How Telegram Shapes the Information War in Ukraine
In this article, we explore how Telegram and Ukraine’s information warfare are intertwined. We look at how the messaging app is influencing the Russia-Ukraine conflict, and how it can be used for good or evil. We also discuss the benefits and risks of using Telegram, as well as how security and freedom of expression can be enhanced with EviCypher NFC HSM technology.
How Telegram Influences the Conflict between Russia and Ukraine
Telegram and the information war in Ukraine are closely related. Telegram is a messaging app that offers users a secure and confidential way to communicate, thanks to its end-to-end encryption system. It has a large user base around the world, especially in Eastern Europe, where it plays a vital role in the information war between Russia and Ukraine.
Telegram’s Usage in Ukraine: Updated Statistics
Popularity and Download Trends
According to the report of the research company SimilarWeb, Telegram is the second most downloaded messaging app in Ukraine, after Viber, with 3.8 million downloads in 2021. It is also the fourth most used app in terms of time spent, with an average of 16 minutes per day. Telegram has about 10 million active users in Ukraine, which is almost a quarter of the country’s population.
Telegram’s Role in Ukrainian Media Landscape
Telegram is particularly appreciated by Ukrainians for its channel functionality, which allows to broadcast messages to a large audience. Some of these channels have become influential but controversial sources of information, as their owners and sources are often unknown. Among the most popular channels in Ukraine, we can mention:
- @Zelenskyi, the official channel of President Volodymyr Zelensky, which has more than 2 million subscribers. It publishes announcements, speeches, interviews and videos of the head of state. It was created in 2019, during Zelensky’s election campaign, who was then an actor and a comedian.
- @NashyGroshi, the channel of the journalistic project “Our Money”, which has more than 1.5 million subscribers. It publishes investigations, reports and analyses on corruption, abuse of power, political scandals and judicial cases in Ukraine. It was created in 2008, by journalist Denys Bihus, who received several awards for his work.
- @Resident, the channel of blogger and activist Anatoliy Shariy, which has more than 1.3 million subscribers. It publishes comments, criticisms and sarcasms on the political and social news in Ukraine. He is known for his pro-Russian, anti-European and anti-government positions. He is currently in exile in Spain, where he is wanted by the Ukrainian justice for high treason and incitement to hatred.
These channels illustrate the diversity and complexity of the Ukrainian media landscape, which is marked by the conflict with Russia, the democratic transition, the fight against corruption and the polarization of society. They are also a reflection of the issues and challenges related to the use of Telegram, which can be both a tool of communication, information and manipulation.
Oleksiy Danilov’s Stance on Telegram’s Usage in Ukraine
Concerns Over National Security
Oleksiy Danilov is the secretary of the National Security and Defense Council of Ukraine, the body responsible for coordinating and controlling the activities of the executive bodies in the fields of national security and defense. He is also the head of cybersecurity of the country, and in this capacity, he expressed his reservations about the use of Telegram by Ukrainians. In February 2022, he stated that some anonymous and manipulative Telegram channels represented a threat to national security, and that they should be de-anonymized and regulated. He particularly targeted the channel @Resident, which broadcasts pro-Russian and anti-Ukrainian comments, and which is suspected of being linked to the Russian intelligence services. He also criticized the channel @Zelenskyi, which according to him, is not controlled by the Ukrainian president, but by advisers who seek to influence his policy.
Debating Telegram’s Influence in Ukraine
These statements provoked mixed reactions in Ukraine. Some supported Danilov’s position, believing that it was necessary to fight against misinformation and propaganda that undermine the sovereignty and democracy of the country. Others denounced an attempt at censorship and an attack on freedom of expression, recalling that Telegram was one of the few spaces where Ukrainians could access independent and diverse information.
How Telegram Influences the Information War in Ukraine
The Benefits and Risks of End-to-End Encryption
Telegram is a messaging app that lets you send messages, photos, videos, documents, and make voice and video calls. Its privacy policy is based on data encryption and non-cooperation with authorities. You can also create groups and channels that can reach thousands or millions of users.
End-to-end encryption is a technology that makes sure only the people in a conversation can read the messages, not even the service provider. Telegram has this option, but it is not on by default. You have to choose it for each chat, by switching to the “secret chat” mode. However, Telegram’s encryption is not based on standard protocols, and security experts have found some flaws.
Anonymous Channels and Their Impact on the Ukrainian Conflict
The channels are spaces where an administrator can send messages to a large audience. They can be public or private, and they can have millions of followers. Some channels are influential but controversial sources of information, as their owners and sources are often unknown. The channels can spread misinformation, propaganda, fake news, or violence.
