How to Create NFC Business Cards with Cardokey
Do you want to create your contact information in a simple, fast and eco-friendly way? Do you want to use NFC technology without spending a fortune or compromising your privacy? Then you need to read this article about Cardokey, the app that’s revolutionizing NFC business cards.
NFC Business Cards: Create your NFC vCard with Cardokey, the Eco-Friendly and Secure NFC App
Are you looking for an eco-friendly way to create contactless business cards? Do you want to benefit from affordable NFC technology and prioritize privacy? You’ll love Cardokey – the app revolutionizing NFC business cards! Cardokey, the NFC business card that connects you while protecting your privacy.
What is Cardokey and how does it work?
Cardokey: Free App for Eco-Friendly NFC Business Cards
You can easily and free create and share your business cards, your social network links or links to your favorite sites for life. Recycle any NFC Tag, NFC Ticket, NFC Sticker or NFC card allowing the use of the NDEF format.
Use of the free Cardokey application is completely anonymous and does not ask for any personal or professional information. You therefore do not need to create an account or identify yourself to use Cardokey.
Cardokey: a compliant and sustainable solution
Cardokey adheres to various standards like ISO/IEC 7816-4, ISO/IEC 14443, NFC Forum Type 2, ISO/IEC 18092, and ISO/IEC 15693 without compromising your privacy or security. It also complies with international data protection laws such as GDPR, PIPEDA, CCPA, and more.
Cardokey is an eco-designed solution that contributes to the UN Goal 12. Consequently, it complies with international standards for eco-responsible practices, circular and solidarity economy, sustainable economy and carbon footprint reduction.
Cardokey: a compatible and versatile app
NFC business cards created with Cardokey are compatible with all NFC phones, Android and iPhone. The application works in real time, offline, without a database, including in airplane mode. This means that you can modify the information contained in the memory of your NFC media at any time. The app also allows you to format any NFC Media to NDEF format and also erase almost all types of NFC chips.
Cardokey: a simple and fast way to share your contact information
Digital business cards created with Cardokey can be shared in seconds. In fact, your interlocutor does not need to download a specific application in order to be able to read the information you wish to share. All he has to do is place the digital business card under his phone equipped with NFC technology to see the information.
How to create an NFC business card with Cardokey that fits the memory size of your NFC media?
The intelligent system of Cardokey
One of the most interesting features of Cardokey is the automatic management of the memory size of forms. The contact form indicates in real time the actual occupancy of the NDEF memory based on the number of characters. The Cardokey user knows the type of vCard information. He can store it according to the memory size. The memory size depends on the NFC media.
The different types of NFC Media and their memory size
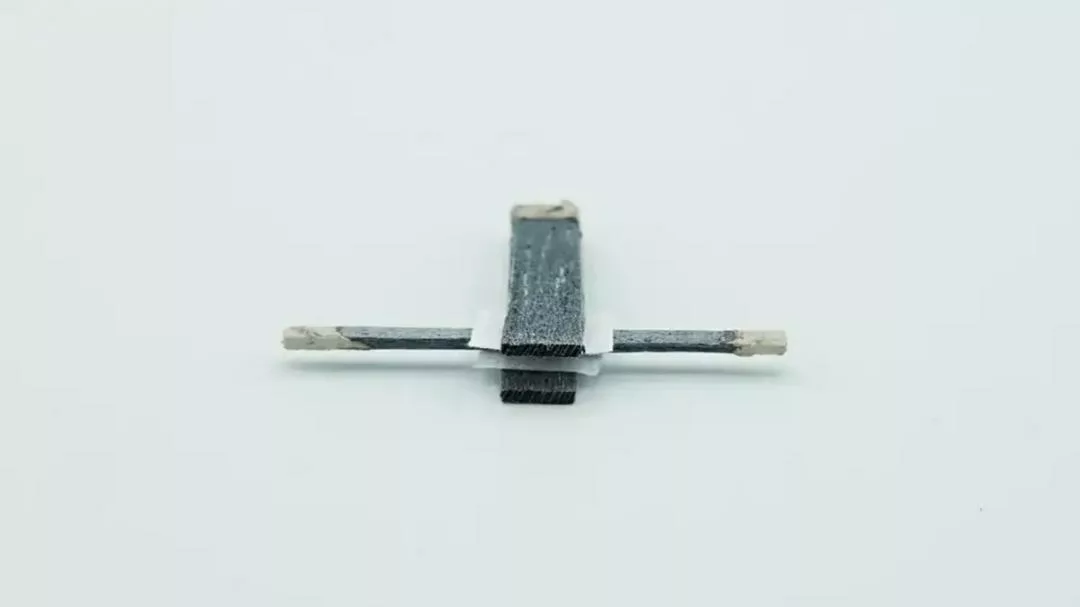
It is possible to make a vCard with a minimum of name, surname and email information for a very small NFC memory4. For example, on an NTAG Nano, which has a capacity of 160 bytes and can store NDEF messages of up to 128 bytes, one can store basic information like a person’s name, surname, phone number, and email address.
