The Controversy of End-to-End Messaging Encryption in the European Union
In a world where online privacy is increasingly threatened, the European Union finds itself at the center of a controversy: Reducing the negative effects of end-to-end encryption of messaging services. This technology, which ensures that only the sender and recipient can read the content of messages, is now being questioned by some EU member states.
Stay informed with our posts dedicated to Cyberculture to track its evolution through our regularly updated topics.
Regulation of Secure Communication in the EU
The European Union is considering measures to regulate secure messaging practices. This technology ensures that only the sender and recipient can read the messages. However, some EU member states are questioning its impact on law enforcement capabilities
Control of Secure Messaging and Fragmentation
If the EU adopts these proposals, it could fragment the digital landscape. Tech companies might need to choose between complying with EU regulations or limiting their encrypted messaging services to users outside the EU. This could negatively affect European users by reducing their access to secure communication tools.
Why the EU Considers End-to-End Messaging Encryption Control
Law enforcement agencies across 32 European states, including the 27 EU member states, are expressing concerns over the deployment of end-to-end encryption by instant messaging apps. Their fear is that this could hinder the detection of illegal activities, as companies are unable to monitor the content of encrypted messages. This concern is one of the key reasons why the EU is considering implementing control over end-to-end message encryption.
Exploring the Details of the Proposed Regulation on Encrypted Messaging
EU Commissioner for Home Affairs, Ylva Johansson, has put forward a proposal that could significantly impact the tech industry. This proposal actively seeks to mandate tech companies to conduct thorough scans of their platforms, extending even to users’ private messages, in an effort to detect any illicit content.
However, this proposal has not been without controversy. It has sown seeds of confusion and concern among cryptographers and privacy advocates alike, primarily due to the potential implications it could have on secure messaging. The balance between ensuring security and preserving privacy remains a complex and ongoing debate in the face of this proposed regulation.
Background of the EU Proposal on Secure Messaging
A significant amount of support can be found among member states for proposals to scan private messages for illegal content, particularly child pornography, as shown in a European Council document. Spain has shown strong support for the ban on end-to-end messaging encryption.
Misunderstanding the Scan Form
Out of the 20 EU countries represented in the document, the majority have declared themselves in favor of some form of scanning encrypted messages. This proposal has caused confusion among cryptographers and privacy advocates due to its potential impact on secure communication protocols.
The Risks of Ending End-to-End Messaging Encryption
Privacy advocates and cryptography experts warn against the inherent risks of weakening encryption. They emphasize that backdoors could be exploited by malicious actors, thus increasing user vulnerability to cyberattacks.
Position of the European Court of Human Rights (ECHR) on Secure Messaging
The European Court of Human Rights (ECHR) has taken a stance on end-to-end messaging encryption. In a ruling dated February 13, the ECHR declared that creating backdoors in end-to-end encrypted messaging services like Telegram and Signal would violate fundamental human rights such as freedom of expression and privacy. This ruling highlights the importance of end-to-end messaging encryption as a tool for protecting privacy and freedom of expression within the context of human rights in Europe.
Messaging Apps’ Stance on End-to-End Encryption Regulation
As the European Union considers implementing control over end-to-end message encryption, several messaging apps have voiced their concerns and positions. Here are the views of major players in the field:
Signal’s Position on End-to-End Messaging Encryption Regulation
Signal, a secure messaging app known for its commitment to privacy, has taken a strong stance against the proposed regulation. Meredith Whittaker, president of Signal, has described the European legislative proposal as “surveillance wine in security bottles.” In the face of this legislative proposal, Signal has even threatened to cease its activities in Europe. Despite this, Whittaker affirmed that the company would stay in Europe to support the right to privacy of European citizens.
WhatsApp’s Concerns on End-to-End Messaging Encryption Regulation
WhatsApp, another major player in the messaging app field, has also expressed concerns about the proposed regulation. Helen Charles, a public affairs representative for WhatsApp, expressed “concerns regarding the implementation” of such a solution at a seminar. She stated, “We believe that any request to analyze content in an encrypted messaging service could harm fundamental rights.” Charles advocates for the use of other techniques, such as user reporting and monitoring internet traffic, to detect suspicious behavior.
