How to Shield Your Digital Life from Keystroke Loggers: An Expert’s Guide
Defending Against Keyloggers is essential to protect your sensitive data. Keyloggers are silent tools that record every keystroke, exposing sensitive data to cyber threats. This guide explores high-profile breaches, innovative attack methods, and strategic defenses. It offers a comprehensive strategy to secure your sensitive data against these ubiquitous threats and provides effective solutions for enhanced protection. Stay informed and proactive with our expert advice in the constantly evolving cybersecurity landscape.
FAQ
What’s the Difference Between Software and Hardware Keyloggers?
Software keyloggers
These programs run discreetly in the background of the computer, recording every keystroke. They can be installed through malware or accidentally downloaded together with other applications. These keyloggers can not only capture keystrokes but also record screenshots and monitor internet activity.
Hardware keyloggers
These devices are usually small physical devices that connect between the keyboard and the computer’s USB or PS/2 port. They log keystrokes directly from the keyboard before the information is transmitted to the operating system. Their physical presence makes them detectable by visual inspection, but they are often very discreet and difficult to notice.
Is a keylogger a virus?
No, keyloggers are tools that can be used for both legitimate monitoring and malicious activities.
How do I know if I am infected with a keylogger?
Regular scans with updated antivirus software and monitoring for unusual system behavior are effective detection methods.
Can mobile devices get infected with keyloggers?
Although less common, mobile devices can indeed be compromised by keyloggers, especially through malicious apps or compromised security software.
What is the best way to protect my devices from keyloggers?
Using comprehensive security solutions like PassCypher and maintaining vigilant cybersecurity practices are your best defenses.
What are the best immediate actions to take if a keylogger is detected?
Disconnect from the internet, change all passwords on a secure device, and use a trusted malware removal tool to clean the infected system.
What is the difference between software and hardware keyloggers?
Software keyloggers
These programs run discreetly in the background of the computer, recording every keystroke. They can be installed through malware or accidentally downloaded together with other applications. These keyloggers can not only capture keystrokes but also record screenshots and monitor internet activity.
Hardware keyloggers
These devices are usually small physical devices that connect between the keyboard and the computer’s USB or PS/2 port. They log keystrokes directly from the keyboard before the information is transmitted to the operating system. Their physical presence makes them detectable by visual inspection, but they are often very discreet and difficult to notice.
How can I detect a keylogger on my computer?
Detection of software keyloggers:
- Use of antivirus and anti-malware software: Make sure your security software is up to date and perform regular scans. Many modern security software programs are equipped to detect keyloggers.
- System Process Monitoring: Use the Task Manager to monitor running processes. Unknown or suspicious processes that use high resources can be signs of a keylogger.
- Checking startup programs: Review the programs that launch when your computer starts. Keyloggers can set up an auto-start to stay active.
Hardware Keylogger Detection:
- Physical inspection: Regularly check the connections between your keyboard and your computer. Look for any unusual devices plugged into the USB or PS/2 port where the keyboard connects.
- Check for unknown devices: Monitor your device manager for any unknown or unrecognized hardware that might be connected to your system.
What are the best practices to protect against keyloggers?
