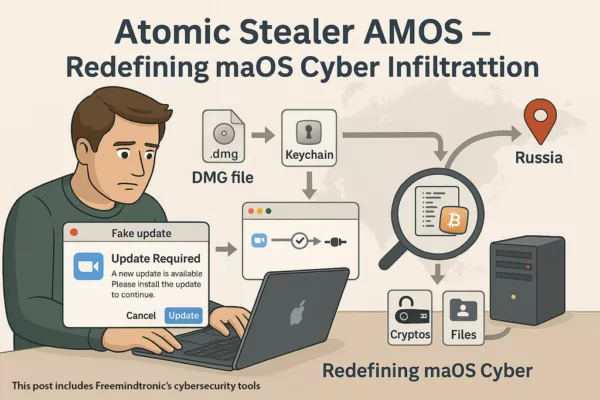
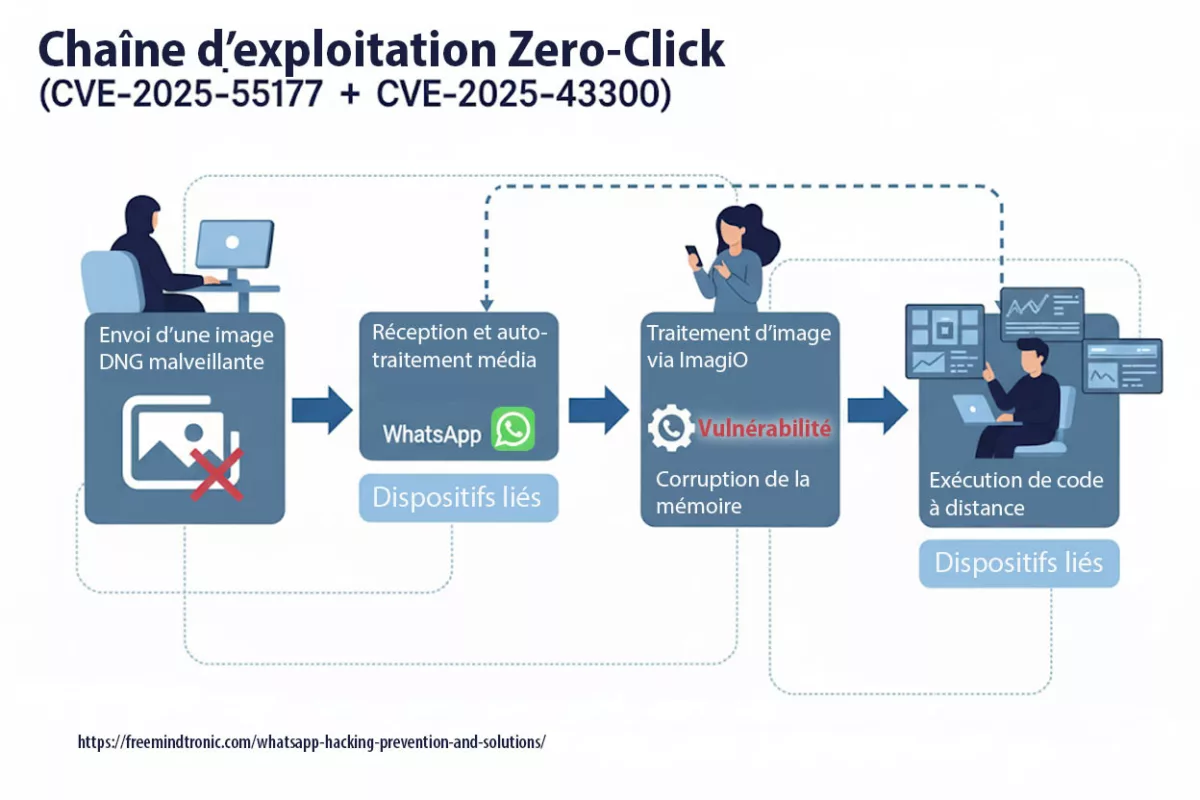
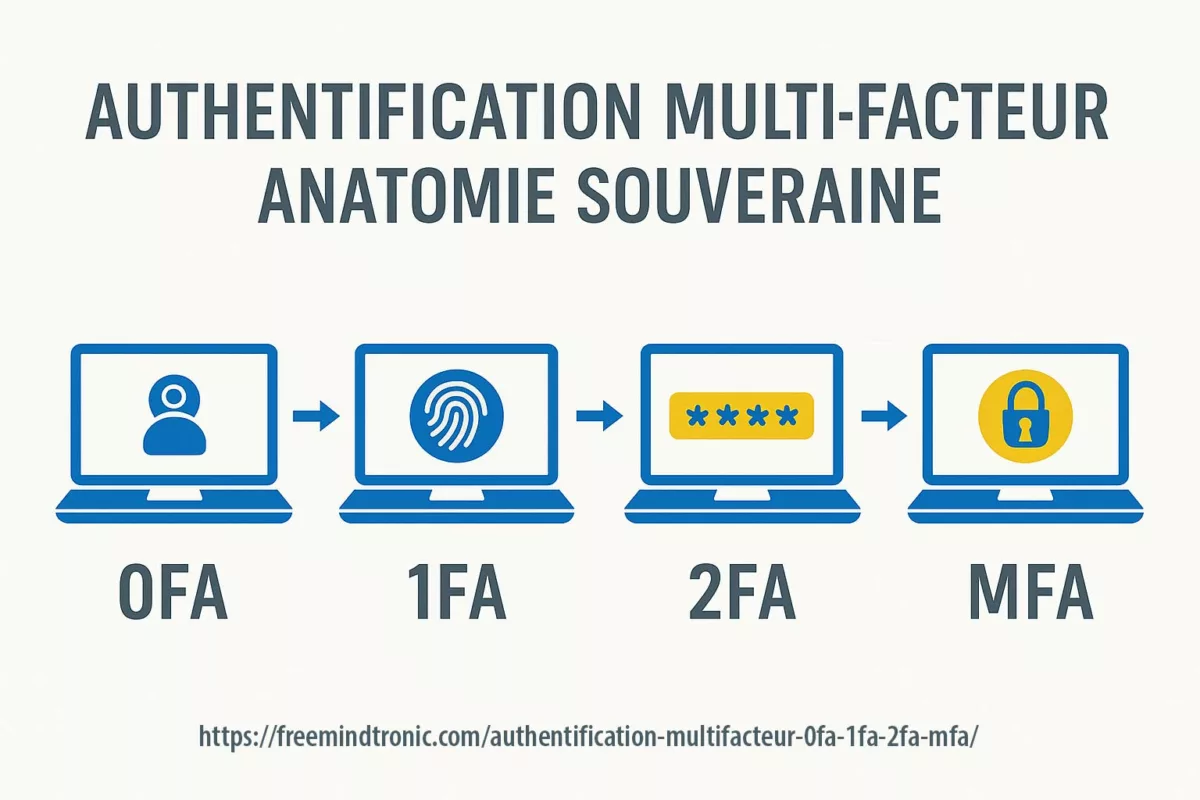
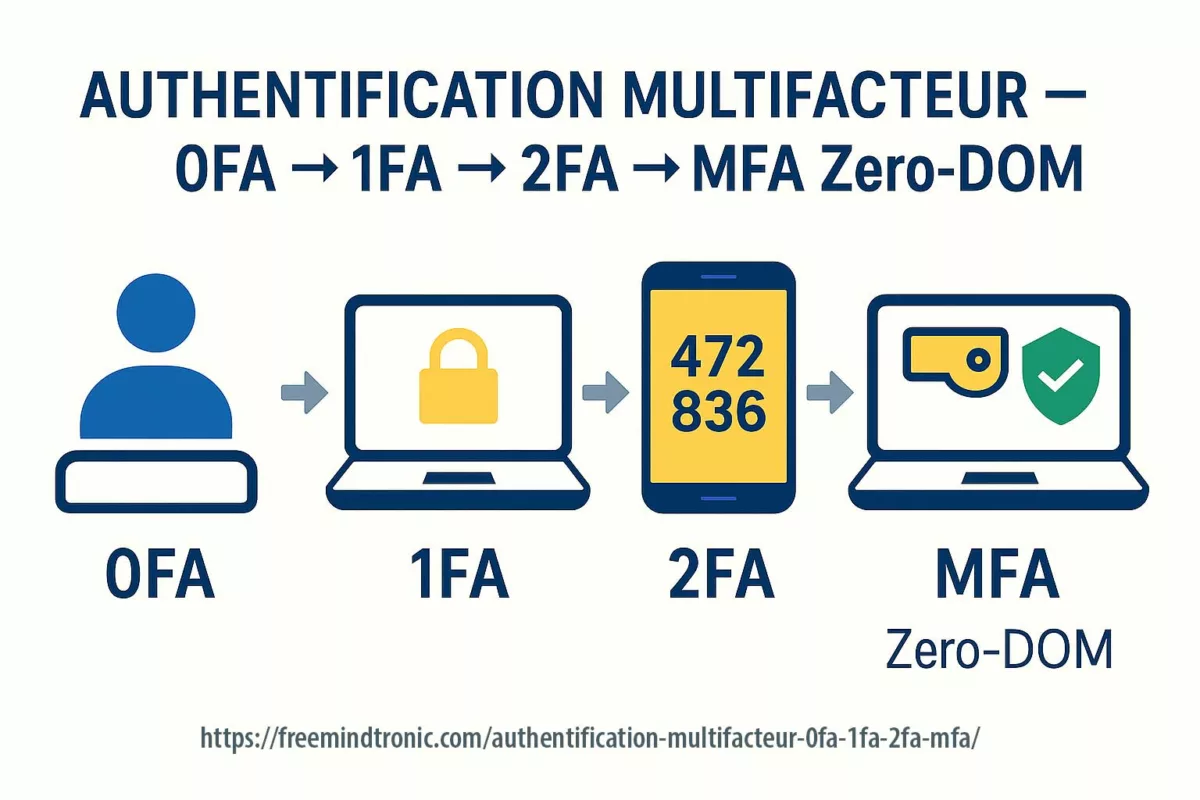
Spyware ClayRat Android illustre la mutation du cyberespionnage : plus besoin de failles, il exploite nos réflexes humains. Ce billet expose la rupture doctrinale opérée par DataShielder NFC HSM Defence, où le message en clair cesse d’exister dans Android.
