Spearphishing APT29 Europe: Unveiling Russia’s Cozy Bear Tactics
APT29 SpearPhishing: Russia’s Stealthy Cyberespionage Across Europe APT29, also known as Cozy Bear or The Dukes, a highly sophisticated Russian statesponsored cyberespionage group, has conducted persistent spearphishing campaigns against a wide range of European entities. Their meticulously planned attacks often target diplomatic missions, think tanks, and highvalue intelligence targets, with the primary objective of longterm intelligence gathering and persistent access. This article provides an indepth analysis of the evolving spearphishing techniques employed by APT29 and outlines essential strategies for robust prevention and detection.
APT29 SpearPhishing Europe: A Stealthy LongTerm Threat
APT29 spearphishing Europe campaigns highlight a persistent and highly sophisticated cyberespionage threat orchestrated by Russia’s Foreign Intelligence Service (SVR), known as Cozy Bear. Active since at least 2008, APT29 has become synonymous with stealthy operations targeting European institutions through phishing emails, Microsoft 365 abuse, supply chain compromises, and persistent malware implants. Unlike APT28’s aggressive tactics, APT29’s approach is patient, subtle, and highly strategic—favoring covert surveillance over immediate disruption. This article examines APT29’s tactics, European targeting strategy, technical indicators, and how sovereign solutions like DataShielder and PassCypher help organizations defend against Russian longterm cyber espionage campaigns.
APT29’s Persistent Espionage Model: The Art of the Long Game in Europe
APT29’s operational model is defined by stealth, longevity, and precision. Their goal is not shortterm chaos but sustained infiltration. Their campaigns frequently last months—or years—without being detected. APT29 rarely causes disruption; instead, it exfiltrates sensitive political, diplomatic, and strategic data across Europe.
APT29 often custombuilds malware for each operation, designed to mimic legitimate network activity and evade common detection tools.
Covert Techniques and Key Infiltration Methods
APT29’s longterm access strategy hinges on advanced, covert methods of penetration and persistence:
Custom Backdoors
Backdoors like “WellMess” and “WellMail” use encrypted communications, steganography, and cloud services to evade inspection. They also include antianalysis techniques such as antiVM and antidebugging code to resist forensic examination.
Supply Chain Attacks
The SolarWinds Orion attack in 2020 remains one of the largest breaches attributed to APT29. This compromise of the supply chain allowed attackers to infiltrate highvalue targets via trusted software. The SUNBURST and TEARDROP implants enabled stealthy lateral movement.
SpearPhishing from Compromised Diplomatic Sources
APT29’s phishing operations often originate from hijacked diplomatic email accounts, lending legitimacy to phishing attempts. These emails target government bodies, international organizations, and embassies across Europe.
Credential Harvesting via Microsoft 365
APT29 abuses cloud infrastructure by executing OAuth consent phishing, targeting legacy authentication protocols, and compromising user credentials to access SharePoint, Outlook, and cloudstored documents.
GRAPELOADER and WINELOADER: New Malware Lures in 2025
In April 2025, APT29 launched a phishing campaign dubbed SPIKEDWINE, impersonating a European Ministry of Foreign Affairs and inviting victims to fake winetasting events. These emails, sent from domains like bakenhof[.]com and silry[.]com, delivered malware via a file named “wine.zip.”
The attack chain begins with GRAPELOADER, a previously undocumented loader, followed by a new variant of the WINELOADER backdoor. This multistage infection shows evolving sophistication in malware design, timing of payload execution, and evasion techniques. The campaign’s targets include multiple European Ministries of Foreign Affairs and nonEuropean embassies in Europe.
Geopolitical Implications of APT29’s European Operations
APT29’s spear-phishing activities are not just technical threats—they are instruments of Russian geopolitical strategy. The group’s consistent targeting of ministries, embassies, and think tanks across Europe aligns closely with key diplomatic and policy moments.
APT29’s operations often intensify ahead of European elections, EU-NATO summits, or major sanctions announcements. Their goal is not only to steal sensitive intelligence, but to subtly influence policymaking by gaining access to classified assessments, private negotiations, or internal dissent.
Notable examples include:
- The 2016 and 2017 attacks on Norwegian government agencies, including the Ministry of Defense and the Norwegian Labour Party (CCDCOE)
- The 2025 campaign targeting diplomats with wine-tasting lures (Check Point Research)
- The 2023 exploitation of WinRAR CVE-2023-38831 against embassies in Greece, Italy, Romania, and Azerbaijan (National Security Archive)
- APT29’s targeting of German political parties ahead of the 2021 elections (Google Cloud Blog, CSO Online)
APT29 acts as a digital vanguard for Russian hybrid warfare, where cyber operations feed into diplomatic leverage, information warfare, and strategic disruption. Understanding this broader agenda is crucial for shaping European cyber defense beyond the technical dimension.
