Cyber espionnage zero day : la fin des spywares visibles marque l’entrée dans une économie mondiale de vulnérabilités inconnues, d’exploits modulaires et de capacités d’intrusion difficilement attribuables. Cette chronique analyse comment le marché du zero day transforme le cyber-espionnage, fait s’effondrer la confiance logicielle et impose des points d’arrêt souverains hors OS, hors réseau et hors automatisation.
Résumé express — Cyber espionnage zero day
⮞ Reading Note
D’abord, ce résumé express (≈ 4 minutes) fournit une compréhension autonome des enjeux du cyber espionnage zero day. Ensuite, le résumé avancé détaillera les mécanismes, les zones permissives et les points d’arrêt.
⚡ Découverte
Depuis quelques années, le cyber-espionnage ne se résume plus aux spywares médiatisés. Au contraire, une transformation plus discrète s’impose : le marché du zero day alimente des intrusions fondées sur des vulnérabilités inconnues, donc non détectables par les mécanismes habituels au moment critique. Ainsi, l’attaque ne dépend plus d’un « produit » unique, mais d’un assemblage de capacités d’exploitation, de livraison et de furtivité.
✦ Impacts immédiats
- D’une part, la compromission devient un état durable du terminal, et non un incident ponctuel.
- D’autre part, les agents de sécurité logiciels perdent leur capacité à prouver qu’ils fonctionnent correctement sur un environnement potentiellement compromis.
- Par conséquent, l’attribution et la réponse deviennent plus incertaines, tandis que la fenêtre d’exposition s’allonge.
⚠ Message stratégique
Cependant, l’essentiel n’est pas le “zero day” comme prouesse technique. En effet, ce qui change, c’est la logique de confiance : si l’OS peut être compromis sans signature connue, il ne peut plus servir de fondation à une preuve logicielle fiable. Dès lors, la sécurité devient une question de limites irréversibles : ce que l’on peut contenir, ce que l’on ne peut plus vérifier, et ce que l’on doit refuser de réintroduire sur un terminal suspect.
🛑 Quand ne pas agir
- Tout d’abord, ne réintroduisez pas de secrets (identifiants, clés, codes, données sensibles) sur un terminal dont l’intégrité n’est pas attestable.
- Ensuite, n’empilez pas des couches de sécurité logicielle “pour compenser” : sur un environnement compromis, cela peut augmenter la surface d’attaque et la complexité d’audit.
- Enfin, ne confondez pas retour au service et restauration de confiance : une reprise rapide peut masquer une persistance invisible.
✓ Principe de contre-espionnage souverain
Ainsi, la réduction de risque ne consiste pas à “nettoyer” l’OS, mais à déplacer la confiance hors de l’environnement compromis : hors OS, hors mémoire, et si nécessaire hors réseau. Par conséquent, l’objectif devient de protéger ce qui ne doit pas être exposé — secrets, identité, décision — même lorsque le terminal est potentiellement hostile.
Paramètres de lecture
Temps de lecture résumé express : ≈ 4 minutes
Temps de lecture résumé avancé : ≈ 6 minutes
Temps de lecture chronique complète : ≈ 35–40 minutes
Date de publication : 2026-01-16
Dernière mise à jour : 2026-01-23
Niveau de complexité : Avancé — cyber-espionnage & souveraineté numérique
Densité technique : ≈ 65 %
Langue principale : FR. EN.
Spécificité : Chronique stratégique — marché du zero day & contre-espionnage
Ordre de lecture : Résumé express → Résumé avancé → Marché du zero day → Zones permissives → Limites irréversibles → Points d’arrêt → Cas d’usage souverain
Accessibilité : Optimisé pour lecteurs d’écran — ancres & balises structurées
Type éditorial : Chronique stratégique — Digital Security
Niveau d’enjeu : 9.2 / 10 — compromission structurelle & perte d’attestation logicielle
À propos de l’auteur : Jacques Gascuel, inventeur, fondateur de Freemindtronic Andorre, titulaire de brevets en protection électrique intelligente, authentification sans fil et segmentation de clés.
Note éditoriale
Cette chronique s’inscrit dans la rubrique Digital Security. Elle prolonge les analyses consacrées au cyber-espionnage (Pegasus, Predator) en abordant le niveau supérieur : le marché mondial du zero day et ses effets irréversibles sur la confiance logicielle. Le propos n’est pas de proposer une « solution », mais de définir des limites opérationnelles et des doctrines de contre-espionnage compatibles avec des environnements civils, à double usage et régaliens européens sous autorisation. Ce contenu s’inscrit dans la continuité des travaux publiés dans : Digital Security. Il suit la Déclaration de transparence IA de Freemindtronic Andorra — FM-AI-2025-11-SMD5.
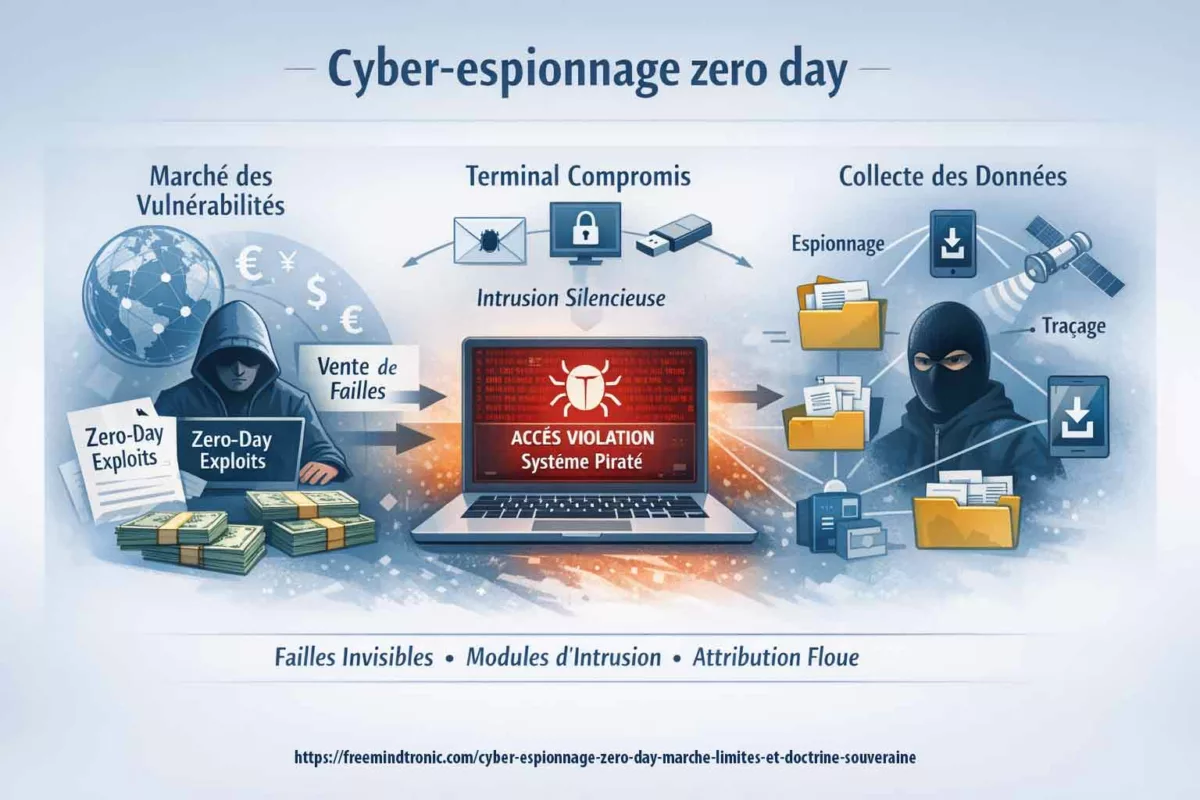
Les chroniques affichées ci-dessus ↑ appartiennent à la section Digital Security. Cependant, cette sélection ne sert pas d’archive : elle prolonge l’analyse des architectures d’intrusion, des risques systémiques liés aux marchés de vulnérabilités, et des pertes d’attestation logicielle. Ainsi, elle complète la présente chronique dédiée au cyber espionnage zero day et au basculement vers des capacités d’intrusion modulaires, renouvelables et difficilement attribuables. En revanche, l’objectif ici n’est pas de « suivre l’actualité », mais d’identifier des limites irréversibles et des points d’arrêt souverains lorsque le terminal ne peut plus être considéré comme fiable.
Key Insights
- Tout d’abord, le cyber espionnage zero day ne vend plus un spyware « produit », mais des capacités d’intrusion modulaires et renouvelables.
- Ensuite, lorsqu’un terminal est compromis par une vulnérabilité inconnue, l’OS ne peut plus attester son propre état ; par conséquent, la sécurité logicielle devient partiellement aveugle.
- Cependant, l’enjeu n’est pas seulement technique : il est aussi géopolitique, car les hubs et juridictions se déplacent pour réduire la traçabilité et contourner les contraintes.
