APT44 QR Code Phishing: How Russian Hackers Exploit Signal
APT44 (Sandworm), Russia’s elite cyber espionage unit, has launched a wave of QR Code Phishing attacks targeting Signal Messenger, leading to one of the largest Signal security breaches to date. Exploiting the growing use of QR codes, these state-sponsored cyber attacks compromised over 500 accounts, primarily within the Ukrainian military, media, and human rights communities. This article explores how QR code scams have evolved into sophisticated espionage tools and offers actionable steps for phishing prevention.
APT44 Sandworm: The Elite Russian Cyber Espionage Unit
Unmasking Sandworm’s sophisticated cyber espionage strategies and their global impact.
APT44, widely recognized as Sandworm, has been at the core of several global cyber espionage operations. The group’s latest method — QR code phishing — targets platforms trusted for privacy, exploiting their vulnerabilities to gain unauthorized access.
Specifically, Russian groups, such as UNC5792 and UNC4221, use malicious QR codes to link victims’ Signal accounts to attacker-controlled devices, enabling real-time interception of messages.
-
- Revealed by: Google Threat Analysis Group
- Targeted Platform: Signal Messenger
- Primary Targets: Ukrainian Military, Journalists, and Human Rights Activists (CERT-UA)
How APT44 Uses QR Codes to Infiltrate Signal
Breaking down APT44’s phishing process and how it targets Signal’s encryption loopholes.
The Google Threat Analysis Group (TAG) discovered that APT44 has been deploying malicious QR codes disguised as legitimate Signal invites or security notifications. When victims scan these QR codes, their devices unknowingly link to systems controlled by APT44, enabling real-time access to sensitive conversations.
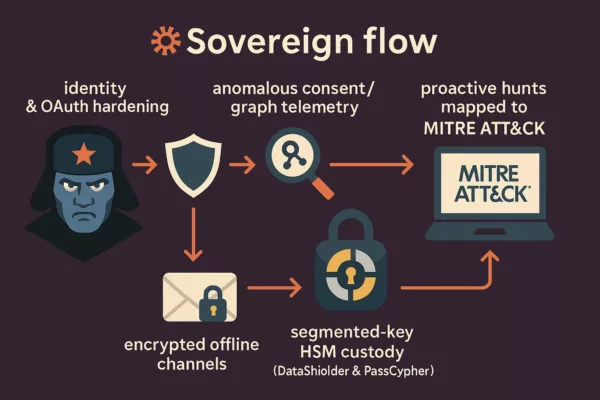
APT44 QR Code Phishing Attack Flow
Step-by-step analysis of APT44’s QR code phishing methodology.
APT44’s Cyber Espionage Timeline (2022-2025)
Tracking APT44’s evolution: From NotPetya to global QR code phishing campaigns.
| 📅 Date | 💣 Attack | 🎯 Target | ⚡ Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| June 2022 | NotPetya Variant | Ukrainian Government | Critical infrastructure disruption |
| February 2024 | QR Code Phishing | Ukrainian Military & Journalists | 500+ Signal accounts compromised |
| January 2025 | QR Code Phishing 2.0 | Global Signal Users | Wider-scale phishing |
Google Unveils Advanced Phishing Techniques
Insights from Google TAG on the most sophisticated QR code phishing tactics used by Russian hackers.
Recent investigations by the Google Threat Analysis Group (TAG), published on February 19, 2025, have exposed sophisticated phishing techniques used by Russian cyber units, notably UNC5792 and UNC4221, to compromise Signal Messenger accounts. These threat actors have refined their methods by deploying malicious QR codes that mimic legitimate Signal linking features, disguised as official security prompts or Signal invites.
When unsuspecting users scan these QR codes, their Signal accounts become silently linked to attacker-controlled devices, granting real-time access to private conversations and the ability to manipulate communications.
Key Discoveries:
- Malicious QR Codes: Hackers use fake Signal invites and security warnings embedded with dangerous QR codes that trick users into linking their accounts.
- Real-Time Access: Once connected, attackers gain instant access to sensitive conversations, allowing them to monitor or even alter the communication flow.