Résumé express — Spyware ClayRat Android : un faux WhatsApp, arme d’espionnage
⮞ En bref
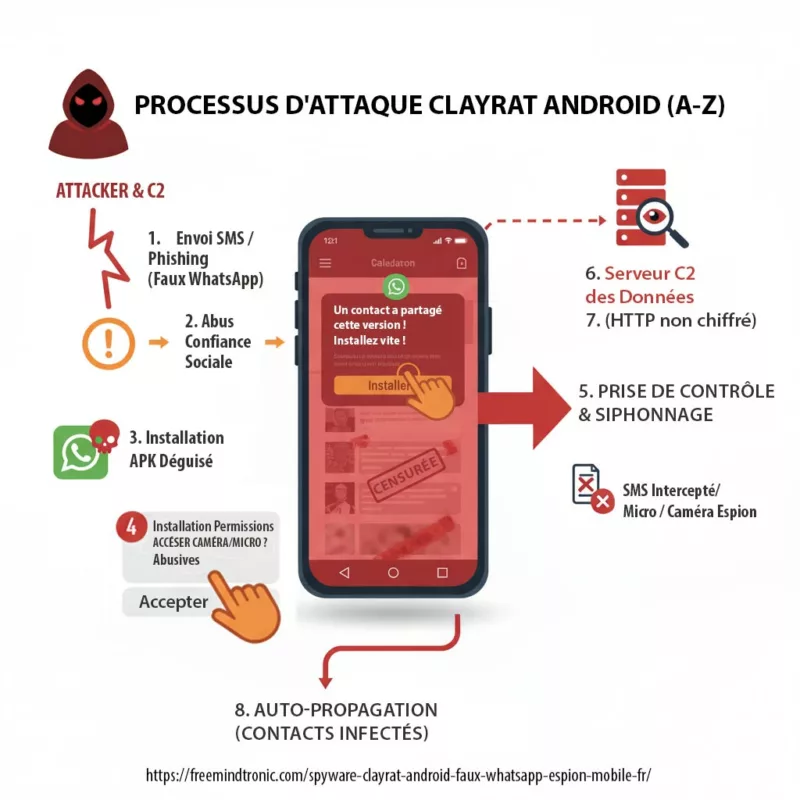
Lecture rapide (≈ 4 minutes) : ClayRat Android est un malware polymorphe qui se déguise en applications populaires (WhatsApp, Google Photos, TikTok, YouTube) pour infiltrer les téléphones Android. Il prend le contrôle des SMS, appels, caméras et microphones sans alerte.