- Dès lors, une doctrine de contre-espionnage crédible repose sur des points d’arrêt et des points de confiance hors OS, sous contrôle humain et, si nécessaire, matériel.
Résumé avancé — comprendre le cyber espionnage zero day
⮞ Reading Note
D’abord, ce résumé avancé approfondit les mécanismes du cyber espionnage zero day. Ensuite, la chronique complète démontrera pourquoi ces mécanismes dépassent durablement les cadres juridiques et techniques actuels.
Du spyware visible aux capacités d’intrusion zero day
Tout d’abord, le cyber espionnage s’est longtemps matérialisé sous la forme de logiciels espions identifiables, installés sur des terminaux ciblés. Cependant, ce modèle reposait sur une hypothèse fragile : celle de la détection possible, même tardive, par analyse comportementale ou signature. Aujourd’hui, avec le cyber espionnage zero day, cette hypothèse s’effondre.
En effet, l’exploitation de vulnérabilités inconnues permet une compromission sans alerte préalable, sans indicateur fiable et sans correctif disponible au moment critique. Ainsi, l’intrusion n’est plus un événement observable, mais un état silencieux, potentiellement persistant, qui invalide toute confiance logicielle.
Pourquoi le modèle Pegasus devient obsolète
Ensuite, il est essentiel de comprendre pourquoi des outils emblématiques comme Pegasus ne représentent plus l’avant-garde du cyber espionnage. Certes, ces spywares ont démontré une efficacité redoutable. En revanche, leur exposition médiatique, juridique et politique a révélé leurs limites structurelles.
Par conséquent, les acteurs du cyber espionnage se sont déplacés vers des modèles moins traçables : exploitation ponctuelle de zero day, chaînes d’attaque fragmentées et externalisation des composants critiques. Dès lors, le spyware comme produit fini devient un risque opérationnel, là où la capacité d’intrusion modulable devient un avantage stratégique.
Marché du cyber espionnage et vulnérabilités zero day
Désormais, le cyber espionnage zero day repose sur un marché structuré de vulnérabilités inconnues. En pratique, chercheurs, courtiers et intégrateurs échangent des failles, des preuves de concept et des chaînes d’exploitation. Ainsi, l’attaque n’est plus centralisée, mais distribuée entre acteurs spécialisés.
Cependant, ce marché ne se limite pas à une logique économique. En réalité, il sert aussi de mécanisme de dilution des responsabilités. Par conséquent, l’attribution devient plus complexe, tandis que la frontière entre acteurs étatiques, شبه-étatiques et privés s’estompe.
Implication centrale pour le contre-espionnage numérique
Enfin, l’implication majeure de ce basculement concerne le contre-espionnage lui-même. Autrefois, il s’agissait de détecter, analyser et neutraliser un outil. Aujourd’hui, il faut décider quand un environnement ne peut plus être considéré comme fiable.
Dès lors, la question n’est plus « comment nettoyer », mais « quand s’arrêter ». En conséquence, les doctrines efficaces intègrent des points d’arrêt, des refus explicites et des mécanismes de protection hors environnement compromis.
À présent, la chronique complète examine en détail le déplacement des hubs, les zones permissives européennes et les limites irréversibles de la sécurité logicielle.
Chronique complète — Cyber espionnage zero day
Désormais, il ne s’agit plus de commenter un outil, ni même une attaque isolée. En effet, le cyber espionnage zero day impose un changement d’échelle : celui d’un système économique mondial fondé sur l’exploitation de vulnérabilités inconnues. Ainsi, pour comprendre les risques actuels, il faut abandonner la logique du spyware visible et analyser la mutation structurelle du modèle.
Cependant, cette mutation ne s’est pas produite brutalement. Au contraire, elle résulte d’une accumulation de signaux faibles : judiciarisation des spywares, exposition médiatique, sanctions internationales et coûts politiques croissants. Dès lors, les acteurs du cyber espionnage ont cherché des modèles plus discrets, plus fragmentés et surtout plus difficiles à attribuer.
Marché du cyber espionnage : anatomie du zero day
D’abord, le marché du cyber espionnage ne se réduit pas à une place de marché visible. Au contraire, il fonctionne comme une chaîne d’approvisionnement : recherche, acquisition, industrialisation, puis intégration dans des capacités d’intrusion. Ainsi, le cyber espionnage zero day se nourrit d’une asymétrie simple : celui qui connaît une vulnérabilité inconnue décide du moment, de la cible et du silence.
Laboratoires de vulnérabilités zero day
Ensuite, les laboratoires de vulnérabilités zero day transforment une connaissance technique en avantage opérationnel. En effet, l’objectif n’est pas seulement de trouver une faille, mais de prouver qu’elle est exploitable, stable et reproductible sur des versions précises d’un système. Par conséquent, cette phase privilégie la discrétion, car la divulgation publique détruit immédiatement la valeur offensive.
Courtiers, intégrateurs et chaînes d exploitation
Cependant, la découverte ne suffit pas. Dès lors, des courtiers et intégrateurs relient laboratoires et opérateurs en assemblant des chaînes d’exploitation complètes : vecteur d’entrée, escalade de privilèges, persistance éventuelle, puis exfiltration. Ainsi, la capacité devient modulaire : si un maillon casse, il est remplacé, tandis que l’intention reste la même.
De plus, cette modularité facilite le double usage : une même vulnérabilité peut alimenter de la recherche défensive, ou bien des intrusions. En revanche, dans le cyber espionnage, la modularité sert surtout à réduire les traces et à accélérer le renouvellement.
Effacement de l attribution et dilution des responsabilités
Or, plus la chaîne est fragmentée, plus l’attribution se complique. En effet, lorsque la vulnérabilité, l’exploit et l’opération sont fournis par des entités distinctes, la responsabilité se dilue mécaniquement. Par conséquent, l’enjeu dépasse la technique : il devient politique, car l’incertitude freine la réponse, la preuve et parfois même la qualification.
Enfin, ce brouillage favorise une zone grise : des acteurs privés peuvent vendre une capacité, tandis que des acteurs étatiques peuvent l’utiliser sans exposition directe. Ainsi, le marché du cyber espionnage zero day sert aussi de mécanisme d’opacité.
Synthèse
En résumé, le marché du cyber espionnage zero day repose sur une chaîne d’approvisionnement discrète : laboratoires → courtiers → intégrateurs. Par conséquent, la fragmentation rend l’attribution instable, tandis que la modularité accélère le renouvellement des capacités d’intrusion.
À ce stade, une question devient incontournable : si le marché du cyber espionnage zero day est fragmenté, modulaire et difficilement attribuable, où ces capacités s’installent-elles concrètement ? En effet, les vulnérabilités ne circulent pas dans un vide juridique. Dès lors, pour comprendre leur impact réel, il faut analyser le déplacement géographique et juridictionnel des hubs opérationnels, là où contraintes, sanctions et réputation redessinent les lignes de fuite.
Cyber espionnage zero day : déplacement des hubs opérationnels
À mesure que le marché du cyber espionnage zero day se structure, une dynamique géographique apparaît clairement. En pratique, les capacités d’intrusion ne disparaissent pas sous la pression réglementaire ; elles se déplacent. Ainsi, lorsque des États renforcent les contrôles, imposent des sanctions ou subissent une exposition médiatique excessive, les acteurs réorganisent leurs implantations.
Cependant, ce déplacement ne relève pas uniquement de l’opportunisme. Il répond aussi à une logique de réduction du risque juridique, politique et réputationnel. Dès lors, certains territoires deviennent des points d’ancrage privilégiés pour des activités à la frontière du légal, du toléré et du non-dit.
Sanctions internationales et effets de réputation
Depuis plusieurs années, les sanctions internationales ont modifié l’économie du cyber espionnage. Lorsqu’un acteur devient trop visible, trop documenté ou trop associé à des abus, il perd de la valeur opérationnelle. En conséquence, la réputation devient un facteur de risque aussi important que la technique elle-même.
De ce fait, les entreprises et laboratoires liés au zero day cherchent à éviter les juridictions où la pression médiatique et politique est forte. Ils privilégient alors des environnements où la traçabilité est faible, la coopération judiciaire limitée ou la régulation encore immature.
Arbitrage juridictionnel et zones permissives
Cet environnement favorise un arbitrage juridictionnel assumé. Concrètement, les acteurs du cyber espionnage zero day choisissent des pays où le cadre légal est flou, fragmenté ou peu appliqué. Par ailleurs, certaines juridictions offrent un avantage décisif : la possibilité d’opérer sans obligation claire de transparence ni contrôle effectif des usages finaux.
Ainsi, des zones dites « permissives » émergent. Elles ne sont pas nécessairement illégales, mais elles offrent une combinaison favorable : attractivité économique, tolérance réglementaire et faible exposition internationale. En revanche, cette permissivité crée un effet d’aspiration qui concentre des capacités sensibles hors de tout véritable contrôle démocratique.
