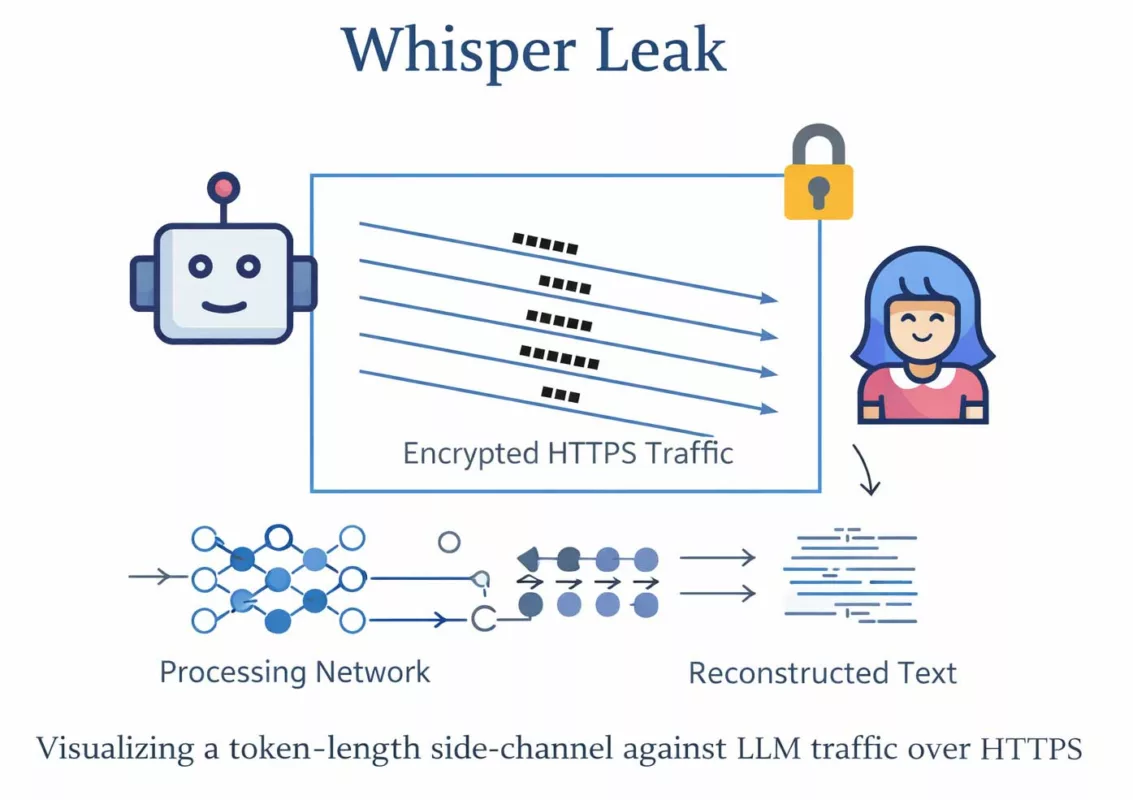
Whisper Leak side-channel: token-length leakage, semantic inference, and the structural limits of HTTPS in large language model (LLM) communications. This Chronicle documents how encrypted transport can still expose sufficient metadata (size, cadence, burst patterns) to infer sensitive topics and operational intent from encrypted traffic shape without breaking TLS. It explains why this is not a cryptographic failure, but an architectural boundary. Finally, it clarifies when mitigation is insufficient—and when deployment posture must change.
Executive summary
Context
The rapid adoption of remote LLM APIs has normalized the assumption that HTTPS transport encryption guarantees confidentiality. However, encryption protects payload content—not structural metadata. In 2024–2025, research demonstrated that token-length leakage and streaming cadence can become statistically learnable signals. As a result, encrypted AI traffic may still reveal semantic intent.