Telegram and Russian propaganda have a strong connection, as many pro-Russian channels use the app to influence the public opinion in Ukraine and other countries. Telegram and the Ukrainian resistance also use the app to communicate and organize their actions against the Russian aggression.
Bots, Payment Services and Unique Usernames: A Double-Edged Sword
Bots are programs that interact with users. They offer services, information, or entertainment. Anyone can create them. They can be part of chats or channels. Bots can be helpful or harmful. They can collect personal data, send spam, or spread viruses.
Payment Services: Handy or Dishonest?
You can also use payment services via Telegram. These features use third-party platforms, such as Stripe or Apple Pay. They need bank or credit card information. Payment services can be handy or dishonest. They can steal sensitive data, scam users, or fund illegal activities.
Unique Usernames: Fun or Troublesome?
Another feature of Telegram is the unique usernames. They let users contact each other easily, without sharing their phone number. Users can create and change them at any time. Unique usernames can be fun or troublesome. They can enable harassment, identity theft, or account sale.
These features of Telegram raise issues of cybersecurity, privacy, end-to-end encryption, and application security. They can be used by bad actors, who want to harm Ukraine or its people. They can also be regulated by the authorities, who want to control the information or access the data of the users.
Telegram and the Information War in Ukraine: A Challenge
One of the main challenges of Telegram and the information war in Ukraine is to balance the freedom of expression and the protection of national security. Telegram and the Ukrainian conflict are closely intertwined. The app is used by both sides to communicate, inform, and influence. Telegram and Russian propaganda have a strong connection. Many pro-Russian channels use the app to sway the public opinion in Ukraine and other countries. Telegram and the Ukrainian resistance also use the app to coordinate and organize their actions against the Russian aggression. Telegram and cybersecurity in Ukraine are also crucial. The app can be a source of threats or a tool of defense.
Telegram VS Other Messaging Apps: A Comparative Analysis
WhatsApp: Popular but Questionable Confidentiality
WhatsApp is the most popular messaging app in the world, with more than 2 billion users. It offers end-to-end encryption by default for all conversations, which guarantees the protection of data. However, it belongs to Facebook, which has a dubious reputation in terms of respect for privacy, and which has raised fears about the sharing of data with other applications of the group. WhatsApp is also subject to the requests of the authorities, who can demand access to the metadata, such as the phone number, the IP address or the location of the users.
Signal: High Security but Limited User Base
Signal is a messaging app that claims to be the most secure and confidential on the market. It also offers end-to-end encryption by default for all conversations, and it does not collect any personal data. It is developed by a non-profit organization, which does not depend on advertising or investors. It is recommended by personalities such as Edward Snowden or Elon Musk. Signal is however less popular than WhatsApp or Telegram, with about 50 million users. It also offers fewer features, such as file sharing, information channels, bots or payment services.
Telegram: Innovative but Security Concerns
Telegram is between these two apps, offering more features than Signal, but less security than WhatsApp. Telegram allows users to choose the level of encryption and privacy they want, by opting for the “secret chat” mode or the “normal chat” mode. Telegram also allows users to enjoy innovative services, such as channels, bots, payments or unique usernames. However, Telegram also presents risks, such as fakes news, inappropriate content, privacy breaches or cyberattacks. Telegram is therefore an app that offers advantages and disadvantages, and that requires vigilance and discernment from users.
Telegram’s Global Perception and Regulation
Russia: Origin and Opposition
Russia is the country of origin of Telegram, but also its main adversary. The Kremlin tried to block the app in 2018, invoking reasons of national security and fight against terrorism. It demanded that Telegram provide it with the encryption keys to access the messages of the users, which Pavel Durov refused. It then ordered the telecom operators to block access to Telegram, but this measure proved ineffective, as Telegram used cloud servers to bypass the blocking. Many Russian users also use VPNs or proxies to access the app. In 2020, the Kremlin finally lifted the ban on Telegram, acknowledging its failure and stating that the app had cooperated with the authorities to remove extremist content. However, some observers suspect that Telegram made concessions to the Kremlin to lift the blocking, such as collaborating with the Russian services or censoring some channels.
France: Striving for Digital Regulation
France is a country that wants to be at the forefront of the regulation of digital platforms, especially in terms of fighting online hate. It adopted in 2020 a law that obliges the platforms to remove illegal content, such as incitement to violence, discrimination or terrorism, within 24 hours, under penalty of financial sanctions. This law also applies to messaging apps, such as Telegram, which must set up reporting and moderation mechanisms for content. France recognizes the right of users to privacy and end-to-end encryption, but it also asks the service providers to cooperate with the law enforcement to access the encrypted data when needed. France is also a country where Telegram is used by radical groups, such as jihadists or yellow vests, who take advantage of the app to organize, mobilize or defend themselves.
