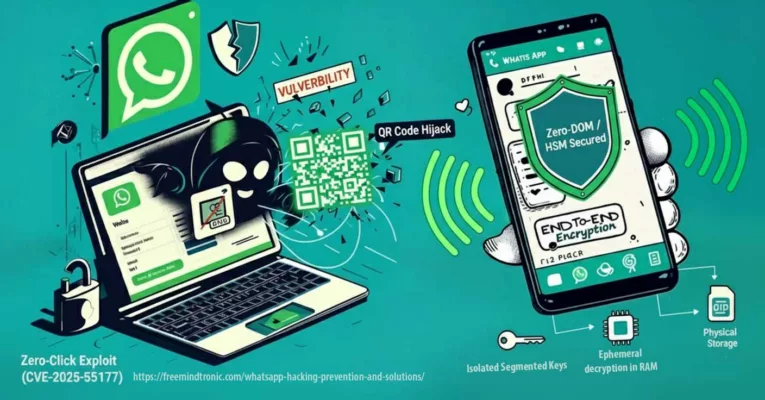
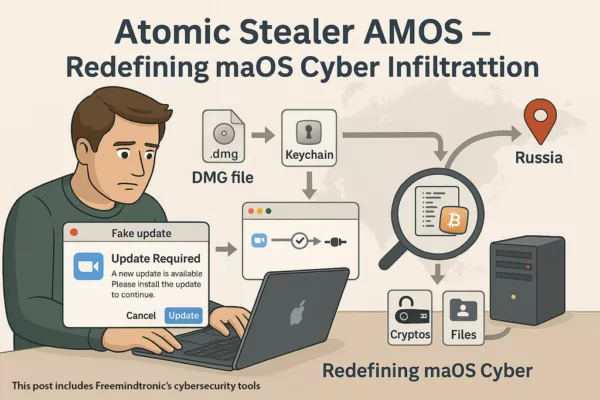
Espionnage invisible WhatsApp n’est plus une hypothèse marginale, mais une réalité technique rendue possible par le détournement de mécanismes légitimes. Sans exploit zero-click ni vulnérabilité apparente, certaines méthodes permettent désormais d’espionner, voire de contrôler un compte WhatsApp sans alerte visible pour l’utilisateur. Cette chronique ne revient pas sur un fait divers médiatique : elle analyse un glissement structurel du modèle de confiance des messageries chiffrées, là où la compromission ne ressemble plus à un piratage.
Résumé express — Espionnage invisible WhatsApp
⮞ Note de lecture
Ce résumé express se lit en ≈ 1 minutes. Il suffit à comprendre l’essentiel du phénomène, ses implications et les leviers de défense.
⚡ La découverte
Des chercheurs en sécurité ont mis en évidence des méthodes permettant d’espionner un compte WhatsApp sans exploiter de vulnérabilité logicielle visible. Ces techniques ne reposent ni sur un piratage classique, ni sur une attaque zero-click, mais sur le détournement discret de mécanismes légitimes du service. Résultat : l’attaquant peut observer, voire piloter un compte, sans provoquer d’alerte perceptible pour l’utilisateur.
✦ Impact immédiat
- Lecture silencieuse des conversations, y compris chiffrées de bout en bout
- Persistance de l’espionnage malgré un changement de mot de passe
- Compromission indétectable pour l’utilisateur non expert
⚠ Message stratégique
Ce phénomène marque une rupture : l’espionnage ne passe plus par une faille technique identifiable, mais par l’abus du modèle de confiance lui-même. Le chiffrement protège le transport des messages, pas l’environnement déjà légitimé. Lorsque l’attaque devient invisible, la notion même de « piratage » perd son sens opérationnel.
⎔ Contre-mesure souveraine
La réduction du risque passe par la limitation des sessions persistantes, l’isolement des secrets d’authentification et des approches Zero-DOM, où l’accès à un service ne repose plus sur un terminal durablement digne de confiance.
Le Résumé enrichi replace ces techniques dans une logique plus large d’abus de confiance numérique et prépare la lecture de la chronique complète.
Paramètres de lecture
Résumé express : ≈ 1 min
Résumé avancé : ≈ 2 min
Chronique complète : ≈ 17 min
Date de publication : 2025-12-21
Dernière mise à jour : 2025-12-21
Niveau de complexité : Avancé — Sécurité des messageries & modèles de confiance
Densité technique : ≈ 65 %
Langues disponibles : FR · EN · ES · CAT
Focal thématique : WhatsApp, sessions persistantes, abus de confiance, espionnage
Type éditorial : Chronique — Freemindtronic Digital Security
Niveau d’enjeu : 8.6 / 10 — profils exposés & contre-espionnage
À propos de l’auteur : Jacques Gascuel, inventeur, fondateur de Freemindtronic Andorre, titulaire de plusieurs brevets en matière de chiffrement souverain, d’authentification sans tiers de confiance et de segmentation de clés.