Purpose
This Chronicle provides a doctrinal analysis of the Whisper Leak side-channel. It explains the mechanics of token-length inference, clarifies its threat model, and distinguishes between patchable weaknesses and irreversible architectural limits. It also defines when mitigation becomes insufficient.
Scope
Scope includes:
- Token-length leakage over HTTPS
- Streaming response cadence analysis
- Traffic-shape inference in LLM communications
- Probabilistic prompt reconstruction
Out of scope: cryptographic break of TLS, vendor-specific exploit code, and operational weaponization details.
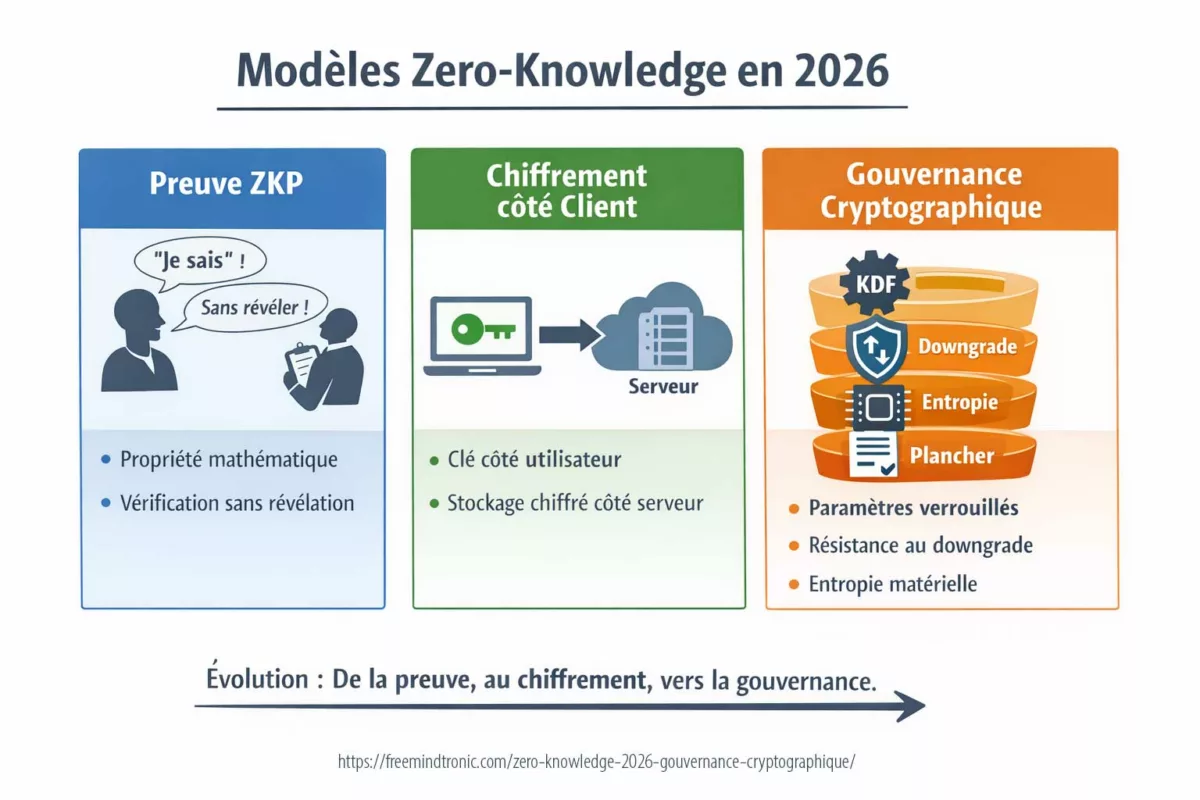
Design doctrine
The Chronicle treats confidentiality as a semantic property, not merely a transport property. It assumes that observable traffic shape can become learnable at scale. Therefore, mitigation must either reduce observability, enforce constant-shape exchanges, or relocate sensitive processing to a sovereign boundary.
