BadPilot: Russia’s Expanding Cyber Threat Against Global Infrastructure
BadPilot Cyber Attacks pose a significant threat to global critical infrastructures, targeting over 50 countries. As a sophisticated cyber-espionage subgroup of Sandworm (APT44), BadPilot has been linked to advanced infiltration campaigns aimed at energy grids, telecommunications, and government networks. This article explores BadPilot’s attack methods, its impact on global cybersecurity, and strategies to prevent future BadPilot cyber threats.
BadPilot Cyber Attacks: Sandworm’s New Weaponized Subgroup
Understanding the rise of BadPilot and its impact on global cybersecurity.
BadPilot, a newly identified subgroup of Russia’s infamous Sandworm unit (APT44), is expanding its cyber-espionage operations, targeting critical infrastructures worldwide. The group’s advanced tactics go beyond typical cyber-espionage, focusing on long-term infiltration and the potential to disrupt essential services.
- Discovered by: Microsoft Threat Intelligence
- Primary Targets: Energy grids, telecommunications networks, and government agencies
- Geographical Reach: Over 50 countries, with heightened activity in the US, UK, and Eastern Europe
BadPilot Cyber Attack Vectors and Infiltration Tactics
How BadPilot gains unauthorized access to critical systems.
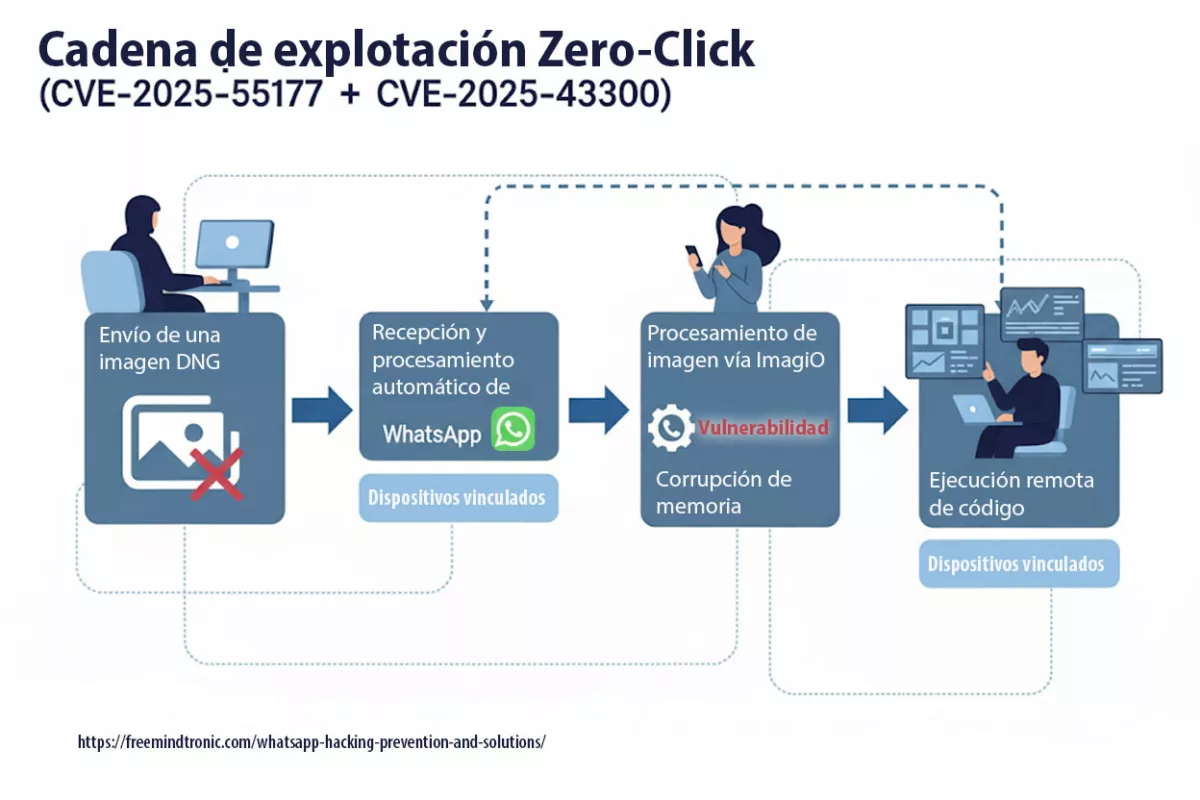
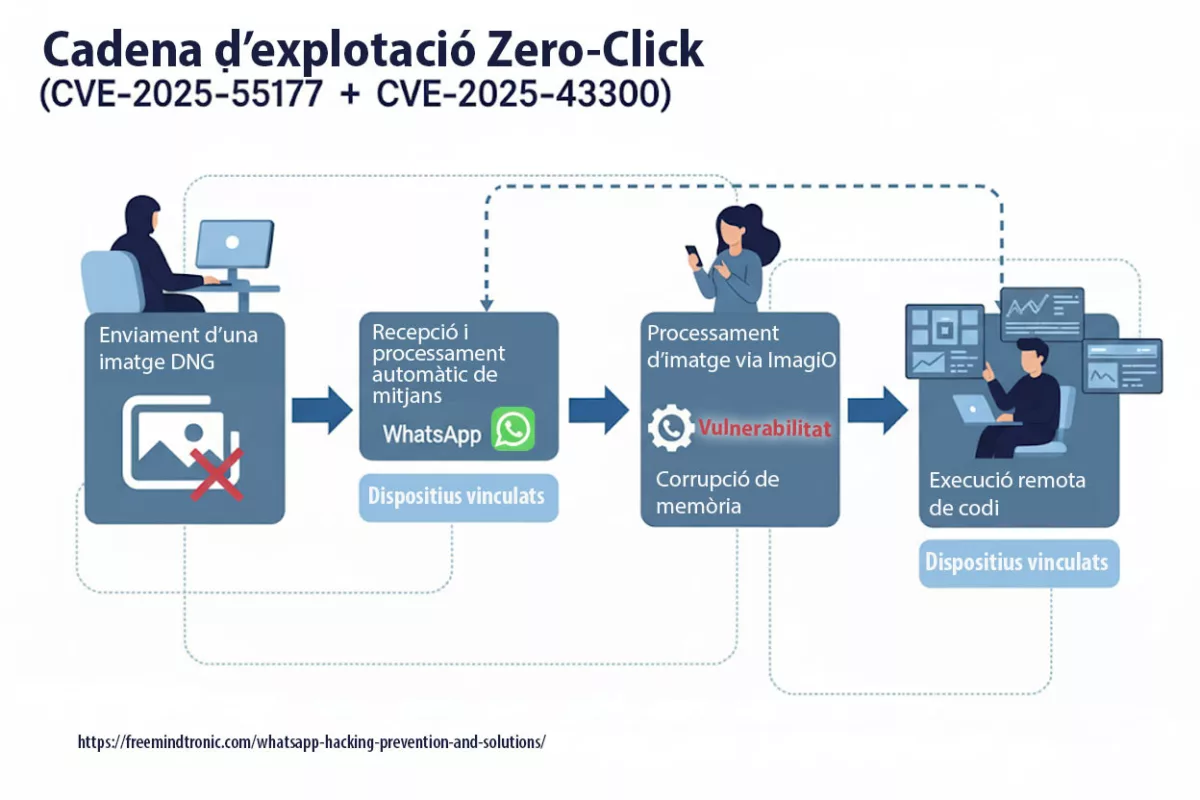
Microsoft’s report outlines BadPilot’s use of sophisticated tactics, including the exploitation of zero-day vulnerabilities in widely-used enterprise tools like Fortinet FortiClient EMS and ConnectWise ScreenConnect. These vulnerabilities allow attackers to gain initial access, followed by the deployment of custom malware for persistence and data exfiltration.