Les chroniques affichées ci-dessus ↑ appartiennent à la rubrique Sécurité Digitale. Elles prolongent l’analyse des architectures souveraines, des marchés noirs de données et des outils de surveillance. Cette sélection complète la présente chronique consacrée à l’espionnage invisible WhatsApp et à l’abus des mécanismes de confiance.
Résumé enrichi — Quand l’espionnage devient une fonction invisible
Du constat factuel à la dynamique structurelle
Ce résumé enrichi complète le premier niveau de lecture. Il ne revient pas sur la découverte elle-même, mais replace l’espionnage invisible WhatsApp dans une dynamique plus profonde : celle de la transformation des messageries chiffrées en plateformes à sessions persistantes, où l’identité, le terminal et la confiance ne coïncident plus.
Le modèle historique de la messagerie : simplicité et corrélation
Historiquement, la sécurité des messageries reposait sur une équation simple : un appareil, un utilisateur, une session. L’apparition du chiffrement de bout en bout a renforcé cette promesse en protégeant le contenu contre les interceptions réseau. Mais l’évolution vers des usages multi-terminaux, synchronisés et continus a introduit une rupture silencieuse : la légitimité n’est plus liée à la personne, mais à la persistance d’un état autorisé.
L’héritage de confiance comme vecteur d’espionnage
Dans ce contexte, certaines techniques d’espionnage n’ont plus besoin de forcer une entrée. Il leur suffit d’hériter d’une confiance déjà accordée. Une session secondaire, un jeton valide ou un état synchronisé deviennent alors des points d’observation parfaitement légitimes du point de vue du service. Le chiffrement fonctionne, les mécanismes de sécurité aussi — mais au bénéfice de l’attaquant.
De la vulnérabilité technique à la bascule stratégique
C’est là que se situe la véritable bascule stratégique. Contrairement aux vulnérabilités zero-click ou aux malwares identifiables, ces méthodes ne génèrent ni crash, ni alerte, ni comportement anormal évident. Elles s’inscrivent dans le fonctionnement nominal du système. Pour l’utilisateur, il n’y a rien à corriger, rien à soupçonner, rien à révoquer clairement.
Quand le risque quitte le code pour l’architecture de confiance
Cette invisibilité pose un problème systémique. Elle remet en cause l’idée selon laquelle la sécurité d’un service peut être évaluée uniquement à l’aune de ses failles corrigées. Lorsque l’attaque exploite la logique même de confiance, la surface de risque ne se situe plus dans le code, mais dans l’architecture décisionnelle : qui est autorisé, combien de temps, depuis quel environnement, et avec quelle possibilité de révocation réelle.
La chronique complète explorera ces mécanismes en détail, montrera pourquoi ils échappent aux réflexes de sécurité classiques et analysera les contre-mesures réellement efficaces face à un espionnage qui ne ressemble plus à une intrusion.
Ce qu’il faut retenir
- Le chiffrement protège les messages, pas l’état de confiance déjà compromis.
- Une session légitime n’est pas synonyme d’utilisateur légitime.
- L’espionnage invisible prospère dans les architectures conçues pour la continuité.
- La détection devient secondaire lorsque l’attaque n’enfreint aucune règle.
⮞ Préambule — Espionnage invisible WhatsApp : quand la messagerie devient une surface d’observation
Les messageries chiffrées occupent désormais une place centrale dans les communications sensibles : échanges personnels, sources journalistiques, coordination professionnelle, décisions stratégiques. Leur promesse repose sur un triptyque largement admis : confidentialité, intégrité et authenticité. Pourtant, l’espionnage invisible WhatsApp révèle une fracture silencieuse entre cette promesse et la réalité opérationnelle.
Cette chronique ne s’intéresse ni à une faille logicielle spectaculaire, ni à un exploit zero-click récemment corrigé. Elle explore un phénomène plus discret : la capacité d’un attaquant à s’inscrire durablement dans un environnement légitime, sans enfreindre explicitement les règles du service. Autrement dit, lorsque l’accès n’est pas forcé, mais hérité.
Dans ce contexte, la notion même de piratage devient insuffisante. Il ne s’agit plus d’une intrusion visible, mais d’une continuité abusive de confiance. Comprendre ce glissement est essentiel pour les journalistes, les décideurs et tous les profils exposés à des enjeux de confidentialité élevés.
Espionnage invisible WhatsApp : ce que WhatsApp autorise explicitement
Comme de nombreuses plateformes modernes, WhatsApp repose sur une logique de sessions persistantes et de synchronisation multi-terminaux. Ces mécanismes sont officiellement documentés et présentés comme des améliorations fonctionnelles : accès depuis plusieurs appareils, continuité de lecture, sauvegarde de l’historique et récupération simplifiée.