Or, more complete information can be stored on a ST25TV02K chip, which has a capacity of 256 bytes and can store NDEF messages of up to 224 bytes. In this case, one can include a person’s name, surname, title, organization, phone number, email address, and postal address.
The steps to create an NFC business card with Cardokey
You can create NFC business cards that fit the memory size of your media without losing information. This allows you to optimize the use of your NFC Media and take advantage of their full capabilities.
To create NFC business cards that fit the memory size of your media, simply follow these steps:
- Open the Cardokey app and choose the type of content you want to create (business card, URL link, social media link).
- Enter the information you want to share in the contact form. The form tells you in real time how much memory your data is occupying and how much memory is available on your media.
- Hover your smartphone to the NFC media of your choice. The app writes the data to the NFC media and confirms that the NFC business card has been created successfully.
- Test your NFC business card by scanning it with your smartphone or another NFC phone. You’ll see the information you’ve shared on the screen.
That’s it, you’ve created an NFC business card adapted to the memory size of your media, thanks to Cardokey’s automatic form memory size management feature
What are the benefits of NFC business cards with Cardokey?
Cardokey is free and anonymous
Cardokey is a free app that lets you create NFC vCard business cards easily. You can create as many NFC business cards as you want, without paying any fees or signing up for any subscriptions. Moreover, Cardokey is completely anonymous and does not ask for any personal or professional information from the user. You don’t need to create an account or fill in any data. Everything works offline, in real-time, without a database.
Cardokey is easy to use
Cardokey is very easy to use, with one-click installation and operation. You don’t need any technical knowledge or specific hardware to create your NFC business cards. All you have to do is download the app on your smartphone, choose the type of content you want to create, enter the information you want to share, and swipe your smartphone on the NFC media of your choice. And there you have it, your NFC business card is ready! Furthermore, Cardokey features an intelligent system that optimizes the NDEF memory management of NFC media. This provides an optimal user experience.
How Cardokey protects your data with EviSwap NFC NDEF technology
The innovative features of EviSwap NFC NDEF technology
Cardokey uses EviSwap NFC NDEF technology by Freemindtronic for cybersecurity. This is an innovative technology that lets you create and share digital contacts contactless for life. With a simple click, you can create NFC business cards on any NFC media, whether it is disposable or not. You can give a new use to NFC tickets, cards, labels, and tags. You can also rewrite your NFC business cards at least a million times without any risk of error. You can use them for more than 40 years without needing a power source.
The standard and secure format of EviSwap NFC NDEF technology
EviSwap NFC NDEF technology is a technology that uses NFC to facilitate data exchange by implementing the NDEF NFC standard. NDEF stands for NFC Data Exchange Format. It is a standardized format that contains structured data, such as contacts, links, texts, images, etc. NDEF files are compatible with most computer and phone terminals, which can read and write them directly on the NFC memory. EviSwap NFC NDEF technology is especially used by Freemindtronic to exchange encrypted data from human to human from an NFC media, ensuring data security and privacy.
The performance and durability of EviSwap NFC NDEF technology for industrial chips
EviSwap NFC NDEF technology is also compatible with all NFC NDEF media, but it has the advantage of being optimized for Freemindtronic’s NFC HSM industrial chips. These chips can operate in a wide range of temperatures, from -40°C to +85°C. They can withstand harsh environments and resist shocks, vibrations, and water. They are ideal for applications that require reliability and robustness, such as logistics, manufacturing, or security. Moreover, EviSwap NFC NDEF technology is optimized to exchange the largest quantity of information stored in a large NFC memory. For example, it is possible to store NDEF messages of up to 7.9 kilobytes on an M24LR64E-R chip, which has a capacity of 8 kilobytes. In this case, one can add all types of vCard data as well as security keys, digital signature keys and other custom data.