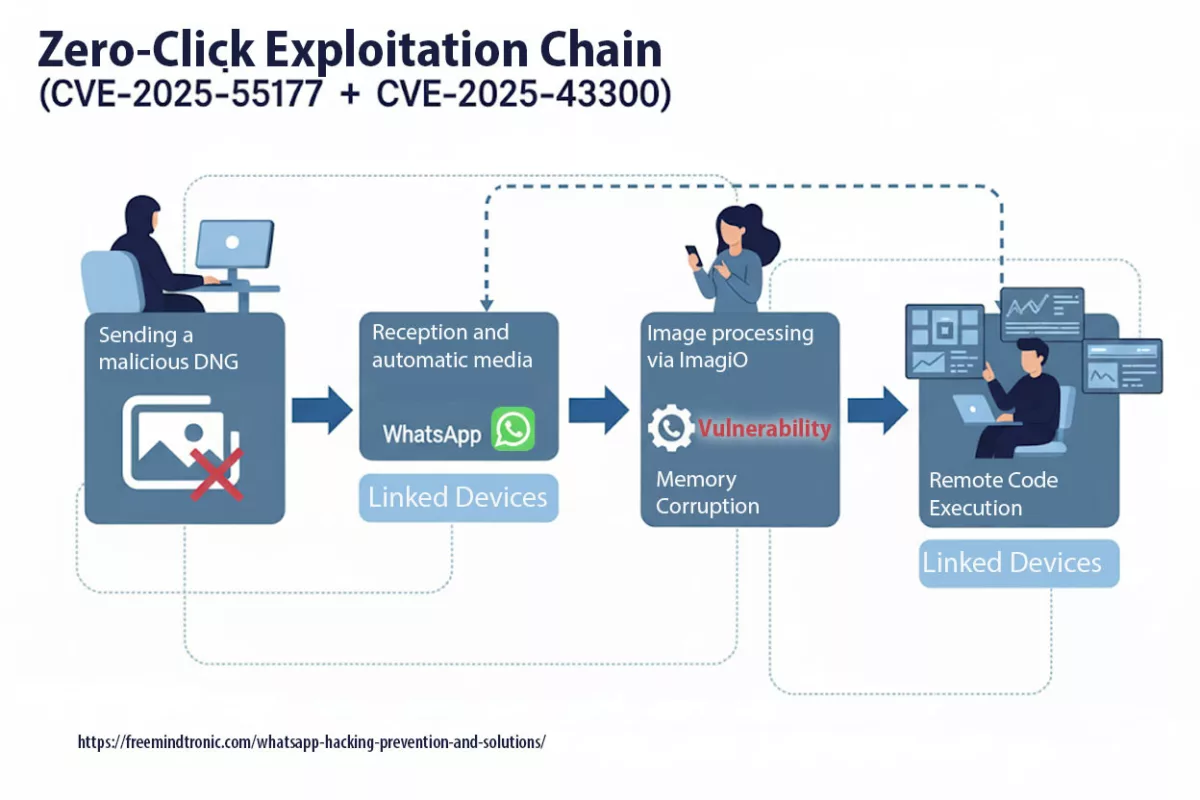
BadPilot Attack Flow
Step-by-step breakdown of BadPilot’s infiltration strategy
Diagram showcasing reconnaissance, infiltration, lateral movement, data exfiltration, and anti-forensic techniques.
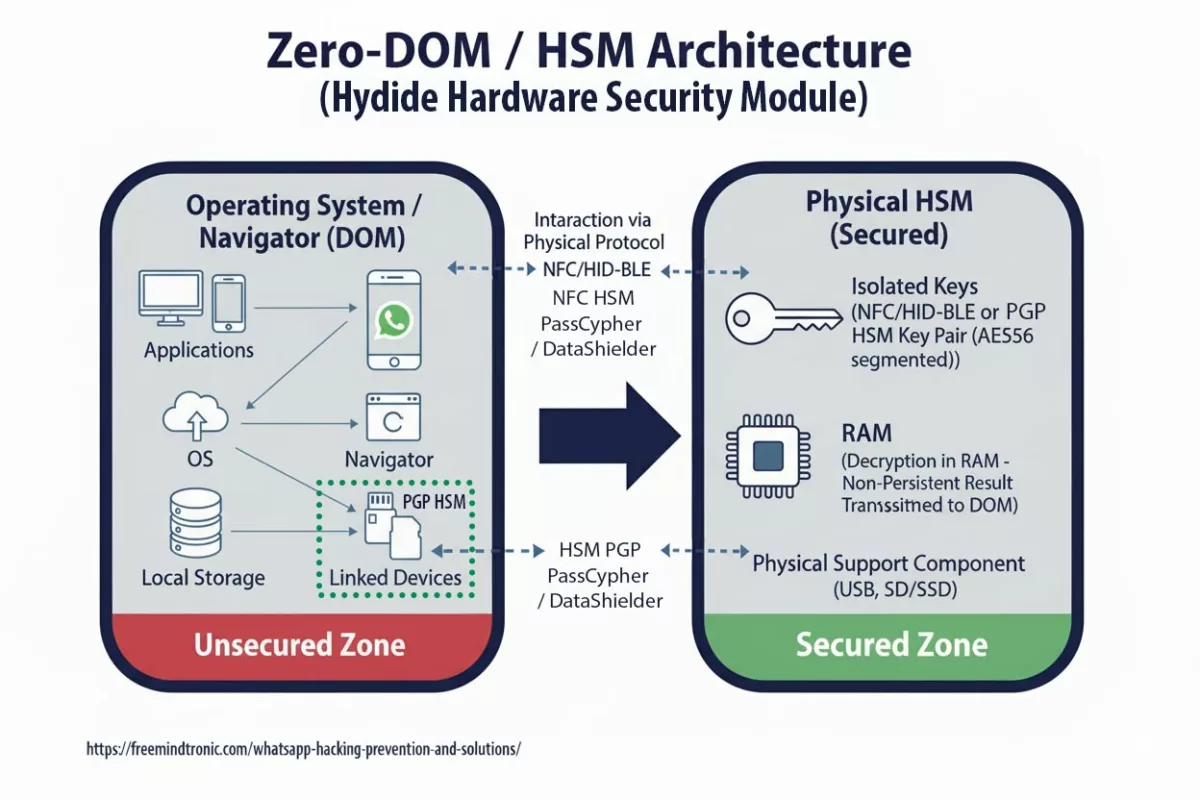
DataShielder NFC HSM Auth & M-Auth: Crucial Defense Against BadPilot Attacks
How DataShielder Strengthens Protection Against Identity Theft and Lateral Movement
The BadPilot campaign heavily relies on techniques like credential theft, privilege escalation, and lateral movement within networks. This is where the DataShielder NFC HSM Auth and M-Auth play a critical role:
-