Strategic differentiator
Many analyses describe token-length leakage as a “metadata issue.” This Chronicle treats it as a semantic exposure problem. That distinction matters. When inference risk becomes unacceptable, the solution is not incremental padding—it is architectural redesign.
Key takeaway
Whisper Leak side-channel shows that HTTPS protects content—not traffic shape. When shape becomes learnable, intent can leak. If that risk is unacceptable, deployment posture—not padding—must change.
If semantic leakage is unacceptable, remote LLM API usage must be reconsidered. Otherwise, mitigation requires strict constant-shape enforcement or sovereign processing boundaries.
Technical note
Express reading time: ≈ 3–4 minutes
Advanced reading time: ≈ 5–6 minutes
Full Chronicle: ≈ 30–40 minutes
Publication date: 2026-02-18
Level: AI Security / Traffic Analysis / TLS Metadata
Posture: Architectural boundary, inference-aware, sovereign deployment
Category: Digital Security
Available languages: EN · FR · CAT · ES
Impact level: 9.1 / 10 — architectural confidentiality risk in AI deployments
- Executive summary
- Advanced summary — Why token sizes can betray LLM prompts
- Chronicle — Whisper Leak as a historical inflection point
- The discovery timeline — why this feels historical
- Why HTTPS still leaks structure — the physics of encrypted traffic
- Attack mechanics — from token sizes to probable text
- Conceptual leakage pipeline — from traffic shape to inferred intent
- Quantifying token-length leakage — signal and entropy reduction
- Formal leakage bound — semantic inference under encryption
- Threat model — who can exploit this
- When not to act — the non-negotiable boundary
- Impact surface — what can leak in the real world
- Mitigations that actually matter
- Constant-shape traffic
- Reduce observability
- Sovereign deployment
- Stop point — when mitigation becomes security theater
- Limitations and counter-arguments
- Signals watch — weak, medium, and strong indicators
- Weak signals
- Medium signals
- Strong signals
- Signals references
- Academic references
- Freemindtronic sovereign use case
- Use case: DataShielder
- Use case: PassCypher
- Glossary — Whisper Leak side-channel and semantic leakage
- FAQ — Whisper Leak side-channel and semantic inference
- What We Didn’t Cover
- Strategic outlook — the new baseline for confidential AI
Advanced summary — Why token sizes can betray LLM prompts
Reading note
≈ 5–6 minutes — extends leakage channels and mitigation limits.
Whisper Leak is best understood as a “shape leak”: TLS encrypts payload bytes, yet the observer still sees packet sizes, burst timing, and directionality.
With LLM APIs, those signals correlate with tokenization and streaming behavior. When a service streams tokens, the response becomes a sequence of measurable chunks; when prompts vary in length, request sizes vary too.
This is not new in cryptography history—traffic analysis has always existed—yet LLMs amplify it because language is statistically learnable.
Key insights include:
- Encryption ≠ opacity: TLS protects content, not structural metadata.
- LLMs are compressible models of language: an attacker can learn mappings from size sequences to likely text.
- Streaming makes the leak richer: chunk cadence becomes an additional signature channel.
- Padding helps only if enforced end-to-end: partial padding is often learnable and bypassable.
- “When not to act” matters: some environments should not use remote LLM APIs for sensitive prompts—period.
| Leak component | What the observer measures | Why it correlates with text | Defensive lever |
|---|---|---|---|
| Prompt length | Request size / upload burst | Tokenization is length-structured | Constant-size requests (padding + batching) |
| Response streaming | Chunk sizes + inter-chunk timing | Token emission patterns are model-dependent | Fixed-rate / fixed-size streaming or disable streaming |
| Conversation patterns | Turn-taking cadence | Task types have distinct interaction signatures | Standardize workflows; avoid “unique” sensitive prompts |
| Protocol behaviors | HTTP/2 framing, retries, keepalive | Transport artifacts add stable features | Harden client stacks; isolate networks; reduce observability |
The historical point is not that “TLS is broken”. It is that privacy requirements changed.