Synthèse
En définitive, le cyber espionnage zero day ne disparaît pas sous la contrainte : il se déplace. Les sanctions et la réputation redessinent la carte des hubs opérationnels, tandis que l’arbitrage juridictionnel crée des zones permissives où les capacités d’intrusion peuvent prospérer avec un minimum de visibilité.
À ce stade, une question centrale se pose : que se passe-t-il lorsque ces capacités trouvent un terrain favorable à l’intérieur même des États censés les contenir ? Pour répondre, il faut désormais examiner les failles internes, les négligences structurelles et les ruptures de loyauté qui fragilisent l’action publique de l’intérieur.
Cyber espionnage et failles internes de l’État
Au-delà des dynamiques de marché et des arbitrages géographiques, une autre réalité s’impose progressivement : le cyber espionnage zero day ne prospère pas uniquement par sophistication externe. Bien souvent, il s’appuie sur des faiblesses internes, plus discrètes mais tout aussi décisives. Autrement dit, la compromission n’entre pas toujours par effraction ; elle trouve parfois une porte déjà entrouverte.
Dans ce contexte, la question n’est plus seulement de savoir qui attaque, mais dans quelles conditions un État devient perméable. À ce titre, les dysfonctionnements organisationnels, les défauts de gouvernance et les chaînes de responsabilité floues jouent un rôle central. Peu à peu, ces fragilités transforment des infrastructures critiques en surfaces d’exposition silencieuses.
Négligence, loyauté et rupture de confiance
D’un côté, certaines compromissions résultent d’une négligence cumulative : systèmes obsolètes, segmentation inexistante, contrôles internes lacunaires. Pris isolément, ces éléments paraissent gérables. Mis bout à bout, ils créent cependant un environnement où une vulnérabilité zero day peut se déployer sans résistance significative.
De l’autre côté, la question de la loyauté devient incontournable. Sans aller jusqu’à la trahison caractérisée, des conflits d’intérêts, des dépendances industrielles ou des logiques de sous-traitance opaques suffisent parfois à rompre la chaîne de confiance. Dans ces conditions, la frontière entre défaillance et compromission intentionnelle devient difficile à tracer.
À terme, cette ambiguïté fragilise la capacité de réponse de l’État. Lorsqu’une fuite ou une intrusion survient, l’incertitude sur les responsabilités ralentit la décision, dilue l’imputabilité et complique toute remédiation crédible. Le cyber espionnage zero day trouve alors un terrain d’expression particulièrement favorable.
Synthèse
En définitive, les failles internes amplifient l’impact du cyber espionnage zero day. Négligence structurelle, dilution des responsabilités et tensions autour de la loyauté transforment des vulnérabilités techniques en crises de confiance institutionnelles.
À partir de là, un constat s’impose : toutes les intrusions ne nécessitent pas un zero day sophistiqué. Il devient donc nécessaire d’examiner comment des architectures centralisées et des pratiques documentaires défaillantes permettent des fuites massives, parfois sans exploitation technique avancée.
Cyber espionnage sans zero day : fuites massives et exfiltration
À première vue, le cyber espionnage est souvent associé à des attaques sophistiquées exploitant des vulnérabilités inconnues. Pourtant, une réalité plus prosaïque se dessine fréquemment. Dans de nombreux cas, des volumes considérables de données sont exfiltrés sans recourir à un zero day, simplement parce que l’architecture elle-même rend la fuite possible.
Dans ce type de scénario, la question n’est pas celle de l’ingéniosité de l’attaquant, mais celle de la concentration des flux et des accès. Lorsque des systèmes agrègent des documents sensibles, des identités et des métadonnées sans cloisonnement réel, l’exfiltration devient une conséquence logique plutôt qu’une prouesse technique.
Quand l’architecture documentaire devient la faille
Très souvent, les plateformes documentaires centralisées sont conçues pour la fluidité administrative plutôt que pour la résilience. En facilitant l’accès, la synchronisation et la mutualisation, elles créent aussi un point de fragilité unique. Une fois l’accès obtenu, même légitimement, l’attaquant n’a plus qu’à collecter.
Dans ce contexte, la distinction entre intrusion et usage abusif devient floue. Un compte compromis, un prestataire mal contrôlé ou un droit excessif suffisent à exposer des milliers de documents. La fuite n’est alors ni instantanée ni spectaculaire, mais progressive, silencieuse et difficile à circonscrire.
Ce glissement est particulièrement préoccupant pour les institutions publiques. À mesure que les données s’accumulent, la valeur de chaque point d’accès augmente. Une simple faiblesse organisationnelle peut alors produire des effets comparables à une attaque avancée, sans déclencher les mécanismes d’alerte traditionnels.
Synthèse
En pratique, une part significative du cyber espionnage contemporain ne repose pas sur des zero day. Des architectures documentaires centralisées, combinées à des contrôles d’accès insuffisants, suffisent à provoquer des fuites massives aux conséquences comparables à celles d’intrusions avancées.
Une fois ce constat établi, une limite apparaît nettement : même une détection parfaite n’efface pas la compromission initiale. Il devient alors indispensable d’examiner pourquoi certaines pertes de confiance ne peuvent plus être réparées par des correctifs ou des audits, mais exigent un changement de doctrine.
Cyber espionnage zero day : limites irréversibles de la sécurité logicielle
Après l’analyse des fuites massives sans exploitation avancée, une limite structurelle se dessine nettement. Même lorsque l’attaque repose sur un zero day sophistiqué, la réponse classique — correctif, durcissement, audit — ne restaure pas nécessairement la confiance. En réalité, dès qu’une compromission invisible est plausible, l’environnement logiciel cesse d’être une base de preuve fiable.
Un zero day rend impossible toute attestation logicielle fiable tant que la compromission n’est pas réfutée hors OS.
Cette position n’est pas spéculative. Elle est désormais partagée par plusieurs autorités techniques européennes et internationales. Ainsi, la sécurité logicielle est reconnue comme fondamentalement dépendante de la capacité à détecter et attribuer une compromission, ce que le zero day remet directement en cause. À titre de référence, l’Agence de l’Union européenne pour la cybersécurité souligne que l’exploitation de vulnérabilités inconnues rend toute attestation post-incident incertaine, notamment lorsque les journaux et mécanismes de surveillance résident sur le système compromis lui-même. — Documentation officielle ENISA — Incident Handling.
Dans la même logique, le National Institute of Standards and Technology rappelle que les contrôles logiciels ne peuvent pas, à eux seuls, garantir l’intégrité d’un système après exploitation inconnue. — NIST SP 800-61r2 — Computer Security Incident Handling Guide Après l’analyse des fuites massives sans exploitation avancée, une limite structurelle se dessine nettement. Même lorsque l’attaque repose sur un zero day sophistiqué, la réponse classique — correctif, durcissement, audit — ne restaure pas nécessairement la confiance. En réalité, dès qu’une compromission invisible est plausible, l’environnement logiciel cesse d’être une base de preuve fiable.
Quand ne pas agir face à une compromission zero day
Dans certains cas, la meilleure décision n’est pas l’action immédiate, mais l’arrêt contrôlé. Lorsqu’un système ne peut plus prouver son intégrité, toute tentative de correction peut aggraver l’exposition. Cette approche est explicitement évoquée dans les doctrines de réponse à incident, où l’isolement prévaut sur la remédiation rapide. Ce principe est également repris par les recommandations européennes sur la gestion de crise cyber, notamment lorsqu’il existe un risque de persistance non détectable. — ENISA — Cyber Crisis Management
Pourquoi le correctif ne restaure pas la confiance
Un correctif supprime une vulnérabilité connue, mais il ne démontre pas l’absence d’exploitation antérieure. En outre, lorsque la chaîne d’attaque inclut une élévation de privilèges ou une modification de l’environnement d’exécution, aucune mise à jour logicielle ne peut prouver que l’état antérieur a été intégralement restauré. C’est précisément pour cette raison que les cadres de sécurité récents insistent sur la séparation entre détection, décision et confiance. Lorsque ces trois dimensions reposent sur le même environnement logiciel, la preuve devient circulaire.
| Approche | Hypothèse implicite | Limite face au zero day |
|---|---|---|
| Correctif logiciel | La faille est connue et unique | Ne prouve pas l’absence d’exploitation passée |
| Audit post-incident | Les journaux sont fiables | Logs potentiellement altérés |
| Agent de sécurité | L’OS est intègre | Agent opère sur environnement compromis |
| Redémarrage / réinstallation | Le support est sain | Firmware, boot ou périphériques non vérifiés |

style=”text-align: center; font-size: 0.85em;”>→ Voir comment ces limites imposent des points de décision matériels
Synthèse
À ce stade, la limite est claire : lorsqu’un cyber espionnage zero day est plausible, la sécurité logicielle ne peut plus prouver son propre état. Correctifs et audits restent nécessaires, mais ils deviennent insuffisants pour restaurer la confiance sans un point d’ancrage externe.