DataShielder NFC HSM Auth secures authentication processes by requiring a physical NFC HSM device to validate user identity. Even if BadPilot manages to steal credentials, unauthorized access is blocked without the NFC hardware.
-
DataShielder NFC HSM M-Auth enhances this by enabling the creation of remote access keys through encrypted QR codes. This provides administrators with the ability to securely manage permissions and revoke access remotely, preventing lateral movement even after initial infiltration.
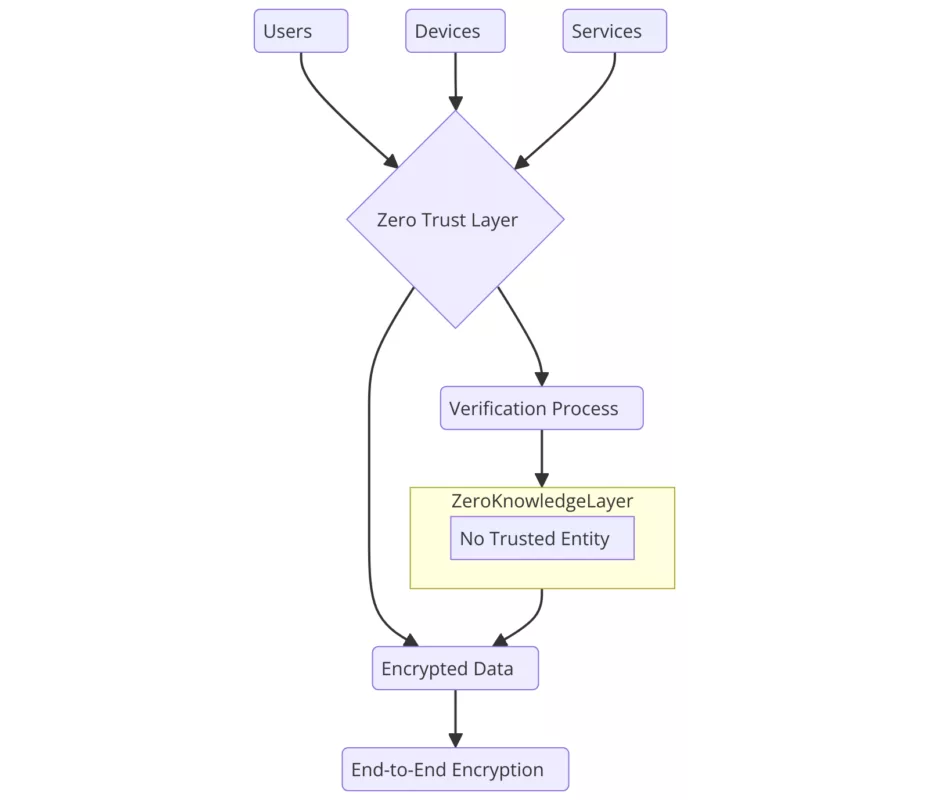
Both tools operate on a Zero Trust, Zero Knowledge model, functioning entirely offline with no servers, no databases, and no user identification, eliminating traditional points of compromise.
