Russian Espionage: How Western Hacking Tools Were Turned Against Their Makers
2026 Cyber Doctrine Cyberculture
Individual Digital Sovereignty: Foundations, Global Tensions, and Proof by Design
2025 Cyber Doctrine Cyberculture
Constitution non codifiée du Royaume-Uni | souveraineté numérique & chiffrement
2025 Cyberculture EviLink
P2P WebRTC Secure Messaging — CryptPeer Direct Communication End to End Encryption
2025 Cyberculture Cybersecurity Digital Security EviLink
CryptPeer messagerie P2P WebRTC : appels directs chiffrés de bout en bout
2025 Cyber Doctrine Cyberculture
Souveraineté individuelle numérique : fondements et tensions globales
2025 Cyberculture
Audit ANSSI Louvre – Failles critiques et réponse souveraine PassCypher
Russian Espionage Hacking Tools: Discovery and Initial Findings
Russian espionage hacking tools were uncovered by Google’s Threat Analysis Group (TAG) on August 29, 2024, during an investigation prompted by unusual activity on Mongolian government websites. These sites had been compromised for several months. Russian hackers, linked to the SVR, embedded sophisticated malware into these sites to target the credentials of government officials, particularly those from the Ministry of Foreign Affairs.
Compromised Websites can be accessed at the Government of Mongolia. It’s recommended to use secure, up-to-date devices when visiting.
Historical Context of Espionage
Espionage has been a fundamental part of statecraft for centuries. The practice dates back to ancient civilizations, with documented use in places like ancient China and Egypt, where it played a vital role in military and political strategies. In modern times, espionage continues to be a key tool for nations to protect their interests, gather intelligence, and navigate the complex web of international relations.
Despite its prevalence, espionage remains largely unregulated by international law. Countries develop or acquire various tools and technologies to conduct espionage, often pushing the boundaries of legality and ethics. This lack of regulation means that espionage is widely accepted, if not officially sanctioned, as a necessary element of national security.
Global Dynamics of Cyber Espionage
In the evolving landscape of cyber espionage, the relationships between nation-states are far from straightforward. While Russia’s Foreign Intelligence Service (SVR) has notoriously employed cyberattacks against Western nations, it’s critical to note that these tactics aren’t limited to clear-cut adversaries. Recently, Chinese Advanced Persistent Threat (APT) groups have targeted Russian systems. This development underscores that cyber espionage transcends traditional geopolitical boundaries, illustrating that even ostensibly neutral or allied nations may engage in sophisticated cyber operations against one another. Even countries that appear neutral or allied on the global stage engage in sophisticated cyber operations against one another. This complexity underscores a broader trend in cyber espionage, where alliances in the physical world do not always translate to cyberspace. Consider splitting complex sentences like this to improve readability: “As a result, this growing web of cyber operations challenges traditional perceptions of global espionage. It compels nations to reassess their understanding of cyber threats, which may come from unexpected directions. Nations must now consider potential cyber threats from all fronts, including those from unexpected quarters.
Recent Developments in Cyber Espionage
Add a transitional sentence before this, such as “In recent months, the landscape of cyber espionage has evolved, with new tactics emerging that underscore the ongoing threat. APT29, known for its persistent cyber operations, has recently weaponized Western-developed spyware tools, turning them against their original creators. This alarming trend exemplifies the adaptive nature of cyber threats. In particular, the group’s activities have exploited new vulnerabilities within the Mongolian government’s digital infrastructure, demonstrating their ongoing commitment to cyber espionage. Moreover, these developments signal a critical need for continuous vigilance and adaptation in cybersecurity measures. As hackers refine their methods, the importance of staying informed about the latest tactics cannot be overstated. This topic brings the most current insights into focus, ensuring that readers understand the immediacy and relevance of these cyber threats in today’s interconnected world.
Who Are the Russian Hackers?
The SVR (Sluzhba Vneshney Razvedki), Russia’s Foreign Intelligence Service, manages intelligence and espionage operations outside Russia. It succeeded the First Chief Directorate (FCD) of the KGB and operates directly under the president’s oversight. For more information, you can visit their official website.
APT29, also known as Cozy Bear, is the group responsible for this operation. With a history of conducting sophisticated cyber espionage campaigns, APT29 has consistently targeted governmental, diplomatic, and security institutions worldwide. Their persistent activities have made APT29 a significant threat to global cybersecurity.
