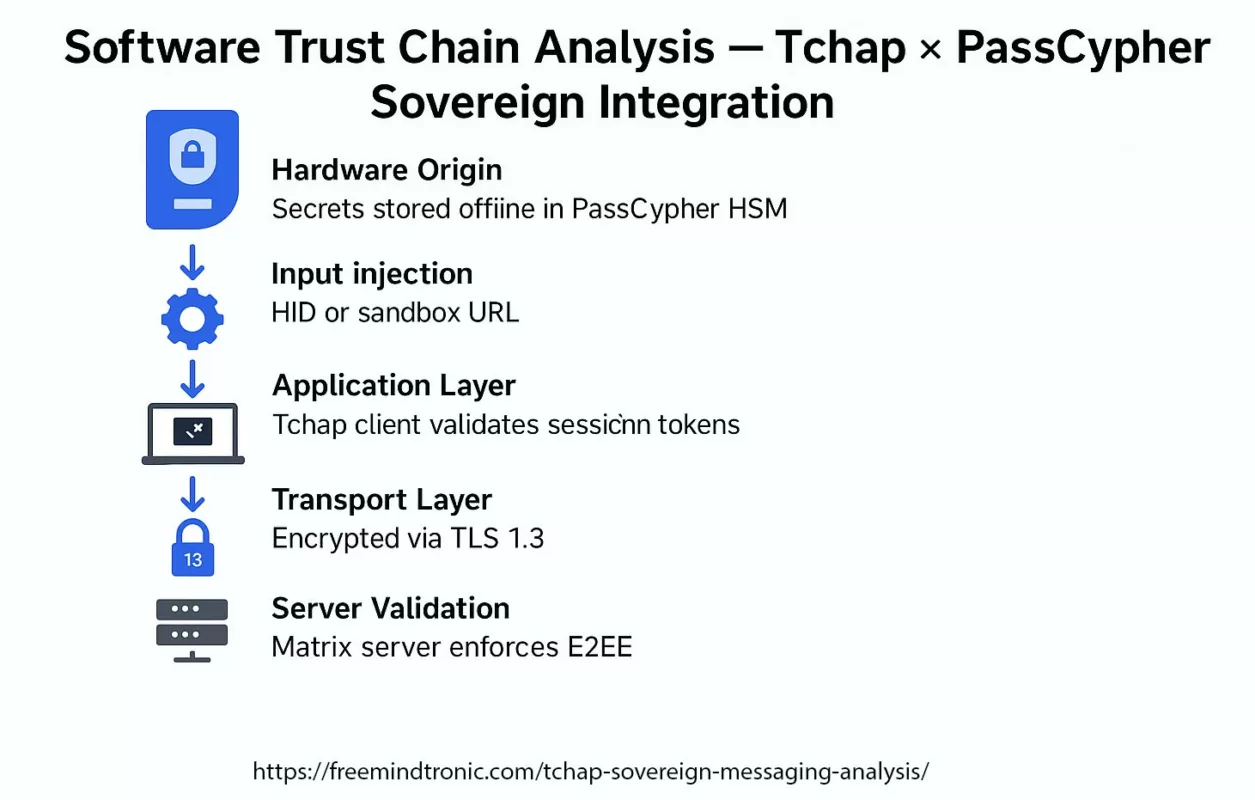 ✪ Software Trust Chain — Mapping the flow of sovereign trust from hardware-generated credentials in PassCypher HSM, through local middleware, Tchap client validation, TLS 1.3 mutual authentication, and E2EE server layers.</caption]
✪ Software Trust Chain — Mapping the flow of sovereign trust from hardware-generated credentials in PassCypher HSM, through local middleware, Tchap client validation, TLS 1.3 mutual authentication, and E2EE server layers.</caption]