Twitter’s Consideration of End-to-End Messaging Encryption
In 2022, Elon Musk discussed the possibility of integrating end-to-end encryption into Twitter’s messaging. He stated, “I should not be able to access anyone’s private messages, even if someone put a gun to my head” and “Twitter’s private messages should be end-to-end encrypted like Signal, so that no one can spy on or hack your messages.”
Mailfence’s Emphasis on End-to-End Encryption
Mailfence, a secure email service, has declared that end-to-end encryption plays a crucial role in setting up secure messaging. They believe it’s extremely important to protect online privacy.
Meta’s Deployment of End-to-End Encryption
Meta (formerly Facebook) recently deployed end-to-end encryption by default for Messenger conversations. This means that only the sender and recipient can access the content of the messages, with Meta being unable to view them.
Other Messaging Apps’ Views on End-to-End Encryption
Other messaging apps have also expressed their views on end-to-end encryption:
Europol’s View
The heads of European police, including Europol, have expressed their need for legal access to private messages. They have emphasized that tech companies should be able to analyze these messages to protect users. Europol’s director, Catherine De Bolle, even stated, “Our homes are becoming more dangerous than our streets as crime spreads online. To ensure the safety of our society and our citizens, we need this digital environment to be secure. Tech companies have a social responsibility to develop a safer environment where law enforcement and justice can do their job. If the police lose the ability to collect evidence, our society will not be able to prevent people from becoming victims of criminal acts”.
Slack’s View
Slack, a business communication platform, has emphasized the importance of end-to-end encryption in preserving the confidentiality of communications and ensuring business security.
Google’s View
Google Messages uses end-to-end encryption to prevent unauthorized interception of messages. Encryption ensures that only legitimate recipients can access the exchanged messages, preventing malicious third parties from intercepting or reading conversations.
Legislative Amendments on End-to-End Messaging Encryption
Several proposed amendments related to end-to-end messaging encryption include:
Encryption, especially end-to-end, is becoming an essential tool for securing the confidentiality of all users’ communications, including those of children. Any restrictions or infringements on end-to-end encryption can potentially be exploited by malicious third parties. No provision of this regulation should be construed as prohibiting, weakening, or compromising end-to-end encryption. Information society service providers should not face any barriers in offering their services using the highest encryption standards, as this encryption is crucial for trust and security in digital services.
The regulation permits service providers to select the technologies they employ to comply with detection orders. It should not be interpreted as either encouraging or discouraging the use of a specific technology, as long as the technologies and accompanying measures adhere to the requirements of this regulation. This includes the use of end-to-end encryption technology, a vital tool for ensuring the security and confidentiality of users’ communications, including those of children.
When implementing the detection order, providers should employ all available safeguards to ensure that the technologies they use cannot be exploited by them, their employees, or third parties for purposes other than compliance with this regulation. This helps to avoid compromising the security and confidentiality of users’ communications while ensuring the effective detection of child sexual abuse material and balancing all fundamental rights involved. In this context, providers should establish effective internal procedures and safeguards to prevent general surveillance. Detection orders should not apply to end-to-end encryption.
Advantages and Disadvantages of End-to-End Messaging Encryption
Advantages:
- Privacy: End-to-end messaging encryption protects users’ privacy by ensuring that only the participants in the conversation can read the messages.
- Security: Even if data is intercepted, it remains unintelligible to unauthorized parties.
Disadvantages:
- Limitation of Detection of Illegal Activities: Law enforcement agencies fear that end-to-end messaging encryption hinders their ability to fight the most heinous crimes, as it prevents companies from regulating illegal activities on their platforms.