D’un point de vue strictement technique, ces fonctionnalités ne constituent pas une vulnérabilité. Elles sont conçues, implémentées et maintenues volontairement. Lorsqu’un terminal secondaire est autorisé, il devient un participant légitime à l’écosystème du compte. Les messages sont chiffrés de bout en bout, transmis correctement et affichés conformément au fonctionnement attendu.
Le problème n’apparaît que lorsque cette légitimité initiale est détournée. Une session valide n’expire pas nécessairement lors d’un changement de mot de passe. Un appareil synchronisé n’est pas toujours visible ou compris par l’utilisateur. Ainsi, un état autorisé peut survivre bien au-delà du moment où la confiance aurait dû être réévaluée.
✓ D’un point de vue du service, tout fonctionne normalement.
⚠ Du point de vue de la sécurité, l’accès n’est plus corrélé à l’intention réelle de l’utilisateur.
Session ≠ identité : la bascule du modèle de confiance
L’erreur la plus répandue consiste à confondre authentification et légitimité. Dans une messagerie moderne, l’authentification n’est plus un instant (un code, un QR, une validation), mais un état persistant : une session active, un appareil lié, un jeton accepté, un contexte déjà approuvé.
Dans ce contexte, c’est précisément ce que les attaquants exploitent. Ils ne cherchent pas toujours à “casser” WhatsApp. Ils cherchent à hériter d’un état déjà reconnu comme valide, puis à s’y maintenir. Dans cette logique, multi-device ≠ multi-trust : la multiplication des terminaux augmente mécaniquement le nombre d’états d’accès, donc le nombre de points d’abus possibles.
Le basculement est stratégique : une session technique peut rester “propre” tout en étant “illégitime” du point de vue humain. Ce n’est pas un bug spectaculaire : c’est une conséquence prévisible d’une architecture conçue pour la continuité.
WhatsApp n’est pas “cassé”. Son modèle de confiance est exploité : session légitime ≠ utilisateur légitime.
Pour cadrer ce raisonnement, la lecture Zero Trust est utile : la confiance n’est jamais acquise “une fois pour toutes”. Elle doit être réévaluée selon le contexte, l’exposition et la sensibilité. C’est exactement ce que rappelle le NIST avec l’architecture Zero Trust (SP 800-207) :référence officielle.
Espionnage invisible sur WhatsApp : de l’authentification instantanée à l’état persistant
Historiquement, l’authentification relevait d’un acte ponctuel : saisir un mot de passe, valider un code, prouver une identité à un instant donné. Une fois l’action terminée, la confiance devait théoriquement être redémontrée. Ce modèle correspondait à des usages simples, limités dans le temps et dans l’espace.
Cependant, les messageries modernes ont progressivement déplacé ce paradigme. L’authentification n’est plus un moment, mais un état. Une fois validé, cet état est conservé, synchronisé et réutilisé sans sollicitation répétée de l’utilisateur. La session devient ainsi un objet durable, indépendant du contexte initial qui l’a rendue légitime.
Dès lors, la sécurité ne repose plus uniquement sur la robustesse du secret initial, mais sur la gestion de cet état persistant : sa durée de vie, sa portabilité, sa révocation effective. C’est précisément dans cette transition que s’ouvre un espace d’exploitation silencieuse. Une authentification réussie une fois peut produire des effets bien au-delà de ce que l’utilisateur perçoit ou maîtrise.
Autrement dit, la compromission ne passe plus nécessairement par la rupture de l’authentification, mais par la captation ou l’héritage d’un état déjà reconnu comme valide.
Surveillance invisible WhatsApp et multi-appareil : continuité fonctionnelle, continuité abusive
L’introduction du multi-appareil répond à une exigence de fluidité : permettre à un utilisateur de retrouver ses échanges sur plusieurs terminaux, sans friction ni réauthentification constante. Sur le plan fonctionnel, cette évolution est cohérente et largement plébiscitée.
Néanmoins, cette continuité repose sur une hypothèse implicite : chaque appareil lié resterait durablement sous le contrôle exclusif de l’utilisateur. Or, cette hypothèse est fragile. Un terminal ajouté à un moment donné peut subsister longtemps après que le contexte de confiance a changé.
Ainsi, le multi-appareil introduit une continuité abusive potentielle. Une fois un terminal synchronisé, il bénéficie d’un accès équivalent aux autres, sans que l’utilisateur ne dispose toujours d’une visibilité claire ou d’un mécanisme de contrôle proportionné. La multiplication des points d’accès ne s’accompagne pas d’une multiplication des capacités de surveillance.
En pratique, multi-appareil ne signifie pas multi-contrôle. Il devient alors possible de maintenir un accès discret, durable et techniquement légitime, sans déclencher d’anomalie perceptible. Ce n’est pas une dérive accidentelle : c’est une conséquence structurelle d’un modèle orienté continuité.