- Expanded Target Base: While the initial campaign focused on Ukrainian military and media personnel, the phishing campaign has now expanded across Europe and North America, targeting dissidents, journalists, and political figures.
📖 Source: Google TAG Report on APT44
Expanding Global Impact of APT44’s Cyber Campaigns
How APT44’s QR code phishing campaigns went global, targeting high-profile individuals.
Initially focused on Ukrainian military personnel, journalists, and human rights activists, APT44’s QR code phishing campaign has now evolved into a global cyber espionage threat. Cybersecurity experts have observed a significant expansion of APT44’s operations, targeting dissidents, activists, and ordinary users across Europe and North America. This shift highlights APT44’s intention to influence political discourse, monitor critical voices, and destabilize democratic institutions beyond regional conflicts.
The widespread use of QR codes in secure communication platforms like Signal has made it easier for attackers to exploit unsuspecting users, despite the platform’s robust encryption protocols. The attackers’ focus on exploiting social engineering tactics rather than breaking encryption underscores a growing vulnerability in user behavior rather than technical flaws.
Global Implications:
- Cross-Border Threats: Russian cyber units now pose risks to journalists, politicians, human rights defenders, and activists worldwide, extending their espionage campaigns far beyond Ukraine.
- Application Vulnerabilities: Even platforms known for strong encryption, like Signal, are susceptible if users unknowingly link their accounts to compromised devices.
- Rising QR Code Exploits: A 40% surge in QR code phishing attacks was reported globally in 2024 (CERT-UA), signaling a broader trend in cyber espionage techniques.
These developments highlight the urgent need for international cooperation and proactive cybersecurity measures. Governments, tech companies, and cybersecurity organizations must work together to improve user education, strengthen security protocols, and share threat intelligence to counter these evolving threats.
Why This Timeline Matters
- Awareness: Helps cybersecurity teams predict APT44’s next move by analyzing past behaviors.
- Real-Time Updates: Encourages regular threat monitoring as tactics evolve.
- Proactive Defense: Organizations can fine-tune incident response plans based on historical attack patterns.
Who’s Been Targeted?
APT44 primarily focuses on:
- Ukrainian military personnel using Signal for tactical communications.
- Journalists and media personnel the ongoing conflict (Pegasus Spyware) have been prime targets.
- Human rights activists and government officials.
Key Insights & Building Long-Term Resilience Against APT44’s QR Code Cyber Threats
Best practices and lessons learned to prevent future phishing attacks.
The Google Threat Analysis Group (TAG) has revealed how Russian cyber units, notably APT44, employ malicious QR codes that mimic legitimate Signal linking features. When unsuspecting users scan these codes, their Signal accounts are silently connected to attacker-controlled devices, granting real-time access to sensitive conversations. This sophisticated phishing method bypasses even the strongest encryption by targeting user behavior rather than exploiting technical vulnerabilities.
While QR codes have become a convenient tool for users, they have also opened new avenues for cyber espionage. The evolving tactics of APT44 emphasize the importance of proactive cybersecurity strategies, especially as QR code phishing continues to rise globally.
Lessons Learned from APT44’s Attacks
- Messaging Security Isn’t Bulletproof: Even end-to-end encrypted platforms like Signal can be compromised if attackers manipulate users into linking their accounts to malicious devices.
- Vigilance Is Global: The expansion of APT44’s operations beyond Ukraine highlights that users worldwide—including journalists, activists, and politicians—are increasingly at risk.
- QR Code Phishing Is Rising: The 40% increase in QR code phishing attacks (CERT-UA, 2024) shows that these techniques are becoming a preferred tool for state-sponsored hackers.
- High-Value Targets Remain Vulnerable: Journalists, activists, and dissidents continue to be primary targets, echoing tactics seen in other high-profile spyware campaigns like Pegasus.
Best Practices for Long-Term Resilience
Simple yet effective strategies to protect against QR code phishing attacks.
To mitigate risks and strengthen defenses against QR code phishing attacks, individuals and organizations should implement the following measures:
- Keep apps and systems up to date to patch potential vulnerabilities.
- Verify the authenticity of QR codes before scanning—especially in messaging platforms.