For decades, traffic analysis was “acceptable leakage” in many consumer contexts. LLM usage pushes sensitive reasoning, private intent, and operational details into the network layer.
So the baseline threat model must evolve: assume observers can learn from metadata and can deploy ML at scale.
Chronicle — Whisper Leak as a historical inflection point
The discovery timeline — why this feels “historical”
Whisper Leak did not appear in a vacuum. It sits at the junction of two mature domains: traffic analysis (old) and generative language modeling (new at scale).
Historically, traffic analysis was associated with broad inferences: who talks to whom, when, and for how long. LLMs add a twist: the payload is language, and language has a learnable statistical structure.
When researchers demonstrated that token-length sequences can predict original text, they effectively turned “metadata leakage” into “semantic leakage”.
That shift is why the moment matters: we are not only measuring communication patterns; we are extracting intent.
And intent is what organizations considered safe to outsource into remote LLM APIs—often under the assumption that “HTTPS = confidentiality”.
Why HTTPS still leaks structure — the physics of encrypted traffic
TLS protects content confidentiality between endpoints, but it cannot erase the fact that communication consumes bandwidth, time, and framing.
An observer (on-path, compromised router, enterprise proxy, hostile Wi-Fi, upstream ISP, or lawful intercept context) can still see: packet sizes, ordering, timing, and direction.
Even when payloads are encrypted, a structured application (like streaming tokens) produces structured traffic.
- Size leakage: if a request is larger, something longer was sent.
- Burst leakage: streaming responses create a distinctive “drip” signature.
- Boundary leakage: message turns, retries, and connection reuse create stable markers.
This is the first irreversible limit of the Chronicle: you cannot “software patch” away physics.
Any mitigation that depends on “hoping observers cannot measure” is fragile by design.
Attack mechanics — from token sizes to probable text
At a high level, the attacker collects encrypted traffic traces and extracts features: request sizes, response chunk sizes, inter-chunk timing, and turn boundaries.
Then they train a model (or a set of models) to map those features to likely strings or likely classes of prompts.
The “hot” part is not encryption breaking; it is inference.
| Step | Attacker action | What is learned | Defender failure mode |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. Capture | Observe encrypted traces at scale | Size + timing distributions | Assuming “encrypted = invisible” |
| 2. Feature extraction | Derive token-length proxies | Stable traffic fingerprints | Leaving streaming and retries unconstrained |
| 3. Training | Supervised/weakly-supervised learning | Mapping features → text likelihoods | Repeated workflows leak consistent patterns |
| 4. Reconstruction | Predict prompt fragments or classes | Probable content / intent | Underestimating “semantic leakage” |
A key nuance: reconstruction does not have to be perfect to be operationally damaging.
If the attacker can infer that a user asked about “M&A”, “incident response”, “legal strategy”, “patient symptoms”, or “credentials rotation”, that may already be enough.
In sensitive environments, inference at the level of intent is the breach.
Conceptual leakage pipeline — from traffic shape to inferred intent
User Prompt (X)
↓
LLM Tokenization
↓
Streaming Output
↓
Observable Traffic Features (S, Δ, D)
↓
Feature Extraction
↓
Statistical / ML Classifier
↓
Topic & Intent Inference (T̂)
Each transformation preserves partial structure. Encryption hides content but does not collapse observability. Therefore, inference emerges from accumulated statistical correlation.
Quantifying token-length leakage — how much signal is enough?
A recurring objection is that token-length leakage is “too noisy” to matter. However, modern traffic analysis does not require perfect reconstruction. It requires statistical advantage.
Signal amplification through repetition
- Let L be token length.
- Let T be topic class.
- If P(T | L) > P(T), leakage exists.
Even a modest classification lift — for example, increasing baseline guessing accuracy from 10% to 45–60% for sensitive topic classes — is operationally significant.
