Cybercrime Treaty at the UN: A New Era in Global Security
UN Cybersecurity Treaty Establishes Global Cooperation
The UN has actively taken a historic step by agreeing on the first-ever global cybercrime treaty. This significant agreement, outlined by the United Nations, demonstrates a commitment to enhancing global cybersecurity. The treaty paves the way for stronger international collaboration against the escalating threat of cyberattacks. As we examine this treaty’s implications, it becomes clear why this decision is pivotal for the future of cybersecurity worldwide.
Cybercrime Treaty Addresses Global Cybersecurity Threats
As cyberattacks surge worldwide, UN member states have recognized the urgent need for collective action. This realization led to the signing of the groundbreaking Cybercrime Treaty on August 9, 2024. The treaty seeks to harmonize national laws and strengthen international cooperation. This effort enables countries to share information more effectively and coordinate actions against cybercriminals.
After years of intense negotiations, this milestone highlights the complexity of today’s digital landscape. Only a coordinated global response can effectively address these borderless threats.
Cybersecurity experts view this agreement as a crucial advancement in protecting critical infrastructures. Cyberattacks now target vital systems like energy, transportation, and public health. International cooperation is essential to anticipate and mitigate these threats before they cause irreparable harm.
For further details, you can access the official UN publication of the treaty here.
Drawing Parallels with the European AI Regulation
To grasp the full importance of the Cybercrime Treaty, we can compare it to the European Union’s initiative on artificial intelligence (AI). Like cybercrime, AI is a rapidly evolving field that presents new challenges in security, ethics, and regulation. The EU has committed to a strict legislative framework for AI, aiming to balance innovation with regulation. This approach protects citizens’ rights while promoting responsible technological growth.
In this context, the recent article on European AI regulation offers insights into how legislation can evolve to manage emerging technologies while ensuring global security. Similarly, the Cybercrime Treaty seeks to create a global framework that not only prevents malicious acts but also fosters essential international cooperation. As with AI regulation, the goal is to navigate uncharted territories, ensuring that legislation keeps pace with technological advancements while safeguarding global security.
A Major Step Toward Stronger Cybersecurity
This agreement marks a significant milestone, but it is only the beginning of a long journey toward stronger cybersecurity. Member states now need to ratify the treaty and implement measures at the national level. The challenge lies in the diversity of legal systems and approaches, which complicates standardization.
The treaty’s emphasis on protecting personal data is crucial. Security experts stress that fighting cybercrime must respect fundamental rights. Rigorous controls are essential to prevent abuses and ensure that cybersecurity measures do not become oppressive tools.
However, this agreement shows that the international community is serious about tackling cybercrime. The key objective now is to apply the treaty fairly and effectively while safeguarding essential rights like data protection and freedom of expression.
The Role of DataShielder and PassCypher Solutions in Individual Sovereignty and the Fight Against Cybercrime
As global cybercrime threats intensify, innovative technologies like DataShielder and PassCypher are essential for enhancing security while preserving individual sovereignty. These solutions, which operate without servers, databases, or user accounts, provide end-to-end anonymity and adhere to the principles of Zero Trust and Zero Knowledge.
- DataShielder NFC HSM: Utilizes NFC technology to secure digital transactions through strong authentication, preventing unauthorized access to sensitive information. It operates primarily within the Android ecosystem.
- DataShielder HSM PGP: Ensures the confidentiality and protection of communications by integrating PGP technology, thereby reinforcing users’ digital sovereignty. This solution is tailored for desktop environments, particularly on Windows and Mac systems.
- DataShielder NFC HSM Auth: Specifically designed to combat identity theft, this solution combines NFC and HSM technologies to provide secure and anonymous authentication. It operates within the Android NFC ecosystem, focusing on protecting the identity of order issuers against impersonation.
- PassCypher NFC HSM: Manages passwords and private keys for OTP 2FA (TOTP and HOTP), ensuring secure storage and access within the Android ecosystem. Like DataShielder, it functions without servers or databases, ensuring complete user anonymity.
- PassCypher HSM PGP: Features patented, fully automated technology to securely manage passwords and PGP keys, offering advanced protection for desktop environments on Windows and Mac. This solution can be seamlessly paired with PassCypher NFC HSM to extend security across both telephony and computer systems.
- PassCypher HSM PGP Gratuit: Offered freely in 13 languages, this solution integrates PGP technology to manage passwords securely, promoting digital sovereignty. Operating offline and adhering to Zero Trust and Zero Knowledge principles, it serves as a tool of public interest across borders. It can also be paired with PassCypher NFC HSM to enhance security across mobile and desktop platforms.
Global Alignment with UN Cybercrime Standards
Notably, many countries where DataShielder and PassCypher technologies are protected by international patents have already signed the UN Cybercrime Treaty. These nations include the USA, China, South Korea, Japan, the UK, Germany, France, Spain, and Italy. This alignment highlights the global relevance of these solutions, emphasizing their importance in meeting the cybersecurity standards now recognized by major global powers. This connection between patent protection and treaty participation further underscores the critical role these technologies play in the ongoing efforts to secure digital infrastructures worldwide.