- Regularly audit linked devices within apps like Signal to detect unauthorized connections.
- Follow official cybersecurity alerts from trusted agencies like CISA and CERT-UA for the latest threat updates.
The Broader Lessons: Safeguarding Global Communications
The critical need for user awareness and international cooperation in combating state-sponsored cyber threats.
APT44’s phishing campaigns highlight the fragility of even the most secure communication systems when user trust is exploited. State-sponsored cyber espionage will continue to evolve, focusing on social engineering tactics rather than technical hacks.
- Education Is Key: Raising awareness about QR code phishing is critical in safeguarding both individual users and organizations.
- Collaboration Is Crucial: International cooperation between governments, tech companies, and cybersecurity agencies is essential to build more resilient defenses.
- Technical Safeguards Matter: Enhanced security features—such as device linking verifications and multi-factor authentication—can help prevent unauthorized access.
As cybercriminal tactics grow more sophisticated, vigilance, education, and proactive security strategies remain the strongest lines of defense against global cyber threats.
International Efforts & Strategic Insights to Counter APT44’s QR Code Phishing
How governments and tech companies are collaborating to neutralize global phishing threats.
As APT44’s cyber campaigns expand globally, the response from governmental agencies, tech companies, and cybersecurity bodies has intensified. The evolution of APT44’s tactics—from traditional malware attacks like NotPetya to advanced QR code phishing—has highlighted the urgent need for collaborative defense strategies and strengthened cybersecurity protocols.
Consistent Evolution of APT44’s Tactics
APT44’s shift from malware to social engineering: What cybersecurity teams need to know.
APT44 has demonstrated its ability to adapt and diversify its attack strategies over time, continually evolving to exploit emerging vulnerabilities:
- From Malware to Social Engineering: Transitioning from large-scale malware like the NotPetya variant to more targeted QR code phishing and supply chain exploits.
- Infrastructure Disruption: APT44 has prioritized attacks on critical infrastructures, including energy grids and water supplies, causing widespread disruptions.
- Global Expansion in 2025: Initially focused on Ukrainian targets, the group has broadened its reach, now actively targeting users across Europe and North America.
International Countermeasures Against QR Code Phishing
The global response to APT44’s expanding cyber campaigns and what’s being done to stop them.
Recognizing the growing threat of APT44’s cyber campaigns, both government bodies and tech companies have stepped up efforts to contain the spread and impact of these attacks.
Collaborative Countermeasures
- Google & Messaging Platforms: Tech companies like Google are partnering with messaging platforms (e.g., Signal) to detect phishing campaigns early and eliminate platform vulnerabilities exploited by malicious QR codes.
- CERT-UA & Global Cybersecurity Agencies: Agencies such as CERT-UA are actively sharing real-time threat intelligence with international partners, creating a united front against evolving APT44 tactics.
Policy Updates & User Protections
- Signal’s Enhanced Security Protocols: In response to these breaches, Signal has rolled out stricter device-linking protocols and strengthened two-factor authentication to prevent unauthorized account access.
- Awareness Campaigns: Government and private organizations have launched global initiatives aimed at educating users about the risks of scanning unverified QR codes, promoting cyber hygiene and encouraging regular device audits.
Proactive Strategies for Users & Organizations
Empowering individuals and companies to defend against APT44’s evolving phishing tactics.
Building resilience against APT44’s phishing attacks requires both policy-level changes and individual user awareness:
- Always verify the authenticity of QR codes before scanning.
- Regularly audit linked devices in messaging platforms to identify unauthorized connections.
- Stay informed through official alerts from cybersecurity bodies like CERT-UA and CISA.
- Encourage education and awareness on evolving phishing tactics among both end-users and organizations.
The Bigger Picture: A Global Call for Cyber Resilience
Why international collaboration is key to protecting digital infrastructures worldwide.
APT44’s ability to consistently evolve and scale its operations from regional conflicts to global cyber campaigns underlines the importance of international cooperation in cybersecurity. By working together, governments, tech companies, and users can build a stronger defense against increasingly sophisticated state-sponsored attacks.