Entropy reduction model
If H(T) is prior entropy of topic distribution, and H(T | L) is conditional entropy after observing token-length sequences:
Leakage = H(T) − H(T | L)
When repeated observations reduce uncertainty by even 1–2 bits per session, cumulative inference becomes feasible at scale.
Therefore, the relevant metric is not “perfect reconstruction” but measurable entropy reduction under observation.
Formal leakage bound — semantic inference under encryption
From an information-theoretic standpoint, encrypted traffic still exposes observable random variables:
- Packet size sequence S = (s₁, s₂, …)
- Inter-arrival timing Δ = (Δ₁, Δ₂, …)
- Directionality D
Let X be the hidden prompt text. TLS ensures that I(Content; Ciphertext) ≈ 0 for an external observer.
However, it does not guarantee:
I(X ; S, Δ, D) = 0
If mutual information I(X ; observable features) > 0, then semantic leakage exists in principle.
Mitigation must therefore aim to minimize I(X ; S, Δ, D), not merely protect ciphertext content.
This reframes the Whisper Leak side-channel as a residual information channel rather than a cryptographic flaw.
Threat model — who can exploit this, and when you must not act
This section is your first explicit stop point. Before implementing mitigations, define whether your environment can accept any semantic leakage at all.
If you operate under regulatory, intelligence, defense, critical infrastructure, or high-stakes confidentiality constraints, “probabilistic inference” may be unacceptable even if it is not deterministic.
When not to act — the non-negotiable boundary
- Do not send sensitive prompts to remote LLM APIs when the prompt itself is confidential (strategy, credentials, investigations, personal data).
- Do not assume VPN/TLS terminators, corporate proxies, or managed Wi-Fi are “neutral” observers.
- Do not “test” mitigations in production by adding padding gradually; partial padding often increases learnability by creating new patterns.
If you cannot change the deployment model (remote API remains mandatory), treat the channel as observable and redesign workflows to reduce what can be inferred.
Otherwise, move the capability to a sovereign boundary: local, isolated, or enclave-based.
Impact surface — what can leak in the real world
Whisper Leak risk scales with repetition and standardization. The more your organization uses consistent prompt templates, the more stable the leakage signature becomes.
Ironically, “prompt hygiene” can become “prompt fingerprinting”.
- Operational intent: what teams are working on, when, and with what urgency.
- Template reconstruction: internal playbooks and structured prompts can be inferred as classes.
- Fragment leakage: in some conditions, parts of the original text become guessable.
- User profiling: individuals can be profiled by interaction rhythm and task types.
Second irreversible limit: even if you rotate keys, rotate endpoints, or rotate sessions, an attacker who observes the channel can still learn patterns if the workflows remain stable.
Rotating secrets does not rotate behavioral signatures.
Mitigations that actually matter — and the point where you must stop
A mitigation is only meaningful if it reduces learnable structure end-to-end.
In practice, many “fixes” fail because they are partial, optional, or inconsistent across clients, models, and streaming modes.
Below are defensive levers ranked by doctrinal strength, not by convenience.
1) Constant-shape traffic (padding + batching), enforced end-to-end
- Pad requests to fixed buckets (or constant length) before encryption.
- Pad responses similarly, or disable token streaming and return fixed-size blocks.
- Batch operations to reduce per-message uniqueness.
2) Reduce observability (network isolation as a security control)
- Segment LLM traffic from general browsing; avoid shared egress points.
- Minimize intermediaries: proxies and inspection boxes increase exposure surface.
- Use dedicated paths for sensitive workflows, with explicit monitoring assumptions.
3) Sovereign deployment (local or enclave boundary)
- Keep the most sensitive prompts and inference flows inside a controlled boundary.
- Prefer architectures where content never becomes a public network conversation.
Stop point — when mitigation becomes security theater
If you cannot guarantee constant-shape exchanges, cannot reduce observability, and cannot change deployment, then “mitigation” risks becoming an audit artifact.
At that point, the responsible answer is not another tweak—it is a policy decision: stop sending sensitive prompts remotely.
