Le browser fingerprinting constitue aujourd’hui l’un des instruments centraux du renseignement par métadonnées appliqué aux environnements numériques civils. Bien au-delà du contenu des communications, ce sont les corrélations comportementales — configurations techniques, temporalités d’usage, régularités d’exécution, contextes matériels — qui structurent désormais la surveillance numérique moderne, civile comme étatique, économique comme publicitaire. Exploité par les plateformes numériques, l’AdTech, les services de renseignement et la cybercriminalité, ce modèle permet d’identifier, de profiler et d’anticiper sans jamais accéder au contenu. Le chiffrement protège les messages, mais pas les empreintes techniques des navigateurs ni les graphes relationnels d’usage. Cette chronique analyse les enjeux stratégiques du browser fingerprinting, ses usages licites, illicites et hybrides, et les conditions d’une véritable souveraineté des métadonnées numériques.
Résumé express — Browser Fingerprinting
⮞ Note de lecture
Ce résumé express se lit en ≈ 3 à 4 minutes. Il permet de comprendre immédiatement l’enjeu central du browser fingerprinting, sans entrer dans l’intégralité de la démonstration technique, juridique et doctrinale.
⚡ Le constat
Le traçage numérique contemporain ne repose plus principalement sur l’exploitation du contenu, mais sur l’extraction et la corrélation de métadonnées techniques. Le browser fingerprinting permet d’identifier un terminal à partir de caractéristiques natives du navigateur et du système — rendu graphique, pile audio, polices, APIs, comportements d’exécution — sans stockage explicite ni trace facilement supprimable. Cette identification persistante rend possible un suivi transversal, y compris lorsque les cookies sont bloqués et le contenu chiffré.
✦ Impact immédiat
- Identification persistante des terminaux sans mécanisme déclaratif
- Reconstruction de profils comportementaux à partir de signaux faibles
- Traçage sans stockage local ni consentement réellement opérant
- Convergence des usages publicitaires, sécuritaires et criminels
⚠ Message stratégique
Le basculement critique n’est pas l’existence du traçage, mais son invisibilisation structurelle. Lorsque l’identification repose sur des propriétés techniques natives, la frontière entre usage licite, surveillance et renseignement devient floue. L’automatisation algorithmique transforme le fingerprinting en un outil probabiliste : l’erreur n’est plus exceptionnelle, elle devient systémique, difficilement contestable et rarement attribuable.
⎔ Contre-mesure souveraine
Il n’existe pas de solution absolue contre le browser fingerprinting. La souveraineté ne consiste pas à devenir indétectable, mais à réduire l’exploitabilité des métadonnées : standardisation des environnements, minimisation des signaux exposés, blocage des scripts avant exécution, et séparation stricte entre identité, usage et contexte. Il s’agit d’une logique de contre-renseignement numérique, pas d’une promesse d’anonymat total.
Bascule du fingerprinting (2025–2026)
Depuis 2024–2025, l’écosystème accélère l’identification sans stockage. Le point décisif n’est pas “la fin des cookies”, mais le déplacement du pouvoir d’identification vers ce qui est observé pendant l’exécution (scripts, iframes, APIs) et vers ce qui est corrélable au niveau réseau. Dès lors, la défense utile n’est pas une collection d’astuces : c’est une architecture cohérente.
Grille Freemindtronic — “3 déplacements” (lecture opératoire)
- Du stockage vers l’exécution : si un script ne s’exécute pas, il ne collecte pas.
- Du navigateur vers la pile complète : navigateur + extensions + OS + réseau doivent rester cohérents.
- De l’identifiant vers la probabilité : une probabilité stable suffit pour profiler et discriminer.
- Trajectoire industrielle instable : la logique devient “choix utilisateur / exceptions / contournements”, pas extinction nette.
- La pression se déplace : quand le stockage est restreint, la collecte remonte vers l’exécution et le réseau.
- Conséquence défensive : standardiser, réduire la surface, et bloquer avant exécution — pas “cosmétique”.
Trois faits non négociables
- Invariant #1 — Le contenu chiffré n’efface pas la forme : l’empreinte exploite des propriétés natives (API, rendu, timings, réseau) et peut persister sans cookies.
- Invariant #2 — L’anti-tracking “cosmétique” peut aggraver l’unicité : l’empilement d’extensions et de réglages rares crée une configuration statistiquement isolée.
- Invariant #3 — La cohérence bat la variété : une stratégie robuste combine standardisation + réduction d’APIs + contrôle d’exécution.
Ce que démontre cette chronique
- Pourquoi le browser fingerprinting est devenu une infrastructure de métadonnées (publicité, sécurité, fraude, renseignement).
- Pourquoi l’évitement total est structurellement impossible — et comment réduire l’exploitabilité.
- Quelles contre-mesures ont un effet mesurable : standardisation, réduction de surface, et blocage avant exécution.
Paramètres de lecture
Résumé express : ≈ 3–4 min
Résumé avancé : ≈ 5–6 min
Chronique complète : ≈ 30–40 min
Date de publication : 2026-01-08
Dernière mise à jour : 2026-01-09
Niveau de complexité : Élevé — cyber, AdTech, renseignement
Densité technique : ≈ 70 %
Langues disponibles : FR · EN
Focal thématique : browser fingerprinting, métadonnées, surveillance, souveraineté
Type éditorial : Chronique — Freemindtronic Digital Security
Niveau d’enjeu : 9.1 / 10 — enjeux civils, économiques, hybrides et étatiques
- Résumé express
- Bascule du fingerprinting (2025–2026)
- Trois faits non négociables
- Ce que démontre cette chronique
- Résumé avancé
- Cookies, sandbox et fingerprinting
- Double trajectoire du traçage
- Cadre juridique et consentement
- Paradoxe de la vie privée
- Chronique complète
- Taxonomie du fingerprinting
- Signaux techniques collectés
- Pourquoi il est impossible à éliminer
- Le piège de la randomisation
- Mesurer son exposition
- Tests EFF et AmIUnique
- Contre-mesures réelles
- PassCypher et EviBITB
- Résultats PassCypher
- Test vidéo
- Tableaux comparatifs
- Enseignements clés
- Signaux faibles
- Signal régulatoire (UK)
- Focus : Dérive d’horloge
- Focus : Biométrie comportementale
- Focus : WebGPU
- Ce que nous n’avons pas couvert
- Perspective stratégique
- FAQs
- Glossaire
Les chroniques affichées ci-dessus ↑ appartiennent à la rubrique Sécurité Digitale. Elles prolongent l’analyse des architectures souveraines, des mécanismes de surveillance invisibles, des marchés de données et des logiques de traçage. Cette sélection complète la présente chronique consacrée au browser fingerprinting comme infrastructure de renseignement par métadonnées.