Technical Implications of Backdoors in End-to-End Messaging Encryption
The introduction of backdoors in encryption systems presents significant technical implications. A backdoor is a covert mechanism deliberately introduced into a computer system that allows bypassing standard authentication processes. It can reside in the core of a software’s source code, at the firmware level of a device, or be rooted in communication protocols. Backdoors can be exploited by malicious actors, increasing user vulnerability to cyberattacks. Detecting backdoors requires constant technological vigilance and rigorous system analysis.
Implications of New Cryptographic Technologies for Content Moderation
Innovation in cryptography is paving the way for new methods that allow effective content moderation while preserving end-to-end messaging encryption. Recent research is delving into advanced cryptographic technologies that empower platforms to detect and moderate problematic content without compromising communication privacy. These technologies, often rooted in artificial intelligence and natural language processing, have the capability to analyze metadata and behavior patterns to identify illicit content. For instance, the EU’s Digital Services Act (DSA) is aiming to make platform recommendation algorithms transparent and regulate online content moderation more effectively.
This could encompass systems that assess the context and frequency of messages to detect abuses without decrypting the content itself. Moreover, solutions like AI-based content moderation offer substantial advantages for managing online reputation, delivering faster and more consistent responses than manual moderation. These systems can be trained to recognize specific patterns of hate speech or terrorist content, enabling swift intervention while respecting user privacy. The integration of these innovations into messaging platforms could potentially resolve the dilemma between public safety and privacy protection. It provides authorities with the necessary tools to combat crime without infringing on individuals’ fundamental rights to communication privacy.
Potential Impact of This Technology on End-to-End Messaging Encryption of Messaging Services
Adopting these new cryptographic technologies represents a major advance in how we view online security and privacy. They offer considerable potential for improving content moderation while preserving end-to-end messaging encryption, ensuring a safer internet while protecting human rights in the digital age. These innovations could play a key role in implementing European regulations on end-to-end messaging encryption, balancing security needs with respect for privacy.
Messaging Services Affected by European Legislation
Among the popular messaging applications that use end-to-end messaging encryption available in Europe are:
- Signal: A secure messaging application that uses end-to-end encryption. It ensures that only the sender and recipient can access message content, even when data is in transit on the network.
- WhatsApp: Adopted end-to-end encryption in 2016. It ensures that messages are encrypted at the sender’s device and only decrypted at the recipient’s device.
- Messenger: Meta (formerly Facebook) plans to generalize end-to-end encryption on Messenger by 2024.
- Telegram: Uses end-to-end encryption for specific features, such as Secret Chats, ensuring message privacy between the sender and recipient.
- iMessage: Apple’s messaging service uses end-to-end encryption for messages sent between Apple devices.
- Viber: Another messaging app that uses end-to-end encryption to secure messages between users.
- Threema: A secure messaging app that employs end-to-end encryption for all communications, providing high privacy standards.
- Wire: Offers end-to-end encryption for messages, calls, and shared files, focusing on both personal and business communication.
- Wickr: Provides end-to-end encryption for messaging and is known for its strong security features.
- Dust: Emphasizes user privacy with end-to-end encryption and self-destructing messages.
- ChatSecure: An open-source messaging app offering end-to-end encryption over XMPP with OTR encryption.
- Element (formerly Riot): A secure messaging app built on the Matrix protocol, providing end-to-end encryption for all communications.
- Keybase: Combines secure messaging with file sharing and team communication, all protected by end-to-end encryption.
Balancing Security and Privacy
The debate over end-to-end messaging encryption highlights the difficulty of finding a balance between security and privacy in the digital age. On the one hand, law enforcement agencies need effective tools to fight crime and terrorism. On the other hand, citizens have the fundamental right to privacy and the protection of their communications.
Alternatives to Weakened End-to-End Messaging Encryption?
It is crucial to explore alternatives that address law enforcement’s public safety concerns without compromising users’ privacy. Possible solutions include developing better digital investigation techniques, improving international cooperation between law enforcement agencies, and raising public awareness about online dangers.