Methodology: How Russian Espionage Hacking Tools Were Deployed
Compromise Procedure:
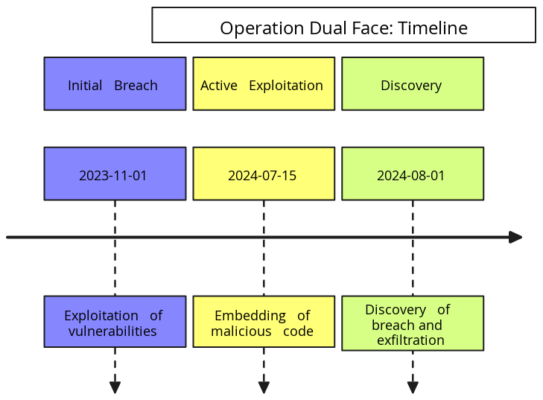
- Initial Breach:
To begin with, APT29 gained unauthorized access to several official Mongolian government websites between November 2023 and July 2024. The attackers exploited known vulnerabilities that had, unfortunately, remained effective on outdated systems, even though patches were available from major vendors such as Google and Apple. Furthermore, the tools used in these attacks included commercial spyware similar to those developed by companies like NSO Group and Intellexa, which had been adapted and weaponized by Russian operatives. - Embedding Malicious Code:
Subsequently, after gaining access, the attackers embedded sophisticated JavaScript code into the compromised web pages. In particular, this malicious code was meticulously designed to harvest login credentials, cookies, and other sensitive information from users visiting these sites. Moreover, the tools employed were part of a broader toolkit adapted from commercial surveillance software, which APT29 had repurposed to advance the objectives of Operation Dual Face. - Data Exfiltration:
Finally, once the data was collected, Russian operatives exfiltrated it to SVR-controlled servers. As a result, they were able to infiltrate email accounts and secure communications of Mongolian government officials. Thus, the exfiltrated data provided valuable intelligence to the SVR, furthering Russia’s geopolitical objectives in the region.
Detecting Russian Espionage Hacking Tools
Effective detection of Russian espionage hacking tools requires vigilance. Governments must constantly monitor their websites for unusual activity. Implement advanced threat detection tools that can identify and block malicious scripts. Regular security audits and vulnerability assessments are essential to protect against these threats.
Enhancing Defense Against Operation Dual Face with Advanced Cybersecurity Tools
In response to sophisticated espionage threats like Operation Dual Face, it is crucial to deploy advanced cybersecurity solutions. Russian operatives have reverse-engineered and adapted elements from Western-developed hacking tools to advance their own cyber espionage goals, making robust defense strategies more necessary than ever. Products like DataShielder NFC HSM Master, PassCypher NFC HSM Master, PassCypher HSM PGP Password Manager, and DataShielder HSM PGP Encryption offer robust defenses against the types of vulnerabilities exploited in this operation.
DataShielder NFC HSM secures communications with AES-256 CBC encryption, preventing unauthorized access to sensitive emails and documents. This level of encryption would have protected the Mongolian government’s communications from interception. PassCypher NFC HSM provides strong defenses against phishing and credential theft, two tactics prominently used in Operation Dual Face. Its automatic URL sandboxing feature protects against phishing attacks, while its NFC HSM integration ensures that even if attackers gain entry, they cannot extract stored credentials without the NFC HSM device.
DataShielder HSM PGP Encryption revolutionizes secure communication for businesses and governmental entities worldwide. Designed for Windows and macOS, this tool operates serverless and without databases, enhancing security and user privacy. It offers seamless encryption directly within web browsers like Chromium and Firefox, making it an indispensable tool in advanced security solutions. With its flexible licensing system, users can choose from various options, including hourly or lifetime licenses, ensuring cost-effective and transient usage on any third-party computer.
Additionally, DataShielder NFC HSM Auth offers a formidable defense against identity fraud and CEO fraud. This device ensures that sensitive communications, especially in high-risk environments, remain secure and tamper-proof. It is particularly effective in preventing unauthorized wire transfers and protecting against Business Email Compromise (BEC).
These tools provide advanced encryption and authentication features that directly address the weaknesses exploited in Operation Dual Face. By integrating them into their cybersecurity strategies, nations can significantly reduce the risk of falling victim to similar cyber espionage campaigns in the future.
Global Reactions to Russian Espionage Hacking Tools
Russia’s espionage activities, particularly their use of Western hacking tools, have sparked significant diplomatic tensions. Mongolia, backed by several allied nations, called for an international inquiry into the breach. Online forums and cybersecurity communities have actively discussed the implications. Many experts emphasize the urgent need for improved global cyber norms and cooperative defense strategies to combat Russian espionage hacking tools.