Il contourne Android 13+, abuse du rôle SMS par défaut, intercepte les notifications et se propage via la confiance sociale des contacts infectés.
Sa nouveauté ? Il ne s’appuie pas sur une faille technique, mais sur une fausse familiarité.
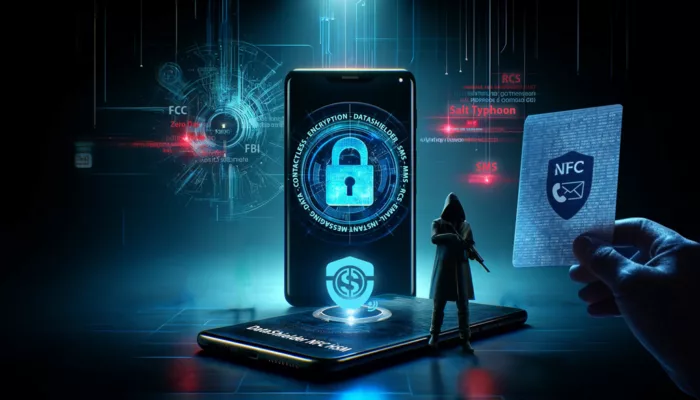
Face à cette menace, DataShielder NFC HSM Defence supprime la vulnérabilité du clair-texte : le message est chiffré matériellement avant même d’exister pour Android.
⚙ Concept clé
Comment neutraliser un spyware comportemental ?
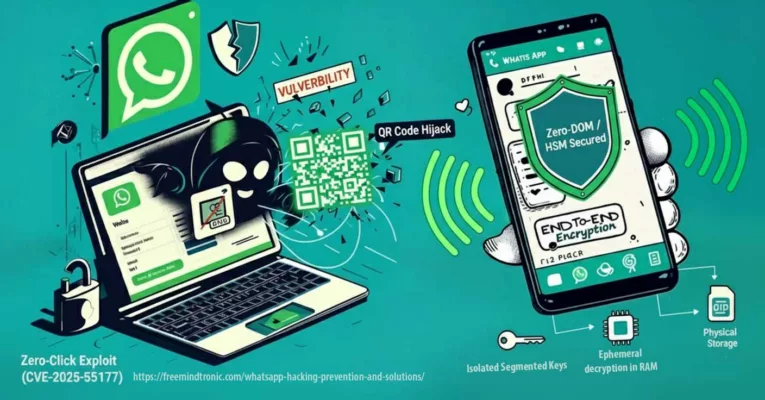
Freemindtronic répond par une approche souveraine : une édition matérielle du message chiffré dans une interface indépendante d’Android. Chaque frappe est chiffrée dans le HSM NFC avant injection. Aucun texte lisible n’est jamais stocké, ni dans le cache, ni dans la RAM Android.
Cette approche rend tout spyware structurellement aveugle, même s’il dispose d’un accès complet à la mémoire du téléphone.
Interopérabilité
Compatible : Android 10 à 14 — toutes messageries (SMS, MMS, RCS, Signal, Telegram, WhatsApp, Gmail, etc.).
Technologies intégrées : EviCore · EviPass · EviOTP · EviCall — toutes issues du socle souverain DataShielder NFC HSM Defence.
Paramètres de lecture
Temps de lecture résumé express : ≈ 4 minutes
Temps de lecture résumé avancé : ≈ 6 minutes
Temps de lecture chronique complète : ≈ 35 minutes
Dernière mise à jour : 2025-10-14
Niveau de complexité : Avancé / Expert
Densité technique : ≈ 71 %
Langues disponibles : EN · FR
Spécificité linguistique : Lexique souverain – terminologie cryptographique normalisée
Ordre de lecture : Résumé → Mécanique → Impact → Défense souveraine → Doctrine → Sources
Accessibilité : Optimisé lecteurs d’écran — ancres éditoriales incluses
Type éditorial : Chronique stratégique — Digital Security · Technical News
À propos de l’auteur : Jacques Gascuel, inventeur et fondateur de Freemindtronic Andorra, expert en architectures de sécurité matérielle NFC HSM et concepteur de solutions de souveraineté numérique (EviCore, DataShielder, PassCypher).
Résumé avancé — ClayRat Android et la fin du message en clair
⮞ En détail
ClayRat Android inaugure une nouvelle génération de spywares fondés sur le mimétisme social. Plutôt que d’exploiter une faille technique, il abuse des comportements humains : installation d’APK familiers, acceptation des permissions SMS et caméra, confiance envers les contacts connus. La réponse de DataShielder NFC HSM Defence est systémique : le chiffrement devient une fonction matérielle indépendante, non plus un processus logiciel. Le message n’existe jamais en clair dans Android. Même si ClayRat accède à la mémoire, il ne lit que des flux cryptés.
Principes souverains de défense
- Isolation matérielle complète (HSM NFC autonome, non adressable par Android)
- Auto-effacement du clair-texte après chiffrement matériel
- Compatibilité universelle avec toutes messageries Android
- Gestion souveraine des contacts et appels via EviCall NFC HSM
- Auto-purge des historiques (SMS, MMS, RCS) liés aux numéros stockés dans le HSM
Key Insights
- ClayRat remplace les vecteurs techniques par des leviers comportementaux.
- Les protections Android 13+ échouent face aux installations par session.
- La résilience ne réside pas dans le chiffrement post-exposition, mais dans l’absence totale de clair-texte.
- DataShielder NFC HSM Defence transforme la messagerie en éditeur matériel, rendant tout spyware structurellement aveugle.

La cybersécurité souveraine ↑ Ce billet appartient à la rubrique Sécurité Digital. Prolongez votre lecture avec du contenu essentiel sur la défense via de modules de sécurité matériel fonctionnant sans contact : vous constaterez ici ainsi que dans les autres billets qui définissent ce concept, comment l’architecture globale DataShielder NFC HSM Defence permet de se protéger nativement contre les attaques silencieuses.
