Executive Summary
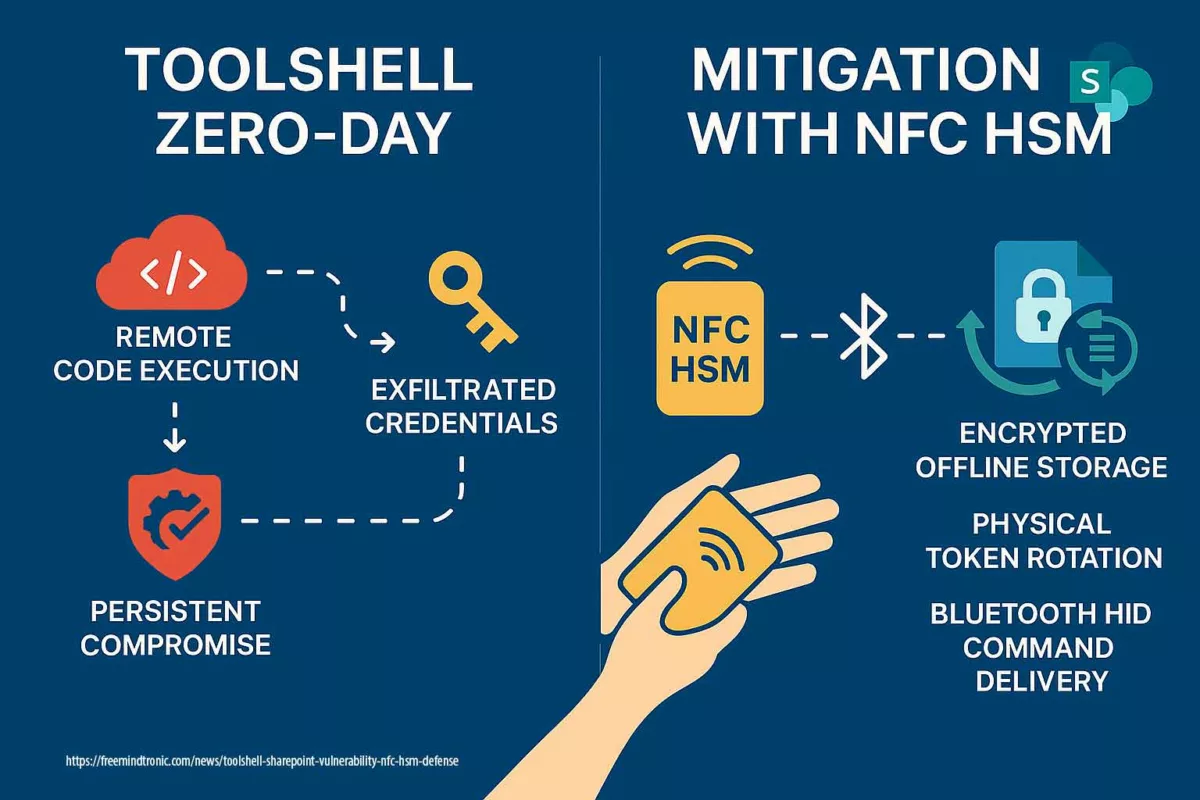
This Chronicle dissects the ToolShell SharePoint vulnerability, which exemplifies the structural risks inherent in server-side token validation mechanisms and underscores the value of sovereign credential isolation. It illustrates how credential exfiltration and token forgery erode server-centric trust models. By contrast, Freemindtronic’s sovereign NFC HSM architectures restore control through off-host credential storage, deterministic command delivery, and token-level cryptographic separation.
In Digital Security ↑ Correlate this Chronicle with other sovereign threat analyses in the same editorial rubric.
Strategic Navigation Index
- Executive Summary
- ToolShell: Context & Exploit Strategy
- NFC HSM Sovereign Countermeasures
- Regulatory Response & Threat Landscape
- Defensive Deployment Scenario
- Deconstructing the Exploitation Chain
- Beyond Patching: Lessons in Architectural Sovereignty
- Breakout Prevention Matrix
- Weak Signal Watch
- Server Trust Decay Test
- CVE ≠ Loss of Control
Key insights include:
- Post-exploitation persists via cryptographic key theft
- NFC HSM disrupts trust hijacking through isolated storage
- Hardware-injected workflows remove runtime risk
- ToolShell renders MFA ineffective by reusing stolen keys
About the Author – Jacques Gascuel, inventor of multiple internationally patented encryption technologies and founder of Freemindtronic Andorra, is a pioneer in sovereign cybersecurity. In this Digital Security Chronicle, he dissects the ToolShell SharePoint zero-day vulnerability and provides a pragmatic defense framework leveraging NFC HSMs and EviKeyboard BLE. His analysis merges hands-on mitigation with field-tested resilience through Bluetooth-injected, offline certificate provisioning.