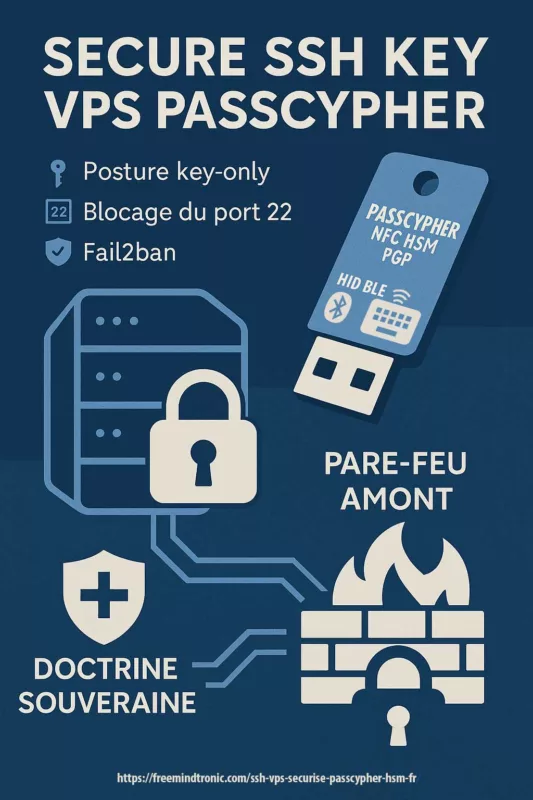
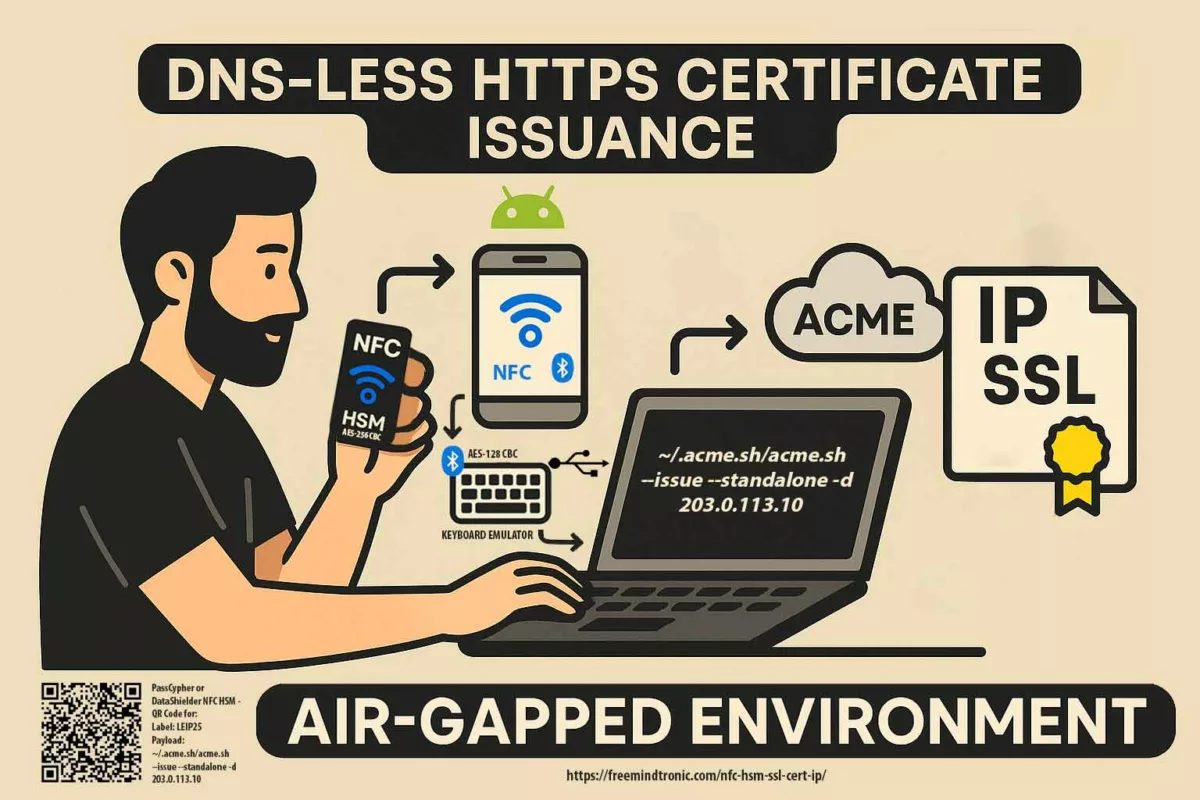
Use our password management software
PassCypher HSM PGP in its free or advanced version or hardware version with PassCyppher NFC HSM to secure your NFC Android phone as well
Robust security
Install and maintain trusted antivirus software that includes protection against keyloggers.
Update your operating system and applications
Regular updates often fix security vulnerabilities that could be exploited by keyloggers.
Be careful with downloads
Avoid downloading software from unverified sources. Favor the official websites of the publishers to reduce the risk of downloading malicious applications.
Education and awareness
Learn how to recognize phishing attempts and other techniques used to install keyloggers. Don’t click on suspicious links or attachments in emails or messages.
Use of password managers
Password managers can autofill your login information without you having to hit the keys, reducing the risks associated with software keyloggers.
Multi-factor authentication (MFA)
Use PassCypher NFC HSM also handles 2FA/MFA OTP two-factor authentication keys (TOTP and HOTP) when possible, especially for important accounts like email and bank accounts. This adds an extra layer of security that doesn’t rely solely on passwords.