European Government Responses to APT29: A Patchwork Defense

This comparison illustrates the fragmented nature of Europe’s institutional responses to state-sponsored cyber threats. While some nations have clearly identified and named APT29, others remain more cautious or reactive.
What if APT29 Had Not Been Detected?
While some operations were eventually uncovered, many persisted for months or years. Had APT29 remained entirely undetected, the implications for Europe’s political and strategic landscape could have been far-reaching:
- Diplomatic Blackmail: With access to confidential negotiations, APT29 could have leaked selective intelligence to disrupt alliances or blackmail key figures.
- Policy Manipulation: Strategic leaks before elections or summits could steer public opinion, weaken pro-EU narratives, or stall collective defense decisions.
- NATO Cohesion Threats: Exfiltrated defense policy data could be used to exploit divisions between NATO member states, delaying or undermining unified military responses.
- Influence Campaign Fuel: Stolen data could be recontextualized by Russian disinformation actors to construct persuasive narratives tailored to fracture European unity.
This scenario highlights the necessity of early detection and sovereign countermeasures—not merely to block access, but to neutralize the geopolitical utility of the exfiltrated data.
Notable APT29 Incidents in Europe
| Date | Operation Name | Target | Outcome |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2015 | CozyDuke | U.S. & EU diplomatic missions | Long-term surveillance and data theft |
| 2020 | SolarWinds | EU/US clients (supply chain) | 18,000+ victims compromised, long undetected persistence |
| 2021–2023 | Microsoft 365 Abuse | EU think tanks | Credential theft and surveillance |
| 2024 | European Diplomatic | Ministries in FR/DE | Phishing via embassy accounts; linked to GRAPELOADER malware |
| 2025 | SPIKEDWINE | European MFA, embassies | GRAPELOADER + WINELOADER malware via wine-tasting phishing lure |
Timeline Sources & Attribution
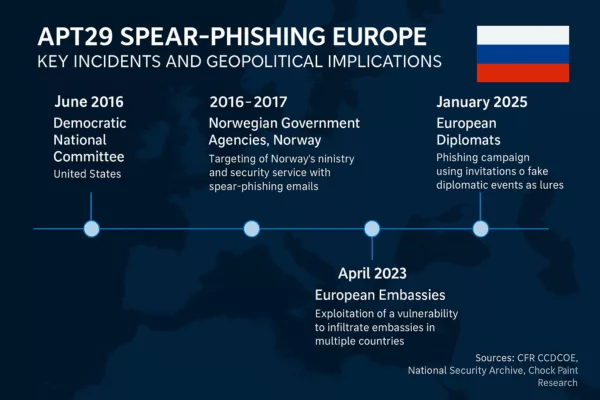
This infographic is based on verified public threat intelligence from:
- Council on Foreign Relations
- Check Point Research
- National Security Archive
- Google Cloud Blog (Mandiant)
- CSO Online
- KnowBe4 Security Blog
These sources confirm that APT29 remains a persistent threat actor with geopolitical aims, leveraging cyber operations as a tool of modern espionage and strategic influence.
APT29 vs. APT28: Divergent Philosophies of Intrusion
| Tactic/Group | APT28 (Fancy Bear) | APT29 (Cozy Bear) |
| Affiliation | GRU (Russia) | SVR (Russia) |
| Objective | Influence, disruption | Longterm espionage |
| Signature attack | HeadLace, CVE exploit | SolarWinds, GRAPELOADER, WINELOADER |
| Style | Aggressive, noisy | Covert, patient |
| Initial Access | Broad phishing, zerodays | Targeted phishing, supply chain |
| Persistence | Common tools, fast flux | Custom implants, stealthy C2 |
| Lateral Movement | Basic tools (Windows) | Stealthy tools mimicking legit activity |
| AntiAnalysis | Obfuscation | AntiVM, antidebugging |
| Typical Victims | Ministries, media, sports | Diplomacy, think tanks, intel assets |
Weak Signals and Detection Opportunities
European CERTs have identified subtle signs that may suggest APT29 activity:
- Unusual password changes in Microsoft 365 without user request
- PowerShell usage from signed binaries in uncommon contexts
- Persistent DNS beaconing to rare C2 domains
- Abnormal OneDrive or Azure file transfers and permission changes
- Phishing emails tied to impersonated ministries and fake event lures
Defensive Strategies: Building European Resilience
Effective defense against APT29 requires:
- ⇨ Hardwarebased MFA (FIDO2, smartcards) to replace SMS/app OTPs
- ⇨ Enforcing least privilege and strict access policies
- ⇨ Monitoring DNS traffic and lateral movement patterns
- ⇨ Deploying EDR/XDR tools with heuristic behavior analysis
- ⇨ Ingesting threat intelligence feeds focused on APT29 TTPs
- ⇨ Running regular threat hunts to detect stealthy TTPs early
Sovereign Protection: PassCypher & DataShielder Against APT29
To counter espionage tactics like those of APT29, Freemindtronic offers two offline, hardwarebased solutions:
- DataShielder NFC HSM: A fully offline, contactless authentication tool immune to phishing and credential replay.