Global Strategy of Russian Cyber Espionage
Russian espionage hacking tools, prominently featured in the operation against Mongolia, are part of a broader global strategy. The SVR, leveraging the APT29 group (also known as Cozy Bear), has conducted cyber espionage campaigns across multiple countries, including North America and Europe. These campaigns often target key sectors, with industries like biotechnology frequently under threat. When mentioning specific industries, ensure accurate references based on the most recent data or reports. If this is speculative or generalized, it may be appropriate to state, “…and key industries, including, but not limited to, biotechnology.”
The Historical Context of Espionage
Espionage is a practice as old as nations themselves. Countries worldwide have relied on it for centuries. The first documented use of espionage dates back to ancient civilizations, where it played a vital role in statecraft, particularly in ancient China and Egypt. In modern times, nations continue to employ espionage to safeguard their interests. Despite its widespread use, espionage remains largely unregulated by international law. Like many other nations, Russia develops or acquires espionage tools as part of its strategy to protect and advance its national interests.
Mongolia’s Geopolitical Significance
Mongolia’s geopolitical importance, particularly its position between Russia and China, likely made it a target for espionage. The SVR probably sought to gather intelligence not only on Mongolia but also on its interactions with Western nations. This broader strategy aligns with Russia’s ongoing efforts to extend its geopolitical influence through cyber means.
The Need for International Cooperation
The persistence of these operations, combined with the sophisticated methods employed, underscores the critical need for international cooperation in cybersecurity. As espionage remains a common and historically accepted practice among nations, the development and use of these tools are integral to national security strategies globally. However, the potential risks associated with their misuse emphasize the importance of vigilance and robust cybersecurity measures.
Global Reach of Russian Espionage Hacking Tools
In the evolving landscape of modern cyber espionage, Russian hacking tools have increasingly gained significant attention. Specifically, while Mongolia was targeted in the operation uncovered on August 29, 2024, it is important to recognize that this activity forms part of a broader, more concerning pattern. To confirm these findings, it is essential to reference authoritative reports and articles. For instance, according to detailed accounts by the UK National Cyber Security Centre (NCSC) and the US Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA), the SVR, acting through APT29 (Cozy Bear), has executed cyber espionage campaigns across multiple countries. These reports highlight the SVR’s extensive involvement in global cyber espionage, which significantly reinforces the credibility of these claims. Moreover, these operations frequently target governmental institutions, critical infrastructure, and key industries, such as biotechnology.
Given Mongolia’s strategic location between Russia and China, it was likely selected as a target for specific reasons. The SVR may have aimed to gather intelligence on Mongolia’s diplomatic relations, especially its interactions with Western nations. This broader strategy aligns closely with Russia’s ongoing efforts to extend its geopolitical influence through cyber means.
The sophistication and persistence of these operations clearly underscore the urgent need for international cooperation in cybersecurity. As nations continue to develop and deploy these tools, the global community must, therefore, remain vigilant and proactive in addressing the formidable challenges posed by cyber espionage.
Historical Context and Comparative Analysis
Historical Precedents
Russia’s use of reverse-engineered spyware mirrors previous incidents involving Chinese state-sponsored actors who adapted Western tools for cyber espionage. This pattern highlights the growing challenge of controlling the spread and misuse of advanced cyber tools in international espionage. Addressing these challenges requires coordinated global responses.
Future Implications and Predictions
Long-Term Impact
The proliferation of surveillance technologies continues to pose a significant threat to global cybersecurity. Nations must urgently collaborate to establish robust international agreements. These agreements will govern the sale, distribution, and use of such tools. Doing so will help prevent their misuse by hostile states.
Visual and Interactive Elements
Operation Dual Face: Timeline and Attack Flow
Timeline:
This visual representation spans from November 2023, marking the initial breach, to the discovery of the cyberattack in August 2024. The timeline highlights the critical stages of the operation, showcasing the progression and impact of the attack.
Attack Flow:
The flowchart details the attackers’ steps, showing the process from exploiting vulnerabilities, embedding malicious code, to exfiltrating data.
Global Impact:
A map (if applicable) displays the geographical spread of APT29’s activities, highlighting other nations potentially affected by similar tactics.
Moving Forward
The Russian adaptation and deployment of Western-developed spyware in Operation Dual Face underscore the significant risks posed by the uncontrolled proliferation of cyber-surveillance tools. The urgent need for international collaboration is clear. Establishing ethical guidelines and strict controls is essential, especially as these technologies continue to evolve and pose new threats.
For further insights on the spyware tools involved, please refer to the detailed articles:








