Google Sheets Malware Threats
On August 29, 2024, Russian operatives from the SVR launched the Voldemort malware in an espionage campaign targeting Mongolian officials. This incident highlights the increasing role of malware in cyber warfare. By understanding these tactics, nations and organizations can effectively safeguard their data and systems against these emerging threats.
2025 Cyberculture
Constitution non codifiée du Royaume-Uni | souveraineté numérique & chiffrement
2025 Cyberculture EviLink
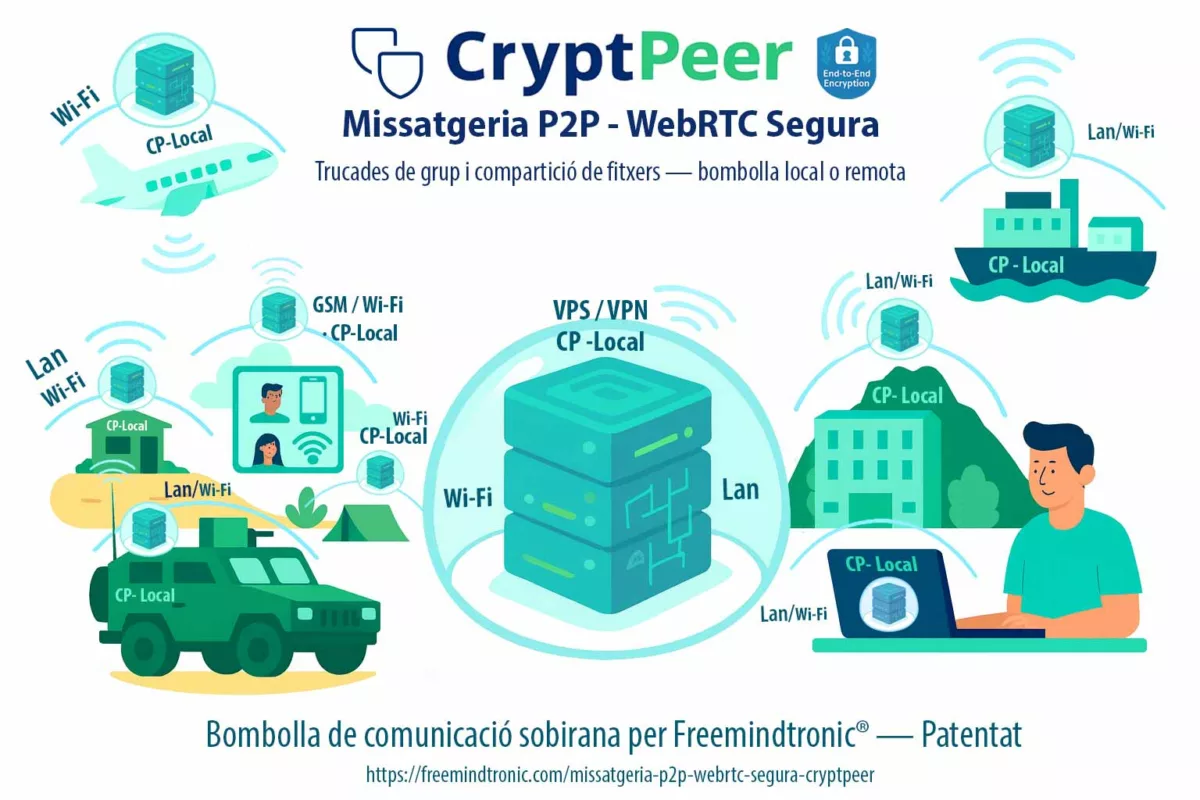
P2P WebRTC Secure Messaging — CryptPeer Direct Communication End to End Encryption
2025 Cyberculture Cybersecurity Digital Security EviLink
CryptPeer messagerie P2P WebRTC : appels directs chiffrés de bout en bout
2025 Cyberculture
Souveraineté individuelle numérique : fondements et tensions globales
2025 Cyberculture
Audit ANSSI Louvre – Failles critiques et réponse souveraine PassCypher
2025 Cyberculture
Sovereign Passwordless Authentication — Quantum-Resilient Security
Sheets Malware: A Growing Cybersecurity Concern
Google Sheets, a widely used collaboration tool, has shockingly become a playground for cybercriminals. Recent cybersecurity research uncovered a sophisticated malware campaign leveraging Google Sheets’ features for large-scale cyberespionage. The malware, dubbed “Voldemort,” is engineered to infiltrate systems, exfiltrate sensitive data, and execute commands remotely. It masks its malicious activities within normal Google Sheets operations, making detection extremely challenging.
Understanding the Google Sheets Malware”
The emergence of Google Sheets malware signals a major shift in cybercriminal strategies. While Google Sheets was once seen as a simple collaboration tool, it is now exploited for cyberespionage operations. The malware uses the cloud-based and collaborative nature of Google Sheets, which complicates detection.