Cardokey: the anonymous and reusable solution for creating NFC business cards
Cardokey is a secure and reusable solution. The Cardokey app works anonymously. It is not connected to a remote service. It does not store in the phone the data. It does not ask you for any information about the user. Finally, it works in real time in Air Gap Network Security . The EviSwap technology also includes an intelligent system to optimize the memory management of NFC media. The goal is to improve the user experience. The intelligent system informs the user in real time of the limits imposed by the maximum size of the NDEF memory available in the media. This allows you to easily store data according to the memory size.
Cardokey, an eco-friendly application
Cardokey isn’t just a universal app for people worldwide; it’s also eco-friendly, allowing you to recycle NFC media and reduce their environmental impact.
How Cardokey recycles NFC Media
NFC media, such as tags, cards or bracelets, are made of several elements and materials, such as PET (polyethylene terephthalate), aluminum or copper for the antenna, a silicon NFC chip, gold or other metals, and an adhesive. These materials are not all easily recyclable, and can cause pollution or waste problems. For example, PET is a common plastic, that is used in many consumer products, like water bottles or packaging. Although PET is recyclable, when it is used in large quantities and in the form of an NFC tag, it is hard to separate PET from other components for recycling, and it tends to clog the treatment filters. Moreover, the metal of an NFC antenna is difficult to recover and recycle. Finally, the NFC chip itself contains precious metals, that are often lost during the recycling process.
To avoid these problems, Cardokey offers an innovative and ecological solution: it allows you to recycle NFC media by reusing them to create new NFC business cards. Instead of throwing away your old NFC tags, cards or bracelets, you can transform them into NFC business cards with Cardokey, and give them a new life. You can also use existing NFC media, such as transport tickets, or access badges, and convert them into NFC business cards with Cardokey. You can thus enjoy all the benefits of NFC technology, without generating additional waste.
How Cardokey works with different types of NFC chips
Cardokey recycles all types of NFC chips (1, 2, 3, 4 and 5), regardless of ISO standards (14443, 15693, 18092). It detects chip types and adjusts accordingly for maximum compatibility. For example, Cardokey can read and write to NFC chips that have enough memory to store information, such as NTAG, MIFARE or ICODE chips. However, Cardokey will not be able to format, erase or modify NFC chips that are permanently locked.
How Cardokey helps you create personalized NFC business cards
By using Cardokey, you can recycle NFC media and turn them into personalized NFC business cards, that contain the information you want to share, such as your name, company, title, website, email, phone number, and more. You can also create URL links to documents or presentations that are useful for your business, such as quotes, contracts, portfolios, and more. You can also create pre-configured links to your favorite social networks, such as Deviantart, Discord, Facebook, Flickr, GitHub, ICQ, Instagram, LinkedIn, Mastodon, Medium, Pinterest, Reddit, Skype, Slack, Snapchat, SoundCloud, Spotify, Steam, Telegram, TikTok, Tumblr, Twitch, Twitter, VKontakte, WeChat, WhatsApp, YouTube, etc. Finally, you can manage your data and contacts in the NFC card, edit or delete them at any time, and view them on your phone or card.
How Cardokey contributes to the preservation of the planet
If we consider the 14 languages available in the Cardokey application, this represents more than 3.7 billion potential users. These potential users can each recycle 10 NFC media each year. This represents 37 billion NFC supports annually. This reduces the environmental impact of NFC and helps preserve the planet.
How Cardokey is eco-friendly and compliant
Cardokey is an eco-designed solution that contributes to the UN Goal 12. This goal aims to ensure sustainable consumption and production patterns. It complies with ISO 14001, Basel and WEEE standards. It also follows international standards for eco-responsible practices, circular and solidarity economy, sustainable economy and carbon footprint reduction. In addition, Cardokey complies with various standards and regulations. These include ISO/IEC 7816-4, ISO/IEC 14443, NFC Forum Type 2, ISO/IEC 18092 and ISO/IEC 15693. It also follows international law rules on the protection of private and professional data. These include the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR), the Personal Information Protection and Electronic Documents Act (PIPEDA), the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA), and others.