Ukraine: Balancing Utility and Risks
Ukraine is a country that has an ambivalent attitude towards Telegram, recognizing its usefulness, but also its dangers. On the one hand, Telegram is a source of information and a tool of resistance for many Ukrainians, who face the threat of Russian aggression and the challenges of democratic transition. On the other hand, Telegram is also a vector of misinformation and propaganda, which can undermine the sovereignty and stability of the country. Ukraine does not have a specific law to regulate Telegram, but it has some legal provisions to protect national security and public order, which can be used to restrict or block the app if necessary. Ukraine also cooperates with international organizations, such as the EU or NATO, to counter the cyber threats and the hybrid warfare that target the country.
EviCypher NFC HSM: Enhancing Telegram’s Security
The Role of Contactless Encryption Technology
One of the main challenges of using Telegram is to ensure the security and confidentiality of the data exchanged, especially in a context of information war. To meet this challenge, a possible solution consists of using EviCypher NFC HSM technology, which is a contactless encryption technology developed by Freemindtronic, an Andorran company specializing in the design of counter-espionage solutions implementing in particular contactless security with NFC technology. EviCypher NFC HSM uses two types of encryption algorithms for data:
- Symmetric encryption in AES-256 for data such as texts (messages), thanks to its sub-technology EviCrypt. It uses a unique key, which is randomly generated and segmented into several parts. This key is used to encrypt and decrypt messages with the AES 256-bit algorithm.
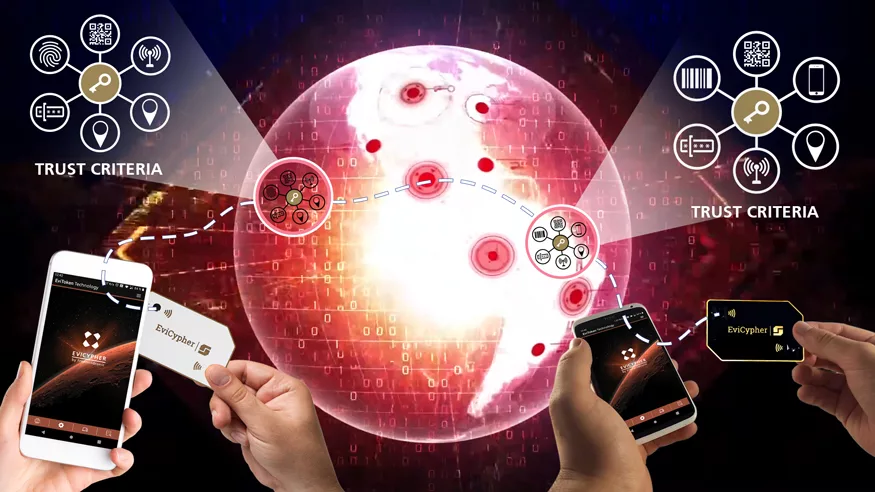
- Asymmetric encryption in RSA-4096 for symmetric encryption keys. It uses a pair of keys, which is generated and used from the NFC HSM device and which is based on the RSA 4096-bit algorithm. This pair of keys is used to share the symmetric key of at least 256 bits between the NFC HSM devices remotely, by encrypting the symmetric key with the public key of the recipient and decrypting the symmetric key with the private key of the recipient. The symmetric key is then stored and re-encrypted in the NFC HSM device of the recipient, with the trust criteria imposed by the sender if he has encapsulated them in the shared encryption key.