As cyber threats continue to adapt, only a coordinated and proactive approach can ensure the integrity of critical systems and protect the privacy of global communications.
Proactive Cybersecurity Measures Against QR Code Phishing
Techniques and tools to detect and block advanced QR code phishing attacks.
In response to APT44’s phishing techniques Digital Security, it is crucial to educate users about the risks of scanning unsolicited QR codes. Enforcing security protocols can mitigate potential breaches, and implementing cutting-edge technology to detect and block phishing attempts is more crucial than ever.
To stay protected from APT44 QR Code Phishing attacks:
- Scrutinize QR Codes Before Scanning
- Update Messaging Apps Regularly
- Monitor Linked Devices
- Use QR Code Scanners with Threat Detection
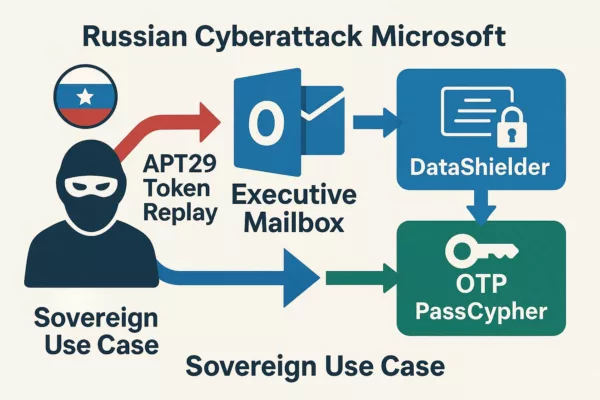
🆔 Protecting Against Identity Theft with DataShielder NFC HSM Auth
How Freemindtronic’s DataShielder protects users from phishing attacks and identity theft.
Phishing attacks often aim to steal user identities to bypass security systems. DataShielder NFC HSM Auth enhances security by providing robust identity verification, ensuring that even if attackers gain access to messaging platforms, they cannot impersonate legitimate users.
Its AES-256 CBC encryption and unique NFC-based authentication block unauthorized access, even during advanced phishing attempts like APT44’s QR code scams.
🔗 Learn more about DataShielder NFC HSM Auth and how it combats identity theft
Stopping Cyber Espionage Before It Starts with DataShielder NFC HSM & DataShielder HSM PGP
The role of hardware-based encryption in preventing cyber espionage.
With DataShielder NFC HSM, even if attackers successfully link your Signal account through QR code phishing, your messages remain encrypted and unreadable. Only the hardware-stored key can decrypt the data, ensuring absolute privacy—even during a breach.
Cyber espionage techniques, such as QR code phishing used by groups like APT44, expose serious vulnerabilities in secure messaging platforms like Signal. Even when sophisticated attacks succeed in breaching a device, the use of advanced encryption solutions like DataShielder NFC HSM and DataShielder HSM PGP can prevent unauthorized access to sensitive data.
💡 Why Use DataShielder for Messaging Encryption?
- End-to-End Hardware-Based Encryption: DataShielder NFC HSM and HSM PGP employ AES-256 CBC encryption combined with RSA 4096-bit key sharing, ensuring that messages remain unreadable even if the device is compromised.
- Protection Against Advanced Threats: Since encryption keys are stored offline within the NFC HSM hardware and never leave the device, attackers cannot extract them—even if they gain full control over the messaging app.
- Independent of Device Security: Unlike software-based solutions, DataShielder operates independently of the host device’s security. This means even if Signal or another messaging app is compromised, the attacker cannot decrypt your messages without physical access to the DataShielder module.
- Offline Operation for Ultimate Privacy: DataShielder works without an internet connection or external servers, reducing exposure to remote hacking attempts and ensuring complete data isolation.
- PGP Integration for Enhanced Security: The DataShielder HSM PGP browser extension enables PGP encryption for emails and messaging platforms, allowing users to protect communications beyond Signal, including Gmail, Outlook, and other web-based services.
🔒 How DataShielder Counters QR Code Phishing Attacks
QR code phishing attacks often trick users into linking their accounts to malicious devices. However, with DataShielder NFC HSM, even if a phishing attempt is successful in gaining access to the app, the contents of encrypted messages remain inaccessible without the physical NFC HSM key. This ensures that:
- Messages remain encrypted even if Signal is hijacked.