Why DataShielder Auth & M-Auth Are Effective Against BadPilot
- Stops Identity Hijacking: Physical authentication ensures credentials alone aren’t enough for unauthorized access.
- Prevents Lateral Movement: By using per-session keys and requiring physical NFC tokens, attackers can’t pivot within networks.
- Real-Time Access Control: Admins can generate and revoke encrypted QR codes for time-sensitive operations.
- Hardware-Based Encryption: Uses AES-256 CBC with segmented keys for end-to-end data protection.
💡 These dual-use tools (civil and military) are available in France and across Europe via AMG Pro and its partners.
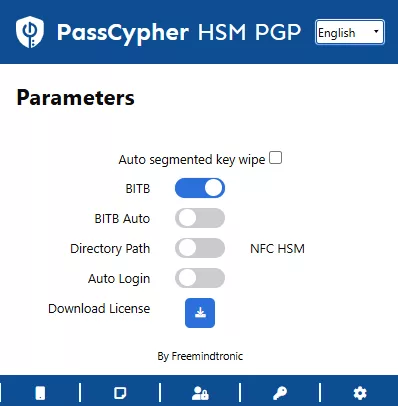
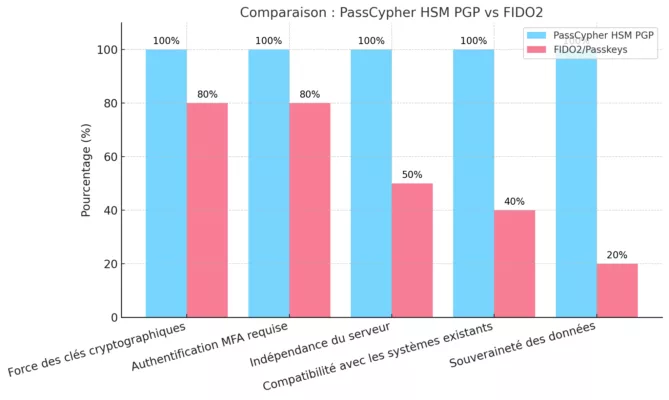
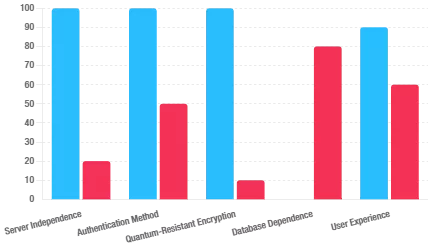
PassCypher NFC HSM & PassCypher HSM PGP: Fortifying Multi-Factor Authentication Against BadPilot
Reinforcing Password Security and TOTP-Based MFA
As BadPilot leverages credential theft and social engineering to bypass traditional security systems, the need for robust multi-factor authentication (MFA) is more critical than ever. PassCypher NFC HSM and PassCypher HSM PGP offer an advanced defense by securing both credentials and time-based one-time passwords (TOTP) with AES-256 CBC PGP encryption using segmented keys.