Contre espionnage numérique : points de décision matériels
Lorsque la sécurité logicielle atteint ses limites, une autre approche devient nécessaire. Plutôt que de tenter de restaurer une confiance fragile, il s’agit de déplacer les décisions critiques hors de l’environnement compromis. Dans cette perspective, les points de décision matériels introduisent une séparation nette entre l’OS potentiellement hostile et les éléments qui ne doivent jamais lui être confiés, notamment en contexte de cyber espionnage zero day.
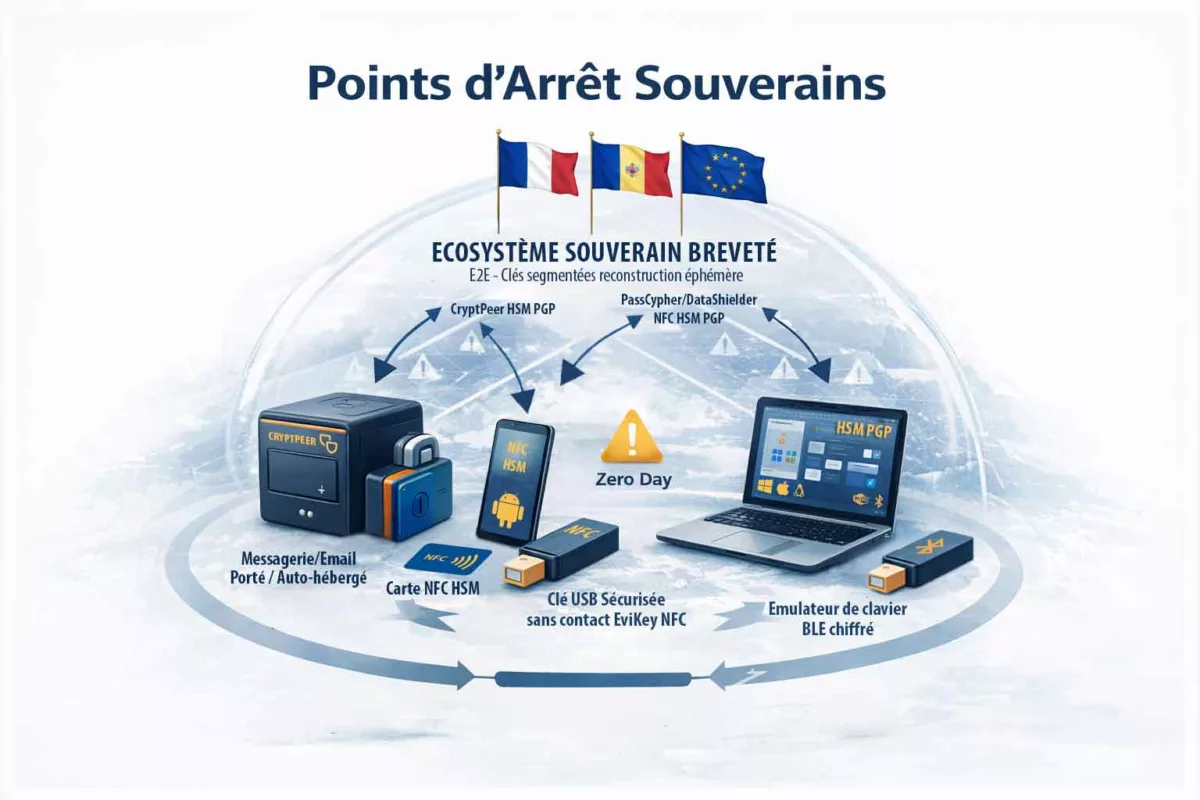
style=”text-align: center; font-size: 0.85em;”>→ Voir la déclinaison des cas d’usage souverains
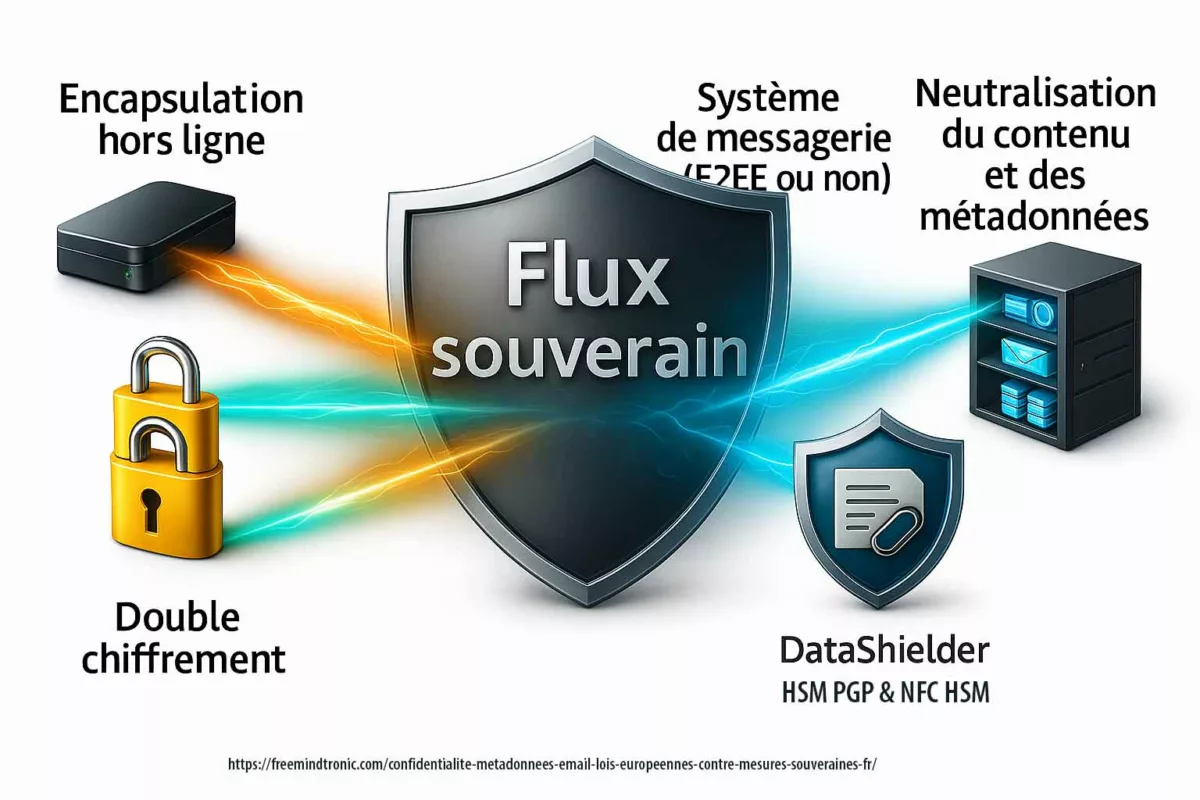
Autrement dit, l’objectif n’est pas de “rendre le terminal sain”, mais de préserver ce qui compte : secrets, identités, décisions et canaux. Pour cela, des dispositifs matériels (dont certains relèvent de logiques HSM selon les cas) et des mécanismes comme le chiffrement segmenté réduisent ce qu’un spyware ou un zero day peut capter, modifier ou automatiser. Repères institutionnels utiles pour cadrer cette doctrine : ENISA — Identity & Access Management · NIST — Hardware Security À ce stade, un point de méthode s’impose : ces mécanismes (contrôle d’accès, authentification à clé segmentée, politiques de confiance et exécution hors infrastructure) reposent sur des technologies protégées par un portefeuille de brevets déposés en France et étendus à l’international. Cette protection n’est pas un argument d’autorité ; en revanche, elle documente l’existence d’une architecture stabilisée et industrialisable, ce qui compte lorsque l’on raisonne en doctrine de contre-espionnage face au zero day.