ToolShell: Context & Exploit Strategy
Severity Level: 🔴 Critical (CVSS 9.8) – remote unauthenticated RCE exploit. CVE Reference: CVE-2025-53770 | CVE-2025-53771 Vendor Bulletin: Microsoft Security Update Guide – CVE-2025-53770 First documented by Eye Security, ToolShell is a fileless backdoor exploiting CVE‑2025‑53770 to gain persistent access to on-prem SharePoint servers. It leverages in-memory payloads and .NET reflection to access MachineKeys like ValidationKey and DecryptionKey, enabling valid payload signature forgery. Security firms observed active exploitation tactics: Symantec flagged PowerShell and Certutil use to deploy binaries such as “client.exe”, while Orca Security reported 13% exposure among hybrid SharePoint cloud deployments. Attribution links these campaigns to APT actors like Linen Typhoon and Storm‑2603. Recorded Future describes ToolShell as an in-memory loader bypassing EDR detection. Microsoft and CISA have acknowledged the active exploitation and advise isolation and immediate patching (see CISA Alert – July 20, 2025).
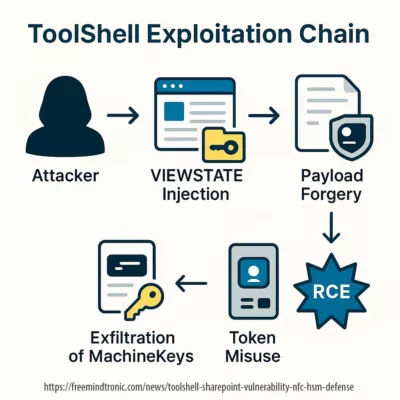
Partial attribution confirmed by Microsoft and Reuters:
APT41 (a.k.a. Linen Typhoon / Salt Typhoon) — a China-based, state-affiliated cluster previously linked to CVE-2023-23397 exploits and credential theft
Storm-2603 — an emerging threat group observed injecting payloads derived from the Warlock ransomware family
We observed both threat groups using MachineKey forgery to sustain long-term access across SharePoint environments and hybrid cloud systems.
– Chronicle: APT41 – Cyberespionage and Cybercrime – https://freemindtronic.com/apt41-cyberespionage-and-cybercrime/
– Chronicle: Salt Typhoon – Cyber Threats to Government Security – https://freemindtronic.com/salt-typhoon-cyber-threats-government-security/
Explore how sovereign credential exfiltration and state-linked persistence mechanisms deployed by Salt Typhoon and APT41 intersect with ToolShell’s exploitation chain, reinforcing their long-term strategic objectives.
⮞ Comparative Insights: Salt Typhoon (APT41) vs ToolShell Attack Chain
Both Salt Typhoon and ToolShell clusters reveal long-term persistence tactics, yet only the ToolShell SharePoint vulnerability leverages MachineKey reuse across hybrid AD join environments.
| Tactic / Vector | Salt Typhoon (APT41) | ToolShell |
|---|---|---|
| Credential Theft | Harvested plaintext credentials via CVE-2023-23397 in Outlook | Extracted MachineKeys (ValidationKey/DecryptionKey) from memory |
| Persistence Method | Registry injection, MSI payloads, webshells | VIEWSTATE forgery, fileless PowerShell loaders |
| Target Scope | Gov networks, diplomatic mail servers, supply chain vendors | Hybrid SharePoint deployments (on-prem/cloud join) |
| Payload Technique | Signed DLL side-loading, image steganography | Certutil.exe, client.exe binaries, memory-resident loaders |
| Command & Control | Steganographic beaconing + encrypted tunnels | Local payload injection (offline, no active beaconing) |
This comparison highlights the evolution of state-affiliated TTPs toward stealthier, credential-centric persistence across heterogeneous infrastructures. Both campaigns demonstrate how hardware-based credential isolation can neutralize these vectors.
