Terrapin Attack: How to Protect Your SSH Security
The Terrapin attack is a serious vulnerability in the SSH protocol that can be used to downgrade the security of your SSH connections. This can allow attackers to gain access to your sensitive data. In this article, we will explain what the Terrapin attack is, how it works, and how you can protect yourself from it.
Terrapin attack: CVE-2023-48795 SSH security vulnerability articles for in-depth threat reviews and solutions. Stay informed by clicking on our scrolling topics.
Protect Yourself from the Terrapin Attack: Shield Your SSH Security with Proven Strategies
SSH is a widely used protocol for secure communication over the internet. It allows you to remotely access and control servers, transfer files, and encrypt data. However, SSH is not immune to attacks, and a recent vulnerability OpenSSH before 9.6 (CVE-2023-48795) has exposed a serious flaw in the protocol itself. This flaw, dubbed the Terrapin attack, can downgrade the security of SSH connections by truncating cryptographic information. In this article, we will explain what the Terrapin attack is, how it works, and how you can protect yourself from it.
Why you should care about the Terrapin attack
The Terrapin attack is not just a theoretical threat. It is a real and dangerous attack that can compromise the security of your SSH connections and expose your sensitive data. The consequences of a successful Terrapin attack can be severe, such as:
- Data breaches: The attacker can access your confidential information, such as passwords, keys, files, or commands, and use them for malicious purposes.
- Financial losses: The attacker can cause damage to your systems, services, or assets, and demand ransom or extort money from you.
- Reputation damage: The attacker can leak your data to the public or to your competitors, and harm your credibility or trustworthiness.
Therefore, it is important to be aware of the Terrapin attack and take the necessary measures to prevent it. In the following sections, we will show you how the Terrapin attack works, how to protect yourself from it, and how to use PassCypher HSM PGP and EviKey NFC HSM to enhance the security of your SSH keys.
A prefix truncation attack on the SSH protocol
The Terrapin attack is a prefix truncation attack that targets the SSH protocol. It exploits a deficiency in the protocol specification, namely not resetting sequence numbers and not authenticating certain parts of the handshake transcript. By carefully adjusting the sequence numbers during the handshake, an attacker can remove an arbitrary amount of messages sent by the client or server at the beginning of the secure channel without the client or server noticing it.
This manipulation allows the attacker to perform several malicious actions, such as:
- Downgrade the connection’s security by forcing it to use less secure client authentication algorithms
- Bypass the keystroke timing obfuscation feature in OpenSSH, which may allow the attacker to brute-force SSH passwords by inspecting the network packets
- Exploit vulnerabilities in SSH implementations, such as AsyncSSH, which may allow the attacker to sign a victim’s client into another account without the victim noticing
To pull off a Terrapin attack, the attacker must already be able to intercept and modify the data sent from the client or server to the remote peer. This makes the attack more feasible to be performed on the local network.
Unveiling the SSH Handshake: Exposing the Terrapin Attack’s Weakness
The SSH Handshake Process
The SSH handshake is a crucial process that establishes a secure channel between a client and server. It consists of the following steps:
- TCP connection establishment: The client initiates a TCP connection to the server.
- Protocol version exchange: The client and server exchange their protocol versions and agree on a common one. Then, the algorithm negotiation takes place.
- Algorithm negotiation: The client and server exchange lists of supported algorithms for key exchange, encryption, MAC, and compression. Then, they select the first matching algorithm.
- Key exchange: The client and server use the agreed-upon key exchange algorithm to generate a shared secret key. They also exchange and verify each other’s public keys. Then, the service request is sent.
- Service request: The client requests a service from the server, such as ssh-userauth or ssh-connection. Then, the client authenticates itself to the server using a supported method, such as password, public key, or keyboard-interactive.
- User authentication: The client authenticates itself to the server using a supported method, such as password, public key, or keyboard-interactive. Then, the channel request is sent.