Practical Applications of EviCypher NFC HSM
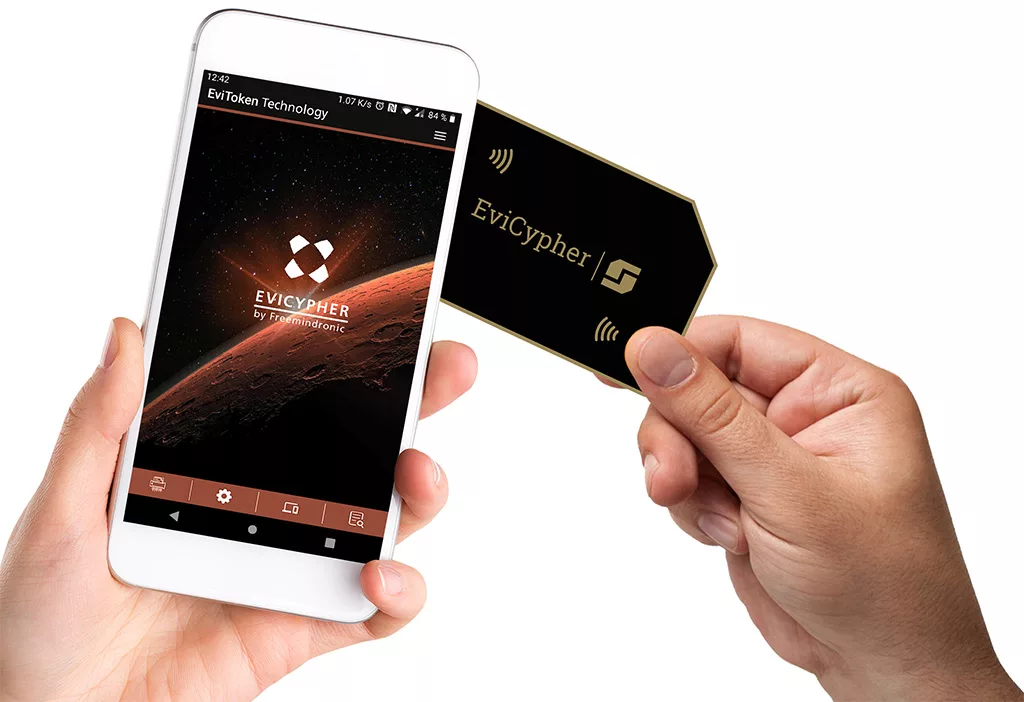
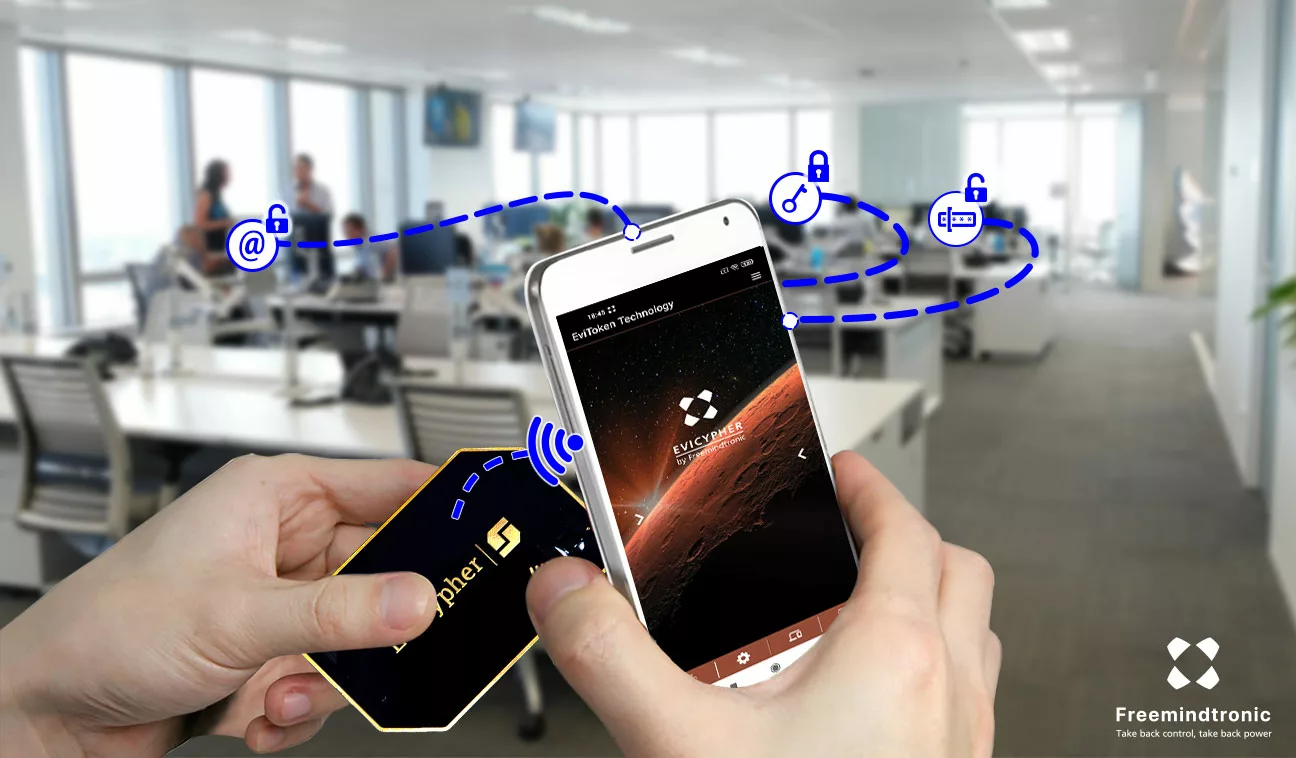
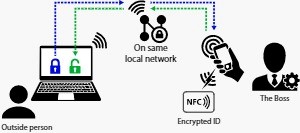
EviCypher NFC HSM is a technology that uses hardware security modules (HSM) to store and use encrypted secrets. It allows contactless encryption with the NFC communication protocol. You can integrate the NFC HSM into various media, such as a card, a sticker, or a key ring. Then, you can pair it with an NFC phone, tablet, or computer. This way, you can encrypt everything before using any messaging service, including Telegram. EviCypher NFC HSM also has anti-cloning, anti-replay, and counterfeit detection mechanisms. It is part of the DataShielder product range, which offers serverless and databaseless encryption solutions.