Résumé avancé — Quand le browser fingerprinting devient une arme de métadonnées
⮞ Note de lecture
Ce résumé avancé se lit en ≈ 5 à 6 minutes. Il consolide le cadre technique et juridique. Ensuite, il prépare l’entrée dans la chronique complète.
Clarifier cookies, sandbox et fingerprinting
Les cookies restent un marqueur visible. Ils sont donc contrôlables. Pourtant, ce contrôle est partiel. Les cookies tiers peuvent être bloqués. Cependant, l’écosystème publicitaire conserve d’autres leviers. Le browser fingerprinting se distingue ici. Il n’a pas besoin de stocker un identifiant. Il extrait une signature. Ensuite, il relie cette signature à des événements. Ainsi, il transforme des signaux techniques en continuité d’identité. La sandbox a tenté d’encadrer le ciblage. Or, le ciblage n’est pas le seul enjeu. L’enjeu central est la persistance. Donc, le fingerprinting agit comme une couche orthogonale. Il fonctionne avec ou sans cookies. Il s’additionne aux autres mécanismes.
Double trajectoire du traçage
Le traçage moderne fonctionne sur deux axes. D’abord, il exploite ce que l’utilisateur autorise, souvent sans le comprendre. Ensuite, il exploite ce qu’il ne peut pas facilement refuser. Les cookies, quand ils existent, offrent une continuité simple. Pourtant, ils restent fragiles. Ils se suppriment. Ils se bloquent. En revanche, le browser fingerprinting est résilient. Il s’appuie sur des caractéristiques natives. Il varie peu à court terme. Donc, il sert de colle. Cette colle relie des sessions. Elle relie aussi des environnements. Par conséquent, le traçage devient cumulatif. Il devient aussi opportuniste. En pratique, un acteur n’a pas besoin d’un seul identifiant. Il lui suffit d’une probabilité stable. Or, la probabilité suffit pour profiler. Elle suffit aussi pour discriminer.
Cadre juridique et consentement
Le cadre européen combine GDPR et ePrivacy. Ainsi, la question n’est pas seulement “cookie ou pas cookie”. La question porte sur l’accès au terminal. Elle porte aussi sur la lecture d’informations. Or, le fingerprinting exploite précisément cette zone. Il lit des propriétés. Il observe des comportements d’API. Ensuite, il dérive une empreinte. Le consentement est donc requis en principe. Cependant, le consentement devient difficile à rendre effectif. D’abord, la collecte est invisible. Ensuite, elle est technique. Enfin, elle est fragmentée entre acteurs. Par conséquent, l’utilisateur ne sait pas à quoi il consent. Il ne sait pas non plus comment s’opposer. De plus, la preuve est asymétrique. L’acteur mesure. L’utilisateur devine. Ainsi, l’illégalité potentielle n’empêche pas l’usage. Elle déplace l’usage. Elle le rend plus discret. Elle le rend aussi plus indirect.
Ce qui change côté doctrine des régulateurs
Le fingerprinting n’est plus traité comme un “détail technique” : il devient un sujet de preuve. Trois exigences reviennent systématiquement, car elles sont opposables dans les faits :
- Transparence : décrire la finalité et la nature du suivi (pas seulement “cookies”).
- Contrôle effectif : rendre l’opposition opérante, même quand la collecte est distribuée (scripts/tiers/iframes).
- Traçabilité de conformité : être capable de démontrer ce qui est collecté, par qui, et à quel moment.
Le nœud conflictuel reste structurel : une collecte invisible et fragmentée produit une asymétrie de preuve. L’acteur mesure ; l’utilisateur subit ou devine.
Le paradoxe de la vie privée
Beaucoup d’outils promettent une protection. Pourtant, ils peuvent augmenter l’unicité. Un VPN masque l’IP. Cependant, il ne masque pas le terminal. Le mode privé efface des traces locales. Or, il ne change pas les signaux exposés. Les extensions bloquent des scripts. Toutefois, elles modifient l’environnement. Ainsi, elles deviennent elles-mêmes des signaux. En pratique, l’excès de personnalisation crée une signature rare. Donc, la bonne stratégie n’est pas l’empilement. C’est la cohérence. D’abord, standardiser l’environnement. Ensuite, réduire les surfaces d’API. Enfin, bloquer ce qui exécute sans nécessité. Par conséquent, on passe d’une logique “privacy gadget” à une logique de contre-renseignement. Cette logique accepte une limite. Elle vise une réduction de risque.
sans stockage et s’additionne aux autres mécanismes. La protection dépend d’une cohérence d’ensemble : standardiser,réduire les APIs exposées,et contrôler l’exécution.
Chronique complète — Le browser fingerprinting comme infrastructure de renseignement
Taxonomie du browser fingerprinting
Le browser fingerprinting n’est pas une technique unique. Il s’agit d’un ensemble de méthodes. Ces méthodes diffèrent par leur profondeur, leur visibilité et leur résilience. D’abord, certaines reposent sur des signaux statiques. Ensuite, d’autres exploitent des comportements dynamiques. Enfin, certaines opèrent de manière indirecte. Cette diversité explique sa robustesse. Elle explique aussi sa difficulté à être neutralisée. Ainsi, parler de “le” fingerprinting est une simplification. En réalité, il faut raisonner en couches. Chaque couche ajoute de l’entropie. Chaque couche renforce la persistance.
Fingerprinting statique
Le fingerprinting statique exploite des caractéristiques peu variables. Par exemple, il observe les polices installées, la résolution d’écran ou le fuseau horaire. Ces éléments changent rarement. Donc, ils offrent une base stable. Cependant, pris isolément, ils sont peu discriminants. En revanche, combinés, ils deviennent puissants. Ainsi, une configuration banale devient unique par accumulation.
Fingerprinting dynamique
Le fingerprinting dynamique repose sur des comportements. Il observe comment le navigateur exécute du code. Par exemple, il mesure des temps de rendu. Il analyse des variations d’audio. Il teste des réactions à des appels d’API. Ces signaux varient légèrement. Pourtant, leur variation est elle-même caractéristique. Donc, le mouvement devient une signature. Par conséquent, le changement n’implique pas l’anonymat. Il peut même renforcer l’identification.
Fingerprinting indirect et par iframe
Certaines techniques n’agissent pas directement. Elles délèguent la collecte. Par exemple, elles utilisent des iframes. Ces iframes chargent des scripts tiers. Ensuite, ces scripts collectent des signaux. Ce modèle complique l’attribution. Il complique aussi le blocage. Ainsi, l’utilisateur voit une page. En arrière-plan, plusieurs contextes s’exécutent. Chacun contribue à l’empreinte globale.