- Channel request: The client requests a channel from the server, such as a shell, a command, or a subsystem. Thus, encrypted communication is enabled.
The Terrapin Attack
The Terrapin attack exploits a vulnerability in the SSH handshake by manipulating the sequence numbers and removing specific messages without compromising the secure channel integrity. This stealthy attack is difficult to detect because it doesn’t alter the overall structure or cryptographic integrity of the handshake.
For example, the attacker can eliminate the service request message sent by the client, which contains the list of supported client authentication methods. This forces the server to resort to the default method, typically password-based authentication. The attacker can then employ keystroke timing analysis to crack the password.
Alternatively, the attacker can target the algorithm negotiation message sent by the server, which lists the supported server authentication algorithms. By removing this message, the attacker forces the client to use the default algorithm, usually ssh-rsa. This opens the door for the attacker to forge a fake public key for the server and deceive the client into accepting it.
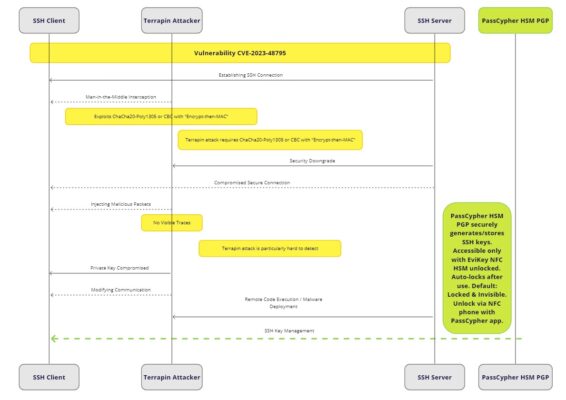
To illustrate the process of a Terrapin attack, we have created the following diagram:
As you can see, the diagram shows the steps from the interception of the communication by the attacker to the injection of malicious packets. It also highlights the stealthiness and the difficulty of detection of the attack.
Summery
The Terrapin attack is a serious threat to SSH security. By understanding how it works, you can take steps to protect yourself from it. Here are some tips:
- Make sure your SSH server is up to date with the latest security patches.
- Use strong passwords or public key authentication.
- Enable SSH key fingerprint verification.
How to protect yourself from the Terrapin attack: Best practices and tools
The Terrapin attack is a serious threat to SSH security, and it affects many SSH client and server implementations, such as OpenSSH, PuTTY, FileZilla, and more. Here are some steps you can take to protect yourself from it:
- Update your SSH client and server to the latest versions. Many vendors have released patches that fix the vulnerability or introduce a strict key exchange option that prevents the attack. You can check if your SSH software is vulnerable by using the Terrapin vulnerability scanner.
- Use strong passwords and public key authentication. Avoid using weak or default passwords that can be easily guessed by the attacker. Use public key authentication instead of password authentication, and make sure your public keys are verified and trusted.
- Use secure encryption modes. Avoid using vulnerable encryption modes, such as ChaCha20-Poly1305 or AES-CBC with default MACs. Use encryption modes that use authenticated encryption with associated data (AEAD), such as AES-GCM or Chacha20-Poly1305@openssh.com.
- Use a VPN or a firewall. If possible, use a VPN or a firewall to encrypt and protect your SSH traffic from being intercepted and modified by the attacker. This will also prevent the attacker from performing other types of attacks, such as DNS spoofing or TCP hijacking.
- Implement a strict security policy on your local networks. Limit the access to your SSH servers to authorized users and devices, and monitor the network activity for any anomalies or intrusions.
How to use PassCypher HSM PGP and EviKey NFC HSM to protect your SSH keys: A secure and convenient solution
A good way to enhance the security of your SSH keys is to use PassCypher HSM PGP and EviKey NFC HSM. These are products from PassCypher), a company specialized in data security. They offer a secure and convenient solution for generating and storing your SSH keys.