NFC HSM Sovereign Countermeasures
Freemindtronic’s NFC HSM technology directly addresses ToolShell’s attack surfaces. It:
- Secures credentials outside the OS using AES-256 CBC encrypted storage
- Delivers commands via Bluetooth HID over a paired NFC phone, avoiding RCE-exposed vectors
- Supports token injection workflows without scripts residing on the compromised server
- Physically rotates up to 100 ACME labels per token, ensuring breach containment
Regulatory Response & Threat Landscape
On July 20, 2025, CISA added CVE‑2025‑53770/53771 to its Known Exploited Vulnerabilities (KEV) catalog. Recommended actions include:
- Rotate MachineKeys immediately
- Enable AMSI for command inspection
- Deploy WAF rules against abnormal POST requests
- Isolate or disconnect vulnerable SharePoint servers
Defensive Deployment Scenario
During ToolShell exploitation, a SharePoint deployment integrated with DataShielder NFC HSM enables administrators to:
-
- Immediately revoke affected credentials with no exposure to central PKI
- Inject new signed certificates using offline physical commands
- Isolate and contain server breach impacts without resetting whole environments
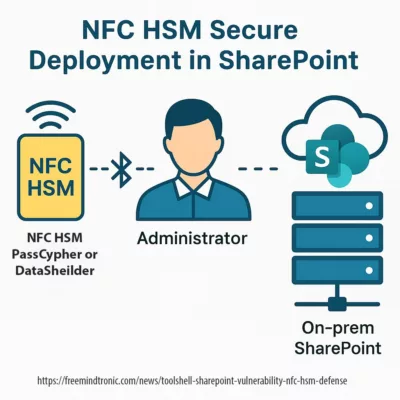
Sovereign deployment architecture — Secure SharePoint trust management using Freemindtronic NFC HSM with Bluetooth HID transmission and air-gapped administrator control.
Our analysis reveals significant global exposure despite Microsoft’s emergency patch, driven by legacy on-prem deployments. The table presents verified threat metrics and authoritative sources that quantify the vulnerability landscape.
| Metric | Value | Source |
|---|---|---|
| Confirmed victims | ~400 organizations | Reuters |
| Potentially exposed servers | 8,000–9,000 | Wiz.io |
| Initial detections | 75 compromised servers | Times of India |
| Cloud-like hybrid vulnerable rate | 9% self-managed deployments | Orca Security |
Real-World NFC HSM Mitigation — ToolShell Reproduction & Protection
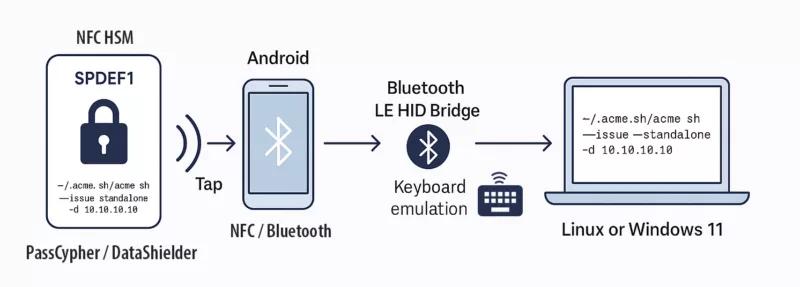
This section demonstrates how to configure a sovereign NFC HSM (AES-256 CDC Encryption) to neutralize ToolShell-like threats via a deterministic, DNS-less and OS-isolated certificate issuance command.
- Label example: (6 chars max)
SPDEF1 - Payload: (55 chars max)
~/.acme.sh/acme.sh --issue --standalone -d 10.10.10.10 - Tested Tools: PassCypher NFC HSM, DataShielder NFC HSM
- Transmission Chain: Android NFC ⬢ AES-128 HID Bluetooth BLE (low energy) ⬢ Windows 11 (EviKeyboard-InputStick) or Linux (hidraw)
Use Case: The injected ACME command issues a new HTTPS certificate to a specified IP without DNS or clipboard, restoring trust anchor independently from the SharePoint server post-compromise.
socatudev- Strategic Benefit: Even if ToolShell exfiltrates server credentials, NFC HSM enables local reissuance of trust chains fully isolated from the infected OS.
Deconstructing the ToolShell SharePoint Vulnerability Exploitation Chain
- Abuse of VIEWSTATE deserialization with stolen MachineKeys
- Use of .NET method invocation without leaving artifacts
- Insertion of loader binaries via signed PowerShell or system tools like Certutil
Such fileless payloads effectively bypass signature-based antivirus and EDR solutions. The attack chain favors stealth and persistence over overt command-and-control traffic, complicating detection.
Beyond Patching: Lessons in Architectural Sovereignty
The ToolShell SharePoint vulnerability reaffirms that patching alone cannot reestablish cryptographic integrity once secrets are compromised. Only physical key segregation ensures post-breach resilience.