Origine du spyware ClayRat : une campagne à façade sociale, sans attribution formelle
Les premières analyses indiquent que ClayRat cible principalement des utilisateurs russophones, avec une diffusion initiale via Telegram, des sites de phishing et des APK hébergés hors Play Store. L’attribution reste ouverte : aucune preuve publique ne permet de relier ClayRat à un acteur étatique ou à une opération APT connue.
- Infrastructure C2 : serveurs de commande et contrôle situés hors de l’Union européenne, souvent hébergés dans des juridictions à faible coopération judiciaire.
- Capacité de reconfiguration : domaines dynamiques, DNS rotatifs, et hébergements volatils pour échapper aux listes de blocage.
- Levier principal : exploitation de la confiance sociale entre pairs pour contourner les mécanismes de vigilance technique.
- Absence de vecteur technique initial : ClayRat ne repose pas sur une vulnérabilité logicielle, mais sur une faille comportementale.
Cette façade sociale rend ClayRat particulièrement difficile à détecter en phase pré-infection. Il ne déclenche pas d’alerte système, ne requiert pas de privilèges root, et s’installe via des sessions utilisateur légitimes. C’est une attaque par mimétisme; où l’interface familière masque une logique d’espionnage.
Evolution rapide de ClayRat
⮞ Contexte actualisé
À la mi-octobre 2025, les dernières données confirment que le spyware Android ClayRat poursuit son expansion au-delà du public russophone initial. Les laboratoires de sécurité (Zimperium, CSO Online, CyberScoop) recensent plus de 600 échantillons APK uniques et plus de 50 variantes de distribution via Telegram et SMS.
Chronologie de l’évolution
- T1 2025 : découverte initiale sur des groupes Telegram russophones, infection par confiance sociale.
- T2 2025 : mutation de l’infrastructure C2 avec DNS dynamique et domaines éphémères (
clayrat.top). - T3 2025 : propagation automatique — les appareils infectés envoient eux-mêmes des SMS malveillants.
- T4 2025 : contournement des protections Android 13+ via de faux écrans de « mise à jour système ».
Capacités observées
- Contrôle silencieux de la caméra et du micro même en mode veille.
- Vol d’identifiants via les services d’accessibilité et l’autoremplissage.
- Liste de commandes dynamique permettant le remplacement du payload.
- Exfiltration de données en HTTP non chiffré vers les C2 distants.
Comparatif des menaces mobiles
| Spyware | Vecteur principal | Caractéristique distinctive |
|---|---|---|
| Pegasus | Exploits sans interaction (zero-click) | Surveillance étatique visant journalistes et diplomates |
| Predator | Vulnérabilités zero-day | Espionnage gouvernemental par faille logicielle |
| FluBot | Hameçonnage SMS | Vol de données bancaires via fausses mises à jour |
| ClayRat | Mimétisme social | Espionnage comportemental sans exploit, basé sur la confiance |
Cette transition illustre le passage stratégique de la faille technique à la faille humaine — la nouvelle frontière du cyberespionnage Android.
Impacts et risques émergents
- Transformation des smartphones infectés en nœuds de diffusion par SMS automatique.
- Propagation dans les environnements BYOD (usage professionnel).
- Intérêt croissant sur les forums darknet pour des kits ClayRat « builder » dérivés.
Recommandations de durcissement
- Désactiver globalement la permission Installer des applications inconnues.
- Filtrer les liens SMS via des passerelles ou politiques EMM.
- Bloquer les motifs DNS du type
*.clayrat.top. - Privilégier une édition matérielle du message via DataShielder NFC HSM Defence pour supprimer toute exposition en clair.
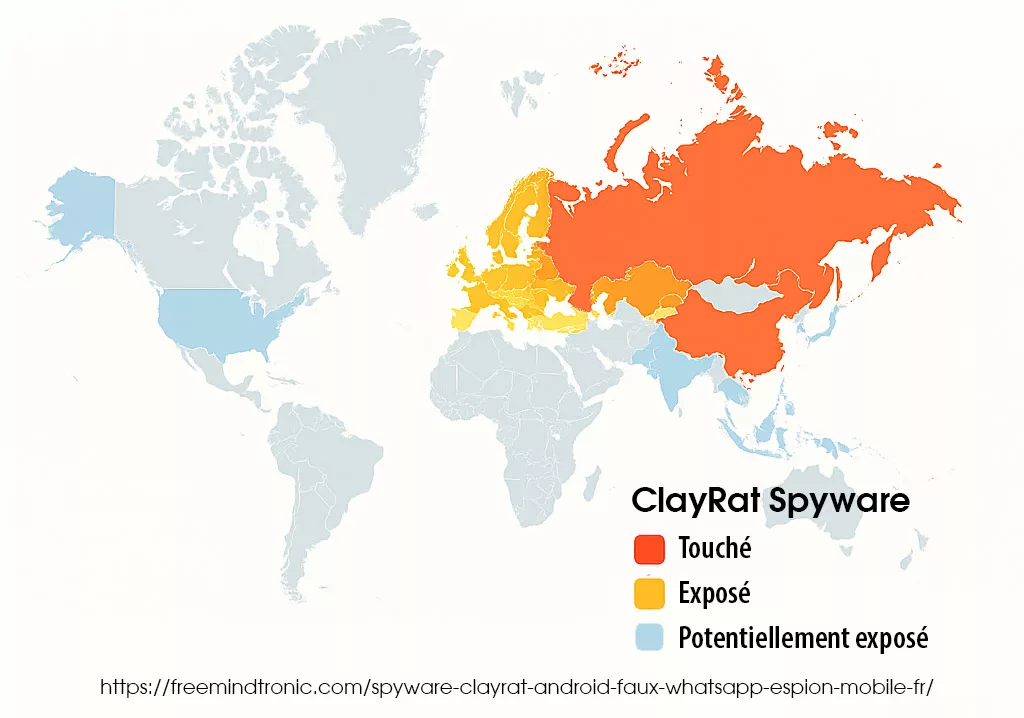
Cartographie géographique & victimes cyber
Cartographie & Heatmap
La carte mondiale ci-dessous illustre la répartition géographique des campagnes du spyware ClayRat Android détectées entre fin 2024 et 2025. D’après la télémétrie de Zimperium et des indicateurs open source, l’épicentre se situe en Russie et dans les pays limitrophes, avec une propagation progressive vers l’Europe de l’Est, la Turquie et une exposition surveillée en Amérique du Nord et en Asie-Pacifique.