Dual-Use Considerations
DataShielder solutions can be classified as dual-use products, meaning they have both civilian and military applications. This classification aligns with international regulations, particularly those discussed in dual-use encryption regulations. These products, while enhancing cybersecurity, also comply with strict regulatory standards, ensuring they contribute to both individual sovereignty and broader national security interests.
Moreover, these products are available exclusively in France through AMG PRO, ensuring that they meet local market needs while maintaining global standards.
Human Rights Concerns Surrounding the Cybercrime Treaty
Human rights organizations have voiced strong concerns about the UN Cybercrime Treaty. Groups like Human Rights Watch and the Electronic Frontier Foundation (EFF) argue that the treaty’s broad scope lacks sufficient safeguards. They fear it could enable governments to misuse their authority, leading to excessive surveillance and restrictions on free speech, all under the guise of combating cybercrime.
These organizations warn that the treaty might be exploited to justify repressive actions, especially in countries where freedoms are already fragile. They are advocating for revisions to ensure stronger protections against such abuses.
The opinion piece on Euractiv highlights these concerns, warning that the treaty could become a tool for repression. Some governments might leverage it to enhance surveillance and limit civil liberties, claiming to fight cybercrime. Human rights defenders are calling for amendments to prevent the treaty from becoming a threat to civil liberties.
Global Reactions to the Cybercrime Treaty
Reactions to the Cybercrime Treaty have been varied, reflecting the differing priorities and concerns across nations. The United States and the European Union have shown strong support, stressing the importance of protecting personal data and citizens’ rights in the fight against cybercrime. They believe the treaty provides a critical framework for international cooperation, which is essential to combat the rising threat of cyberattacks.
However, Russia and China, despite signing the treaty, have expressed significant reservations. Russia, which initially supported the treaty, has recently criticized the final draft. Officials argue that the treaty includes too many human rights safeguards, which they believe could hinder national security measures. China has also raised concerns, particularly about digital sovereignty. They fear that the treaty might interfere with their control over domestic internet governance.
Meanwhile, countries in Africa and Latin America have highlighted the significant challenges they face in implementing the treaty. These nations have called for increased international support, both in resources and technical assistance, to develop the necessary cybersecurity infrastructure. This call for help underscores the disparity in technological capabilities between developed and developing nations. Such disparities could impact the treaty’s effectiveness on a global scale.
These varied reactions highlight the complexity of achieving global consensus on cybersecurity issues. As countries navigate their national interests, the need for international cooperation remains crucial. Balancing these factors will be essential as the global community moves forward with implementing the Cybercrime Treaty (UNODC) (euronews).
Broader Context: The Role of European Efforts and the Challenges of International Cooperation
While the 2024 UN Cybercrime Treaty represents a significant step forward in global cybersecurity, it is essential to understand it within the broader framework of existing international agreements. For instance, Article 62 of the UN treaty requires the agreement of at least 60 parties to implement additional protocols, such as those that could strengthen human rights protections. This requirement presents a challenge, especially considering that the OECD, a key international body, currently has only 38 members, making it difficult to gather the necessary consensus.
In Europe, there is already an established framework addressing cybercrime: the Budapest Convention of 2001, under the Council of Europe. This treaty, which is not limited to EU countries, has been a cornerstone in combating cybercrime across a broader geographic area. The Convention has been instrumental in setting standards for cooperation among signatory states.
Furthermore, an additional protocol to the Budapest Convention was introduced in 2022. This protocol aims to address contemporary issues in cybercrime, such as providing a legal basis for the disclosure of domain name registration information and enhancing cooperation with service providers. It also includes provisions for mutual assistance, immediate cooperation in emergencies, and crucially, safeguards for protecting personal data.
However, despite its importance, the protocol has not yet entered into force due to insufficient ratifications by member states. This delay underscores the difficulties in achieving widespread agreement and implementation in international treaties, even when they address pressing global issues like cybercrime.
Timeline from Initiative to Treaty Finalization
The timeline of the Cybercrime Treaty reflects the sustained effort required to address the growing cyber threats in an increasingly unstable global environment. Over five years, the negotiation process highlighted the challenges of achieving consensus among diverse nations, each with its own priorities and interests. This timeline provides a factual overview of the significant milestones:
- 2018: Initial discussions at the United Nations.
- 2019: Formation of a working group to assess feasibility.
- 2020: Proposal of the first draft, leading to extensive negotiations.
- 2021: Official negotiations involving cybersecurity experts and government representatives.
- 2023: Agreement on key articles; the final draft was submitted for review.
- 2024: Conclusion of the treaty text during the final session of the UN Ad Hoc Committee on August 8, 2024, in New York. The treaty is set to be formally adopted by the UN General Assembly later this year.
This timeline underscores the complexities and challenges faced during the treaty’s formation, setting the stage for understanding the diverse global responses to its implementation.
List of Treaty Signatories
The Cybercrime Treaty has garnered support from a coalition of countries committed to enhancing global cybersecurity. The current list of countries that have validated the agreement includes:
- United States
- Canada
- Japan
- United Kingdom
- Germany
- France
- Spain
- Italy
- Australia
- South Korea
These countries reflect a broad consensus on the need for international cooperation against cybercrime. However, it is important to note that the situation is fluid, and other countries may choose to sign the treaty in the future as international and domestic considerations evolve.