Use robust security software
Install and maintain trusted antivirus software that includes protection against keyloggers.
Update your operating system and applications
Regular updates often fix security vulnerabilities that could be exploited by keyloggers.
Be careful with downloads
Avoid downloading software from unverified sources. Favor the official websites of the publishers to reduce the risk of downloading malicious applications.
Education and awareness
Learn how to recognize phishing attempts and other techniques used to install keyloggers. Don’t click on suspicious links or attachments in emails or messages.
Use of password managers
Password managers can autofill your login information without you having to hit the keys, reducing the risks associated with software keyloggers.
Software keyloggers
These programs run discreetly in the background of the computer, recording every keystroke. They can be installed through malware or accidentally downloaded together with other applications. These keyloggers can not only capture keystrokes but also record screenshots and monitor internet activity.
Hardware keyloggers
These devices are usually small physical devices that connect between the keyboard and the computer’s USB or PS/2 port. They log keystrokes directly from the keyboard before the information is transmitted to the operating system. Their physical presence makes them detectable by visual inspection, but they are often very discreet and difficult to notice.
No, keyloggers are tools that can be used for both legitimate monitoring and malicious activities.
Regular scans with updated antivirus software and monitoring for unusual system behavior are effective detection methods.
Although less common, mobile devices can indeed be compromised by keyloggers, especially through malicious apps or compromised security software.
Using comprehensive security solutions like PassCypher and maintaining vigilant cybersecurity practices are your best defenses.
Disconnect from the internet, change all passwords on a secure device, and use a trusted malware removal tool to clean the infected system.
Software keyloggers
These programs run discreetly in the background of the computer, recording every keystroke. They can be installed through malware or accidentally downloaded together with other applications. These keyloggers can not only capture keystrokes but also record screenshots and monitor internet activity.
Hardware keyloggers
These devices are usually small physical devices that connect between the keyboard and the computer’s USB or PS/2 port. They log keystrokes directly from the keyboard before the information is transmitted to the operating system. Their physical presence makes them detectable by visual inspection, but they are often very discreet and difficult to notice.
Detection of software keyloggers:
- Use of antivirus and anti-malware software: Make sure your security software is up to date and perform regular scans. Many modern security software programs are equipped to detect keyloggers.
- System Process Monitoring: Use the Task Manager to monitor running processes. Unknown or suspicious processes that use high resources can be signs of a keylogger.
- Checking startup programs: Review the programs that launch when your computer starts. Keyloggers can set up an auto-start to stay active.
Hardware Keylogger Detection:
- Physical inspection: Regularly check the connections between your keyboard and your computer. Look for any unusual devices plugged into the USB or PS/2 port where the keyboard connects.
- Check for unknown devices: Monitor your device manager for any unknown or unrecognized hardware that might be connected to your system.
Use our password management software
PassCypher HSM PGP in its free or advanced version or hardware version with PassCyppher NFC HSM to secure your NFC Android phone as well
Robust security
Install and maintain trusted antivirus software that includes protection against keyloggers.
Update your operating system and applications
Regular updates often fix security vulnerabilities that could be exploited by keyloggers.
Be careful with downloads
Avoid downloading software from unverified sources. Favor the official websites of the publishers to reduce the risk of downloading malicious applications.
Education and awareness
Learn how to recognize phishing attempts and other techniques used to install keyloggers. Don’t click on suspicious links or attachments in emails or messages.
Use of password managers
Password managers can autofill your login information without you having to hit the keys, reducing the risks associated with software keyloggers.
Multi-factor authentication (MFA)
Use PassCypher NFC HSM also handles 2FA/MFA OTP two-factor authentication keys (TOTP and HOTP) when possible, especially for important accounts like email and bank accounts. This adds an extra layer of security that doesn’t rely solely on passwords.
Use robust security software
Install and maintain trusted antivirus software that includes protection against keyloggers.
Update your operating system and applications
Regular updates often fix security vulnerabilities that could be exploited by keyloggers.
Be careful with downloads
Avoid downloading software from unverified sources. Favor the official websites of the publishers to reduce the risk of downloading malicious applications.
Education and awareness
Learn how to recognize phishing attempts and other techniques used to install keyloggers. Don’t click on suspicious links or attachments in emails or messages.
Use of password managers
Password managers can autofill your login information without you having to hit the keys, reducing the risks associated with software keyloggers.