Fingerprinting réseau et TLS
Enfin, le fingerprinting ne s’arrête pas au navigateur. Il s’étend au réseau. Des caractéristiques TLS peuvent être observées. Des modèles de négociation apparaissent. Même chiffrée, la communication révèle une forme. Donc, le chiffrement protège le contenu. Cependant, il ne supprime pas les métadonnées de transport. Cette couche complète les autres. Elle renforce la corrélation.
Empreintes TLS : de JA3 à JA4+
Le fingerprinting ne se limite pas au navigateur : une partie de l’identification peut être dérivée de la négociation TLS (ClientHello). Historiquement, JA3 a popularisé une signature construite à partir de paramètres TLS. Cependant, l’écosystème a évolué vers des approches de type JA4 / JA4+, conçues pour mieux résister aux contournements et mieux caractériser les clients et bibliothèques réseau.
- Impact stratégique : même si le contenu est chiffré, la “forme” du trafic (handshake, extensions, ordres) reste corrélable.
- Conséquence défensive : la protection ne peut pas être uniquement “browser-level” ; elle doit aussi considérer le réseau, les proxies, les piles TLS et la cohérence globale.
Fingerprinting matériel et micro-architectural (timings, jitter, signatures physiques)
Une partie du fingerprinting le plus avancé n’exploite plus seulement des APIs applicatives, mais des caractéristiques physiques mesurables : micro-variations d’exécution, jitter, effets thermiques, stabilité probabiliste de timings. Cette famille ne fournit pas un identifiant “parfait”, mais une signature statistiquement stable qui devient exploitable lorsqu’elle est recoupée avec d’autres couches (browser + réseau + comportement).
“Device intelligence” (anti-fraude / anti-bot) : le dilemme fonctionnel
Le fingerprinting sert aussi à la détection de fraude : cohérence d’empreinte, détection d’anomalies, indices de détournement de session. Le problème stratégique n’est donc pas “pour ou contre” : c’est la frontière entre un usage sécuritaire proportionné et une industrialisation publicitaire non contestable. La souveraineté consiste à imposer des conditions d’usage, de preuve et de cloisonnement, pas à nier la fonction.
Fingerprinting temporel : dérive d’horloge (Clock Skew)
Au-delà des propriétés logicielles, une partie du fingerprinting moderne explore des signaux temporels issus du matériel. La dérive d’horloge (clock skew) exploite le fait qu’un système réel n’exécute jamais le temps “parfaitement” : micro-variations liées à l’oscillateur, aux conditions thermiques et à la charge. Dans certaines conditions, des mesures répétées (timings) permettent de produire une signature probabiliste, y compris entre machines très proches.
Ce point ne doit pas être surinterprété : côté navigateur, la précision des timers est souvent réduite et le bruit complique l’exploitation. Néanmoins, la trajectoire stratégique est claire : le traçage cherche aussi des invariants physiques et non seulement des réglages.
Fingerprinting comportemental : biométrie d’interaction
Le traçage ne se limite plus à la machine : il peut s’étendre à l’utilisateur via l’analyse de comportements d’interaction. La biométrie comportementale agrège des signaux tels que la cadence de frappe (keystroke dynamics), les trajectoires et micro-corrections de la souris, ou certains schémas gestuels sur mobile. L’objectif n’est pas l’identification “civile” immédiate, mais une continuité d’usage exploitable, même si l’environnement technique change.
- Atout offensif : résilience au changement de navigateur, de cookies ou de réseau.
- Limite structurelle : bruit, erreurs, et risque de fausses corrélations (la preuve est rarement opposable côté utilisateur).
- Lecture stratégique : l’humain devient une couche de métadonnées — donc une surface de discrimination.
Le dilemme sécurité : anti-fraude vs vie privée
Le fingerprinting a une ambivalence fonctionnelle. Il est aussi utilisé en anti-fraude : cohérence d’empreinte lors d’une transaction, détection d’anomalies, suspicion de détournement de session. Le problème 2026 n’est donc pas “pour ou contre” : c’est la gouvernance. Comment bénéficier d’un signal défensif sans dériver vers une infrastructure de profilage publicitaire, et sans rendre l’opposition inopérante ?
WebGPU : le fingerprinting haute fidélité
Le passage de WebGL à WebGPU augmente la surface d’observation du GPU depuis le navigateur. Au-delà du rendu, l’accès à des primitives de calcul (compute) et à des comportements d’ordonnancement rend possibles des profils plus fins : latences, micro-variations de pipeline, patterns de scheduling sous charge. Le risque ne tient pas à un “identifiant GPU” explicite, mais à la dérivation d’une signature à partir de comportements mesurables.
Conséquence : la défense ne peut plus être uniquement “browser-level”. Elle doit intégrer une logique de réduction d’exposition (surface d’API) et surtout de contrôle d’exécution (bloquer ce qui ne doit pas s’exécuter, avant collecte), faute de quoi les APIs haute performance deviennent des capteurs.
Signaux techniques réellement collectés
La collecte ne repose pas sur un seul indicateur. Elle agrège des dizaines de signaux. D’abord, le rendu graphique est analysé. Ensuite, la pile audio est sollicitée. Les polices installées sont listées. Le matériel sous-jacent est inféré. Le fuseau horaire est comparé. De plus, certaines APIs exposent des états internes. Ainsi, chaque appel ajoute une information. Isolée, elle semble anodine. Corrélée, elle devient identifiante.
Cette collecte est souvent silencieuse. Elle ne déclenche pas d’alerte visible. Pourtant, elle s’exécute dès le chargement. Par conséquent, l’empreinte se forme rapidement. Elle se met à jour progressivement. Elle accompagne la navigation.
Pourquoi il est impossible à éliminer
L’élimination totale supposerait une uniformité parfaite. Or, cette uniformité est irréaliste. Les systèmes diffèrent. Les usages diffèrent aussi. Chaque variation crée de l’entropie. Ensuite, l’entropie s’additionne. Ainsi, même une faible différence compte. De plus, certaines propriétés sont physiques. Elles dépendent du matériel. Elles dépendent aussi du système. Donc, elles ne sont pas entièrement simulables.
En pratique, on peut réduire l’exposition. On peut aussi déplacer le point d’observation. Cependant, on ne peut pas supprimer toute signature. Cette limite est structurelle. Elle n’est pas un échec d’outil. Elle est une conséquence statistique.
Le piège de la randomisation
La randomisation est souvent présentée comme une solution. Pourtant, elle comporte un paradoxe. Modifier des paramètres peut sembler protecteur. Cependant, chaque modification ajoute une variation. Or, une variation supplémentaire augmente parfois l’unicité. Ainsi, randomiser sans cadre peut produire l’effet inverse. Le navigateur devient rare. Donc, il devient plus identifiable.
