Introduction to BitLocker Security
If you use a Windows computer for data storage or processing, securing it is critical. BitLocker provides full-volume encryption using the Advanced Encryption Standard (AES). This method ensures that your data is unreadable without a decryption key. The Trusted Platform Module (TPM) securely manages these keys. This security chip protects your data even when the system is powered off.
The TPM ensures device integrity by verifying the boot process. It only releases the encryption key if the boot code matches trusted values. For added security, BitLocker also supports multi-factor authentication by combining TPM with a personal PIN or a startup key on a USB drive.
Windows BitLocker integrates with TPM 2.0, providing robust encryption for Windows 10 and Windows 11 devices. By securing encryption keys in the TPM, BitLocker ensures protection against boot-level attacks. Devices that support TPM offer a higher level of security, reducing risks of unauthorized access.
Elevating Data Protection on Windows with BitLocker Security
Are you utilizing a Windows computer for personal or professional data storage and processing? Aiming to shield your information from theft, loss, or exposure risks during device disposal? Seeking a straightforward, effective security solution without additional software installations? BitLocker, integrated within Windows, provides a formidable solution.
BitLocker: A Cornerstone of Windows Security
It emerges as a key security feature in Windows, enabling the encryption of entire volumes — be it partitions or hard drives. By deploying robust encryption algorithms like the Advanced Encryption Standard (AES), BitLocker converts your data into a format unreadable to unauthorized individuals lacking the encryption key.
This encryption key is securely generated and stored by the Trusted Platform Module (TPM), a specialized security chip embedded in the motherboards of select computers. The TPM’s role extends to generating and storing encryption keys, digital signatures, boot measurements, and even biometric identifiers. Crucially, TPM 2.0 is mandated for the installation and operation of Windows 11, Microsoft’s latest operating system.
Moreover, the TPM assures device integrity when offline — that is, when your computer is shut down or in sleep mode. It assesses the boot code executed at device startup against a reference value within the TPM. A match allows the TPM to unlock the encryption key, facilitating normal device startup. A mismatch, however, results in the TPM securing the key, thereby thwarting the device’s boot process.
Further enhancing security, BitLocker can condition the normal startup process on the provision of a personal code (PIN) or the insertion of a removable device containing a startup key. These added authentication measures fortify BitLocker security, necessitating multi-factor authentication. Without the correct PIN or startup key at each boot, BitLocker retains the encryption key, preventing data access.
BitLocker in TPM-Only Mode: A Risky Shortcut
Relying solely on TPM-only mode may seem convenient, but it exposes your data to physical attacks. Without user interaction, it becomes easier for attackers to steal encryption keys using inexpensive tools. Researchers found vulnerabilities like faulTPM, which impacts AMD’s firmware-based TPM (fTPM). Attackers can manipulate these weaknesses to extract sensitive data from the system, jeopardizing BitLocker encryption security. These vulnerabilities show how important it is to add another layer of protection like a PIN or startup key.
Actionable Tips:
- Enable TPM with a PIN: This adds an extra layer of security to your encryption.
- Use Complex Passphrases: Opt for long, non-numerical passphrases to resist brute-force attacks.
While TPM-only mode offers convenience, adding a second layer of security through PINs is essential to counter physical tampering.
In This Article, Discover:
- BitLocker’s Mechanisms: Learn how BitLocker securely encrypts entire volumes.
- BitLocker Security Benefits: Explore how BitLocker strengthens data protection.
- Navigating BitLocker’s Vulnerabilities: Understand the risks to BitLocker and how to protect against them.
- BitLocker Activation and Configuration: Step-by-step guidance for setting up BitLocker on Windows.
- Enhancing BitLocker Security with EviPass NFC HSM, EviCypher NFC HSM, and EviKeyboard BLE: can enhance BitLocker’s defenses.
- Recent TPM 2.0 Vulnerabilities: Learn about the hidden risks related to CVE-2023-1017 and CVE-2023-1018.
Case Study: faulTPM and SRTM Vulnerabilities in Action
Recent attacks on TPMs that use Static Root of Trust for Measurement (SRTM) systems have shown how attackers can manipulate power states. These manipulations allow them to compromise the boot-up process. As a result, attackers can falsify the chain of trust and bypass BitLocker encryption protections.