Continuing to iterate can increase exposure by generating more training data for adversaries observing your channel.
Signals watch — weak, medium, and strong indicators
Whisper Leak is no longer a niche hypothesis. Since late 2025, it has been formalized publicly as a streaming traffic side-channel relying on packet size sequences and inter-arrival timing, with reported cross-provider evaluation and partial mitigations. Consequently, the relevant question is not whether the class exists, but how quickly it becomes operationalized across surveillance tiers.
Weak signals
- Normalization drift: security discussions increasingly treat “metadata leakage” as an acceptable residual risk in AI, even when the metadata encodes intent.
- Template rigidity: enterprises standardize prompts and workflows for productivity, inadvertently stabilizing traffic fingerprints that can be learned over time.
- Defense overconfidence: “random padding” is deployed inconsistently (UI vs API, product vs gateway), creating heterogeneous patterns that can be re-identified.
Medium signals
- Public formalization: Whisper Leak is documented as topic inference from encrypted streaming traffic patterns, shifting the debate from anecdotal to methodological.
- Mitigation productization: network-layer or gateway mitigations are announced for token-length side-channels, which implies both demand and credible attacker models.
- Cross-layer fusion trend: research and practitioner notes increasingly combine packet metadata with other signals (endpoint telemetry, caching artifacts) to strengthen inference.
Strong signals
- Industry-wide exposure framing: the attack is positioned as broadly applicable to streaming LLMs and relevant to ISP-level and local-network observers.
- High-precision targeting narrative: the emphasis moves from “recovering text” to “reliably flagging sensitive topics,” which is sufficient for surveillance and coercion use cases.
- Persistent residual leakage: evaluated mitigations reduce attack effectiveness but do not fully eliminate metadata-based inference, reinforcing the architectural boundary argument.
Signals references:
- Cloudflare (2024): https://blog.cloudflare.com/ai-side-channel-attack-mitigated/
- arXiv (2025): https://arxiv.org/abs/2511.03675
- Microsoft Security Blog (2025): https://www.microsoft.com/en-us/security/blog/2025/11/07/whisper-leak-a-novel-side-channel-cyberattack-on-remote-language-models/
- Schneier on Security (2026): https://www.schneier.com/blog/archives/2026/02/side-channel-attacks-against-llms.html
Theoretical and academic foundations:
- Shannon, C. E. (1948). A Mathematical Theory of Communication.
https://people.math.harvard.edu/~ctm/home/text/others/shannon/entropy/entropy.pdf
- Panchenko et al. (2016). Website Fingerprinting at Internet Scale. IEEE Symposium on Security & Privacy.
https://www.ieee-security.org/TC/SP2016/papers/0824aPanchenko.pdf
- Dyer et al. (2012). Peek-a-Boo, I Still See You: Why Efficient Traffic Analysis Countermeasures Fail.
https://www.cs.columbia.edu/~angelos/Papers/peekaboo-oakland2012.pdf
Weak signals indicate normalization and repeatability. Medium signals indicate validation and productization. Strong signals indicate operational relevance: topic inference becomes actionable without decryption. Therefore, “confidential AI” must be defined as semantic confidentiality under observation, not merely TLS correctness.
Freemindtronic sovereign use case — preventing semantic leakage by design
A sovereign posture treats “prompt secrecy” as a property that must survive hostile observation.
That requires architectural controls, not only transport controls. Here is a concrete doctrine-aligned pattern using Freemindtronic building blocks.
Use case: DataShielder as a sovereign boundary for sensitive prompts
- Objective: ensure sensitive prompt material never becomes a public network conversation.
- Method: keep the most sensitive reasoning steps offline or inside a controlled enclave, and only export non-sensitive summaries.
- Operational benefit: even if traffic is observed, the “semantic core” is absent.
Use case: PassCypher for controlled secrets handling (stop secrets from entering prompts)
- Objective: prevent credentials and long-lived secrets from ever appearing in LLM prompts.