Espionnage invisible WhatsApp : l’invisibilité comme rupture stratégique
Les attaques “classiques” laissent des traces. Un SIM-swap déclenche souvent des ruptures de service. Le phishing laisse des indices (liens, écrans suspects). Même un malware finit par provoquer des anomalies. À l’inverse, l’espionnage invisible repose sur une idée simple : ne pas ressembler à une attaque.
Dès lors, on passe ainsi de l’attaque détectable à la présence silencieuse. La différence est déterminante : si l’utilisateur ne voit rien, il n’agit pas. Et si l’organisation ne détecte rien, elle ne révoque rien.
- Usurpation de ligne : rupture visible, signaux forts
- Hameçonnage : indices comportementaux, traçabilité
- Session persistante : opacité, normalité apparente
C’est un changement de paradigme stratégique, pas une vulnérabilité classique. Ce glissement n’est pas une évolution marginale. Le modèle “mise à jour = sécurité” devient insuffisant quand la menace n’exploite pas une faille, mais un état de confiance autorisé.
Espionnage WhatsApp sans alerte : comparaison des modèles d’attaque visibles et invisibles
Pour mesurer la portée du changement en cours, il est utile de comparer les modèles d’attaque traditionnels avec ceux fondés sur la persistance silencieuse. Les premiers reposent sur une rupture identifiable, les seconds sur une normalité apparente.
Les attaques visibles — usurpation de ligne, hameçonnage, logiciel espion — produisent des signaux. Elles perturbent l’usage, génèrent des incohérences, ou laissent des traces exploitables. Ces signaux constituent autant de déclencheurs pour la vigilance de l’utilisateur ou des équipes de sécurité.
À l’inverse, l’espionnage fondé sur une session persistante ne provoque aucune discontinuité. Les messages arrivent, les conversations se déroulent normalement, le service fonctionne conformément à sa documentation. L’attaque ne se distingue pas du fonctionnement attendu.
Dès lors, la différence n’est pas seulement technique, mais stratégique. Une attaque visible appelle une réaction. Une présence invisible s’installe dans la durée. En supprimant le signal d’alerte, elle neutralise les réflexes de défense et transforme la compromission en état stable.
Ce basculement marque l’abandon du modèle « intrusion → détection → correction » au profit d’un modèle bien plus difficile à contrer : autorisation → persistance → invisibilité.
L’invisibilité est une rupture stratégique : elle supprime le signal d’alerte qui déclenche habituellement la défense.
Chiffrement de bout en bout et espionnage invisible sur WhatsApp
Le chiffrement de bout en bout est souvent présenté comme une garantie absolue contre l’espionnage. En réalité, il protège le transport des messages entre les terminaux, pas l’environnement dans lequel ces messages sont déchiffrés. Une fois arrivés sur un appareil autorisé, les contenus deviennent lisibles par toute entité disposant d’un accès légitime à cet environnement.
C’est précisément là que s’opère le contournement. L’attaquant n’intercepte pas le flux chiffré : il s’insère dans la chaîne de confiance existante. Session persistante, terminal synchronisé ou état autorisé suffisent à rendre la lecture possible, sans casser le chiffrement ni violer le protocole.
Ainsi, le chiffrement fonctionne correctement — mais il ne répond pas à la menace dominante ici. Lorsque l’espionnage exploite la légitimité côté client, la protection du canal devient secondaire. Le risque ne se situe plus dans le transport, mais dans la persistance de la confiance accordée au terminal.
Détournement du multi-appareil : “multi-device” n’implique pas “multi-contrôle”
Le multi-appareil est conçu pour le confort : travailler sur ordinateur, poursuivre sur mobile, synchroniser sans friction. Or, cette continuité crée une surface d’abus : une fois un appareil lié, il devient un point d’accès durable. Si l’attaquant parvient à lier un terminal, il obtient une fenêtre d’observation qui n’a plus besoin d’être renouvelée en permanence.
C’est pourquoi il faut analyser les attaques d’espionnage invisible non comme des “piratages”, mais comme des abus de mécanismes légitimes : documentation officielle de sécurité WhatsApp.
Le détournement n’a rien d’exceptionnel. Il repose sur l’exploitation normale d’un mécanisme prévu, documenté et fonctionnel. C’est précisément ce qui le rend difficile à identifier et à contester.
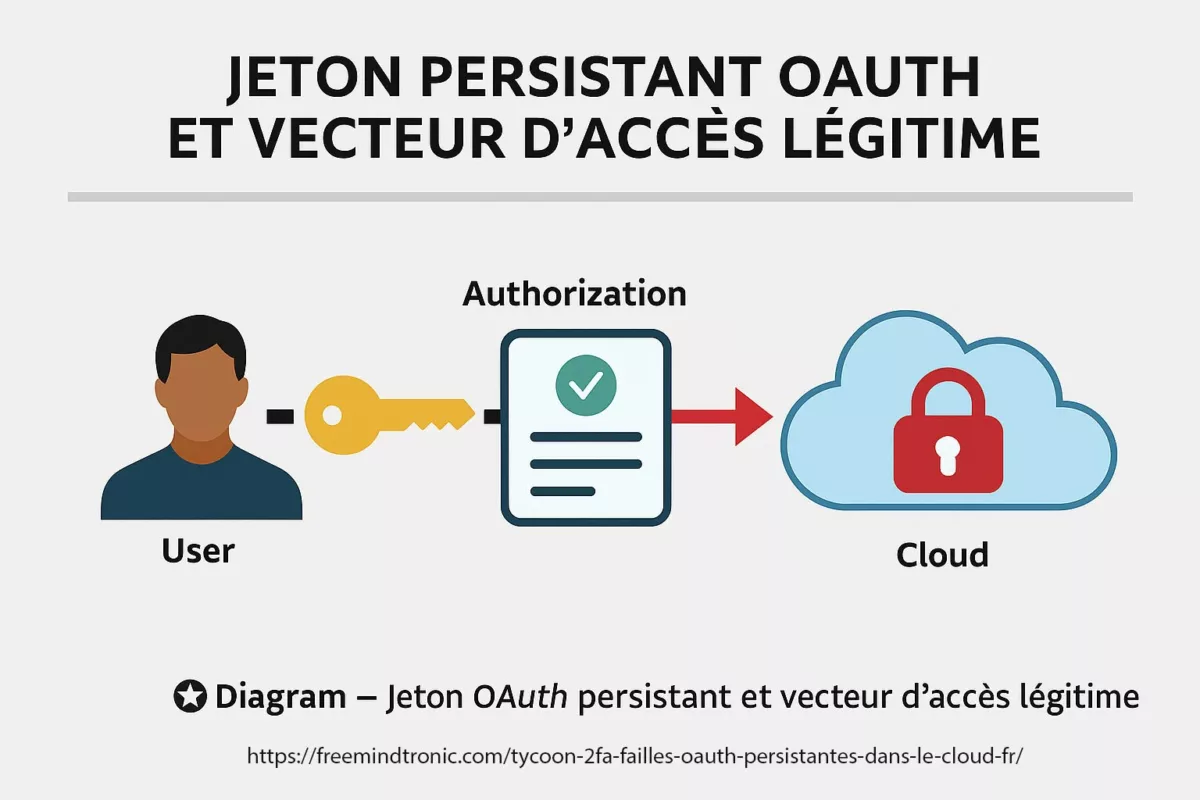
Extraction de jetons et états persistants : quand la clé n’est plus un mot de passe
Dans de nombreuses architectures modernes, l’attaquant n’a pas besoin du mot de passe. Il lui suffit d’un jeton ou d’un état d’autorisation déjà validé. C’est l’une des raisons pour lesquelles changer un mot de passe peut ne pas suffire : l’identité n’est pas uniquement portée par un secret saisi, mais par des états conservés.
⚠ Cette logique renforce l’illusion “E2EE = inviolable”. Le chiffrement protège le transport. Il ne protège pas un endpoint déjà autorisé, ni la lecture “légitime” côté client.
Par conséquent, cette réalité alimente un faux sentiment de sécurité autour du chiffrement de bout en bout. Celui-ci protège le transport des messages, pas leur lecture sur un terminal déjà autorisé. La confidentialité réseau ne neutralise pas une compromission locale légitime.
Le chiffrement protège le transport, pas l’endpoint compromis : E2EE n’empêche pas le mirroring, le clonage logique, ni la lecture côté client.
Persistance & révocation : la vraie bataille
Quand une attaque est invisible, la priorité n’est plus “détecter la faille”, mais réduire la persistance. Autrement dit : limiter la durée de vie des sessions, durcir la révocation, et rendre la confiance réversible.
Cela suppose une discipline opérationnelle : vérifier les appareils liés, contrôler les accès, et traiter tout terminal comme un environnement potentiellement hostile. Cette logique rejoint les principes d’hygiène et de compromission terminale détaillés par l’ANSSI : guide officiel.
✓ Objectif : si un état d’accès a été hérité, il doit être récupérable et révocable rapidement.
≠ Sinon, la sécurité devient une hypothèse, pas un contrôle.
Dans un modèle fondé sur la persistance, la sécurité dépend moins de la détection que de la capacité à rendre la confiance réversible. Cela suppose des mécanismes clairs de contrôle des appareils liés, de limitation temporelle et de remise à zéro effective des états hérités.