Researchers have found that well-known vendors like Intel and Dell are especially vulnerable. Even devices using AMD’s firmware-based TPM (fTPM) are also at risk. These incidents highlight the need to take proactive steps to secure TPM-equipped devices.
Key Recommendations:
- For users seeking Windows TPM 2.0 vulnerability fixes, it’s essential to update your TPM firmware regularly to guard against threats like CVE-2023-1017 and CVE-2023-1018. These fixes often include critical patches that strengthen BitLocker’s defenses against potential attacks.
- Consider hardware with advanced protections, such as Intel’s Converged Security and Manageability Engine (CSME), which can mitigate many of these risks.
- Enable TPM remote attestation to detect tampering and ensure the security of your device’s integrity.
To mitigate these risks, it is crucial to update your TPM firmware regularly. For those looking for the best multi-factor authentication for BitLocker in 2024, combining TPM with a PIN or startup key provides unmatched protection against unauthorized access. Utilize startup keys or PINs to further secure your encrypted drives from physical tampering.
The Advantages of BitLocker for Protecting Data
With BitLocker, users enjoy extensive benefits for data security, such as:
- Preventing Unauthorized Data Access: Through advanced encryption and TPM-stored keys, BitLocker shields data against both software attacks and physical disk tampering.
- Securing Data on Disposed Devices: Ensuring data on discarded BitLocker-protected devices remains unreadable without proper encryption or authentication methods.
- Protection Against Device Theft or Loss: By requiring a PIN or startup key, BitLocker offers multi-factor authentication, significantly reducing unauthorized access risks.
- Reducing Exposure to Cyber Attacks: By encrypting sensitive data, BitLocker reduces exposure to threats from malware, ransomware, and phishing attacks. Encryption with AES-256 ensures your data remains secure, even if the system is compromised.
By integrating BitLocker into your data protection strategy, you enhance the security layer around sensitive information. This guide not only elucidates BitLocker’s significance and operational mechanics but also introduces “EviPass NFC HSM, EviCypher NFC HSM, and EviKeyboard BLE” as pivotal in advancing BitLocker security against diverse threats. Stay tuned for an in-depth exploration of these enhancements towards the article’s end.
To maximize this security, enable multi-factor authentication (MFA). Combining TPM with a PIN or startup key significantly reduces the risk of unauthorized access.
How to Solve BitLocker Recovery Mode Issues After the July 2024 Windows Update
In July 2024, Microsoft introduced changes to BitLocker’s default configuration through the KB5040442 update, adding Platform Configuration Register (PCR) 4 to the default Trusted Platform Module (TPM) measurements. This modification aimed to enhance system security but inadvertently caused widespread issues. Many users found their devices unexpectedly booting into BitLocker recovery mode after the update, leading to confusion and frustration.
Why Did This Happen?
The addition of PCR4 altered the way the TPM measured the system’s boot environment. Any changes to system firmware, bootloader configurations, or connected hardware could trigger a mismatch in the TPM’s measurements, forcing BitLocker to initiate recovery. This sudden shift highlighted a lack of user preparation and adequate documentation from Microsoft regarding the implications of the change.
Mitigating the Impact of PCR4 Changes
To address these issues and avoid recovery lockouts, users should consider the following:
- Prepare Recovery Keys: Always back up your BitLocker recovery key securely. Save it to a trusted location, such as your Microsoft account or an encrypted external drive.
- Review Update Implications: Before applying updates, review release notes to understand potential impacts on security configurations, particularly for critical services like BitLocker.
- Modify PCR Settings: Advanced users can customize PCR settings to exclude PCR4 from TPM measurements if it causes unnecessary lockouts. However, this should be done cautiously to maintain security integrity.
- Stay Updated: Microsoft has since acknowledged the issue and provided fixes in subsequent updates. Ensure your system remains updated with the latest patches.
Lessons Learned
The 2024 BitLocker update serves as a reminder of the delicate balance between advancing security and maintaining usability. Organizations and individual users alike must remain vigilant, ensuring proper preparations for updates that alter critical systems.
While BitLocker remains a robust encryption tool, events like the PCR4 update emphasize the importance of proactive security practices and clear communication between software providers and end-users. By understanding the potential impacts of updates and taking preventive measures, users can minimize disruptions while maintaining high security.