Cas de victimes vérifiées & Secteurs ciblés
À ce jour (octobre 2025), aucune victime publiquement confirmée — qu’il s’agisse d’un gouvernement, d’une ONG ou d’un média — n’a pu être reliée de manière forensique au spyware ClayRat Android. Cependant, les renseignements open source confirment une cible prioritaire : les utilisateurs russophones d’Android, via des canaux Telegram, des sites de phishing et des APK diffusés hors Play Store.
- Broadcom recense le spyware ClayRat Android comme une menace active pour Android, sans citer de victimes précises.
- Zimperium indique que les appareils infectés servent de relais de diffusion, propageant des variantes polymorphes.
- En comparaison, Pegasus et Predator ont fait l’objet de cas avérés impliquant des journalistes, des ONG et des responsables publics — soulignant la nature plus furtive et comportementale de ClayRat.
Impact du cyberespionnage mobile : de la vie privée à la souveraineté mobile
L’impact de ClayRat dépasse largement le vol de données personnelles. Il s’inscrit dans une logique de compromission silencieuse, où la frontière entre espionnage individuel et atteinte systémique devient floue. Voici les trois niveaux d’impact observés :
- Atteinte à la vie privée : ClayRat intercepte les messages, images, journaux d’appels, et peut activer caméra et micro sans alerte. L’utilisateur ne perçoit aucune anomalie, tandis que ses échanges les plus intimes sont siphonnés en temps réel.
- Propagation en milieu professionnel : En exploitant les contacts de confiance, ClayRat se diffuse dans les environnements d’entreprise sans déclencher de détection classique. Il contourne les solutions MDM et s’infiltre dans les chaînes de communication internes, compromettant la confidentialité des échanges stratégiques.
- Risque systémique : En combinant espionnage, mimétisme applicatif et diffusion sociale, ClayRat provoque une perte de souveraineté des communications mobiles. Les infrastructures critiques, les chaînes de commandement et les environnements diplomatiques deviennent vulnérables à une surveillance invisible, non attribuée, et potentiellement persistante.
Ce triple impact — personnel, organisationnel et systémique — impose une rupture dans les doctrines de sécurité mobile. Il ne suffit plus de détecter l’intrusion : il faut supprimer les zones de clair-texte avant qu’elles ne deviennent exploitables.
Score de dangerosité typologique : ClayRat atteint 8.2 / 10
ClayRat n’exploite pas une faille zero-day au sens technique. Il ne contourne pas une vulnérabilité logicielle inconnue, mais détourne des mécanismes Android documentés, en s’appuyant sur la confiance sociale et l’interface utilisateur. À ce titre, il mérite une évaluation typologique de dangerosité, inspirée du modèle CVSS.
| Critère | Évaluation | Justification |
|---|---|---|
| Vecteur d’attaque | Réseau (via SMS/phishing) | Propagation sans contact physique |
| Complexité de l’attaque | Faible | Installation via confiance sociale, pas de root requis |
| Privilèges requis | Élevés (accordés par l’utilisateur) | Usurpation du rôle SMS et accès aux contacts |
| Impact sur la confidentialité | Critique | Vol de messages, images, appels, caméra |
| Impact sur l’intégrité | Modéré | Envoi de SMS malveillants à l’insu de l’utilisateur |
| Impact sur la disponibilité | Faible | Espionnage passif, pas de blocage système |
Score typologique estimé : 8.2 / 10 — Menace critique par mimétisme comportemental
Rupture doctrinale : pourquoi les solutions classiques de sécurité mobile échouent face à ClayRat
Avec un score de dangerosité typologique de 8.2/10, ClayRat impose une remise en question profonde des approches de sécurité mobile. Les solutions classiques — antivirus, sandbox, MDM, chiffrement logiciel — échouent non pas par obsolescence technique, mais parce qu’elles interviennent après l’exposition du message en clair. Il est temps de changer de paradigme.
Face à ClayRat, les solutions de sécurité traditionnelles — antivirus, sandbox, MDM, chiffrement logiciel — montrent leurs limites. Elles interviennent après l’exposition, ou protègent un contenu déjà lisible par le système. Or, ClayRat ne cherche pas à casser le chiffrement : il intercepte le message avant qu’il ne soit protégé.
- Antivirus : inefficaces contre les APK déguisés et les installations par session utilisateur.
- Sandbox : contournées par l’activation différée et le mimétisme applicatif.
- MDM/EMM : incapables de détecter une application qui se comporte comme une messagerie légitime.
- Chiffrement logiciel : exposé à la mémoire vive, lisible par le système avant chiffrement.
Le resultat est sans appel : tant que le système d’exploitation détient le message en clair, il peut être compromis. Il ne suffit plus de protéger le contenu — il faut supprimer son existence lisible dans l’environnement Android.
Permissions abusives : ClayRat et les vecteurs d’accès système
ClayRat ne repose pas sur une faille technique, mais sur une exploitation stratégique des permissions Android. Lors de l’installation, il demande un ensemble de droits étendus, souvent acceptés sans vigilance par l’utilisateur, car l’application se présente comme un service de messagerie légitime.
- Lecture des SMS : pour intercepter les messages entrants, y compris les OTP bancaires ou d’authentification.
- Accès aux contacts : pour identifier les cibles de propagation sociale.
- Gestion des appels : pour intercepter ou initier des appels sans interaction utilisateur.
- Accès à la caméra et au micro : pour capturer des données visuelles et sonores à l’insu de l’utilisateur.
Ces permissions, bien que légitimes dans le cadre d’une messagerie, deviennent des vecteurs d’espionnage lorsqu’elles sont accordées à une application déguisée. Elles soulignent la nécessité d’une interface souveraine indépendante du système, où le message ne transite jamais en clair.
Exfiltration réseau du spyware ClayRat : flux non chiffrés vers le C2
Une fois les données collectées, ClayRat les exfiltre vers ses serveurs de commande et contrôle (C2), identifiés notamment sous le domaine clayrat.top. L’analyse réseau révèle une communication en clair via HTTP, facilitant l’analyse mais aussi la compromission.
- Protocole : HTTP non sécurisé (pas de TLS)
- Méthode : requêtes POST contenant des
payloads JSONavec les données volées - Contenu : messages, contacts, journaux d’appels, métadonnées système
Cette exfiltration non chiffrée confirme que ClayRat n’intègre pas de chiffrement de bout en bout — il compte sur l’accès au message en clair. Une architecture où le message est déjà chiffré matériellement rend cette exfiltration inutile : le spyware ne peut transmettre que du bruit cryptographique.