Why the ToolShell SharePoint vulnerability invalidates patch-only defense strategies
- Non-centralized credential issuance and rotation (PKI independence)
- Client-side trust anchors that bypass server-side compromise
- Automation workflows with air-gapped execution paths
NFC HSM fits this paradigm by anchoring identity and authorization logic outside vulnerable systems. This enforces zero-access trust models by default and mitigates post-patch reentry by adversaries with credential remnants.
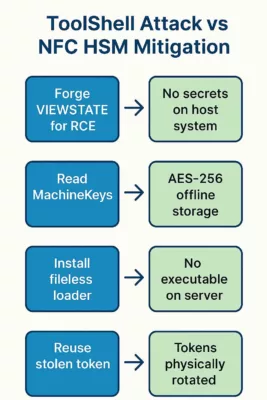
Breakout Prevention Matrix
| Attack Phase | ToolShell Action | NFC HSM Response |
|---|---|---|
| Access Gain | RCE via VIEWSTATE forging | Physical HSM stores no secrets on host |
| Credential Theft | Read MachineKeys from memory | Offline AES-256 CBC storage in HSM |
| Persistence | Install fileless ToolShell loader | No executable context accessible to attacker |
| Privilege Escalation | Reuse token for lateral movement | Token rotation blocks reuse vector |
Weak Signal Watch
- Emergence of VIEWSTATE forgery patterns in Exchange Server and Outlook Web Access (OWA)
- Reappearance of ToolShell-style loaders in signed PowerShell execution chains
- Transition from beacon-based C2 to steganographic delivery mechanisms such as image-encoded payloads.
- Reuse of stolen MachineKeys across hybrid Azure AD join infrastructures
ToolShell’s exploitation chain appears to have seeded new attack patterns beyond SharePoint:
– Exchange and OWA now exhibit signs of credential forgery via deserialization vectors
– Warlock ransomware variants use image steganography to silently load persistence payloads
– PowerShell-based implants inherit ToolShell’s memory-resident design to bypass telemetry
– MachineKey reuse across identity-bound Azure environments raises systemic trust decay issues
Server Trust Decay Test
Even after mitigation, the ToolShell SharePoint vulnerability demonstrates how credential remnants allow adversaries to retain stealth access, unless a sovereign hardware countermeasure is applied.
An attacker steals the MachineKeys on a Friday. The following Monday, the organization applies the patch but fails to rotate the credentials. The access persists. With NFC HSM::
- Compromise is contained via off-host cryptographic separation
- Token usage policies enforce short-term validity
- No command lives on the server long enough to be hijacked
CVE ≠ Loss of Control
Being vulnerable does not equal being compromised — unless critical secrets reside on vulnerable systems. NFC HSM inverts this logic by anchoring control points in hardware, off the network, and out of reach from any CVE-based exploit.
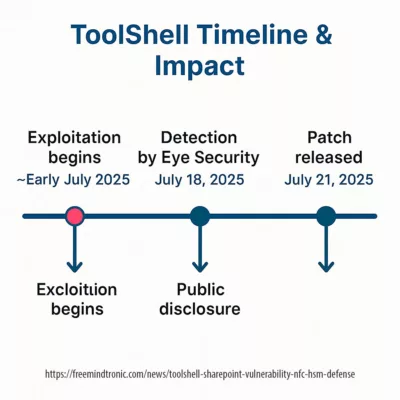
ToolShell Timeline & Impact Exposure
| Event | Date | Comment |
|---|---|---|
| Vulnerability exploitation begins (undisclosed phase) | ~Early July 2025 (est.) | Attributed to stealth campaigns before detection (Eye Security) |
| First mass detection by Eye Security | July 18, 2025 | Dozens of compromised servers spotted |
| Microsoft public disclosure | July 20, 2025 | Emergency advisory + patch instructions |
| CISA KEV catalog update | July 20, 2025 | CVE-2025-53770/53771 classified as actively exploited |
| Widespread patch availability | July 21–23, 2025 | Full mitigation for supported SharePoint editions |
In my deployments, I validated that both DataShielder NFC HSM and PassCypher NFC HSM securely store and inject a 55-character offline command like:
This deterministic payload is physically embedded and cryptographically sealed in the NFC HSM. No clipboard. No DNS. No runtime script on the compromised host. Just a sovereign injection path that stays off the radar — and off the network.In a ToolShell-type breach, these tokens allow administrators to revoke, reissue, and restore certificate trust locally. The attack chain is not just mitigated — it’s rendered structurally ineffective.
~/.acme.sh/acme.sh --issue --standalone -d 10.10.10.10