How PassCypher Strengthens Cybersecurity Against BadPilot:
- 🔒 Private TOTP Key Management:
Secure storage of TOTP keys within hardware-encrypted containers, eliminating the risk of key exfiltration. - ⚡ Seamless Auto-Authentication (PassCypher HSM PGP):
On Windows and MacOS, it auto-fills TOTP PIN codes into login forms, preventing keyloggers and man-in-the-middle attacks. - 📱 Controlled Manual Authentication (PassCypher NFC HSM):
On Android, displays TOTP PIN codes for manual input, adding an additional layer of human verification. - 🛡️ Advanced Anti-Phishing Mechanisms (PassCypher HSM PGP):
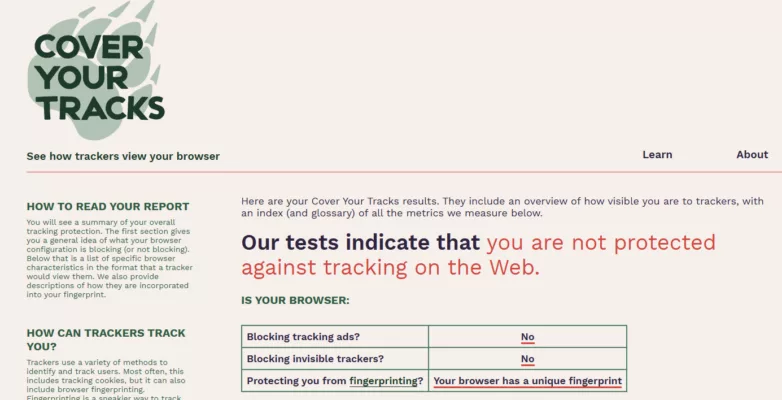
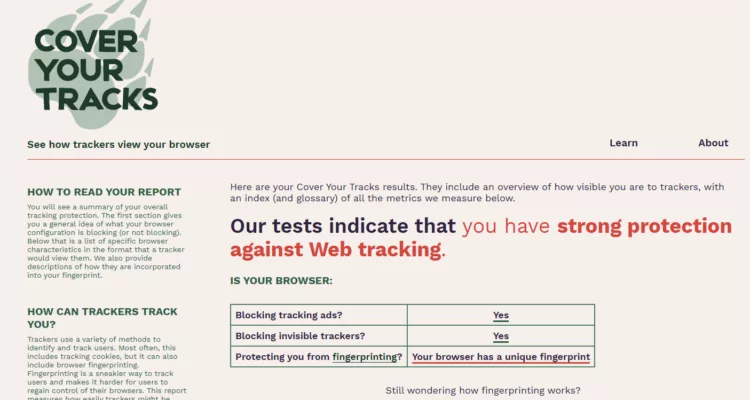
- Anti-Typosquatting: Detects domain name impersonations to prevent login on fake websites.
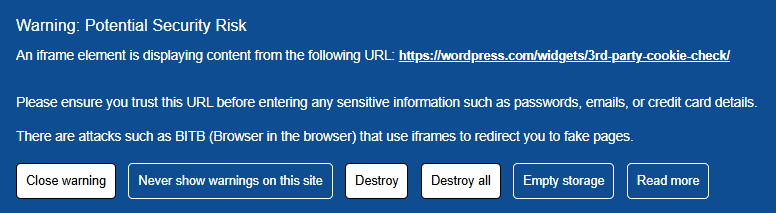
- BITB Attack Prevention (Browser-in-the-Browser): Blocks fake browser windows used in phishing schemes.
- Password Breach Monitoring (Pwned Passwords Integration): Automatically checks stored passwords against known data breaches, alerting users if credentials have been compromised.
- 🧮 AES-256 CBC PGP with Segmented Keys:
Guarantees that both stored credentials and TOTP keys remain secure, even in case of partial system compromise.
Why PassCypher Is Critical Against BadPilot Tactics:
-
- Prevents TOTP Code Theft:
Since BadPilot aims to hijack MFA codes, PassCypher’s encrypted containers safeguard TOTP keys from exfiltration. - Neutralizes MFA Bypass Attempts:
Even if attackers gain login credentials, they cannot generate valid TOTP codes without the physical HSM. - Thwarts Lateral Movement:
Using per-session TOTP codes and segmented key encryption, attackers can’t pivot within networks post-compromise. - Protects Against Phishing and Credential Theft:
PassCypher HSM PGP’s built-in anti-phishing tools (anti-typosquatting, BITB protection, and password breach checks) mitigate common attack vectors exploited by groups like BadPilot.