Indicateurs de compromission (IoC) techniques pour ClayRat : CERT et SOC
Pour les équipes de réponse à incident (CERT, SOC), voici les principaux IoC publics liés à ClayRat, issus de la veille ThreatFox et Zimperium :
| Type | Valeur | Source |
|---|---|---|
| Domaine C2 | clayrat.top |
ThreatFox |
| IP associée | 185.225.73.244 | abuse.ch |
| Hash APK | f3a1e2c9d8b6e1f3... (extrait) |
Zimperium |
Ces indicateurs doivent être intégrés dans les systèmes de détection réseau (IDS/IPS) et les outils de threat hunting. Pour des raisons de sécurité opérationnelle, la liste complète est réservée aux entités habilitées.
Pour une analyse complète des tactiques de ClayRat, voir le rapport de Zimperium.
Comparatif : ClayRat face aux autres spywares Android (FluBot, SpyNote)
| Critère | ClayRat | FluBot | SpyNote |
|---|---|---|---|
| Diffusion | SMS + confiance sociale | SMS massif | APK sur forums |
| Ciblage | Russophone | Europe | Global |
| C2 | clayrat.top (non chiffré) | rotatif (DNS) | IP fixes |
| Particularité | Usurpation rôle SMS | Overlay bancaire | Contrôle caméra/micro |
Recommandations opérationnelles CERT/SOC face au spyware ClayRat Android
- Bloquer les domaines et IP liés à
clayrat.topdans les pare-feux et proxys d’entreprise. Surveiller les journaux de connexions sortantes pour détecter toute tentative résiduelle. - Interdire l’installation d’APK hors Play Store (sideload) via les politiques MDM/EMM. Restreindre les applications aux sources vérifiées et tracer les exceptions justifiées.
- Surveiller les flux HTTP non chiffrés sortants vers des domaines inconnus. Une connexion persistante en clair doit être considérée comme un indicateur de compromission.
- Renforcer la sensibilisation des utilisateurs à la reconnaissance des faux messages WhatsApp, TikTok ou Google Photos. Encourager la vérification des sources et le signalement immédiat des liens suspects.
- Déployer une messagerie souveraine chiffrée matériellement — et utiliser un outil de surchiffrement tel que DataShielder NFC HSM Lite / Master / Auth / m.Auth / Defence — afin d’éliminer toute présence de message en clair dans Android, même avant l’envoi.
- Auditer régulièrement les permissions SMS par défaut et identifier les usurpations silencieuses du rôle de gestionnaire de messagerie. Révoquer toute application non autorisée.
- Maintenir une veille active des indicateurs de compromission (IoC) en s’appuyant sur les bases ThreatFox et abuse.ch, ainsi que les bulletins de Zimperium.
Ces mesures immédiates permettent de réduire l’exposition organisationnelle à ClayRat.
Elles s’inscrivent dans une doctrine de résilience structurelle où le message n’est plus un actif à protéger, mais une donnée inexistante en clair.
C’est cette rupture — l’édition matérielle de messages chiffrés indépendante du système d’exploitation — que concrétise DataShielder NFC HSM Defence.
Note doctrinale :
Dans la logique souveraine de Freemindtronic, la sécurité ne repose plus que sur la détection d’une menace, mais sur la suppression de toute surface exploitable.
L’approche DataShielder NFC HSM ne cherche pas à protéger un message après son exposition — elle en empêche l’existence même en clair.
C’est cette neutralisation du concept de vulnérabilité qui fonde la souveraineté numérique embarquée.
Explorons maintenant en profondeur la rupture doctrinale souveraine incarnée par DataShielder NFC HSM Defence.
Cette solution ne protège pas un message exposé, elle en abolit la forme lisible avant même son transfert dans Android. Grâce à une interface cryptographique indépendante du système, chaque mot, chaque octet et chaque contact sont chiffrés matériellement dès leur création, rendant tout spyware structurellement aveugle.
Nous verrons comment DataShielder combine les briques technologiques EviCore, EviPass, EviOTP et EviCall NFC HSM pour établir un écosystème de communication souverain, où la confidentialité n’est plus un choix, mais une propriété native du message.
Défense souveraine avec DataShielder NFC HSM Defence : la fin du clair-texte Android
C’est cette rupture doctrinale qui ouvre la voie à une nouvelle génération de défense : l’édition matérielle de messages chiffrés, indépendante du système d’exploitation. C’est précisément ce que réalise DataShielder NFC HSM Defence.