Unlike other NFC business card solutions, which are often paid, limited, complex or not very environmentally friendly, Cardokey offers you a free, unlimited, simple and eco-designed solution.
Cardokey therefore offers you an innovative and ecological solution to create NFC business cards that look like you and that suit your needs. Thanks to its recycling feature, you can also reuse NFC media and turn them into personalized NFC business cards.
Cardokey: a universal app
Cardokey is designed to let you create and manage your NFC business cards in a simple and efficient way. But did you know that Cardokey is also a universal app, which can be used by people from all over the world, regardless of their language?
Indeed, Cardokey is available in 14 languages: Arabic, Catalan, Chinese, English, French, German, Hindi, Italian, Japanese, Portuguese, Romanian, Russian, Spanish, and Ukrainian. This represents more than 86.02% of the languages spoken in the world, and more than 3.7 billion people who can use the app in their native language or in a language they master.
Moreover, Cardokey automatically adapts to the language of the phone where it is installed. If the user changes the language of their phone, Cardokey will do the same. Thus, you can create and manage your NFC business cards in the language of your choice, and enjoy all the features of the app.
You can also choose to share your information in multiple languages, by creating different profiles for each language. For example, you can have a profile in French for your French-speaking contacts, a profile in English for your English-speaking contacts, and a profile in Chinese for your Chinese contacts.
Cardokey offers you great flexibility and creativity to create NFC business cards that suit you and your needs.
How NFC vCards work
NFC stands for Near Field Communication. It is a technology that allows two media to communicate with each other when they are close to each other. NFC business cards with Cardokey use this technology to share your contact information in a simple and fast way.
An NFC tag is a media that contains a tiny electronic chip that can store and exchange data. It can have different shapes, such as stickers, keychains or physical cards. When you bring your smartphone near an NFC tag, the data associated with the tag appears automatically on your screen.
NFC vCard business cards with Cardokey are a great alternative to paper business cards, which are often thrown away, lost or outdated. They are eco-friendly, reusable and updated. They also save you time and money, as you don’t need to print or carry them. Moreover, they are more secure and anonymous, as you don’t need to share your personal data or connect to the Internet to use them.
What are the features of Cardokey NFC vCard business cards?
Cardokey offers many features that allow you to create and manage your NFC digital business cards. Here’s a table that summarizes Cardokey’s features:
| Function | Available | |
| Create a vCard (contact) taking into account the available space | ✔️ | |
| Create an NDEF NFC Vcard (Manually) | ✔️ | |
| Create a vCard from an existing contact in the phone | ✔️ | |
| Modify any existing NFC vCard created by other paid or free apps to make it easier to recycle and update them | ✔️ | |
| Delete data stored in the NDEF of an NFC media | ✔️ | |
| Format all types of NFC media to add NDEF compatibility | ✔️ | |
| Create and store in the NDEF memory of any existing NFC media: your pre-configured links for social networks, the url of your choice, a vCard contact | ✔️ | |
| Data management in the NFC Media: Create, Read, Update, Delete (CRUD) | ✔️ | |
| Explanation of each pcictogram and its feature in the application | ✔️ | |
| Show contact on phone and NFC Media | ✔️ | |
| Automatic management of the memory size of the NFC card | ✔️ | |
| Translation into 14 languages: CA, FR, EN, UK, ES, DE, IT, PT, RO, RU, AR, HI, ZH,JP | ✔️ | |
| Information de contact de Freemindtronic | ✔️ | |
| Information about the publisher of the Freemindtronic software | ✔️ | |
| Direct link on the play store to buy the Cardokey Pro version and NFC Medial | ✔️ | |
| Cardokey is a recycling solution for all types of disposable or non-disposable NFC Media | ✔️ | |
With these features, you can create a custom NFC business card, which contains the information you want to share, such as your name, company, title, website, email, phone number, and more. You can also create URL links to documents or presentations that are useful for your business, such as quotes, contracts, portfolios, and more. You can also create pre-configured links to your favorite social networks, such as Deviantart, Discord, Facebook, Flickr, GitHub, ICQ, Instagram, LinkedIn, Mastodon, Medium, Pinterest, Reddit, Skype, Slack, Snapchat, SoundCloud, Spotify, Steam, Telegram, TikTok, Tumblr, Twitch, Twitter, VKontakte, WeChat, WhatsApp, YouTube, etc. Finally, you can manage your data and contacts in the NFC card, edit or delete them at any time, and view them on your phone or card. These features give you a lot of freedom and creativity to create NFC business cards that look and match you.