Certaines extensions modifient le canvas ou l’audio. D’autres changent l’agent utilisateur. En pratique, ces changements ne sont pas synchronisés. Ils créent des incohérences. Ensuite, ces incohérences deviennent des signaux. Par conséquent, l’empreinte se renforce. Elle n’est plus stable. Elle est distinctive.
Les navigateurs orientés vie privée ont tiré une leçon claire. Ils privilégient la standardisation. Autrement dit, ils rendent les utilisateurs semblables. Tor et Mullvad suivent cette logique. Ils limitent les variations. Ils réduisent les surfaces d’API. Ainsi, ils diminuent l’entropie exploitable. À l’inverse, une personnalisation excessive isole. Elle signale une configuration atypique.
En résumé, randomiser n’est pas anonymiser. Cela peut aider ponctuellement. Cependant, sans cohérence globale, cela expose davantage. La protection repose donc sur la sobriété. Elle repose aussi sur l’alignement des couches.
Mesurer son exposition : ce que montrent réellement les tests
Mesurer l’exposition est une étape clé. Toutefois, les résultats sont souvent mal interprétés. Des outils publics existent. Ils comparent une configuration à une base de référence. Ensuite, ils estiment une unicité. Cependant, cette unicité est statistique. Elle n’est pas une preuve d’identification directe.
Les tests analysent plusieurs dimensions. D’abord, ils évaluent les traceurs connus. Ensuite, ils mesurent l’empreinte du navigateur. Enfin, ils observent la stabilité dans le temps. Un score “unique” ne signifie pas un suivi certain. Il signifie une probabilité élevée. À l’inverse, un score “non unique” ne garantit rien. Il indique seulement une ressemblance.
Il faut donc lire ces résultats avec méthode. Comparer avant et après un changement est utile. Comparer entre navigateurs l’est aussi. En revanche, chercher le score parfait est une erreur. Aucun outil ne peut certifier l’absence de fingerprinting. Il peut seulement montrer des tendances.
Ainsi, les tests servent à orienter. Ils servent aussi à vérifier des hypothèses. Ils ne remplacent pas une stratégie. Ils l’éclairent. Par conséquent, ils doivent être intégrés dans une démarche globale.