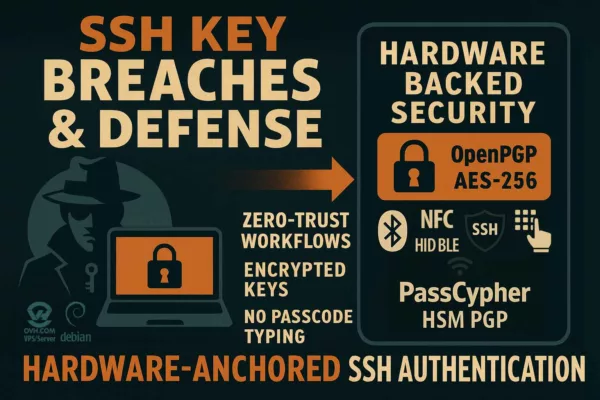
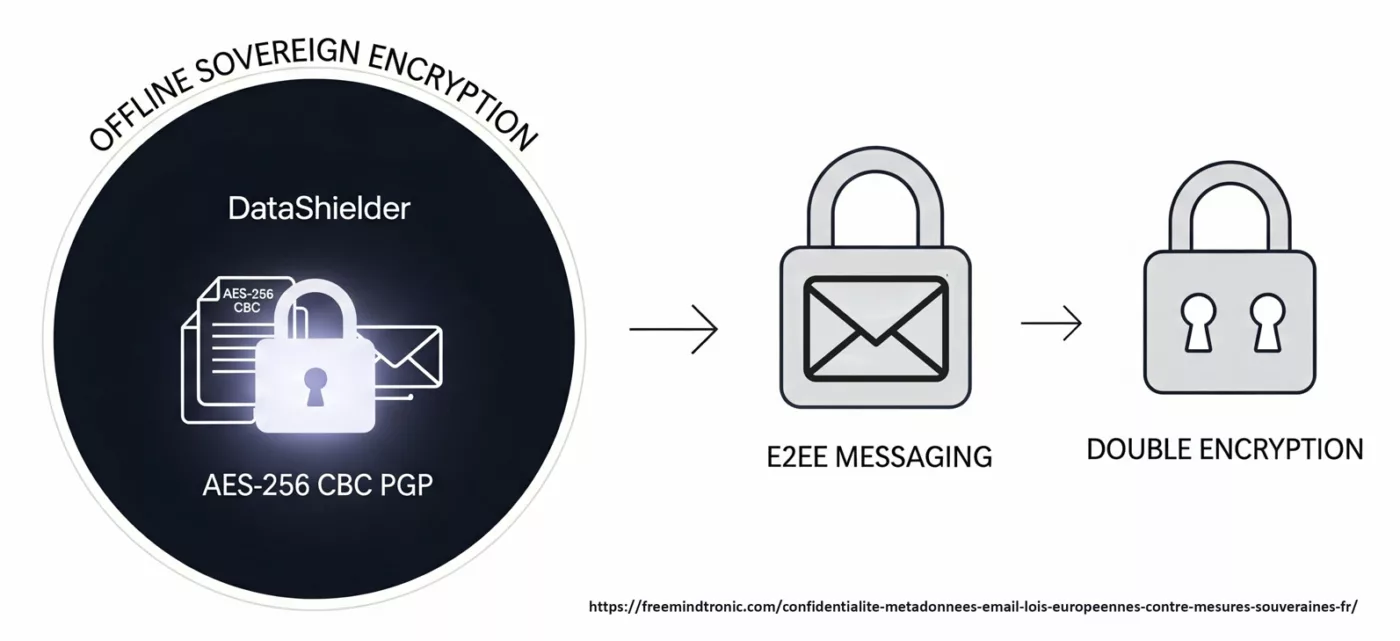
PassCypher NFC HSM et HSM PGP : secrets hors OS, clés segmentées et auto-login chiffré en mémoire volatile
Dans un contexte de cyber espionnage zero day, la compromission d’un terminal ne vise pas seulement les fichiers. Elle vise surtout l’accès : identifiants, OTP, secrets de connexion, et automatismes d’authentification. Dès que ces secrets sont “manipulés” par l’OS, ils deviennent capturables, rejouables ou industrialisables par un implant. C’est précisément ce point que PassCypher cherche à neutraliser : déplacer la gestion des secrets hors du périmètre où l’OS peut mentir sur son état.
PassCypher NFC HSM : un point d’arrêt matériel pour la gestion de secrets
PassCypher NFC HSM repose sur des dispositifs NFC HSM sans contact pour stocker et délivrer des secrets sous contrôle matériel, sans serveur, sans base de données et sans compte utilisateur. Cette approche réduit la valeur d’un terminal compromis : même si l’attaquant observe l’interface, il ne dispose pas d’un stockage “OS” exploitable à grande échelle. En pratique, cela limite l’escalade post-compromission, car les secrets restent corrélés à une action volontaire et à une présence physique.
PassCypher HSM PGP : conteneurs chiffrés, clé segmentée et déchiffrement éphémère en RAM
PassCypher HSM PGP étend cette logique en introduisant une automatisation complète via des conteneurs chiffrés (URL, identifiant, mot de passe, et paramètres associés). Les données de connexion sont chiffrées en AES-256 CBC PGP puis stockées sur un support choisi par l’utilisateur (USB, SSD, NAS, etc.). Lors de la connexion, le système lit le conteneur, le déchiffre brièvement en mémoire volatile, injecte les champs nécessaires, puis détruit immédiatement les données déchiffrées. L’objectif opérationnel est clair : empêcher qu’un malware récupère des identifiants par affichage, presse-papiers, ou persistance en clair. Le cœur de la défense repose sur une clé segmentée : un segment est conservé localement dans le navigateur, tandis qu’un second segment réside sur un support externe. Sans ce second segment, l’accès automatisé ne peut pas fonctionner. Autrement dit, même si un terminal est compromis, l’attaque ne peut pas industrialiser l’accès sans réunir les conditions matérielles attendues.
Pourquoi c’est pertinent face au cyber espionnage zero day
Dans cette chronique, PassCypher n’est pas présenté comme une “solution miracle”, mais comme un mécanisme de réduction de dégâts. Il vise à casser deux capacités clés du cyber espionnage moderne : la collecte silencieuse de secrets à grande échelle, et l’automatisation des connexions sur un terminal dont l’intégrité n’est plus attestable. Cela transforme la compromission en événement coûteux et moins reproductible, plutôt qu’en avantage durable. Sur le plan industriel et juridique, ces mécanismes s’inscrivent dans un portefeuille de brevets déposés en France et étendus à l’international, couvrant notamment des architectures de contrôle d’accès et d’authentification à clé segmentée. Références officielles : PassCypher NFC HSM · Fonctionnement PassCypher HSM PGP · Brevets internationaux Freemindtronic
DataShielder NFC HSM et HSM PGP : chiffrement segmenté, zéro persistance et anti-automatisation
DataShielder vise une zone rarement traitée correctement face au cyber espionnage zero day : le moment d’usage. Lorsque l’OS ne peut plus être attesté, la question n’est pas seulement de chiffrer, mais d’empêcher la captation des clés, la reproduction des accès et l’automatisation silencieuse des opérations. Dans ce cadre, l’approche DataShielder repose sur une logique centrale : la clé n’est jamais “posée” en entier là où un implant peut la copier.
DataShielder NFC HSM : gestionnaire de clés contactless, hors ligne et à clé segmentée
D’abord, DataShielder NFC HSM se positionne comme un gestionnaire de clés de chiffrement contactless conçu pour fonctionner en environnement zero-trust : entièrement hors ligne, sans serveur, sans cloud et sans base de données. La sécurité ne dépend donc pas d’une infrastructure, mais d’une architecture à clé segmentée et d’une reconstitution en mémoire volatile au moment strictement nécessaire, suivie d’un effacement après usage.
Ensuite, l’accès aux secrets peut être conditionné par des critères locaux : PIN, biométrie locale, QR, géozone, BSSID, empreinte de terminal et politiques d’accès. Autrement dit, même si une compromission logicielle contrôle l’interface, elle ne transforme pas automatiquement l’accès en capacité réutilisable, car l’opération dépend de conditions de confiance non triviales à rejouer.
Par ailleurs, l’intérêt anti-espionnage ne se limite pas au mobile. DataShielder NFC HSM peut aussi opérer dans des scénarios multi-équipements via des mécanismes de transfert contrôlé (proximité ou partage distant), ainsi que des intégrations orientées entreprise (BYOD/COPE/CYOD) lorsque la connectivité devient une vulnérabilité en soi.
DataShielder HSM PGP : chiffrement avancé côté navigateur, clé segmentée (2×256) et automatisation serverless
Ensuite, DataShielder HSM PGP étend cette doctrine au poste de travail via une logique “browser-first”. Le principe reste identique : une clé est segmentée en deux parties indépendantes. Un segment est conservé localement dans le navigateur, tandis que l’autre segment est stocké sur un support externe. La reconstitution ne se produit qu’au moment d’une opération cryptographique, en mémoire volatile, puis disparaît immédiatement après usage.
Cette segmentation produit un matériau de clé issu de deux segments de 256 bits. L’objectif opérationnel n’est pas d’annoncer un algorithme “AES 512”, mais d’augmenter la difficulté d’un attaquant : il doit compromettre deux emplacements distincts et réunir les segments au bon instant, ce qui réduit la valeur d’un implant zero day focalisé sur un seul environnement (OS ou navigateur).
Sur le plan cryptographique, la solution s’appuie sur AES-256 (mode CBC selon la documentation produit) et sur SHA-256 pour l’intégrité. De plus, la compatibilité OpenPGP et l’automatisation côté navigateur permettent des workflows interopérables, sans dépendance à un service tiers. Dans une chronique zero day, c’est un point clé : déplacer la confiance hors des plateformes, sans basculer vers un “cloud de sécurité” qui re-centralise le risque.