- Prevents TOTP Code Theft:
🔰 Enhanced Defense Against APT44:
PassCypher’s advanced TOTP management not only strengthens MFA but also acts as a critical countermeasure against APT44’s sophisticated attack vectors. By encrypting TOTP codes using AES-256 CBC PGP with segmented keys, PassCypher ensures that even if credentials are compromised, attackers cannot bypass the second layer of authentication.Furthermore, its anti-phishing protections—including anti-typosquatting, BITB attack prevention, and real-time password breach checks—serve as vital shields against social engineering tactics leveraged by BadPilot.
For more information on PassCypher and advanced MFA solutions, click on the links below:
- 🔐 PassCypher HSM PGP — Advanced password manager with TOTP auto-authentication and built-in anti-phishing protections, including typosquatting detection, BITB attack prevention, and breached password checks.
- 📱 PassCypher NFC HSM Lite — Portable solution for displaying TOTP PIN codes for manual input, with contactless anti-phishing protections through an Android phone.
- 🛡️ PassCypher NFC HSM Master — Advanced NFC HSM for managing segmented keys and secure TOTP generation, combined with contactless anti-phishing protections by Android phone.
Microsoft’s Findings: BadPilot’s Multi-Year Cyber Campaign
Long-term infiltration tactics and global implications.
According to Microsoft’s analysis, BadPilot’s campaigns date back to at least 2021, with an increasing number of attacks in 2024 and 2025. The group uses spear-phishing, supply chain attacks, and exploitation of critical infrastructure vulnerabilities to establish long-term access.
Key Findings:
-
-
- Supply Chain Attacks: BadPilot has targeted software vendors to indirectly infiltrate their client networks.
- Persistent Access: Once inside, attackers use legitimate credentials and stealthy malware to maintain long-term access.
- Potential for Physical Disruption: BadPilot’s attacks on energy grids and water treatment facilities raise concerns about real-world consequences beyond data breaches.
-
Global Impact: Over 50 Countries Affected
How BadPilot’s cyber operations pose a threat to global stability.
BadPilot’s attacks are not limited to a single region. With confirmed activity across North America, Europe, Asia, and the Middle East, the group has demonstrated its capacity to affect international energy markets, disrupt communication networks, and compromise national security infrastructures.
Most Impacted Sectors:
-
-
- ⚡ Energy and utilities
- 📡 Telecommunications providers
- 🏛️ Government agencies
- 🏥 Healthcare infrastructures
-
Proactive Defense Against BadPilot Cyber Threats
Implementing Stronger Encryption and Authentication Measures
Given the complexity of BadPilot Cyber Attacks, organizations must adopt a multi-layered cybersecurity approach to mitigate the growing impact of these advanced cyber threats.This includes:
- 🔄 Regularly updating and patching systems.
- 🔑 Employing Zero Trust security frameworks.
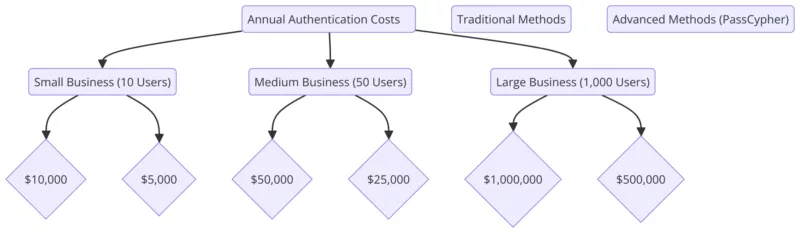
- 💾 Using hardware-based encryption tools like DataShielder NFC HSM, HSM PGP, Auth, M-Auth, and PassCypher HSM PGP for advanced multi-factor authentication, an essential defense against BadPilot Cyber Attacks.
- 👁️ Implementing continuous monitoring for unusual network activity.
DataShielder NFC HSM Auth and M-Auth offer an additional layer of protection against credential theft and unauthorized access, making them essential tools in defending against state-sponsored attacks like those from BadPilot.