Tests recommandés : EFF et AmIUnique
Ces tests ne prouvent pas une invisibilité. Cependant, ils indiquent une tendance. Ainsi, ils servent à comparer des configurations et à valider des hypothèses.
- Cover Your Tracks (EFF) : mesure l’unicité et la présence de traceurs.
- Am I Unique : détaille les composantes d’empreinte et leur rareté.
Contre-mesures : ce qui fonctionne réellement
Toutes les contre-mesures ne se valent pas. Certaines réduisent le risque. D’autres déplacent simplement le problème. Il faut donc distinguer les effets réels des effets perçus. D’abord, la standardisation est la plus efficace. Elle rend les environnements similaires. Ainsi, elle dilue l’unicité. Les navigateurs comme Tor ou Mullvad appliquent ce principe. Ils limitent les variations. Ils figent certains paramètres. Par conséquent, l’empreinte devient moins exploitable.
Ensuite, la réduction de surface est essentielle. Moins d’APIs exposées signifie moins de signaux. Bloquer l’accès inutile au canvas, à l’audio ou au stockage réduit l’entropie. Cependant, cette réduction doit rester cohérente. Une coupure brutale peut créer une anomalie. Or, l’anomalie est elle-même un signal.
Le blocage des scripts intervient plus en amont. Il empêche l’exécution. Donc, il empêche la collecte. Cette approche est efficace. Toutefois, elle doit être sélective. Un blocage total casse l’usage. En pratique, il faut arbitrer. Enfin, certaines mesures sont inefficaces seules. Changer l’agent utilisateur ou multiplier les VPN ne suffit pas. Ces actions modifient un paramètre. Elles laissent les autres intacts. Ainsi, elles offrent une fausse impression de contrôle.
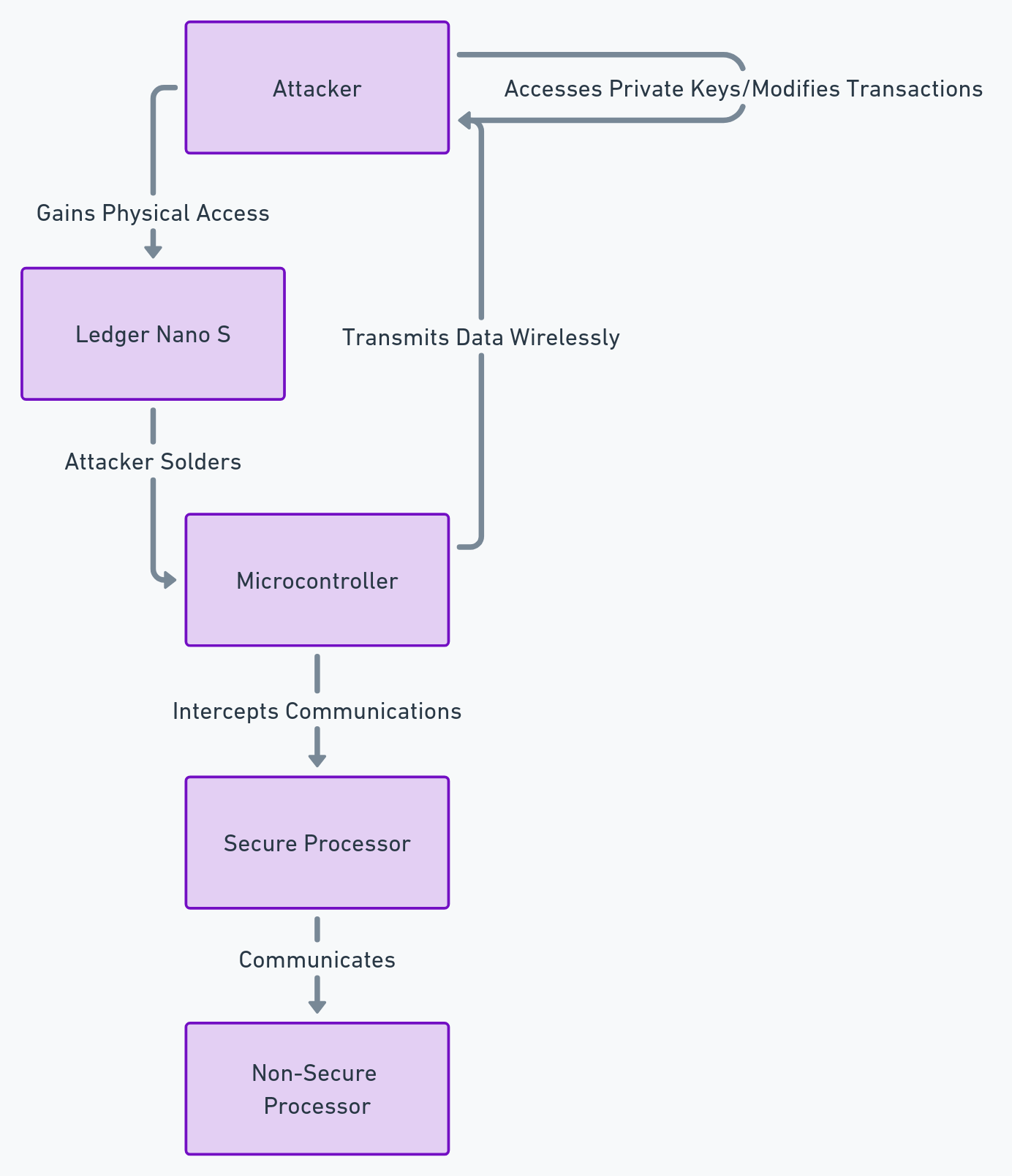
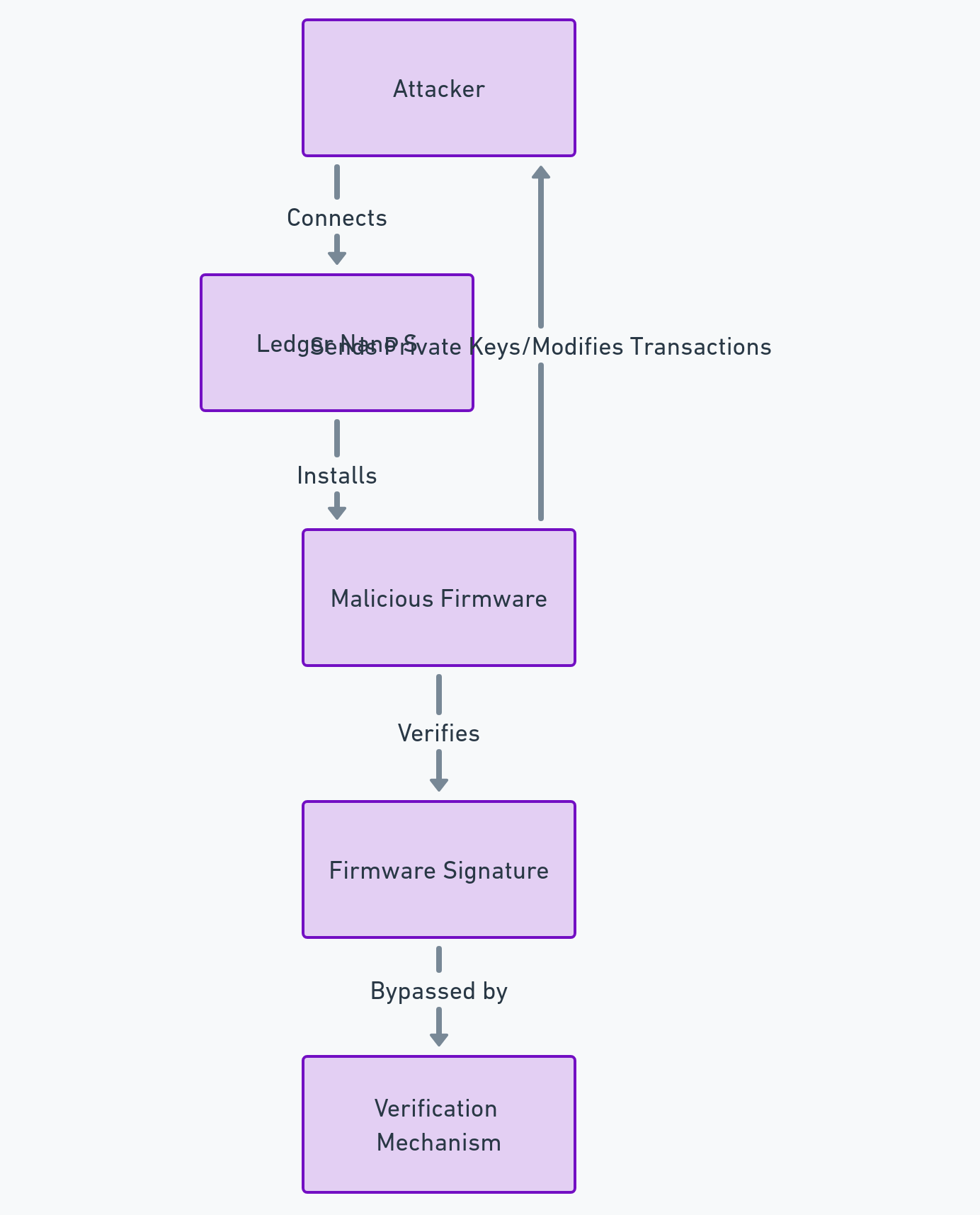
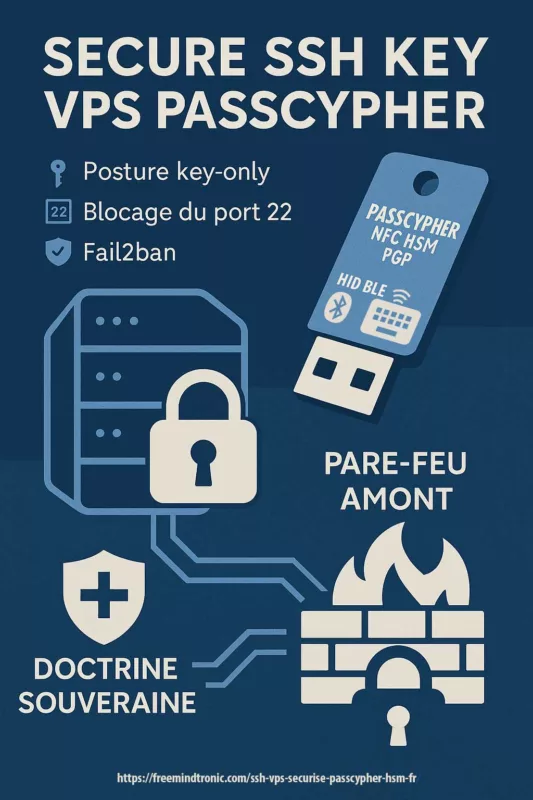
PassCypher et EviBITB : une contre-mesure structurelle
La majorité des outils agissent après coup. Ils modifient des valeurs. Ils masquent certains signaux. EviBITB adopte une logique différente. Il agit avant l’exécution. Autrement dit, il empêche certains scripts de s’exécuter. Cette différence est fondamentale. Si le script ne s’exécute pas, aucune empreinte n’est collectée à ce niveau.