Enfin, l’architecture intègre EviEngine et DataShielder Engine pour automatiser des actions et gérer l’activation de fonctions sans serveurs ni bases de données, avec une logique de droits liée au matériel plutôt qu’à un compte utilisateur. Cette approche limite l’exposition aux identifiants, à la collecte et aux répertoires d’utilisateurs, qui deviennent fréquemment des cibles en espionnage.
Références officielles :
DataShielder NFC HSM — gestionnaire de clés contactless ·
DataShielder HSM PGP — chiffrement à clé segmentée ·
DataShielder Defense NFC HSM ·
Écosystème DataShielder.
Repère de conformité dual-use (cadre UE, sans interprétation) :
Règlement (UE) 2021/821 — biens à double usage
EviKey NFC : clé USB de sécurité, invisibilité matérielle et contrôle d’accès physique
EviKey NFC n’est ni un système de chiffrement ni un HSM. Il s’agit d’une clé USB de sécurité matérielle, conçue pour contrôler l’accès aux données par un mécanisme d’invisibilité physique et de verrouillage électronique autonome. Son rôle n’est pas de chiffrer l’information, mais d’empêcher qu’elle soit détectable, accessible ou exploitable tant que les conditions physiques et logiques ne sont pas réunies.
Lorsque l’EviKey est verrouillée, le support USB devient invisible pour tout ordinateur ou système hôte : aucun périphérique de stockage n’est détecté, aucun volume n’apparaît, et une exfiltration automatisée ne peut pas démarrer parce que le support n’existe pas du point de vue de l’OS. Cette propriété est directement pertinente face au cyber espionnage zero day, car elle réduit la capacité d’industrialisation de l’attaque sur un poste compromis.
Le déverrouillage repose sur une authentification NFC de proximité via un smartphone Android appairé et l’application Fullkey ou Fullkey Plus. Cette opération peut combiner appairage, code administrateur, code utilisateur ou PIN selon le niveau de sécurité défini. Tant que la séquence n’est pas validée, la clé demeure indétectable.
EviKey NFC n’embarque aucun chiffrement interne : l’utilisateur reste libre d’appliquer le chiffrement de son choix (BitLocker, Opal 2.0, PGP, chiffrement logiciel ou matériel externe). EviKey agit donc en amont, comme une barrière d’accès et de visibilité compatible avec tout système cryptographique.
Références officielles :
EviKey NFC — caractéristiques ·
EviKey NFC pour clés USB ·
EviKey USB — mode indétectable.
Cette invisibilité matérielle introduit un point d’arrêt non scriptable, ce qui constitue une rupture directe avec les chaînes d’attaque zero day automatisées.
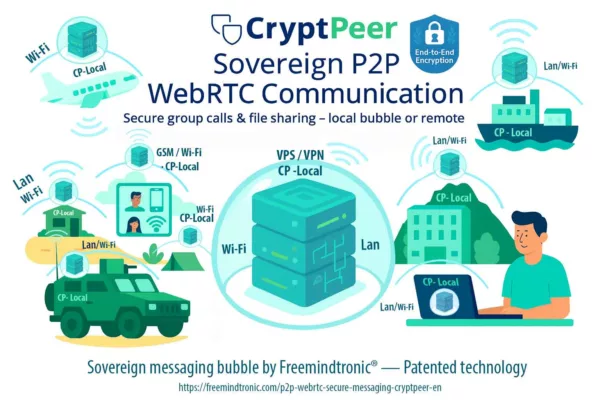
CryptPeer : communications chiffrées de bout en bout, collaboration et réduction des intermédiaires
CryptPeer couvre un périmètre plus large que le simple échange de messages. Il intègre une messagerie instantanée chiffrée de bout en bout, des appels audio et vidéo — y compris en mode groupe — ainsi que des mécanismes de transfert de fichiers sécurisés. L’ensemble est conçu pour fonctionner sans dépendre de plateformes centralisées exposant les flux, les contenus ou les métadonnées.
Le service inclut également un client de messagerie électronique chiffrée de bout en bout, compatible avec tous les systèmes acceptant OpenPGP (formats .asc). Le chiffrement est appliqué automatiquement côté expéditeur, avant tout transit réseau. Ainsi, même lorsque l’acheminement du courrier repose sur des serveurs tiers, le contenu demeure inaccessible aux intermédiaires.
En complément, CryptPeer propose un bloc-notes collaboratif chiffré de bout en bout. Cette fonctionnalité vise un angle souvent négligé du cyber espionnage : les espaces de travail partagés et les outils collaboratifs, qui constituent des gisements de données à forte valeur lorsqu’ils sont centralisés ou indexables.
Dans une chronique consacrée au cyber espionnage zero day, cet ensemble répond à une problématique précise : la compromission ne se limite pas au terminal. Elle s’étend aux canaux de communication, aux services de visioconférence, aux transferts de fichiers et aux plateformes collaboratives. En réduisant la dépendance à ces intermédiaires, CryptPeer diminue la surface exploitable par l’espionnage indirect, même lorsque l’environnement logiciel ne peut plus être pleinement attesté. Site web officiel :
CryptPeer® — Messagerie & Appels P2P Auto-Hébergés Chiffrés de Bout en Bout.
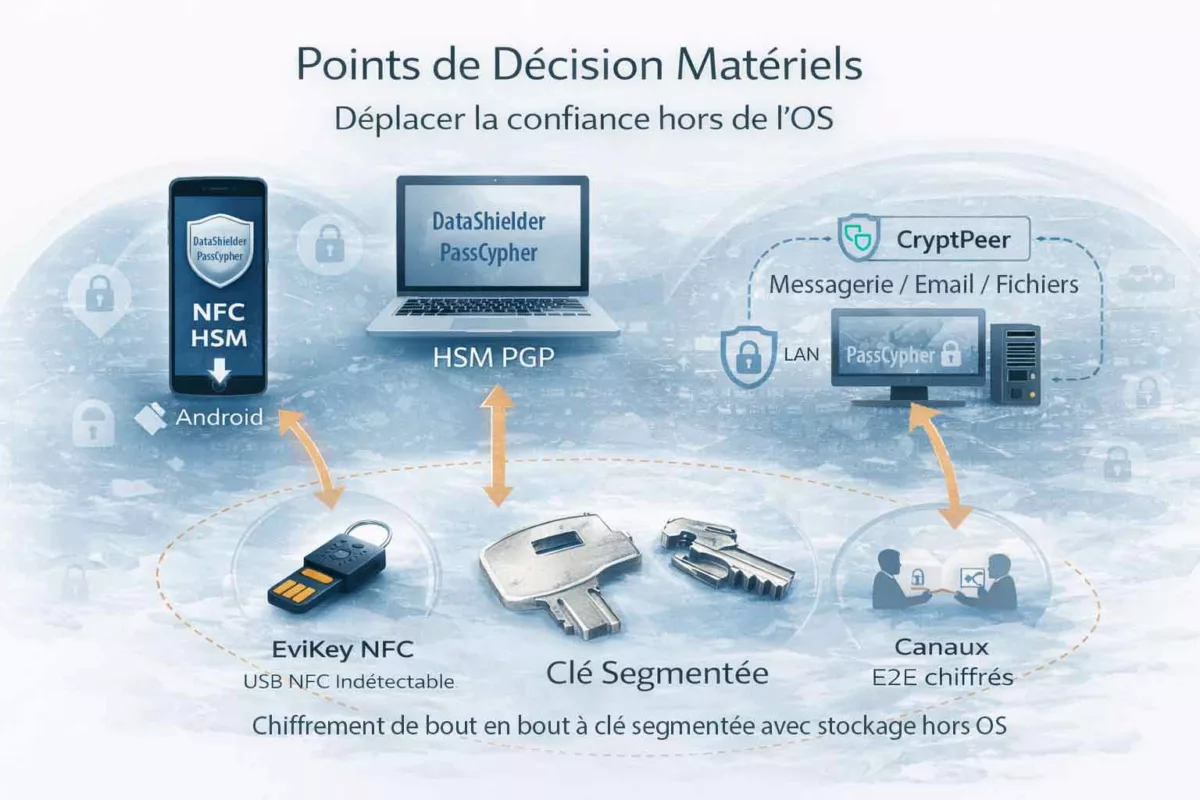
Lecture systémique face au cyber espionnage zero day
Dans ces modèles de contre-espionnage, la sécurité ne repose plus sur la confiance accordée aux plateformes, mais sur la maîtrise locale et matérielle des clés, des décisions et des canaux. Autrement dit, même en cas de compromission partielle du terminal, l’attaquant ne peut ni automatiser l’accès ni étendre l’attaque sans réunir des conditions hors OS. De cette manière, l’industrialisation du cyber espionnage zero day devient plus coûteuse, plus lente et plus risquée.
| Composant | Point de décision déplacé | Apport en contexte zero day |
|---|---|---|
| PassCypher (NFC HSM / HSM PGP) | Accès aux identifiants et “moment de dévoilement” (clé segmentée + déchiffrement éphémère) | Réduit la collecte de secrets et casse l’automatisation de la connexion sur un poste suspect |
| DataShielder (NFC HSM / HSM PGP) | Gestion souveraine de clés segmentées + reconstruction en mémoire volatile + échanges hors serveur | Réduit l’exfiltration de clés, limite l’effet d’un implant, et maintient des flux chiffrés en environnement à confiance dégradée |
| EviKey NFC | Existence du support et accès aux données (invisibilité matérielle + contrôle NFC) | Empêche la détection du support et bloque l’exfiltration automatisée tant que la clé reste verrouillée |
| CryptPeer | Canaux de communication et collaboration (chiffrement de bout en bout + réduction des intermédiaires) | Réduit l’exposition des contenus et des espaces de travail aux plateformes centralisées et à la collecte indirecte |

Synthèse
En pratique, ces points de décision ne “réparent” pas un terminal compromis. À l’inverse, ils déplacent la confiance vers des mécanismes hors OS (clé segmentée, exécution éphémère en mémoire volatile, support indétectable, canaux chiffrés de bout en bout), ce qui limite l’escalade et réduit l’automatisation malveillante.