Latest BitLocker Vulnerabilities: CVE-2022-41099 and CVE-2024-38058
Recent discoveries have revealed critical vulnerabilities in BitLocker, underscoring the importance of proactive security measures.
CVE-2022-41099: A Persistent Risk
In November 2022, Microsoft identified a vulnerability (CVE-2022-41099) that allowed attackers to bypass BitLocker encryption, exposing sensitive data. The issue was addressed through the KB5012170 security update, released on November 8, 2022. However, as this case demonstrates, full mitigation required manual intervention to enable additional protections, highlighting the necessity of administrative diligence.
Patch details: KB5012170 November 2022 Update.
CVE-2024-38058: A New Threat
Disclosed in January 2024, CVE-2024-38058 represents another significant risk for BitLocker users. This vulnerability allows attackers to exploit weaknesses in encryption mechanisms, potentially leading to unauthorized data access. Microsoft released a fix through the KB5024487 update on January 10, 2024, urging users to apply the patch promptly.
Patch details: KB5024487 January 2024 Update.
Why These Vulnerabilities Matter
As these vulnerabilities highlight, BitLocker is not impervious to exploitation. They emphasize the dynamic nature of cybersecurity threats and the critical need for ongoing vigilance. Regular updates, combined with multi-layered defenses, are essential to mitigating such risks.
Given these risks, incorporating advanced tools like PassCypher and DataShielder becomes vital to reinforcing BitLocker against emerging vulnerabilities and physical exploits.
Strengthening BitLocker with DataShielder and PassCypher
To elevate BitLocker’s security, integrating solutions like DataShielder and PassCypher provides significant protection. DataShielder uses AES-256 encryption to safeguard data on various storage devices, while PassCypher offers contactless password management, making password breaches far less likely. These tools enhance the overall security framework, addressing weaknesses in BitLocker, particularly physical attacks.
BitLocker Security: Analyzing Attacks and Vulnerabilities in TPM and TPM 2.0
Introduction to BitLocker’s Encryption Technology
BitLocker is an integral encryption technology within Windows, designed to protect data on hard drives and removable media. Utilizing the Advanced Encryption Standard (AES), BitLocker secures data with a secret key. This key can be stored in a Trusted Platform Module (TPM), a security chip on the motherboard, or through alternative methods like passwords, PINs, USB keys, or certificates. While BitLocker significantly enhances protection against data theft, loss, and unauthorized system boot or code alterations, it is not without vulnerabilities. These include the necessity of recovery key backups, compatibility issues with certain hardware and software, and susceptibility to specific attack techniques. This article delves into the various attack possibilities and vulnerabilities associated with TPM and TPM 2.0, detailing their mechanisms, consequences, and countermeasures.
TPM 1.2: Security Functions and Vulnerabilities
The Trusted Platform Module (TPM) 1.2 offers security functions like random number generation, secure cryptographic key creation, and digital signatures. While it bolsters BitLocker data security, TPM 1.2 is vulnerable to several attack types:
Preventing Cold Boot Attacks on BitLocker Encryption Keys with TPM 2.0
Cold Boot attacks involve rebooting a TPM-enabled device to access and extract BitLocker encryption keys from RAM before it clears. These attacks expose BitLocker-encrypted data due to TPM 1.2’s lack of effective RAM clearing mechanisms and data decryption prevention without authentication.
How to Protect BitLocker from Cold Boot Attacks
Protecting BitLocker from Cold Boot attacks requires implementing the following strategies:
- Enable Memory Overwrite Requests (MOR): Activate the MOR bit in your system’s TPM settings. This ensures that RAM is automatically cleared during every system restart or shutdown, preventing attackers from accessing residual data.
- Physical Security Measures: Restrict physical access to your devices by using physical locks, safes, or secure storage locations. Limiting access significantly reduces the risk of Cold Boot exploits.
- Implement Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA): Combine TPM-based encryption with a personal PIN or startup key. This added layer of authentication ensures that even if encryption keys are exposed, they cannot be used without the secondary authentication factor.
- Upgrade to TPM 2.0: Transition to TPM 2.0, which introduces enhanced protections like “Lockout Mode” and improved memory management. These features significantly reduce the risks associated with Cold Boot attacks.