Cloisonnement souverain avec EviPass NFC HSM : sécurité sans contact
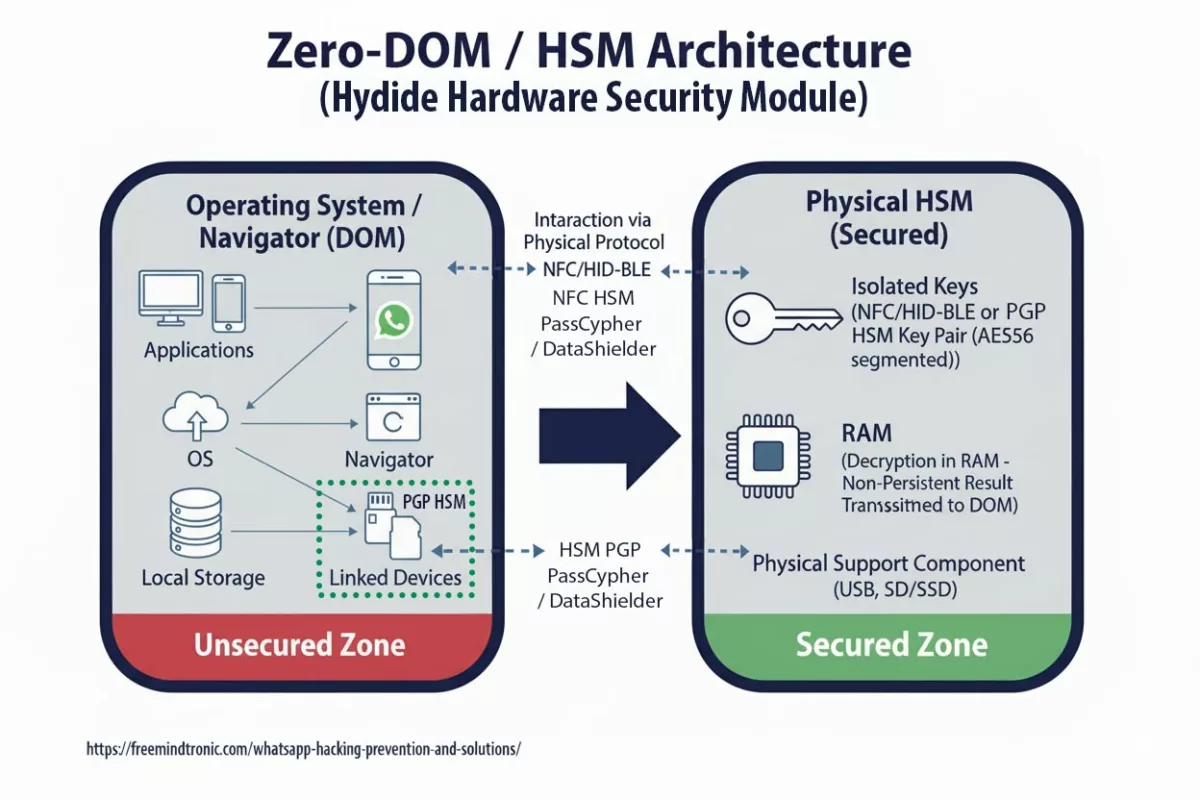
Contrairement aux applications classiques qui dépendent du sandbox Android, DataShielder embarque une technologie souveraine issue de EviCore NFC HSM, déclinée ici sous la forme EviPass NFC HSM. Ce cloisonnement matériel et logiciel permet d’exécuter les opérations cryptographiques dans un environnement isolé, indépendant du système d’exploitation.
- Sandbox URL dédiée : chaque instance dispose d’un espace d’exécution cloisonné, inaccessible aux autres processus Android.
- EviPass NFC HSM : gestionnaire décentralisé de secrets, sans cloud ni stockage local, piloté depuis l’application propriétaire.
- Version Defence : intègre EviOTP NFC HSM, générateur matériel d’OTP souverain, compatible TOTP/HOTP, totalement hors ligne.
Ce cloisonnement natif garantit que ni Android, ni un spyware comme ClayRat ne peuvent accéder aux identifiants, aux messages ou aux OTP générés. Il s’agit d’une sandbox souveraine embarquée, conçue pour fonctionner même dans un environnement compromis.
Architecture hybride DataShielder : l’avantage EviCore NFC HSM
DataShielder repose sur une architecture hybride brevetée issue de EviCore NFC HSM, combinant :
- Un NFC HSM ultra-passif blindé, contenant les clés segmentées et le système de contrôle d’accès matériel.
- Une intelligence logicielle agile, responsable de l’interface, de l’orchestration cryptographique et des mises à jour dynamiques.
Cette combinaison permet une édition matérielle souveraine du message, tout en conservant la souplesse d’adaptation logicielle. Le HSM ne contient aucune logique exécutable — il agit comme un coffre-fort cryptographique, tandis que le logiciel pilote les opérations sans jamais exposer le contenu en clair et sans stocker les secrets, uniquement présents chiffrés dans la mémoire EPROM du NFC HSM.
Interface souveraine de messagerie chiffrée
Dans DataShielder NFC HSM Defence, la rédaction d’un message s’effectue dans une interface cryptographique propriétaire indépendante d’Android. Le texte en clair n’existe que dans la mémoire volatile interne à cette interface. Dès que l’utilisateur valide, le message est immédiatement chiffré depuis le NFC HSM, seul à disposer des clés, puis injecté chiffré dans la messagerie choisie (SMS, MMS, RCS ou app tierce). Le texte en clair est effacé et ne transite jamais dans Android.
| Approche | Exposition du message | Résilience face à ClayRat |
|---|---|---|
| Chiffrement logiciel | Message en clair dans Android avant chiffrement | Vulnérable |
| Édition hybride souveraine (DataShielder NFC HSM) | Message jamais lisible par Android | Résilient |
⮞ Mécanisme cryptographique
- Chiffrement AES-256 dans le HSM NFC, sans signature nécessaire.
- Message clair inexistant dans Android, seulement en RAM sécurisée le temps de la frappe.
- Injection universelle : toutes les messageries reçoivent un contenu déjà chiffré.
- Auto-purge : destruction immédiate du message clair après chiffrement.
- Compatibilité multi-messagerie : SMS, MMS, RCS, Signal, Telegram, WhatsApp, etc..
Les algorithmes utilisés sont conformes aux standards internationaux : AES-256 (FIPS 197) et OpenPGP RFC 9580.
Contrairement aux architectures nécessitant une signature logicielle, DataShielder repose sur un chiffrement et déchiffrement exclusifs entre HSM NFC. Toute tentative de modification rend le message indéchiffrable par conception. Le HSM agit comme un éditeur matériel de messages chiffrés, rendant tout spyware aveugle par nature.
Technologies embarquées — EviCore et ses dérivés
- EviCore NFC HSM : fondation technologique embarquée dans tous les modules souverains
- EviPass NFC HSM : gestionnaire décentralisé de mots de passe et secrets
- EviOTP NFC HSM : générateur matériel d’OTP souverain, hors ligne
- EviCypher NFC HSM : module dédié au chiffrement depuis un NFC HSM des messages, fichiers, emails
- EviCall NFC HSM : gestionnaire souverain de contacts et apple téléphoniques depuis une NFC HSM, exclusif à DataShielder Defence
Ce que notre billet ne traite pas (volontairement)
Ce billet se concentre sur les contre-mesures souveraines embarquées face à ClayRat. Certains aspects techniques ou opérationnels sont volontairement exclus pour préserver la lisibilité, la sécurité et la pertinence contextuelle :
- Indicateurs de compromission complets (IoC) — disponibles via Zimperium et ThreatFox, réservés aux CERT et SOC pour éviter toute diffusion non maîtrisée.
- Techniques forensiques sur appareils compromis — à traiter dans un cadre dédié, avec outils spécialisés et procédures validées.
- Adaptations iOS — ClayRat cible exclusivement Android à ce jour, mais une veille croisée reste recommandée pour anticiper toute mutation.
- Comparatifs antivirus/MDM classiques — non pertinents ici, car dépassés par la logique d’édition matérielle souveraine.
- Analyse comportementale des campagnes SMS — abordée dans un billet complémentaire dédié à la tactique de diffusion.
Ces exclusions sont stratégiques : elles permettent de concentrer l’analyse sur la rupture doctrinale et les solutions embarquées, sans diluer le message ni exposer des données sensibles.
Strategic Outlook : vers une souveraineté numérique embarquée et la fin définitive du clair-texte
En substance, ClayRat marque la fin d’une ère pour la sécurité mobile : la protection ne se limite plus à surveiller les intrusions, mais bien à éliminer les zones de clair-texte. De ce fait, l’exposition temporaire du message devient une faille en soi — même sans vulnérabilité logicielle connue.
C’est pourquoi DataShielder NFC HSM Defence incarne cette rupture doctrinale : une architecture matérielle où la confidentialité précède le transport, et où le chiffrement souverain n’est plus une opération logicielle, mais s’impose comme une édition matérielle souveraine.
Par conséquent, le système d’exploitation n’a plus rien à protéger — puisqu’il ne détient plus rien de lisible. Le message, l’identifiant, l’OTP, le contact : en effet, tout est généré, utilisé et purgé dans un environnement cloisonné, totalement hors du champ d’action des spywares Android.
Au final, cette approche inaugure une nouvelle génération de cybersécurité embarquée, où la souveraineté ne dépend plus d’un cloud, d’un OS ou d’un fournisseur tiers, mais bien d’un cycle de vie cryptographique maîtrisé — depuis la frappe jusqu’à l’injection.
Ainsi, elle ouvre la voie à des usages critiques et sensibles : défense, diplomatie, infrastructures, journalistes sous surveillance, et toute entité pour qui l’absence de lisibilité du message est la seule garantie de sécurité numérique.
Sources techniques et officielles
- Analyse primaire : Zimperium – ClayRat Android Spyware Targeting Russia
- Base IoC : ThreatFox / abuse.ch (C2 clayrat.top)
- Veille souveraine : Freemindtronic – Digital Security
- Solutions : Tech Fixes & Security Solutions
Glossaire typologique : termes clés de la cybersécurité, chiffrement matériel et souveraineté numérique
- APK : Android Package — il s’agit du fichier d’installation standard d’une application Android. Par conséquent, le téléchargement d’un APK non officiel est l’une des principales failles d’entrée exploitées par le spyware ClayRat.
- APT : Advanced Persistent Threat — En effet, une menace persistante avancée désigne un acteur souvent étatique ou très organisé, capables de mener des campagnes d’espionnage sophistiquées. C’est le niveau de menace potentiel derrière la conception de ClayRat.
- C2 : Command & Control — Autrement dit, c’est le serveur distant essentiel qu’un malware mobile utilise pour recevoir des ordres ou, ce qui est crucial, exfiltrer les données piratées.
- CVSS : Common Vulnerability Scoring System — Ainsi, c’est un système standardisé international d’évaluation de la gravité des vulnérabilités de sécurité, permettant de classer les risques de manière objective.
- DNS : Domain Name System — De fait, ce système traduit les noms de domaines (comme l’adresse du C2 de ClayRat, `clayrat.top`) en adresses IP. Les DNS rotatifs sont une technique d’évasion très utilisée par les attaquants.
- EMM / MDM : Enterprise Mobility Management / Mobile Device Management. Bien que ces solutions logicielles visent à gérer et sécuriser les appareils mobiles en entreprise, elles sont fréquemment contournées par les attaques comportementales comme ClayRat.
- HSM : Hardware Security Module — Fondamentalement, c’est un composant matériel dédié au chiffrement, au stockage et à la gestion sécurisée des clés cryptographiques. Sa sécurité intrinsèque est supérieure aux solutions logicielles.
- IoC : Indicateurs d’Compromission — Par exemple, ce sont des données techniques (adresses IP, hachages de fichiers d’un APK, noms de domaines) utilisées par les SOC et CERT pour détecter une activité malveillante sur un réseau, notamment les connexions au C2 de ClayRat.
- MMS : Multimedia Messaging Service — Il s’agit du service de messagerie permettant l’envoi de contenus multimédias (images, vidéos, sons). Aujourd’hui, il est partiellement remplacé par le RCS.
- NFC HSM : HSM Hybride (Matériel/Logiciel) — En conclusion, ce système de sécurité souverain est au cœur de DataShielder. Un Composant Matériel de Sécurité (HSM) est piloté par l’application Android *Freemindtronic* (DataShielder) et fonctionne sans contact via la technologie NFC. Par conséquent, ce concept garantit une isolation complète et un chiffrement matériel totalement indépendant par rapport à l’OS Android.
- OTP : One-Time Password — Très souvent utilisé pour l’authentification à deux facteurs, le mot de passe à usage unique est une cible privilégiée de ClayRat, puisqu’il intercepte les SMS entrants.
- RAM : Random Access Memory — Généralement, cette mémoire vive du téléphone est l’endroit où un spyware peut lire le texte en clair du message avant qu’il ne soit chiffré par un logiciel classique. C’est le risque que DataShielder élimine.
- RCS : Rich Communication Services — De plus, ce protocole est le successeur moderne du SMS/MMS, offrant des fonctionnalités enrichies. Il est également concerné par la compromission des données non chiffrées.
- Sandbox : Initialement, une Sandbox est un environnement d’exécution isolé. Dans le contexte Android, c’est l’isolation logicielle des applications. Néanmoins, dans le contexte DataShielder, il s’agit d’un cloisonnement matériel souverain indépendant d’Android, beaucoup plus résilient.
- Sideload : Typiquement, il s’agit de l’Installation d’une application en dehors du Play Store officiel (via un fichier APK). C’est d’ailleurs la méthode de diffusion principale du spyware ClayRat.
- SMS : Short Message Service — Historiquement, ce service de messages texte est l’un des premiers moyens d’interception et de phishing utilisé par les malwares mobiles comme ClayRat.
- TOTP/HOTP : Time-based / HMAC-based One-Time Password — Finalement, ce sont les standards pour la génération d’OTP, basés soit sur le temps, soit sur un algorithme cryptographique. Leur génération matérielle par DataShielder assure une sécurité maximale.