Contre mesures souveraines face au cyber espionnage zero day
À présent, il ne suffit plus de “durcir” un poste ou d’empiler des outils de sécurité. Au contraire, la priorité consiste à définir des règles de fonctionnement qui restent valables lorsque l’intégrité du terminal est incertaine. Autrement dit, une contre-mesure souveraine vise moins à détecter l’attaque qu’à empêcher qu’elle devienne décisive.
Dans cette optique, trois principes se dégagent. D’une part, réduire ce qui peut être capté (secrets, sessions, identités). D’autre part, réduire ce qui peut être automatisé (exfiltration, connexion, signature, transfert). Enfin, imposer des points d’arrêt explicites, c’est-à-dire des situations où l’on cesse d’exécuter, même si “tout semble fonctionner”.
- Premièrement, séparer secrets et interfaces : le terminal peut afficher, mais il ne doit pas stocker ni décider.
- Ensuite, privilégier la reconstruction éphémère en mémoire volatile, plutôt que la persistance en clair ou semi-clair.
- Par ailleurs, rendre certains actes non scriptables : présence physique, contrôle d’accès autonome, support indétectable.
- Enfin, documenter des procédures d’arrêt : quand une opération est jugée trop risquée, elle doit être stoppée avant l’irréversible.
Transition stratégiqueÀ partir de ces principes, il reste à trancher une question d’usage : quelles variantes appliquer selon qu’on se situe en contexte civil, en double usage, ou en environnement régalien européen sous autorisation ? La section suivante déroule ces cas d’emploi, avec leurs contraintes et leurs compromis.
Cyber espionnage et exfiltration des communications : un phénomène mondial
Le constat est global. Les cibles changent. Les vecteurs aussi. En revanche, le résultat converge : messages, pièces jointes, espaces collaboratifs et décisions internes finissent copiés, parfois pendant des mois.
Pour être lisible, voici une synthèse par régions et par types d’incidents. L’objectif n’est pas l’exhaustivité. Il s’agit d’illustrer une propriété structurelle : quand la plateforme “voit” le contenu, l’attaquant finit par le voir aussi.
| Zone | Exemple d’incident | Systèmes ciblés | Mécanisme dominant | Enseignement opérationnel |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| États-Unis | OPM (2015) ; DNC (2016) ; SolarWinds (2020) ; Exchange/Hafnium (2021) | Email, annuaires, plateformes internes | Compromission longue + exfiltration | Les boîtes mail restent une “mine” stratégique. Le temps d’accès vaut plus que le bruit. |
| États-Unis | SignalGate (2025) | Messagerie civile utilisée hors cadre | Erreur d’aiguillage + mauvais usage | Le chiffrement ne corrige pas la gouvernance. La discipline de canal est décisive. |
| Europe | Fuites documentaires et intrusions confirmées sur des systèmes publics | Docs, emails, comptes partagés | Accès initial + collecte massive | La centralisation documentaire amplifie l’impact. Une fois l’accès obtenu, la fuite devient mécanique. |
| Global | Campagnes récurrentes contre Slack / Teams et écosystèmes collaboratifs | Espaces collaboratifs + intégrations | Comptes compromis + jetons + apps tierces | Les intégrations élargissent la surface. Les permissions deviennent une voie d’exfiltration. |
Ce qui est recherché n’est pas seulement “un message”. Ce sont des routines : qui parle à qui, quand, avec quelles pièces, et sur quels sujets.
Le schéma qui se répète partout
On retrouve les mêmes invariants, quel que soit le pays. Les attaquants privilégient les systèmes qui concentrent l’information. Ils cherchent aussi les environnements où l’usage dévie.
| Invariant | Ce que l’attaquant obtient | Pourquoi c’est critique | Mesure de réduction de risque |
|---|---|---|---|
| Boîtes email et archives | Décisions, pièces jointes, historiques | L’email relie personnes, sujets et pièces. Il reconstruit l’organisation. | Chiffrement du contenu + clés sous contrôle local, hors serveur. |
| Espaces collaboratifs | Plans, documents, commentaires, versions | Les outils collaboratifs exposent le “raisonnement en cours”, pas seulement le résultat. | Réduire les intermédiaires + E2E sur les contenus, pas seulement le transport. |
| Comptes et jetons | Accès durable, parfois silencieux | Un compte vaut une présence. Un jeton vaut une session réutilisable. | Limiter les secrets dans l’OS. Exiger des décisions hors OS. |
| Mauvais usage d’outils civils | Fuite par erreur, capture sur terminal compromis | La crypto ne compense pas l’absence de gouvernance. L’erreur humaine suffit. | Doctrines de canal + chiffrement des contenus avant partage. |
Synthèse
Le problème est mondial, car il découle d’une architecture mondiale : centraliser les communications et faire confiance aux plateformes. Dès que l’accès système est obtenu, l’exfiltration devient une question de temps.
À partir de là, la doctrine devient concrète : séparer décision, clés et canaux de l’OS et des plateformes. La section suivante décline ces principes en cas d’usage : civil, double usage et régalien européen.
Cas d usage souverain : civil, double usage, régalien européen
Ici, l’objectif est simple : adapter la doctrine au contexte et éviter les erreurs de catégorie. Un même levier de sécurité ne se déploie jamais de la même manière selon l’environnement. Les contraintes changent, les responsabilités évoluent et les risques ne se manifestent pas au même endroit.
1) Contexte civil : réduire l’exposition sans complexifier l’usage
Dans le civil, la menace est le plus souvent diffuse et opportuniste. Pourtant, l’effet d’un zero day reste brutal lorsqu’il survient. L’enjeu n’est donc pas la sophistication maximale, mais la réduction de l’exfiltration et la rupture de l’automatisation, sans transformer l’usage quotidien en contrainte permanente.
- Priorité : éviter tout stockage durable de secrets dans l’OS.
- Ensuite : conditionner l’accès à une action physique ou locale réellement volontaire.
- Enfin : conserver une procédure d’arrêt claire, compréhensible et répétable.
Concrètement, cela favorise des gestes simples, comme déverrouiller un support uniquement à proximité ou injecter un secret sans jamais l’afficher à l’écran.
2) Double usage : arbitrer entre souveraineté, traçabilité et conformité
Le double usage modifie profondément la nature du problème. Il ne s’agit plus seulement de sécurité opérationnelle, mais d’un arbitrage permanent entre souveraineté, traçabilité et cadre légal. Dans l’Union européenne, le repère structurant demeure le règlement sur les biens à double usage, qui encadre strictement l’export, le courtage et les transferts. Référence officielle : Règlement (UE) 2021/821.
Dès lors, la question centrale n’est plus « est-ce efficace ? », mais « dans quel périmètre cet usage est-il autorisé, documenté et gouverné ? ».
- D’abord : classifier précisément l’usage réel (civil, protection, défense, renseignement).
- Ensuite : documenter la chaîne de responsabilité.
- Puis : cadrer la distribution et la gestion de flotte.
- Enfin : prévoir des audits d’usage, et non de simples audits techniques.
La conformité ne constitue pas un frein. Elle devient un élément de résilience, réduisant à la fois le risque juridique et le risque politique.
3) Régaliens européens : doctrine stricte, gouvernance forte, séparation des rôles
En environnement régalien, la pression change d’échelle. La cible est structurellement plus exposée et l’adversaire nettement plus organisé. La réflexion ne porte plus sur des outils, mais sur des fonctions : qui décide, qui exécute, qui valide. Cette séparation devient centrale pour limiter les abus, les erreurs et les contournements.
Dans ce cadre, les points de décision matériels prennent une forme plus rigoureuse. Les barrières se multiplient, les exceptions sont réduites et la tolérance au contournement devient quasi nulle.
- Principe : aucun secret durable sur le poste de travail.
- Corollaire : accès conditionné par la présence, par des critères locaux et par des rôles définis.
- Complément : canaux chiffrés, mais surtout réduction du nombre d’intermédiaires.