- Method: store and manage secrets with a controlled mechanism; inject only minimal, time-scoped, non-reusable tokens when strictly required.
- Boundary statement: do not “mask” secrets in prompts and assume safety. Masking often preserves length patterns and can remain inferable.
✓ Sovereign Countermeasures
- Prefer sovereign/local processing for sensitive prompts.
- Separate “reasoning payload” from “network payload” (export only what can be observed safely).
- Prevent secrets from entering prompts via controlled handling (no ad-hoc copy/paste).
Glossary — Whisper Leak side-channel and semantic leakage
Traffic analysis
What leaks without decrypting
Traffic analysis in encrypted LLM communications
Traditionally, traffic analysis refers to extracting intelligence from metadata—such as packet size, timing, frequency, and direction—without decrypting the payload.
However, in the era of large language models, this discipline acquires renewed doctrinal weight.
Indeed, once language generation becomes statistically structured and machine-learnable, traffic metadata transforms into a potential semantic proxy.
Accordingly, Whisper Leak should be understood not as a cryptographic failure, but as the predictable evolution of traffic analysis under AI-scale observability.
Token-length leakage
When observable shape becomes meaning
Token-length leakage and semantic inference boundaries
Token-length leakage arises when request or response sizes correlate with tokenized language structure in remote LLM APIs.
In principle, encrypted HTTPS protects content confidentiality.
Yet, in practice, token emission patterns and streaming cadence create measurable traffic signatures.
Consequently, repeated observations enable statistical mapping between traffic shape and likely topic or intent.
At that point, the issue shifts from simple metadata exposure to semantic inference under encryption.
Constant-shape exchange
Padding done right — structurally, not cosmetically
Constant-shape exchange as architectural mitigation doctrine
A constant-shape exchange enforces fixed-size or fixed-bucket traffic patterns end-to-end across encrypted LLM communications.
In theory, this reduces correlation between tokenization and observable packet structure.
However, unless applied consistently across requests, responses, retries, and streaming flows, residual patterns remain learnable.
Therefore, mitigation must be architectural rather than optional.
Otherwise, what appears as a defensive control becomes a cosmetic adjustment—insufficient against inference-aware adversaries.
What We Didn’t Cover
This Chronicle focused on token-size and traffic-shape inference over HTTPS. We did not deep-dive into formal leakage bounds, specific paper-by-paper datasets, or vendor-by-vendor implementation details. Those deserve separate notes with reproducibility constraints.
Limitations and counter-arguments
Noise and variability
At first glance, network jitter, congestion, and protocol buffering introduce stochastic variability that appears to weaken inference precision. Indeed, encrypted LLM traffic over HTTPS is never perfectly deterministic. However, from a doctrinal standpoint, randomness does not equate to protection. On the contrary, large-scale observation and aggregation smooth transient noise. Consequently, statistical models trained on sufficient traces recover stable distributional patterns despite local fluctuations.
Model diversity
Admittedly, different LLM architectures, tokenization schemes, and streaming strategies may alter traffic signatures. In principle, this diversity increases heterogeneity across sessions. Nevertheless, inference systems do not rely on exact token mappings but on probabilistic regularities. Therefore, classifiers adapt to distributional features rather than model-specific artifacts. In practice, diversity modifies the feature space; it does not eliminate learnable structure.
Cost of observation
It must also be acknowledged that large-scale inference requires sustained visibility—whether at ISP level, enterprise proxy, managed infrastructure, or compromised network vantage points. Accordingly, exposure is contingent upon the threat model and adversary capability. However, where persistent observability exists, cost becomes a scaling parameter rather than a categorical barrier. In high-value contexts, the economic threshold for surveillance is often lower than assumed.