Sans cette capacité de révocation réelle, la sécurité devient une hypothèse théorique. La compromission, même ancienne ou indirecte, continue de produire ses effets dans le silence.
Key Insights — Synthèse opérationnelle
- Ce n’est pas un bug spectaculaire : c’est un modèle de confiance exploité.
- Multi-device ≠ multi-trust : plus d’états autorisés, plus d’abus possibles.
- Le chiffrement E2EE protège le transport, pas un endpoint déjà autorisé.
- L’invisibilité transforme l’attaque en présence silencieuse, donc durable.
- La bataille se joue sur la révocation, pas uniquement sur les patchs.
Signaux faibles — vers une industrialisation de l’invisible
- ↻ Glissement des attaques “choc” vers des compromis durables et faiblement détectables.
- ↔ Convergence entre pratiques de spyware et abus de mécanismes “légitimes”.
- ✓ Montée de la valeur des états autorisés : sessions, terminaux liés, tokens, contextes.
- ⚠ Externalisation de la menace : sous-traitance, mercenariat, outils semi-industriels.
Ces signaux faibles se connectent à la question plus large de la souveraineté individuelle et du contrôle local des secrets : analyse Freemindtronic.
FAQ — WhatsApp, sessions persistantes et espionnage invisible
Non. Les techniques décrites exploitent des mécanismes légitimes — sessions persistantes, synchronisation multi-appareils et états autorisés — sans enfreindre explicitement les règles du service. C’est précisément ce qui rend ces pratiques difficiles à détecter et à contester.
Pas nécessairement. Si des sessions ou des appareils liés demeurent actifs, ils peuvent conserver un accès valide indépendamment du secret initial. Le mot de passe protège l’entrée, pas toujours la persistance.
Le chiffrement protège le transport des messages. Il ne protège pas leur lecture sur un terminal déjà autorisé. Une fois déchiffrés côté client, les contenus deviennent accessibles à toute entité disposant d’un accès légitime à l’environnement d’exécution.
Parce que l’accès espionné s’inscrit dans le fonctionnement normal du service. Il n’y a ni rupture, ni anomalie visible, ni alerte explicite. L’espionnage se confond avec l’usage attendu.
Une attaque visible déclenche une réaction : alerte, suspicion, correction. Une compromission invisible supprime ce déclencheur. Elle transforme l’espionnage en présence durable tant que la confiance n’est pas explicitement révoquée.
Ce que nous n’avons pas couvert
Cette chronique s’est concentrée sur les abus de confiance, la persistance et l’invisibilité. Les aspects juridiques (preuve, responsabilité), la criminalistique mobile avancée, et les contre-mesures plateforme-côté fournisseur seront traités séparément.
Perspective stratégique — sortir du réflexe “appli sûre”
Le point d’inflexion est simple : lorsque l’accès devient un état persistant, la sécurité devient un problème de gouvernance de session. Ce qui était autrefois un piratage visible devient une présence silencieuse. Dans ce cadre, l’exigence n’est plus “avoir la meilleure appli”, mais disposer d’une architecture où la confiance est révocable, les secrets hors terminal, et l’exposition réduite par conception.
→ C’est ici que les approches Zero-DOM et les modèles souverains prennent leur sens : non pour “sécuriser une appli”, mais pour réduire structurellement la surface d’espionnage, même quand le terminal est douteux.
Espionnage invisible WhatsApp : reprendre le contrôle hors du terminal
Les techniques d’espionnage invisible WhatsApp montrent une limite structurelle des messageries grand public : tant que les clés, les sessions ou les états d’authentification résident durablement sur un terminal connecté, ils peuvent être hérités, clonés ou observés sans déclencher d’alerte.
Dans ce contexte, les contre-mesures réellement efficaces ne relèvent pas d’un simple durcissement logiciel. Elles impliquent un changement d’architecture, où la confiance n’est plus déléguée au système d’exploitation ni à la persistance des sessions.
Pourquoi les durcissements logiciels sont insuffisants
Face à l’espionnage invisible WhatsApp, le premier réflexe consiste souvent à renforcer la couche logicielle : mises à jour fréquentes, durcissement du système d’exploitation, permissions restrictives, antivirus ou solutions de détection comportementale. Ces mesures sont utiles, mais elles ne traitent pas le cœur du problème.
En effet, les techniques analysées dans cette chronique ne reposent pas sur l’exploitation d’une vulnérabilité logicielle active. Elles s’appuient sur des états légitimes : sessions persistantes, appareils synchronisés, autorisations déjà accordées. Dans ce cadre, le logiciel ne se comporte pas de manière anormale. Il applique exactement les règles qui lui ont été définies.
Autrement dit, renforcer un environnement qui fonctionne “comme prévu” ne permet pas de neutraliser un abus de confiance. Le durcissement logiciel agit efficacement contre des attaques visibles — élévation de privilèges, injection de code, comportements malveillants identifiables — mais il reste largement impuissant face à une présence silencieuse qui ne viole aucune règle.