Cold Boot Attack Process
To further illustrate the mechanics of Cold Boot attacks and how TPM 2.0 mitigates their impact, refer to the diagram below:

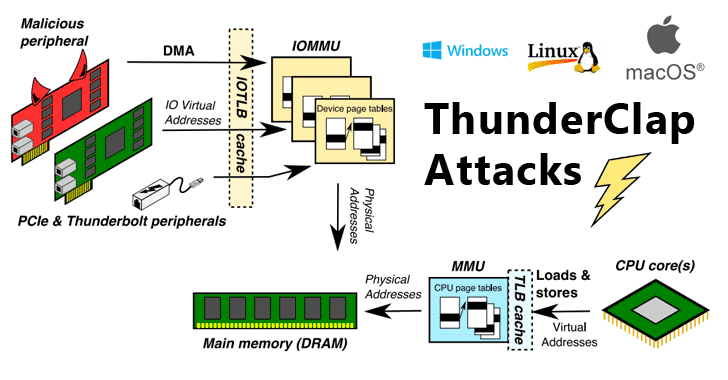
DMA Attacks on TPM 1.2

- This diagram explains the complex process of ThunderClap Attacks, which can bypass BitLocker Security measures on different operating systems.
DMA (Direct Memory Access) attacks use external devices to directly access the RAM of a TPM 1.2-enabled device, potentially reading or modifying BitLocker encryption keys. Such attacks compromise BitLocker security due to TPM 1.2’s inefficiencies in RAM protection and data integrity verification.
To defend against DMA attacks, it’s recommended to:
- Disable or secure device DMA ports, such as FireWire or Thunderbolt.
- Use a PIN or startup key to lock device booting, preventing access to BitLocker-encrypted data without proper credentials.
- Encrypt data on external storage devices to prevent them from becoming attack vectors.
RAM Analysis Attacks on TPM 1.2
RAM analysis attacks use specialized software or hardware to scan a device’s RAM for sensitive information, including BitLocker keys. TPM 1.2’s inability to protect RAM or verify data integrity leaves BitLocker-encrypted data vulnerable. Upgrading to TPM 2.0, which employs Device Encryption to bind data encryption to device hardware, mitigates these risks by not exposing the encryption key to RAM.
TPM 2.0: Enhanced Security Features and Vulnerabilities
TPM 2.0 introduces advanced security functions, including improved random number generation, secure cryptographic key creation, and digital signatures. These enhancements strengthen BitLocker security but do not render TPM 2.0 impervious to attacks:
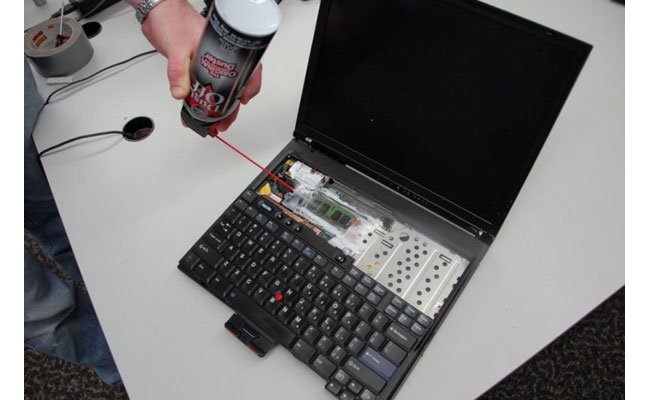
Cold Boot Attacks on TPM 2.0

- A cold spray can be used to preserve the data in the RAM after shutting down or restarting the system, exposing the BitLocker encryption keys to an attacker
Similar to TPM 1.2, TPM 2.0 is susceptible to cold boot attacks, where sensitive information like BitLocker keys can be extracted from RAM following a device reboot. TPM 2.0’s lack of effective RAM clearing mechanisms and data decryption prevention without authentication leaves BitLocker-encrypted data vulnerable. Utilizing TPM 2.0’s Lockout Mode, which limits decryption attempts and imposes delays between attempts, along with employing a PIN or startup key for device booting, enhances security against cold boot attacks.