Le fingerprinting indirect repose souvent sur des iframes. Ces iframes chargent des contextes tiers. Ensuite, ces contextes collectent des signaux. EviBITB cible précisément ce mécanisme. Il bloque ou neutralise les iframes suspectes. Ainsi, il coupe une chaîne entière de collecte. Ce n’est pas une modification. C’est une suppression du vecteur.
Cette approche est aussi pertinente contre les attaques de type Browser-in-the-Browser. Le principe est similaire. Une iframe simule une interface légitime. Elle capte des interactions. En bloquant l’iframe, on bloque à la fois le phishing et la collecte. Par conséquent, la protection devient transversale. Elle protège l’identité. Elle protège aussi l’authentification.
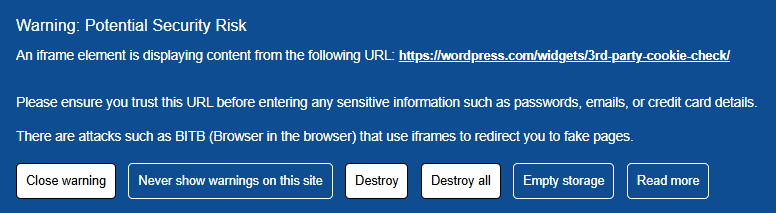
⚠️ Point clé : le BITB est stoppé au niveau du vecteur (iframe) avant que l’interface frauduleuse ne puisse capturer des identifiants — et avant que des scripts tiers ne collectent des signaux de fingerprinting.
Il faut toutefois être clair. EviBITB ne supprime pas tous les signaux. Les caractéristiques statiques restent visibles. C’est pourquoi cette solution doit être combinée. Elle s’intègre dans une stratégie. Elle complète la standardisation du navigateur. Elle complète aussi la réduction de surface. Ensemble, ces couches forment une défense cohérente.
Résultats de test : PassCypher avec et sans EviBITB
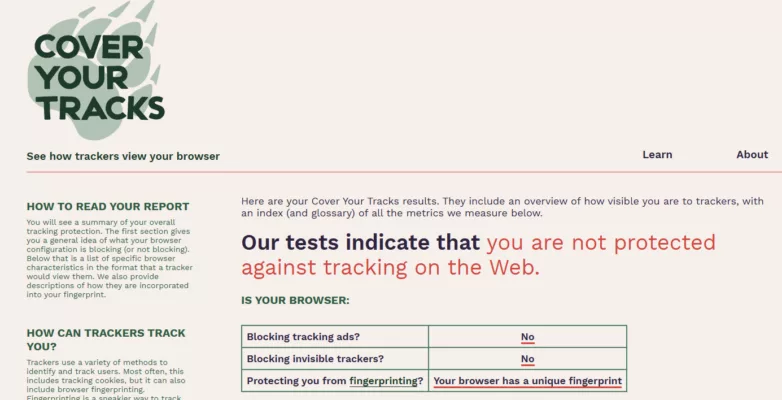
Ces résultats illustrent un point simple. D’abord, un script qui s’exécute collecte. Ensuite, une iframe qui persiste corrèle. Ainsi, le blocage avant exécution change la dynamique.
Test 1 : sans EviBITB
- Les traceurs publicitaires ne sont pas stoppés de manière fiable.
- Des traceurs invisibles peuvent rester actifs.
- Les scripts de fingerprinting s’exécutent, donc l’empreinte se consolide.
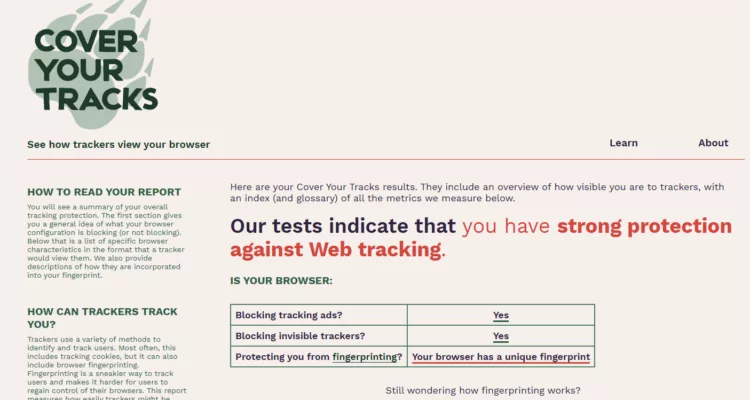
Test 2 : avec EviBITB activé
- Les vecteurs indirects via iframes sont bloqués plus tôt.
- La chaîne d’exécution est interrompue avant collecte.
- Cependant, les caractéristiques statiques du navigateur restent observables.
Point de méthode
Ces tests ne “prouvent” pas une invulnérabilité. En revanche, ils montrent un effet : neutraliser l’exécution dans les iframes réduit un vecteur entier de collecte. Pour réduire aussi l’unicité statique, il faut combiner avec un navigateur standardisé (Mullvad ou Tor).
Test vidéo : blocage avant exécution
Cette démonstration illustre le principe. D’abord, l’attaque s’appuie sur une iframe. Ensuite, l’interface simule une fenêtre légitime. Ainsi, la neutralisation précoce évite la collecte et réduit le risque de capture.
Matrice comparative des solutions
Comparer les solutions est indispensable. Cependant, la comparaison doit être honnête. Aucune solution ne couvre tout. Chaque outil agit sur une couche précise. D’abord, certains réduisent l’unicité. Ensuite, d’autres bloquent l’exécution. Enfin, certains se contentent de masquer des signaux. Ainsi, une matrice permet de clarifier. Elle montre ce que chaque approche fait réellement. Elle montre aussi ce qu’elle ne peut pas faire.
Les navigateurs standardisés réduisent fortement l’entropie. Toutefois, ils n’empêchent pas tous les scripts de s’exécuter. Les extensions de blocage filtrent des ressources. Cependant, elles modifient l’environnement. Les VPN masquent l’adresse IP. En revanche, ils n’affectent pas l’empreinte du terminal. EviBITB agit différemment. Il supprime des vecteurs d’exécution. Donc, il complète les autres approches. Par conséquent, la protection efficace est composite. Elle repose sur la cohérence, pas sur un outil unique.
| Solution | Bloque les iframes | Protection fingerprinting | Protection statique | Protection BITB | Blocage exécution | Facilité | Coût |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PassCypher HSM PGP Free + Mullvad Browser | Oui | Élevée | Approfondie (UA, audio, canvas) | Oui | Oui | Simple | Gratuit |
| Tor Browser | Non | Élevée | Approfondie (UA, canvas) | Non | Non | Exigeant | Gratuit |
| Mullvad Browser (seul) | Non | Élevée | Standardisation | Non | Non | Simple | Gratuit |
| Brave (mode strict) | Non | Moyenne | Partielle (canvas/WebGL) | Non | Non | Simple | Gratuit |
| Désactiver JavaScript | Oui | Élevée | Par suppression | Non | Oui | Contraignant | Gratuit |
| VPN + chaînes proxy | Non | Moyenne | Aucune | Non | Non | Contraignant | Payant |
| uBlock Origin + CanvasBlocker | Non | Faible à moyenne | Canvas surtout | Non | Non | Simple | Gratuit |
| Changer l’agent utilisateur | Non | Faible | UA seulement | Non | Non | Technique | Gratuit |
| Mode privé + multi-navigateurs | Non | Très faible | Aucune | Non | Non | Simple | Gratuit |
⮞ Point clé
— La matrice montre l’essentiel : la protection robuste vient d’une combinaison cohérente,et pas d’un outil isolé.