Padding effectiveness under strict enforcement
Theoretically, full constant-shape enforcement can significantly reduce mutual information between hidden prompt text and observable traffic features. Under rigorous end-to-end implementation, entropy leakage may approach negligible levels. Yet such enforcement is operationally expensive, difficult to standardize across heterogeneous environments, and rarely universal. Consequently, partial deployment often reintroduces residual patterns—thereby restoring inference potential.
In summary: The Whisper Leak attack class is probabilistic rather than deterministic. However, doctrinally, probabilistic inference remains operationally sufficient in high-stakes environments. When intent, priority, or strategic direction can be inferred with statistical confidence, semantic confidentiality is already compromised—irrespective of cryptographic integrity.
Strategic outlook — the new baseline for “confidential AI”
Whisper Leak forces a doctrine shift: confidentiality for AI is no longer “encrypt the pipe” but “control the shape”. In other words, once traffic structure becomes observable and learnable, transport-layer secrecy is necessary yet insufficient.
Consequently, the organizations that will struggle first are those that standardized prompts, workflows, and templates without isolating the semantic core. Standardization improves productivity; however, it also stabilizes leakage signatures. As a result, repeatable interactions become repeatable inferences.
Meanwhile, attackers will keep improving because the method scales. They can capture traces, learn mappings, and infer intent—often without needing perfect reconstruction. Even partial semantic leakage can be operationally decisive when it reveals priorities, investigations, negotiations, or incident response posture.
Therefore, the durable answer is to engineer systems where sensitive semantics do not traverse observable channels, and where the remaining traffic is deliberately non-informative by design. Practically, that means either enforcing constant-shape exchanges end-to-end or moving critical inference to sovereign boundaries where observation is structurally constrained.
This is not a feature request, nor a vendor checkbox. Instead, it is an architectural boundary—and it must be treated as such in governance, procurement, and operational security policy. Otherwise, “confidential AI” remains a label applied after the fact, rather than a property enforced before deployment.
FAQ — Whisper Leak side-channel, token-length leakage, and semantic inference in encrypted LLM traffic
Is Whisper Leak a break of TLS encryption?
No decryption required
Whisper Leak and TLS — Is encryption actually broken?
No. Whisper Leak is not a TLS cryptographic break. Instead, it is a token-length and streaming side-channel exploiting observable HTTPS metadata. In other words, packet sizes, burst timing, directionality, and streaming cadence in encrypted LLM traffic remain measurable. Therefore, while the cryptography remains intact, structural signals persist. This means encrypted AI traffic can leak semantic intent without decryption.
Can attackers reconstruct full prompts?
Topic & intent are enough
Prompt reconstruction vs topic inference — What really leaks?
Public research on LLM traffic analysis and token-length side-channels primarily demonstrates high-confidence topic inference and intent classification. Consequently, perfect verbatim reconstruction is not required for operational damage. In regulated or strategic environments, identifying the subject already constitutes a semantic confidentiality breach.
Does padding solve the token-length side-channel problem?
Only if enforced end-to-end
Padding strategies — mitigation or illusion?
Padding reduces token-length leakage only when enforcing a constant-shape traffic model end-to-end, covering both requests and responses. However, partial or inconsistent padding leaves residual learnable patterns. Without architectural enforcement, padding risks becoming security theater.
Who is most exposed to semantic leakage in LLM APIs?
Repetition increases learnability
Exposure surface — who faces the highest risk?
Exposure rises when remote LLM APIs process sensitive operational intent. Regulated sectors, legal strategy, medical contexts, cybersecurity incidents, procurement negotiations, and investigations are particularly exposed. Repeated templates create stable traffic fingerprints, improving inference accuracy.
What is the safest posture for “confidential AI”?
Architecture, not labels
Confidential AI architecture — what truly protects?
When semantic confidentiality is critical, transport encryption alone is insufficient. The strongest posture relies on architectural controls: sovereign or enclave-based deployment, separation between reasoning payload and network payload, and deliberate reduction of observable structure. Confidential AI must mean semantic confidentiality under observation, not merely HTTPS correctness.