For additional information on defending against cold boot attacks on TPM 2.0, explore:
Fault Injection Attacks on TPM 2.0
Fault injection attacks induce errors in TPM 2.0’s operation by altering physical conditions, such as voltage, temperature, or radiation, potentially causing information leaks or malfunctions. Common techniques include “glitching,” where electrical impulses disrupt TPM operations, revealing sensitive information or compromising data integrity. These vulnerabilities, tracked as CVE-2023-1017 and CVE-2023-1018, highlight the importance of updating TPM firmware and employing fault-resistant TPMs or physical isolation measures to protect against such attacks.
To further understand fault injection attacks on TPM 2.0, consider:
- “Fault Injection Techniques and Tools for Embedded Systems Reliability Evaluation,” presenting fault injection principles, methods, and tools.
- “Fault Injection Attacks on Cryptographic Devices: Theory, Practice, and Countermeasures,” analyzing fault injection attacks on cryptographic devices and offering effective countermeasures.
- A video on fault injection attacks on TPMs, demonstrating attack execution and prevention methods.
Phishing and Social Engineering Attacks on TPM 2.0
TPM 2.0 cannot safeguard against phishing or social engineering attacks that manipulate users into divulging sensitive information, such as passwords or encryption keys. These attacks use deceptive communication methods, posing as legitimate entities like Microsoft or technical support, to exploit user emotions, needs, or weaknesses. To defend against such attacks, never disclose personal information to unknown or suspicious entities, verify the credibility of sources before trusting them, and utilize TPM 2.0’s Lockout Mode to limit decryption attempts and impose delays between attempts. Additionally, educating users on phishing and social engineering techniques and reporting suspicious activities to authorities are crucial countermeasures.
For more insights into phishing and social engineering attacks on TPM 2.0, explore:
- “Phishing and Social Engineering,” describing attack characteristics, consequences, and prevention tips.
- “BitLocker Security FAQ,” answering common questions about BitLocker security and explaining TPM 2.0’s Lockout Mode defense against phishing and social engineering attacks.
- How to spot and avoid phishing scams, a tutorial on recognizing and avoiding phishing attempts, offering tools and services for protection.
The Bus Pirate Attack on TPM 2.0
To better understand how a Bus Pirate attack works, here’s a video made by security researcher Stacksmashing, who successfully extracted the BitLocker encryption key from a laptop using a Raspberry Pi Pico, a microcontroller that costs less than 10 euros. He then used Dislocker software to decrypt the hard drive with the obtained key.
Extracting the BitLocker key
The attacker opened the laptop case, located the TPM’s SPI port, and connected the Raspberry Pi Pico with wires. Using a Python script, he read and wrote to the TPM, and extracted the BitLocker encryption key. He then removed the hard drive from the laptop, connected it to another computer, and decrypted the data with the Dislocker software and the key. The Raspberry Pi Pico served as a tool to “sniff” BitLocker keys and to create a debugging and glitch attack tool.
The Pirate Bus
The Bus Pirate is a hardware hacking tool that communicates with various electronic bus protocols. It supports serial protocols such as 1-wire, 2-wire, 3-wire, UART, I2C, SPI and HD44780 LCD. It can access the TPM via the SPI port, which is a synchronous communication protocol that transfers data between a master and one or more slaves. The TPM is a slave that responds to the master’s commands.
Stacksmashing video
To understand how a Bus Pirate attack works, watch this video by security researcher Stacksmashing, who extracted the BitLocker encryption key from a laptop using a Raspberry Pi Pico, a cheap microcontroller. He then decrypted the hard drive with the Dislocker software and the key, showing how the attack can bypass BitLocker security.
TPM 2.0 vulnerabilities
The Bus Pirate attack exploits the SPI communication vulnerabilities of TPM 2.0, allowing attackers to intercept BitLocker encryption keys by “eavesdropping” on unencrypted communications. This method requires physical access to the target computer and specialized hardware, and can potentially enable arbitrary code execution and cryptographic information extraction.