- PassCypher HSM PGP: Stores passwords and cryptographic secrets in a hardware vault, protected from keylogging, memory scraping, and BITB attacks.
Both tools decrypt only in volatile memory, ensuring no data is written locally, even temporarily.
Regulatory Compliance
- ⇨ French Decree No. 20241243: Encryption devices for dualuse (civil/military)
- ⇨ EU Regulation (EU) 2021/821 (latest update 2024)
- ⇨ Distributed exclusively in France by AMG PRO:
Threat Coverage Table: PassCypher & DataShielder vs. APT29
This table evaluates sovereign cyber defenses against known APT29 TTPs.
| Threat Type | APT29 Presence | PassCypher Coverage | DataShielder Coverage |
|---|---|---|---|
| Targeted spearphishing | ✔ | ✔ Secure Input, No Leakage |
✔ Offline Authentication |
| Supply chain compromise | ✔ | ✔ Endtoend encrypted communication; passwords and OTPs decrypted in volatile memory only |
✔ Offline preencryption; data decrypted only in memory during reading |
| Microsoft 365 credential harvesting | ✔ | ✔ Offline Storage, BITB Protection |
✔ Offline Authentication |
| Trusted cloud abuse (OneDrive, Azure) | ✔ | ✔ URL Filtering, Secure Vault |
✔ Offline Authentication |
| Persistent implants | ✔ | ✔ Encrypted session use; keys and OTPs inaccessible without HSM |
✔ Offline encrypted data cannot be used even with full system compromise |
| Exploits via infected documents | ✔ | ✔ Encrypted Sandbox Links |
✔ Encrypted Key Context |
| Phishing via diplomatic accounts | ✔ | ✔ Secure Input, Spoofing Protection |
✔ Offline Credential Isolation |
| Lateral movement (PowerShell) | ✔ | ✔ Credentials isolated by HSM; attacker gains no usable secrets |
✔ Persistent encryption renders accessed data useless |
| DNS beaconing | ✔ | ✔ Decryption keys never online; exfiltrated data stays encrypted |
✔ Offline encrypted messages never intelligible without HSM |
Legend: ✔ = Direct mitigation | ⚠ = Partial mitigation | ✘ = Not covered
Note: PassCypher and DataShielder focus not on preventing all access, but on neutralizing its strategic value. Isolated credentials and persistently encrypted data render espionage efforts ineffective.
Towards a Sovereign and Proactive Defense Against the APT29 Threat in Europe
APT29’s quiet and persistent threat model demands proactive, sovereign responses. Passive, reactive security measures are no longer enough. European organizations must integrate national technologies like PassCypher and DataShielder to ensure digital sovereignty, compartmentalization, and offline security.
The adoption of segmented, resilient, and hardwarebacked architectures enables:
- Independence from cloudbased MFA
- Resistance to credential reuse and session hijacking
- Full data lifecycle control with no data remnants
CISOs, critical infrastructure operators, and government entities must evaluate the security coverage and complementarity of each tool to craft a cohesive strategy against persistent Russian cyber threats.
To explore our full methodology and technical breakdown APT29 read the complete article.
Glossary (for Non-Technical Readers)
- Spear-phishing: A targeted email attack that appears personalized to trick specific individuals into clicking malicious links or attachments.
- C2 (Command and Control) Infrastructure: A network of hidden servers controlled by attackers to manage malware remotely and exfiltrate stolen data.
- OAuth Consent Phishing: A technique where attackers trick users into granting access permissions to malicious applications through legitimate cloud services.
- Anti-VM / Anti-Debugging: Techniques used in malware to avoid being detected or analyzed by virtual machines or security researchers.
- Supply Chain Attack: An attack that compromises trusted software or service providers to distribute malware to their clients.
- Volatile Memory Decryption: A security method where sensitive data is decrypted only in the device’s memory (RAM), never stored unencrypted.
- Persistent Threat: An attacker who remains within a network for a long time without being detected, often for intelligence gathering.