Telegram and the Ukrainian conflict
EviCypher NFC HSM is compatible with Telegram, a messaging app that influences the information war between Russia and Ukraine. It offers more security and confidentiality than Telegram’s end-to-end encryption, which is not based on recognized standards. It also gives you more flexibility and control than Telegram’s secret chat mode, as you can choose the trust criteria for the encryption keys. Moreover, it is more convenient and simple than Telegram’s normal chat mode, as you can encrypt and decrypt messages with a simple gesture.
Telegram and cybersecurity in Ukraine
EviCypher NFC HSM is a useful technology with Telegram, as it enhances the security and confidentiality of the data exchanged, especially in a context of information war. It is also a universal technology, as you can use it with any other messaging app, such as WhatsApp, Signal, Messenger, etc. It is also an innovative technology, as it uses the NFC communication protocol to perform contactless encryption, without requiring any connection or installation.
Concluding Insights on Telegram’s Role in Ukraine
In this article, we have seen how Telegram plays a vital role in the information war between Russia and Ukraine, and what issues and challenges there are in using this messaging app. We have also seen how the technology EviCypher NFC HSM can be a useful solution to enhance the security and confidentiality of the data exchanged with Telegram. We hope that this article has been informative and interesting for you, and that it has helped you to better understand the situation of Telegram in Ukraine and in other countries. Thank you for reading.
Overview of Cited Sources
Here are the sources of the article, which are valid, reliable, relevant and if possible official links that allow to justify and verify the statements made in this article:
- [Liga.net]: the news site that published the interview of Oleksiy Danilov on November 2, 2023, in which he expresses his concerns about Telegram.
- [NV.ua]: the news site that reported the statement of Oleksiy Danilov, who alerted the nation to the critical vulnerabilities of Telegram, on November 2, 2023.
- [RT – Pravda]: the Ukrainian news site that related the remarks of Oleksiy Danilov, who answered the questions of journalists during a press conference on November 3, 2023.
- [Number of Telegram Users in 2023? 55 Telegram Stats (backlinko.com)]: an article that gives figures on the use of Telegram in the world and in Ukraine.
- [NV.ua -NSDC]: the official website of the National Security and Defense Council of Ukraine, which published the press release of Oleksiy Danilov, who clarified his recent comments on Telegram, on November 15, 2023
- [Ukrainians turn to encrypted messengers, offline maps and Twitter amid Russian invasion]: an article that describes how Ukrainians use Telegram and other digital tools to protect themselves and get informed in the face of the Russian aggression.
- [Pravda – France 24]: the French news site that contains a video of the interview of Oleksiy Danilov with the journalist Gulliver Cragg, dated January 23, 2023.
- [NFC HSM Technology – Freemindtronic]: an article that explains the NFC HSM technologies and how they work.
- [EviCypher NFC HSM technology – Freemindtronic]: a page that contains articles and videos on the NFC HSM technologies.
- [FAQ for the Technically Inclined – Telegram APIs]: a page that provides technical information about the Telegram APIs and the MTProto protocol.





















 Fabrice Crasnier is the director of Research & Development departement of FREEMINDTRONIC. Freemindtronic, Andorran start-up designs and manufactures tailor-made solutions for its customers in the field of safety and cyber security of information systems and computer systems.
Fabrice Crasnier is the director of Research & Development departement of FREEMINDTRONIC. Freemindtronic, Andorran start-up designs and manufactures tailor-made solutions for its customers in the field of safety and cyber security of information systems and computer systems.