Differentiating the EU’s Role from Member States’ Participation
It is essential to clarify that the European Union as a whole has not signed the UN Cybercrime Treaty. Instead, only certain individual EU member states, such as Germany, France, Spain, and Italy, have opted to sign the treaty independently. This means that while the treaty enjoys support from some key European countries, its enforcement and application will occur at the national level within these countries rather than under a unified EU framework.
This distinction is significant for several reasons. First, it highlights that the treaty will not be universally enforced across the entire European Union. Each signing member state will be responsible for integrating the treaty’s provisions into their own legal systems. Consequently, this could result in variations in how the treaty is implemented across different European countries.
Moreover, the European Union has its own robust cybersecurity policies and initiatives, including the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) and the EU Cybersecurity Act. The fact that the EU as an entity did not sign the treaty suggests that it may continue to rely on its existing frameworks for governing cybersecurity. At the same time, individual member states will address cybercrime through the treaty’s provisions.
Understanding this distinction is crucial for recognizing how international cooperation will be structured and the potential implications for cybersecurity efforts both within the EU and on a global scale.
Countries Yet to Sign the Cybercrime Treaty
Several countries have opted not to sign the Cybercrime Treaty, citing concerns related to sovereignty and national security. In a world marked by conflicts and global tensions, these nations prioritize maintaining control over their cybersecurity strategies rather than committing to international regulations. This list includes:
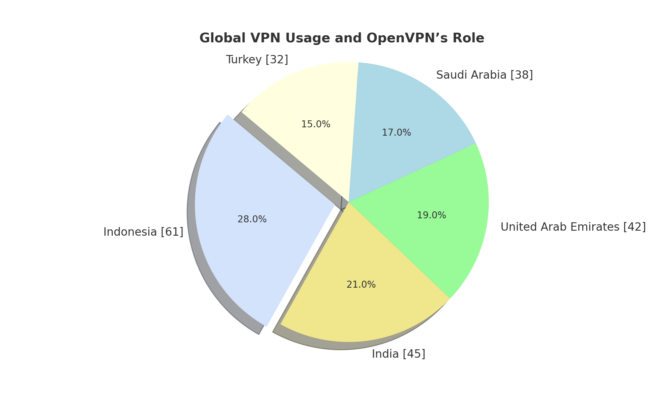
- Turkey: Concerns about national security and digital sovereignty.
- Iran: Fears of surveillance by more powerful states.
- Saudi Arabia: Reservations about alignment with national cyber policies.
- Israel: Prefers relying on its cybersecurity infrastructure, questioning enforceability.
- United Arab Emirates: Concerns about sovereignty and external control.
- Venezuela: Fear of foreign-imposed digital regulations.
- North Korea: Potential interference with state-controlled internet.
- Cuba: Concerns over state control and national security.
- Andorra: Has not signed the treaty, expressing caution over how it may impact national sovereignty and its control over digital governance and cybersecurity policies.
While these countries have not signed the treaty, the situation may change. International pressures, evolving cyber threats, and diplomatic negotiations could lead some of these nations to reconsider their positions and potentially sign the treaty in the future.
Download the Full Text of the UN Cybercrime Treaty
For those interested in reviewing the full text of the treaty, you can download it directly in various languages through the following links:
- EN: UN Cybercrime Treaty – English
- FR: UN Cybercrime Treaty – French
- AR: UN Cybercrime Treaty – Arabic
- CN: UN Cybercrime Treaty – Chinese
- ES: UN Cybercrime Treaty – Spanish
- RU: UN Cybercrime Treaty – Russian
These documents provide the complete and official text of the treaty, offering detailed insights into its provisions, objectives, and the framework for international cooperation against cybercrime.
Global Implications and Challenges
This title more accurately reflects the content, focusing on the broader global impact of the treaty and the challenges posed by the differing approaches of signatory and non-signatory countries. It invites the reader to consider the complex implications of the treaty on international cybersecurity cooperation and state sovereignty.
A Global Commitment to a Common Challenge
As cyberattacks become increasingly sophisticated, the Cybercrime Treaty offers a much-needed global response to this growing threat. The UN’s agreement on this treaty marks a critical step toward enhancing global security. However, much work remains to ensure collective safety and effectiveness. Furthermore, concerns raised by human rights organizations, including Human Rights Watch and the Electronic Frontier Foundation, emphasize the need for vigilant monitoring. This careful oversight is crucial to prevent the treaty from being misused as a tool for repression and to ensure it upholds fundamental freedoms.
In this context, tools like DataShielder offer a promising way forward. These technologies enhance global cybersecurity efforts while simultaneously respecting individual and sovereign rights. They serve as a model for achieving robust security without infringing on the essential rights and freedoms that are vital to a democratic society. Striking this balance is increasingly important as we navigate deeper into a digital age where data protection and human rights are inextricably linked.
For additional insights on the broader implications of this global agreement, you can explore the UNRIC article on the Cybercrime Treaty.