- Enfin : journalisation déplacée hors OS lorsque cela est possible.
Pour cadrer l’approche, deux repères publics structurent la doctrine : ENISA — Identity & Access Management · NIST — Hardware Security.
Matrice décisionnelle : relier le besoin au point d’arrêt
Pour éviter toute confusion, une matrice de lecture permet de relier chaque besoin opérationnel à un point d’arrêt concret.
| Besoin | Point d’arrêt | Pourquoi c’est utile face au zero day |
|---|---|---|
| Protéger les identifiants | Secret hors OS + dévoilement éphémère | Réduit la capture et empêche l’auto-login détourné |
| Protéger les clés | Clé segmentée + reconstruction volatile | Empêche la récupération d’une clé complète sur un seul poste |
| Protéger les supports | Support indétectable tant que verrouillé | Bloque les scans et l’exfiltration automatisée |
| Protéger les échanges | Chiffrement de bout en bout + réduction des intermédiaires | Réduit la collecte indirecte et l’exploitation des métadonnées |
Synthèse
Dans le contexte civil, la priorité reste la simplicité maîtrisée. En ce qui concerne le double usage, la conformité devient un levier de résilience. Pour un environnement régalien européen mais pas seulement, la gouvernance et la séparation des rôles priment sur toute considération purement technique.
Signaux faibles du marché du cyber espionnage
Les crises visibles surviennent rarement sans avertissement. Bien en amont, des signaux faibles apparaissent, souvent discrets mais persistants. Leur répétition annonce une perte progressive de contrôle et, à terme, un basculement vers des situations irréversibles.
1) Dérives d’usage : quand le contournement devient la norme
Le premier signal est d’ordre culturel. Sous la pression du temps ou du confort, les équipes commencent à contourner les canaux officiels. Elles privilégient des outils perçus comme plus rapides, ce qui entraîne un déplacement progressif de l’information hors périmètre maîtrisé.
- Des échanges sensibles transitent par des outils civils, par simple habitude.
- Des groupes “temporaires” s’installent durablement comme canaux de décision.
- Des fichiers sortent des coffres sécurisés pour “dépanner”.
Dans ce contexte, le problème n’est pas la cryptographie elle-même, mais l’usage. Un mauvais canal suffit à rendre l’erreur fatale, parfois à la suite d’un simple ajout involontaire.
2) Centralisation documentaire : le multiplicateur d’impact
Un second signal, plus structurel, concerne l’organisation documentaire. À mesure que les documents se centralisent, les permissions s’élargissent et les liens se multiplient. Dès qu’un accès tombe, la fuite devient alors mécanique.
- Des répertoires transverses grossissent sans segmentation réelle.
- Des comptes de service conservent des droits excessifs.
- Les exports et synchronisations deviennent des gestes ordinaires.
Dans ces conditions, l’attaque peut rester simple, tandis que l’impact, lui, devient massif.
3) Terminaux : la cible réelle, pas le serveur
Un troisième signal est clairement opérationnel. Les attaques modernes déplacent le point d’entrée vers le terminal et visent l’usage quotidien, en particulier le moment où le secret est manipulé.
- Le smartphone devient un véritable poste de décision.
- Les applications s’empilent et finissent par se mélanger.
- Les secrets se retrouvent exposés à l’OS et aux applications.
Dans ce contexte, le zero day rend toute attestation d’intégrité incertaine. Le réflexe défensif consiste alors à sortir les secrets de l’OS.
4) Intégrations : jetons, connecteurs et automatisations
Un autre signal, plus silencieux, réside dans la prolifération des intégrations techniques. Les jetons créent de la persistance, tandis que les connecteurs ouvrent des chemins invisibles à l’audit.
- Une application tierce lit des canaux pour indexer.
- Un bot publie, mais peut également collecter.
- Un jeton fuit et offre un accès durable.
Le risque principal n’est plus l’intrusion initiale, mais la continuité d’accès. L’attaquant privilégie la discrétion et la copie progressive.
5) Gouvernance : négligence, confusion des rôles et zones grises
Lorsque la gouvernance se fragilise, l’incident devient probable. Progressivement, les responsabilités se diluent, tandis que les alertes sont relativisées. À mesure que les contrôles s’affaiblissent, les exceptions finissent par devenir la règle.
- Qui autorise l’usage d’un outil non prévu ?
- Qui valide un partage sensible ?
- Qui décide d’arrêter un système “qui fonctionne encore” ?
Dans ces environnements, l’erreur humaine rencontre la faille technique, et leur combinaison devient explosive.
Tableau de repérage : du signal faible au dommage
| Signal faible | Ce que cela annonce | Risque principal | Point d’arrêt recommandé |
|---|---|---|---|
| Outils civils utilisés pour du sensible | Contournement durable | Erreur d’aiguillage, fuite par usage | Chiffrer le contenu avant partage, hors plateforme |
| Centralisation et droits larges | Exfiltration à grande échelle | Copie massive de documents | Segmentation, minimisation, contrôles d’accès stricts |
| Multiplication d’intégrations | Surface invisible | Jetons, bots, connecteurs | Audit des applications et réduction des permissions |
| Décision sur smartphone | Dépendance au terminal | Capture au moment du secret | Secrets et clés hors OS, décisions non scriptables |
| Rôles flous et exceptions | Perte de gouvernance | Crise institutionnelle | Séparation des rôles et procédures d’arrêt |
Synthèse
Un signal faible n’est jamais anodin. Il annonce un incident en formation. Lorsque l’usage dérive, la technique ne suffit plus : la gouvernance devient alors une mesure de sécurité à part entière.
FAQ — cyber espionnage zero day
Qu’est-ce qu’un zero day, au sens opérationnel ?
Définition
Définition opérationnelle
Un zero day est une vulnérabilité inconnue du défenseur au moment critique. Aucun correctif n’est disponible immédiatement. L’attaquant gagne du temps et du silence.
Peut-on détecter un cyber espionnage zero day ?
Détection
Pourquoi la détection est tardive
Parfois, mais rarement au bon moment. Les traces peuvent être faibles, et les journaux peuvent être altérés si l’OS est compromis. Il faut donc prévoir l’hypothèse du doute.
Pourquoi un correctif ne suffit-il pas ?
Limite
La faille est corrigée, pas la compromission
Un correctif ferme une porte. Il ne prouve ni l’absence d’exploitation passée, ni l’absence de persistance. La confiance n’est restaurée que si elle peut être attestée hors OS.
Que faire en cas de suspicion raisonnable ?
Action
Réflexe de contre-espionnage
- Stopper l’usage des secrets sur le terminal suspect.
- Isoler l’environnement et réduire les flux.
- Décider sur une base externe, puis documenter le périmètre.
Glossaire — cyber espionnage zero day
Zero day
Définition
Vulnérabilité inconnue au moment critique
Vulnérabilité non corrigée et non détectable par le défenseur au moment de l’attaque. Elle offre un avantage de surprise, de silence et de tempo.
Capacité d’intrusion
Concept
Assemblage modulaire d’attaque
Ensemble combinant exploit, livraison, furtivité, exfiltration et parfois persistance. Il remplace le “spyware produit” unique par une chaîne remplaçable.
Attestation logicielle
Limite
Pourquoi la preuve devient circulaire
Capacité à prouver l’état d’un système. Face au zero day, elle devient fragile si la mesure et la décision reposent sur l’environnement potentiellement compromis.
Point d’arrêt
Doctrine
Règle de stoppage avant l’irréversible
Décision explicite qui stoppe une action (réintroduction de secrets, reprise d’activité, transfert) lorsque l’intégrité n’est plus attestable.
Ce que nous n’avons pas couvert
Cette chronique assume une limite claire. Elle expose une doctrine. Elle ne prétend ni remplacer un guide d’intervention, ni couvrir l’ensemble d’une politique interne complète.
Attribution et preuves judiciaires
L’attribution repose sur des sources, des méthodes et des chaînes de conservation strictes. Ce travail dépasse volontairement ce format. Le propos se concentre ici sur le risque et sur les décisions qu’il impose.
Techniques offensives détaillées
Aucune étape d’exploitation n’est décrite. Aucune recette d’intrusion n’est fournie. Le positionnement reste défensif et assumé comme tel. La logique est doctrinale, non opérationnelle.
Implémentations exactes et configuration fine
Les paramètres concrets varient selon les environnements. Ils dépendent aussi des contraintes légales et organisationnelles. Toute configuration sérieuse doit être auditée et testée en conditions réelles.
Plans complets de continuité et de crise
La continuité exige un cadre formel. Elle suppose des rôles définis, des exercices réguliers et des arbitrages budgétaires. Ici, seuls les principes sont posés. Un PCA ou PRA complet dépasse volontairement ce périmètre.
Synthèse
Ces limites ne constituent pas une faiblesse. Elles clarifient le message. Une doctrine efficace doit rester lisible, ciblée et actionnable.