PassCypher HSM PGP is a system that embeds a SSH key generator, allowing you to choose the type of algorithm – RSA (2048, 3072, 4096) or ECDSA (256,384, 521), and ED25519. The private key is generated and stored in a secure location, making it inaccessible to attackers.
EviKey NFC HSM is a contactless USB drive that integrates with PassCypher HSM PGP. It provides an additional layer of security and convenience for users who can easily unlock their private SSH key with their smartphone.
To show how PassCypher HSM PGP and EviKey NFC HSM can protect your SSH keys from the Terrapin attack, we have created the following diagram:
As you can see, the diagram shows how this solution effectively protects your SSH keys from the Terrapin attack. It also shows the benefits of using a contactless USB drive, such as:
- Enhanced security: The private key is physically externalized and protected with a contactless authentication mechanism.
- Convenience: Easy unlocking with a smartphone.
- Ease of use: No additional software required.
- Industrial-grade security: Equivalent to SL4 according to the standard IEC 62443-3-3.
Safeguarding Your SSH Keys with a Contactless USB Drive: A Comprehensive Guide
If you’re seeking a comprehensive guide to securely store your SSH keys using a contactless USB drive, look no further than this detailed resource: [Link to the article ([https://freemindtronic.com/how-to-create-an-ssh-key-and-use-a-nfc-hsm-usb-drive-to-store-it-securely/])]
This guide meticulously walks you through the process of:
- Generating an SSH key pair leveraging PassCypher HSM PGP
- Protecting the private SSH key within the EviKey NFC HSM USB drive
- Unlocking the private SSH key employing your smartphone
- Establishing a secure connection to an SSH server using the EviKey NFC HSM USB drive
Alongside step-by-step instructions, the guide also includes illustrative screenshots. By adhering to these guidelines, you’ll effectively safeguard and conveniently manage your SSH keys using a contactless USB drive.
Statistics on the Terrapin attack: Facts and figures
Statistics on the Terrapin attack: Facts and figures
The Terrapin attack is a serious cybersecurity threat that affects SSH connections. We have collected some statistics from various sources to show you the scale and impact of this attack. Here are some key facts and figures:
- The Shadowserver Foundation reports that nearly 11 million SSH servers exposed on the internet are vulnerable to the Terrapin attack. This is about 52% of all IPv4 and IPv6 addresses scanned by their monitoring system.
- The most affected countries are the United States (3.3 million), China (1.3 million), Germany (1 million), Russia (704,000), Singapore (392,000), Japan (383,000), and France (379,000).
- The Terrapin attack affects many SSH client and server implementations, such as OpenSSH, PuTTY, FileZilla, Dropbear, libssh, and more. You can see the complete list of known affected implementations here).
- You can prevent the Terrapin attack by updating your SSH software to the latest version, using secure encryption modes, and enabling strict key exchange. You can also use the Terrapin vulnerability scanner, available on GitHub, to check your SSH client or server for vulnerability.
- A team of researchers from the Horst Görtz Institute for IT Security at Ruhr University Bochum in Germany discovered and disclosed the Terrapin attack. They published a detailed paper and a website with the technical details and the implications of the attack. Conclusion: How to stay safe from the Terrapin attack
The Terrapin attack is a serious threat to SSH security. It lets hackers break into SSH servers by exploiting a vulnerability in the protocol. To protect yourself effectively, you need to do the following:
- Update your SSH software to the latest version
- Use two-factor authentication
- Store your SSH keys securely
- Use PassCypher HSM PGP and EviKey NFC HSM
Conclusion: How to stay safe from the Terrapin attack
The Terrapin attack is a serious threat to SSH security. It allows hackers to break into SSH servers by exploiting a vulnerability in the protocol. To protect yourself effectively, you need to update your SSH software, use two-factor authentication, store your SSH keys securely, and use PassCypher HSM PGP and EviKey NFC HSM. If you found this article useful, please feel free to share it with your contacts or leave us a comment.