De plus, le terminal lui-même constitue un point de faiblesse structurel. Même parfaitement à jour, un smartphone demeure un environnement complexe, connecté, exposé à des interactions multiples et difficilement auditable en continu. Dès lors que des secrets, des clés ou des états d’authentification y résident durablement, ils restent susceptibles d’être observés, hérités ou reproduits.
C’est pourquoi la réponse ne peut pas se limiter à « mieux sécuriser le logiciel ». Tant que la confiance repose sur un terminal généraliste et sur des sessions persistantes exportables, le risque demeure. La question centrale devient alors architecturale : où résident les secrets, et qui peut en hériter dans le temps.
Cette limite explique le déplacement vers des approches où la sécurité ne dépend plus exclusivement de l’intégrité du système d’exploitation, mais de la séparation stricte entre terminal et confiance. Sortir les secrets du logiciel n’est pas un renforcement marginal ; c’est un changement de paradigme.
DataShielder NFC HSM — chiffrement hors terminal
Le DataShielder NFC HSM repose sur un principe fondamental : les clés cryptographiques ne résident jamais dans le terminal. Elles sont générées, stockées et utilisées dans un module matériel hors ligne, sans exposition mémoire, sans session exportable et sans synchronisation silencieuse.
✓ Même si le smartphone est compromis, aucune clé exploitable n’est accessible.
≠ L’attaquant peut observer l’interface, mais pas hériter de la confiance cryptographique.
DataShielder HSM PGP — souveraineté des échanges sensibles
Le DataShielder HSM PGP étend cette logique aux échanges chiffrés de bout en bout, indépendamment des plateformes de messagerie. Les opérations cryptographiques sont réalisées hors du terminal, selon une doctrine Zero-DOM : aucune clé, aucun secret, aucun état de session persistant n’est présent côté logiciel.
Cette approche neutralise les attaques par session héritée, par jeton valide ou par synchronisation multi-terminaux. Elle transforme la compromission du terminal en incident limité, non exploitable pour un espionnage durable.
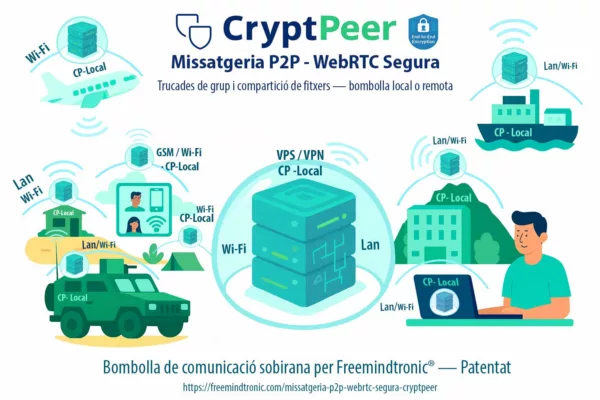
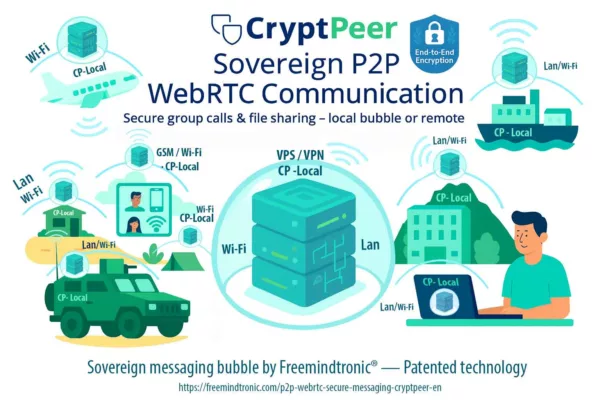
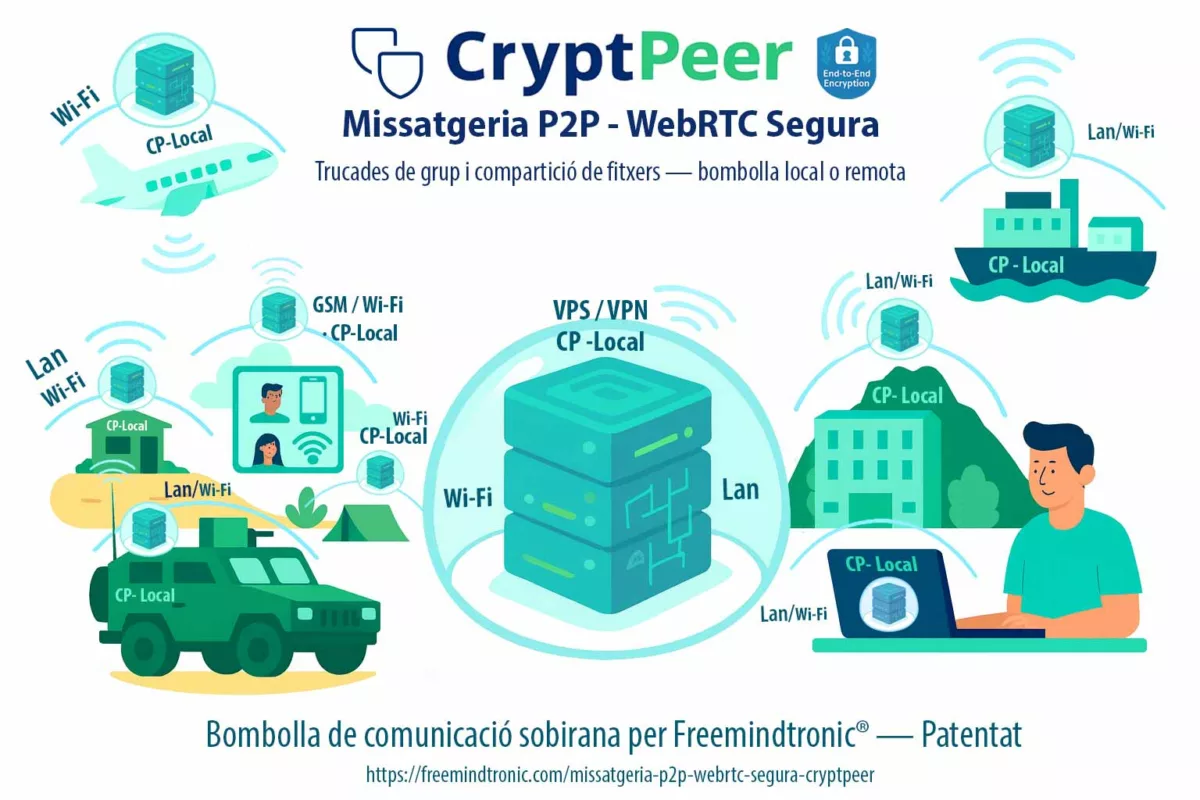
Changer de paradigme : CryptPeer (disponible fin janvier 2026)
Au-delà des contre-mesures défensives, une autre option consiste à changer de modèle de messagerie. CrytPeer, solution de messagerie souveraine développée par Freemindtronic, adopte nativement une architecture incompatible avec les abus de sessions persistantes.