Protective measures
To mitigate these risks, use TPM 2.0 models that resist fault injection attacks, improve the physical isolation of TPM 2.0, and protect the SPI port from unauthorized access or manipulation. This video demonstrates a Bus Pirate attack on TPM 2.0, where security researcher Stacksmashing extracted a BitLocker encryption key using a Raspberry Pi Pico. After the key extraction, Stacksmashing decrypted the hard drive with the Dislocker software and the key, revealing the attack’s ability to circumvent BitLocker security. To prevent such attacks, secure the TPM’s SPI port physically, update the TPM firmware regularly, and use tamper-evident seals to detect any unauthorized access. Moreover, implement SPI firewalls, update security patches, follow the principle of least privilege, enforce strong password policies, use multi-factor authentication, and consider physical security measures to avoid unauthorized access.
BitLocker Security Vulnerabilities: Navigating the Risks
TPM 2.0 has been affected by critical buffer overflow vulnerabilities (CVE-2023-1017 and CVE-2023-1018), which allow local attackers to access or modify protected data. These flaws expose sensitive cryptographic keys used by BitLocker, making data vulnerable to unauthorized access.
For example, Lenovo devices using Nuvoton TPM chips were among the systems impacted by this vulnerability. Attackers could bypass TPM protections by sending maliciously crafted commands, causing data corruption or code execution within the TPM. These attacks can go undetected, even by robust security measures.
Understanding BitLocker encryption vulnerabilities and TPM 2.0 weaknesses is crucial for securing your Windows computer. This section explores how to mitigate risks and implement data encryption best practices, ensuring robust protection.
Emphasize that these flaws aren’t just theoretical risks, but tangible weaknesses in widely used systems.
Brute Force Attacks on TPM and TPM 2.0
Brute force attacks attempt to guess passwords or encryption keys by systematically testing all possible combinations. Such attacks can compromise BitLocker security, as TPM and TPM 2.0 lack mechanisms to effectively limit or slow down authentication attempts. To counter brute force attacks, use long and complex passwords or keys, employ TPM 2.0’s Lockout Mode to restrict decryption attempts and impose delays between attempts, and educate users on recognizing and reporting suspicious brute force attack attempts.
By understanding and addressing the vulnerabilities associated with TPM and TPM 2.0, users can significantly enhance BitLocker’s encryption effectiveness. Implementing technological countermeasures, updating system firmware, and educating users on potential threats are crucial steps in fortifying BitLocker’s defenses against a range of attack methodologies.
Exploiting Secure Boot: CVE-2023-21563 and Its Impact on BitLocker
In 2023, a critical vulnerability labeled CVE-2023-21563 highlighted weaknesses in Secure Boot and its interaction with BitLocker encryption. This flaw enables attackers to exploit legacy bootloader mechanisms, bypass Secure Boot protections, and access encrypted data.
How Does CVE-2023-21563 Work?
- Bypassing Secure Boot Mechanisms: Secure Boot ensures that only verified bootloaders run on a device. However, CVE-2023-21563 allows attackers to load outdated and vulnerable bootloaders, circumventing security protocols.
- Extracting BitLocker Keys: Once Secure Boot is compromised, attackers can extract BitLocker encryption keys from memory. These keys are vital for decrypting encrypted volumes, rendering the data unprotected.
- Physical Access Requirement: Successful exploitation requires physical access to the target device, allowing attackers to manipulate BIOS/UEFI settings and introduce malicious bootloaders.
The Impact of CVE-2023-21563
- Compromised Data Protection: Once attackers retrieve encryption keys, they can decrypt sensitive data on BitLocker-protected drives.
- Real-World Exploits: Security researchers have demonstrated successful exploits of this vulnerability on Windows 10 and 11 systems, exposing the need for proactive defenses.
Mitigation Strategies
- Update Secure Boot Databases: Regularly update Secure Boot revocation lists to block known vulnerable bootloaders.
- Secure BIOS/UEFI Settings:
- Use strong administrative passwords for BIOS/UEFI access.
- Disable legacy boot options to limit exposure to outdated mechanisms.
- Strengthen BitLocker: Combine BitLocker with a startup PIN or USB key for added authentication layers. Regularly update TPM firmware to address emerging threats.
- Enable Remote Attestation: Remote attestation tools can detect unauthorized changes to Secure Boot configurations, providing additional security insights.
Why CVE-2023-21563 Matters
This vulnerability underscores the interconnected nature of security mechanisms like Secure Boot, TPM, and BitLocker. Any compromise in one layer can cascade, exposing encrypted data and undermining overall system integrity.