How Google Sheets Malware Operates
Voldemort malware inserts itself into Google Sheets, allowing it to perform its tasks discreetly. It executes several key actions, making it a powerful tool for cybercriminals.
Exfiltrating Sensitive Data with Google Sheets Malware
Voldemort is designed to infiltrate targeted systems and steal sensitive data, including login credentials, personal information, and trade secrets. By using Google Sheets, the malware can exfiltrate this data unnoticed, blending seamlessly with regular operations. Security systems often fail to detect this unauthorized activity because it looks legitimate.
Remote Command Execution Through Google Sheets Malware
Beyond data theft, Voldemort enables cybercriminals to execute remote commands on infected machines. Google Sheets becomes their command center, where attackers send instructions to the malware, enabling it to perform specific actions. This method conceals malicious activity within legitimate network traffic.
The Appeal of Google Sheets for Cybercriminals
Google Sheets has become an attractive tool for cybercriminals for several reasons:
- Simplicity of Use: Google Sheets is intuitive and widely understood. This ease of use makes it easy for attackers to set up their malicious infrastructure.
- Global Reach: With millions of users globally, Google Sheets provides a vast attack surface. This widespread use increases the potential impact of any malware deployed within it.
- Difficulty of Detection: Malicious activities conducted through Google Sheets can easily blend in with legitimate use. This complicates efforts to identify and mitigate threats effectively.
The Consequences of Google Sheets Malware Attacks
The discovery of Google Sheets malware like Voldemort highlights the constant evolution of cyber threats. The consequences of such attacks can be severe. These include the theft of sensitive data, significant reputational damage, business disruptions, and substantial financial losses. This threat underscores the importance of vigilance and robust cybersecurity practices.
Discovery and Updates on the Voldemort Malware Campaign
In August 2024, Proofpoint researchers uncovered a sophisticated cyberespionage campaign that utilized Google Sheets as a Command-and-Control (C2) platform. The malware, named Voldemort, primarily targeted sectors such as insurance, aerospace, and finance. Over time, it became evident that the campaign affected more than 70 organizations across 18 verticals, including healthcare and transportation.
Since its discovery, Voldemort gained attention for its advanced phishing tactics, including sending over 20,000 emails impersonating tax authorities from various countries such as the U.S., U.K., France, Germany, and Japan. These emails contained Google AMP Cache URLs, which redirected victims to a landing page that examined the user’s operating system. If the system ran Windows, the malware used the search-ms protocol and disguised PDF files to initiate DLL side-loading for system infection
One of Voldemort’s most unique features is its use of Google Sheets to exfiltrate data and execute remote commands. This method blends malicious activity with legitimate operations, making it extremely difficult for traditional security tools to detect. By storing stolen data in Google Sheets cells, the malware ensures a low detection profile, making it highly effective in evading security protocols .
Additionally, the malware exploits legitimate software like Cisco WebEx via DLL side-loading and executes Python scripts from remote WebDAV shares to collect system information, steal credentials, and execute malicious commands
Researchers recommend mitigating future attacks by:
- Blocking suspicious URLs,
- Monitoring for unusual network traffic,
- Restricting PowerShell execution,
- And implementing advanced defenses like sandboxing and encryption to protect against this and similar advanced threats.
For more information, you can access the full Proofpoint report titled The Malware That Must Not Be Named: Suspected Espionage Campaign Delivers ‘Voldemort’.
The Role of Artificial Intelligence in Cybersecurity
AI is increasingly playing a dual role in cybersecurity. Cybercriminals are using AI to develop more advanced malware, customizing attacks based on their targets’ behaviors and automating large-scale attacks. On the other hand, cybersecurity professionals are also leveraging AI to enhance threat detection and response capabilities, which helps counter these threats more effectively.
Challenges Posed by Remote Work and Google Sheets Malware
Remote work has heightened the risks of using tools like Google Sheets. Employees often access sensitive data from unsecured personal devices, expanding the security perimeter. This makes it harder to protect against malware like Voldemort. Additionally, remote work environments often lead to lower employee vigilance, increasing the risk of human error, which attackers can exploit.
Advanced Solutions for Protecting Against Google Sheets Malware
As malware like Voldemort continues to evolve and exploit collaborative tools such as Google Sheets, it’s crucial to implement advanced security solutions that offer robust protection. Freemindtronic Andorre provides a range of cutting-edge tools designed to counter cyberespionage, identity theft, and data breaches. These solutions help safeguard users and organizations from sophisticated threats like the Voldemort malware, which employs phishing, malicious URLs, and command-and-control tactics through Google Sheets.