⮞ Synthèse
— Le browser fingerprinting fonctionne par couches,agrège des signaux techniques et réseau,et ne peut pas être supprimé totalement. La stratégie réaliste combine standardisation,réduction de surface et blocage en amont,au lieu d’une randomisation incohérente.
Enseignements clés
Le browser fingerprinting est structurel : il transforme des métadonnées en continuité d’identité. La réponse durable est architecturale.
Cadre Freemindtronic — “FM-TRACE” (5 principes opératoires)
- Réduire la surface : moins d’APIs, moins de signaux exploitables.
- Standardiser : ressembler à un groupe vaut mieux que devenir “rare”.
- Bloquer avant exécution : empêcher la collecte plutôt que masquer après coup.
- Séparer les contextes : identité, usage, contexte ne doivent pas se recoller automatiquement.
- Vérifier par tests : mesurer l’effet d’un changement, pas “chercher un score parfait”.
Signaux faibles
Radar Freemindtronic (2026) — 9 surfaces à surveiller
- CTV / TV connectées : environnements peu standardisés, forte corrélation d’usage, SDK publicitaires opaques.
- Consoles et “app browsers” : surfaces hybrides, permissions floues, instrumentation par tiers.
- Chaînes publicitaires multi-acteurs : attribution diffuse, responsabilité fragmentée, exécution distribuée (tags/iframes).
- Fingerprinting réseau : corrélation de flux et signatures TLS en soutien du browser-level.
- Identité probabiliste : moins d’identifiants, plus de scores, de rapprochements et de “device graphs”.
- IA de corrélation : exploitation de micro-variations à grande échelle (signaux faibles rendus opératoires).
- WebGPU / compute dans le navigateur : surface haute-fidélité (GPU, scheduling, contention).
- Fingerprinting matériel (timings) : dérive, jitter, signatures thermiques et micro-variations d’exécution.
- Biométrie comportementale : cadence de frappe, dynamique de souris, inerties et gestuelles.
Signal régulatoire (UK) — retour du “digital fingerprinting” dans l’AdTech (dont CTV) et montée en vigilance
Le basculement notable n’est pas seulement technique : il devient doctrinal. Fin 2024, l’assouplissement annoncé par Google sur ses politiques publicitaires a ravivé la controverse autour du fingerprinting dans l’AdTech, en particulier sur des surfaces comme la CTV, difficiles à auditer et à contrôler côté utilisateur. La réaction publique attribuée à l’autorité britannique (ICO) illustre un point central : quand l’identification migre vers des signaux “sans stockage”, le consentement devient moins opérant, la preuve plus asymétrique et la contestation plus coûteuse.
Source officielle (ICO) :
- https://support.google.com/adspolicy/answer/14346586
- https://blog.google/technology/safety-security/google-2024-update-to-digital-advertising-policies/
Contexte doctrinal (ICO) : l’ICO replace explicitement les “storage and access technologies” (dont les formes de fingerprinting) au cœur d’une stratégie de guidance et de consultation, signe que le sujet sort du seul débat “cookies”.
Focus — Dérive d’horloge (Clock Skew) : le renseignement au cœur du silicium
Au-delà des logiciels, le fingerprinting tend à exploiter des imperfections physiques : micro-variations d’exécution, jitter, effets thermiques, bruit électronique. La logique “clock skew” consiste à inférer une signature temporelle à partir de mesures répétées : ce n’est plus un identifiant stocké, mais une stabilité statistique issue du matériel. Cela marque une étape : l’empreinte n’est plus uniquement dans le code, elle est aussi dans les propriétés physiques observables par la mesure.
Point défensif : les mitigations récentes réduisent la précision des timers et encadrent certaines métriques ; mais la tendance globale reste celle d’une mesure probabiliste et d’une corrélation multi-sources.
Focus — Biométrie comportementale : l’humain comme métadonnée ultime
Le traçage ne s’arrête plus à la machine. Le behavioral fingerprinting analyse la dynamique d’interaction : cadence de frappe, latences, trajectoires de souris, gestuelles sur mobile. Ces signaux, collectés passivement, produisent un profil “biométrique numérique” difficile à contrefaire. Même si l’environnement technique change (navigateur/VPN), la manière d’interagir peut rester suffisamment stable pour soutenir une corrélation.
Point souverain : ces méthodes déplacent le débat de la “privacy” vers la preuve et la contestation : ce qui discrimine n’est pas visible, et l’erreur devient structurelle.
Focus — WebGPU : fingerprinting haute-fidélité et fin de l’opacité matérielle
WebGPU élargit la surface d’observation du matériel (GPU) et des comportements d’exécution (compute, scheduling, contention). La menace n’est plus limitée au rendu d’une image : elle peut passer par l’observation de micro-comportements de calcul et de contention, donc par une identification plus “haute fidélité”.
Point défensif : plus la performance est exposée, plus la mitigation doit être pensée comme une architecture de réduction d’exploitabilité (standardisation + réduction d’APIs + blocage avant exécution), et pas comme une collection d’astuces.
Ce que nous n’avons pas couvert
Cette chronique n’aborde pas tout. Le fingerprinting mobile avancé reste hors champ. Le fingerprinting matériel pur aussi. Les approches au niveau du système d’exploitation ne sont pas détaillées. De même, les contre-mesures basées sur le matériel sécurisé ne sont qu’évoquées. Ces choix sont assumés. Ils préservent la cohérence. Ils laissent aussi la place à de futures analyses.
Perspective stratégique
Le traçage va continuer. Il deviendra plus discret. Il sera aussi plus distribué. Les utilisateurs conserveront une marge de manœuvre. Cependant, cette marge sera technique. Elle ne sera pas déclarative. Les régulateurs tenteront d’encadrer. Pourtant, ils ne supprimeront pas les métadonnées. La seule réponse durable est architecturale. Elle repose sur la sobriété, la standardisation et le contrôle de l’exécution. Autrement dit, sur une forme de contre-renseignement numérique.