What are the use cases for NFC business cards with Cardokey?
There are many of them, whether for business or personal needs. Here are some examples of use cases:
Andorra: keep in memory a special event
During the winter, a family visits Andorra’s Granvalira for their child’s first ski lesson and to experience their first snowflake, star, etc. The family keeps the NFC ski ticket formatted in NDEF format. Then, they save a URL that links to a page with all the photos and videos of this event. The ski ticket has become a souvenir object that will be kept for several years. In this case, Cardokey allows you to create an NFC business card with a URL that links to a page where there are all the photos, videos of this event.
Exhibitor: a connected poster with NFC tags
At a booth event, Marius uses self-adhesive NFC tags that they stick behind a poster holder advertising their products with a URL link that directs the visitor to their product information on the poster. The exhibitor can change the poster of his support with Cardokey. He can put a new poster and change the URL link of his new poster. This way, the exhibitor makes a simple poster a connected poster. In this case, Cardokey allows you to create an NFC business card with a URL link that directs the visitor to your product information on the poster.
Goodies: Offer NFC business cards
During a trade show, Mary offers her visitors NFC business cards with her brand as goodies. This allows her to make herself known and retain the loyalty of his potential clients, who will be able to scan her NFC business card with their smartphone to access her website, her LinkedIn profile, her portfolio, etc. Mary can purchase her NFC media from any NFC media e-commerce site or order from Cardokey NFC Cards with an extremely long lifespan of up to 1 million writes and 40 years of vCard retention NFC or URL or network link. In this case, Cardokey allows you to create an NFC vCard with all of Mary’s contact details to offer to her visitors.
Tourist: NFC business cards in different languages
While traveling abroad, Tao uses Cardokey to create his NFC business card with his contact details in his native language. This allows him to easily introduce himself to the people he meets. In fact, they will be able to scan his vcard with their smartphone to see the information translated into their language. He can also use Cardokey to save URL links to websites or applications useful for his trip, such as tourist guides, maps, booking services, etc. In this case, Cardokey allows you to create an NFC business card with your contact details in your native language.
Family: An NFC business card collecting memories
During a family reunion, a family member uses Cardokey to store links to photos and memories on NFC media. Before leaving each other, everyone takes their NFC media. Later, they will be able to relive their life moments with their loved ones, who will simply scan the NFC vcards with their smartphone to view their images, videos, messages, etc. They will also be able to use Cardokey to create URL links to websites or applications that are important to them, such as associations, causes, passions, etc. In this case, Cardokey allows you to create an NFC business card with your photos and memories.
How to download and install Cardokey?
To use Cardokey, you need an NFC-enabled smartphone, i.e. one that has an NFC chip and can read and write NFC data. Most recent smartphones are NFC-enabled, but you can check your smartphone’s compatibility on the Cardokey website.
Cardokey is available in 14 languages (Arabic, Catalan, Chinese, German, English, French, Hindi, Italian, Japanese, Portuguese, Romanian, Russian, Ukrainian). You can download it in any country that accepts the Google play store or app store platform.
To download and install Cardokey on your smartphone, all you need to do is follow these steps:
- Go to the Google Play Store or App Store and search for “Cardokey”.
- Select the app and click “Install”.
- Open the app and agree to the terms of use.
- Start creating your NFC business cards!
If you are interested in Cardokey, feel free to download it now by clicking on the following link:
In short
Cardokey is a free, user-friendly, eco-conscious app compliant with global privacy and data protection laws. It allows you to create NFC vCard business cards for all Android and iPhone NFC phones. It also lets you reuse and customize NFC media.
Cardokey is the NFC business card that connects you without revealing you. It lets you exchange your contact details without contact and without paper. It offers you a free, unlimited, simple and eco-designed solution.
Definition of technical terms:
- NFC (Near Field Communication): a technology that allows two devices to communicate with each other when they are close to each other.
- NDEF (NFC Data Exchange Format): a standard format for storing and exchanging data on NFC media.
- vCard: a digital format for storing and sharing contact information, such as name, phone number, email address, etc.
- Air Gap