PassCypher NFC HSM: Comprehensive Protection Against Phishing and Credential Theft
PassCypher NFC HSM is a cutting-edge identity and password manager that offers quantum-secure encryption and robust protection against phishing, typosquatting, and credential theft.
- Automatic URL Sandboxing: PassCypher NFC HSM automatically registers the original website during the first login and verifies future logins against the saved URL, preventing redirections to malicious sites. This protects users from phishing tactics like those employed by the Voldemort malware.
- EviOTP Technology for Enhanced Authentication: PassCypher NFC HSM integrates EviOTP (NFC HSM TOTP & HOTP) technology, generating one-time passwords for two-factor authentication (2FA). This ensures additional security, even if credentials are compromised.
- Auto-Fill and Contactless Login: Using NFC-enabled Android devices, PassCypher NFC HSM allows secure, contactless login and auto-fill of credentials without storing them locally. This makes it impossible for malware like Voldemort to intercept or steal login information, as all NFC communications are encrypted.
Pairing with PassCypher HSM PGP/Free for Extended Protection on Computers
By pairing PassCypher NFC HSM with PassCypher HSM PGP Free or PassCypher HSM PGP over a local network, you unlock additional security features tailored for use on computers. This combination actively enhances protection by incorporating EviBITB technology, which effectively counters Browser-in-the-Browser (BITB) attacks. Furthermore, it continuously monitors the Darknet for any signs of compromised credentials, immediately alerting you if your credentials appear in pwned databases.
This extended layer of protection proves especially valuable when using PassCypher NFC HSM for auto-fill operations on computers. It ensures that your credentials remain secure across multiple platforms, shielding you from phishing attacks and Voldemort-style credential theft.
DataShielder NFC HSM: Comprehensive Data Encryption and Protection
DataShielder NFC HSM provides advanced encryption and secure key management, protecting data from sophisticated threats like Voldemort:
- Upfront Encryption and Contactless Security: DataShielder NFC HSM ensures that data is encrypted at the source, before it is transmitted or stored. This upfront encryption eliminates any risk of exfiltration in plaintext by malware. The contactless security feature adds another layer of protection for mobile work environments.
- Pairing with PassCypher HSM PGP for Extended Security: When paired with PassCypher HSM PGP, DataShielder NFC HSM benefits from BITB protection, Darknet monitoring, and sandbox URL security. This allows for enhanced cross-device protection, ensuring that data remains secure even if accessed on different platforms.
By deploying these advanced solutions, organizations and individuals can effectively protect against Google Sheets malware like Voldemort and mitigate the risk of cyberattacks that target credentials, personal data, and sensitive information.
These products are available in France through AMG PRO, providing easy access to top-tier security solutions.
Legal Implications of Google Sheets Malware Attacks
Malware attacks targeting collaborative tools like Google Sheets raise several legal questions:
- Responsibility of Software Vendors: Are vendors like Google responsible for security vulnerabilities in their products that are exploited by cybercriminals?
- Corporate Responsibility: To what extent are companies liable for data breaches resulting from malware attacks on tools like Google Sheets?
- Data Protection Compliance: How can organizations balance the need for collaboration with stringent data protection requirements?
Best Practices for Protecting Against Google Sheets Malware
To protect against Google Sheets malware, individuals and organizations should implement the following security measures:
- Be Wary of Suspicious Emails and Links: Always verify the authenticity of email senders before opening attachments or clicking on links.
- Use Strong Passwords and Two-Factor Authentication: Protect accounts with strong, unique passwords and enable two-factor authentication (2FA) for an added layer of security.
- Regularly Update Software: Ensure that all software, including browsers and operating systems, is up-to-date with the latest security patches.
- Deploy Reliable Security Tools: Use trusted antivirus and firewall solutions to protect against malware and other cyber threats.
- Raise Employee Awareness: Conduct regular cybersecurity training to educate employees on the risks of phishing, malware, and other threats. Simulate attacks to test their resilience and preparedness.
Securing Collaborative Tools in the Enterprise
To protect collaborative tools like Google Sheets, businesses must implement robust security measures. First, train employees regularly on cybersecurity risks and conduct simulations to ensure they are prepared. Then, enforce strict access controls by limiting privileges and requiring strong authentication. Additionally, ensure device and data security by encrypting sensitive information and updating systems regularly. Finally, monitor for suspicious activity and collaborate with vendors to stay informed about the latest threats and security patches.
Maintaining Vigilance and Adapting
As cyber threats like Voldemort evolve, it becomes essential for organizations and individuals to take action. By recognizing the tactics used in these attacks and implementing robust security measures, such as PassCypher and DataShielder, you can effectively counter these risks. Moreover, adopting these solutions ensures that your data remains secure in the face of increasingly sophisticated malware. Going forward, staying informed and continually improving your cybersecurity defenses will keep you one step ahead, safeguarding both your operations and sensitive information.