Integrating PassCypher for Stronger MFA Security:
In addition to DataShielder solutions, organizations should implement advanced multi-factor authentication (MFA) using PassCypher.
- PassCypher HSM PGP — Provides auto-filled TOTP PIN codes with anti-phishing measures such as anti-typosquatting, BITB attack prevention, and breached password checks.
- PassCypher NFC HSM Lite — Displays TOTP PIN codes for manual input on Android, ensuring secure 2FA even without a connected system.
- PassCypher NFC HSM Master — Offers segmented key management and TOTP generation with contactless anti-phishing protections.
These tools actively mitigate BadPilot’s phishing-based TOTP theft tactics while bolstering defenses against identity hijacking and lateral movement.
Stay Vigilant Against BadPilot Cyber Attacks and State-Sponsored Threats
As BadPilot continues to expand its reach, organizations must strengthen their cybersecurity strategies. Utilizing robust hardware encryption solutions like DataShielder NFC HSM Auth and M-Auth provides an essential layer of defense against infiltration and lateral movement tactics commonly used by APT44.
🔒 For more information on DataShielder and advanced cybersecurity solutions :
DataShielder NFC HSM Auth & DataShielder NFC HSM MAuth
Expanding Knowledge: Emerging Cyber Threats Linked to BadPilot
For further insights into APT44’s evolving tactics, explore our dedicated article on their recent QR Code Phishing campaigns:
🔗 APT44 QR Code Phishing: New Cyber-Espionage Tactics
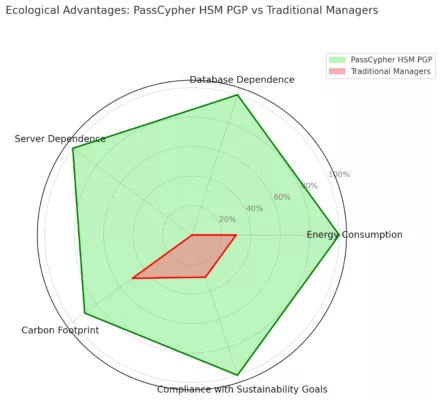
Stopping Cyber Espionage Before It Starts with DataShielder NFC HSM & DataShielder HSM PGP
DataShielder NFC HSM (for Android phones) and DataShielder HSM PGP (for Windows and MacOS) provide double-layered protection against cyber-espionage. These dual-use tools (civil and military) are available in France and across Europe via AMG Pro and its partners.
-
-
- DataShielder NFC HSM: Works with Android phones, encrypting data directly on the device through a secure NFC module.
- DataShielder HSM PGP: Operates as a browser extension, offering AES-256 CBC PGP encryption via segmented keys for emails, instant messaging, and cloud services.
- Both solutions operate offline, with no servers, no databases, and no user identification, ensuring Zero Trust and Zero Knowledge security models.
-
Global Collaboration is Key
How governments, tech companies, and cybersecurity experts are joining forces to combat BadPilot.
Recognizing the growing threat posed by BadPilot, international agencies and private tech firms are strengthening cooperation. Microsoft, in collaboration with national cybersecurity agencies like CISA (USA) and NCSC (UK), is actively sharing intelligence and working to close exploited vulnerabilities.
Key Partnerships:
-
-
- 🔗 Microsoft Threat Intelligence Report
- 🌐 CERT-UA — Monitoring and sharing real-time alerts on Russian cyber threats
- 🏛️ National Cyber Security Centre (UK) — Assisting in policy-making and vulnerability management
-
Stay Vigilant Against State-Sponsored Cyber Threats
As BadPilot continues to expand its reach, organizations must strengthen their cybersecurity strategies. Utilizing robust hardware encryption solutions like DataShielder NFC HSM Auth and M-Auth provides an essential layer of defense against infiltration and lateral movement tactics commonly used by APT44.
🔑 Strengthen MFA Against BadPilot Cyber Attacks with PassCypher
To effectively counter BadPilot Cyber Attacks and prevent MFA bypass attempts, integrating PassCypher into your security strategy is crucial. With encrypted TOTP management and real-time anti-phishing protections, PassCypher offers robust defense mechanisms against the sophisticated methods used by APT44.