Navigating Encryption: Security and Regulatory Impediments
Limitations and Challenges of Advanced Cryptographic Technologies
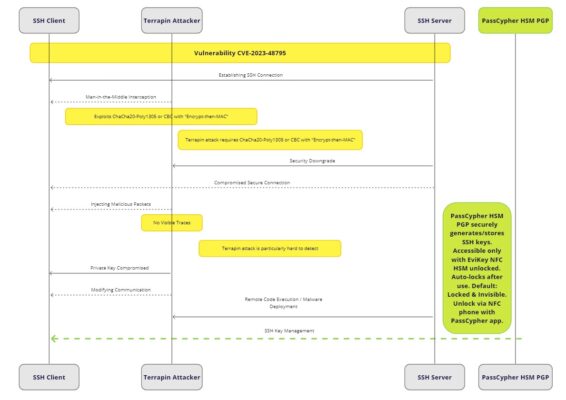
Hardware security modules (HSMs), such as PGP, actively enhance messaging and file encryption security. Similarly, Near Field Communication (NFC) hardware security modules, like DataShielder, significantly bolster protection. Yet, we must confront the significant limitations that regulations introduce; these aim to curtail the protection of both private and corporate data. By encrypting data before transmission, these solutions robustly defend against interception and unauthorized access, whether legal or otherwise. Additionally, this technology stands resilient to AI-driven content moderation filters. In particular, this pertains to messages and files that systems like DataShielder encrypt externally; subsequently, these services are employed for communication.
Ineffectiveness of AI-Based Moderation Filters
Content moderation systems relying on artificial intelligence face a major obstacle: they cannot decrypt and analyze content protected by advanced encryption methods. As a result, despite advances in AI and natural language processing, these filters become inoperative when confronted with messages or files encrypted via HSM PGP or NFC HSM.
Consequences for Security and Privacy
This limitation raises important questions about platforms’ ability to detect and prevent the spread of illicit content while respecting user privacy. It highlights the technical challenge of developing solutions that strike a balance between privacy protection and public safety requirements.
Towards a Balanced Solution
It is imperative to continue researching and developing new cryptographic technologies that enable effective moderation without compromising privacy. The goal is to find innovative methods that respect fundamental rights while providing authorities with the tools needed to fight criminal activities.
HSM PGP and NFC HSM: Alternatives to End-to-End Messaging Encryption
In addition to end-to-end encrypted messaging services, there are alternative solutions like Hardware Security Modules (HSM PGP) and Near Field Communication Hardware Security Modules (NFC HSM) that offer potentially higher levels of security. These devices are designed to protect cryptographic keys and perform sensitive cryptographic operations, ensuring data security throughout its lifecycle.
DataShielder NFC HSM and DataShielder HSM PGP are examples of products that use these technologies to encrypt communications and data anonymously. These tools allow encryption of not only messages but also all types of data, providing a versaced solution that uses Freemindtronic’s EviEngine technology to provide secure and flexible encryption, meeting the diverse needs of professionals and businesses. This solution is designed to operate without a server or database, enhancing security by keeping all data under the user’s control and reducing potential vulnerabilities.
Impact of HSM PGP and NFC HSM on End-to-End Messaging Encryption
HSM PGP and NFC HSM integration adds a vital layer to cybersecurity. They provide a robust solution for information security.
Specifically, DataShielder HSM PGP offers advanced protection. As the EU considers encryption regulation, DataShielder technologies emerge as key alternatives. They ensure confidentiality and security amidst digital complexity. These technologies advocate for encryption as a human rights safeguard. Simultaneously, they address national security issues.
Conclusion
The European legislator faces complexity in harmonizing regulation with Member States. They aim to finalize it by next year. Clearly, preserving end-to-end encryption requires exploring alternatives. This includes better cooperation between law enforcement and advanced investigative techniques.
HSM PGP and NFC HSM transform messaging into secure communication. They do so without servers or identification. Thus, they provide strong protection for organizational communication and data. These measures balance privacy needs with public safety requirements. They offer a comprehensive digital security approach in a complex environment.