Disponible à partir de fin janvier 2026, CrytPeer repose sur :
- l’absence de sessions persistantes héritables,
- un contrôle strict des états d’authentification,
- une séparation radicale entre identité, terminal et secret cryptographique.
→ Là où les messageries grand public cherchent la continuité et la fluidité, CrytPeer privilégie la réversibilité, la maîtrise locale et la réduction systémique de la surface d’espionnage.
⚠ Ce changement n’est pas cosmétique. Il correspond à un choix stratégique : accepter moins de confort apparent pour éliminer une classe entière d’attaques invisibles.
Cas d’usage souverain — quand la compromission devient inopérante
Pour mesurer concrètement l’impact des techniques d’espionnage invisible WhatsApp, il est utile de les confronter à un environnement conçu selon une logique inverse : absence de sessions persistantes exploitables, secrets hors terminal et confiance strictement réversible.
Prenons le cas d’un journaliste d’investigation, d’un décideur public ou d’un cadre exposé, utilisant un smartphone potentiellement compromis — sans en avoir conscience. Dans un modèle classique de messagerie, cette situation suffit à rendre possibles la lecture silencieuse des échanges, la persistance de l’accès et l’espionnage prolongé.
Dans une architecture Zero-DOM, fondée sur des dispositifs matériels indépendants du terminal, ce scénario change radicalement. Les clés cryptographiques ne résident ni dans le système d’exploitation, ni dans la mémoire applicative, ni dans un état de session exportable. Elles sont générées, stockées et utilisées hors terminal, sans synchronisation silencieuse possible.
Ainsi, même si le smartphone est observé, cloné logiquement ou instrumenté, l’attaquant ne peut ni hériter de la confiance cryptographique, ni maintenir un accès durable aux contenus protégés. La compromission du terminal devient un incident local, non un point d’entrée systémique.
Ce type d’approche ne cherche pas à « sécuriser une application », mais à rendre structurellement inopérantes les attaques fondées sur la persistance, l’héritage d’état et l’invisibilité. Il s’agit d’un choix doctrinal : accepter une rupture avec la continuité confortable pour restaurer un contrôle effectif.
Cette logique s’inscrit plus largement dans les réflexions sur la souveraineté individuelle numérique , où la protection des communications ne dépend plus de la confiance accordée à un environnement d’exécution, mais de la maîtrise locale et matérielle des secrets.