FAQs — Browser fingerprinting
Le mode navigation privée empêche-t-il le browser fingerprinting ?Réponse
Non. Il limite surtout les traces locales. Cependant, il ne modifie pas les signaux techniques exposés par le navigateur et le système. Par conséquent,l’empreinte reste exploitable.
Bloquer les cookies suffit-il à empêcher le traçage ?Réponse
Non. Bloquer les cookies réduit une partie du suivi. Toutefois,le fingerprinting fonctionne sans stockage local. Ainsi,l’identification peut persister même sans cookies.
Un VPN protège-t-il contre le fingerprinting ?Réponse
Un VPN masque l’adresse IP. C’est utile. En revanche,il ne change pas l’empreinte du navigateur. Donc,il protège surtout le réseau,pas l’environnement applicatif.
Les extensions anti-fingerprinting sont-elles efficaces ?Réponse
Elles peuvent aider. Cependant,elles modifient parfois l’environnement et augmentent l’unicité. L’efficacité dépend donc de la cohérence globale,et pas d’une extension isolée.
Pourquoi changer souvent l’agent utilisateur peut-il exposer davantage ?Réponse
Parce que cela crée des incohérences. Si l’agent utilisateur ne correspond pas au reste de l’environnement,la configuration devient rare. Ainsi,l’unicité peut augmenter au lieu de diminuer.
Peut-on mesurer précisément son niveau de protection ?Réponse
Pas précisément. Les tests publics donnent des indications statistiques. Ils servent surtout à comparer des configurations et à suivre des tendances,plutôt qu’à certifier une “absence de fingerprinting”.
Le browser fingerprinting permet-il d’identifier une personne ?Réponse
Pas directement. Il identifie d’abord un terminal. Toutefois,ce terminal peut être relié à une identité par corrélation et accumulation de données. Donc,l’identification devient progressive.
Peut-on éliminer totalement le browser fingerprinting ?Réponse
Non. L’uniformité parfaite est irréaliste. En revanche,on peut réduire fortement l’exploitabilité en standardisant l’environnement,en réduisant la surface d’API et en bloquant certains vecteurs d’exécution.
Le fingerprinting est-il encadré juridiquement en Europe ?Réponse
Oui,le cadre combine RGPD et ePrivacy. En principe,la collecte de signaux du terminal doit être encadrée et justifiée. Cependant,l’exécution est souvent invisible et distribuée entre acteurs. Donc,l’effectivité du consentement reste difficile.
Que change le signal régulatoire UK (ICO) sur le “digital fingerprinting” — notamment pour l’AdTech et la CTV ?
Il change la nature du débat : le fingerprinting n’est plus un “détail technique” de remplacement des cookies, mais un objet doctrinal traité comme technologie d’accès/collecte difficilement contrôlable par l’utilisateur.
En pratique, cela renforce l’exigence de transparence, de contrôle effectif et de démontrabilité — particulièrement sur des surfaces comme la CTV où l’audit et l’opposition utilisateur sont faibles.
Source officielle ICO :https://ico.org.uk/about-the-ico/media-centre/news-and-blogs/2024/12/our-response-to-google-s-policy-change-on-fingerprinting/
Le fingerprinting “sans stockage” échappe-t-il aux règles (consentement / accès au terminal) ?
Non. “Sans stockage” ne signifie pas “hors cadre”. Les régulateurs raisonnent aussi en termes d’accès/lecture d’informations sur le terminal et de finalité.
Autrement dit, l’absence de cookie n’est pas un laissez-passer : la question devient ce qui est collecté, comment, par qui, et si l’utilisateur a un contrôle réel.
Référence ICO (cookies & similar technologies / storage & access) :
https://ico.org.uk/for-organisations/uk-gdpr-guidance-and-resources/cookies-and-similar-technologies/cookies-and-similar-technologies/
Pourquoi la réduction de précision des timers (timing defenses) revient toujours dans le débat ?
Parce que beaucoup de signaux avancés reposent sur la mesure : micro-latences, jitter, variations d’exécution, comportements GPU/Audio/Canvas.
Réduire la précision (ou ajouter du bruit) dégrade la qualité des “mesures fingerprinting”. Ce n’est pas une protection totale, mais une mitigation structurante.
Référence W3C (guidance de mitigation du fingerprinting dans les specs Web) :
https://www.w3.org/TR/fingerprinting-guidance/
La dérive d’horloge (Clock Skew) est-elle un vrai levier de fingerprinting ?
Oui, mais surtout comme signature statistique et souvent en combinaison multi-couches (réseau + navigateur + comportement).
Historiquement, des travaux ont montré que des micro-variations de temps peuvent permettre un fingerprinting à distance.
Côté navigateur, les mitigations (timer precision, bruit) compliquent la reproductibilité, mais la trajectoire reste claire : chercher des invariants “physiques” mesurables.
Référence académique (clock skew / fingerprinting à distance) :
https://www.cs.tau.ac.il/~tromer/papers/clockskew.html
WebGPU augmente-t-il réellement le risque de fingerprinting ?
WebGPU élargit la surface d’observation et peut servir de base à des mesures plus fines (compute, contention, comportements micro-architecturaux côté GPU).
La recherche a déjà montré des scénarios exploitant WebGPU pour bâtir des timers et des attaques side-channel liées au GPU, ce qui renforce l’intérêt d’une défense “bloquer avant exécution” + réduction de surface.
Référence (WebGPU + GPU cache/side-channel dans le navigateur) :
https://arxiv.org/abs/2401.04349
La biométrie comportementale est-elle du fingerprinting “au-delà du navigateur” ?
Oui. Elle déplace le suivi vers l’utilisateur : cadence de frappe, micro-corrections, gestes, inerties.
Ce n’est pas toujours une “identification civile” directe ; c’est souvent une continuité d’usage (corrélation) qui devient exploitable pour discriminer, scorer, ou détecter des anomalies — avec une contestation difficile côté utilisateur.
Comment distinguer un usage anti-fraude légitime d’un profilage publicitaire non contestable ?
Par les conditions d’usage : finalité explicite, minimisation, durée courte, transparence vérifiable, séparation stricte des usages (anti-fraude ≠ AdTech), et preuve auditable.
Sans ces garde-fous, la “device intelligence” bascule vers une infrastructure de profilage invisible, où l’opposition devient théorique.
Pourquoi les CTV / TV connectées sont-elles un accélérateur de fingerprinting ?
Parce que l’environnement est peu standardisé, souvent peu auditable, et fortement corrélable par l’usage (foyer, temporalités, contenus).
De plus, la chaîne publicitaire y est fréquemment opaque (SDK, acteurs multiples), ce qui rend l’attribution et le contrôle utilisateur plus difficiles que sur navigateur classique.
Que faut-il tester en priorité pour savoir si une page “instrumente” le fingerprinting ?
D’abord l’exécution : scripts tiers, iframes, tags et leur ordre de chargement.