- Attackers cannot decrypt historical or future communications without the hardware key.
- Real-time encryption and decryption occur securely within the DataShielder module, not on the vulnerable device.
💬 Protecting More Than Just Signal
Expanding DataShielder’s protection to email, cloud storage, and instant messaging platforms.
While this article focuses on Signal, DataShielder NFC HSM and DataShielder HSM PGP support encryption across various messaging platforms, including:
- 📱 Signal
- ✉️ Email services (Gmail, Outlook, ProtonMail, etc.)
- 💬 Instant messaging apps (WhatsApp, Telegram, etc.)
- 📂 Cloud services and file transfers
Even If Hacked, Your Messages Stay Private
Unlike standard encryption models where attackers can read messages once they gain account access, DataShielder NFC HSM ensures that only the physical owner of the NFC HSM key can decrypt messages.
🛡️ Zero-Access Security: Even if attackers link your Signal account to their device, they cannot read your messages without the physical NFC HSM.
💾 Hardware-Based Encryption: AES-256 CBC and RSA 4096 ensure that all sensitive data remains locked inside the hardware key.
⚡ Post-Attack Resilience: Compromised devices can’t expose past or future conversations without the NFC HSM.
🚀 Strengthen Your Defense Against Advanced ThreatsCyber Threats
Why organizations need hardware-based encryption to protect sensitive data from sophisticated attacks.
In an era where phishing attacks and cyber espionage are increasingly sophisticated, relying solely on application-level security is no longer enough. DataShielder NFC HSM Lite or Master and DataShielder HSM PGP provide an extra layer of defense, ensuring that even if attackers breach the messaging platform, they remain locked out of your sensitive data.
Collaborative Efforts to Thwart APT44’s Attacks
Cybersecurity experts and organizations worldwide are joining forces to prevent QR code phishing:
- Google Threat Intelligence Group — Continues to track APT44’s evolving tactics. (Google TAG Report)
- CERT-UA — Provides real-time alerts to Ukrainian organizations. (CERT-UA Alert)
- Signal Developers — Introduced stricter device-linking protocols in response to these attacks. (Signal Security Update)
Strategies for Combating APT44’s Phishing Attacks
Collaboration among cybersecurity professionals is essential to develop effective defenses against sophisticated threats like those posed by APT44. Sharing knowledge about QR code phishing and other tactics enhances our collective security posture.
The Broader Lessons: Safeguarding Global Communications
The revelations surrounding APT44’s phishing campaigns offer critical lessons on the evolving landscape of state-sponsored cyber espionage:
- Messaging Security Isn’t Bulletproof: Even end-to-end encrypted platforms like Signal can be compromised through social engineering tactics like QR code phishing.
- Global Awareness Is Key: Users beyond conflict zones are now prime targets, emphasizing the importance of widespread cybersecurity education.
- QR Code Phishing on the Rise: The surge in QR code-based scams underscores the need for both user vigilance and technical safeguards.
As cybercriminal tactics evolve, so too must our defenses. Collaborative efforts between tech companies, governments, and end-users are essential to protect global communications.
Additional Resources
📖 Official Reports and Alerts
- 🔗 Google Threat Analysis Group Report on APT44
- 🔗 CERT-UA Alert on Signal Phishing
- 🔗 SiliconANGLE Coverage on Russian Espionage
🔗 Related Freemindtronic Articles
- 🔗 Communication Security Vulnerabilities 2023 — Explore key vulnerabilities in modern communication systems and strategies to mitigate security risks.
- 🔗 Cyber Threats — A comprehensive collection of articles addressing the latest cyber threats and tactics used by hackers worldwide.
- 🔗 Predator Files Spyware — In-depth analysis of Predator spyware and its role in cyber espionage targeting journalists and activists.
- 🔗 Pegasus: The Cost of Spying — A detailed look at the Pegasus spyware scandal, its capabilities, and its impact on global surveillance practices.
- 🔗 Digital Security — Resources and best practices for enhancing digital security against modern cyber threats and data breaches.