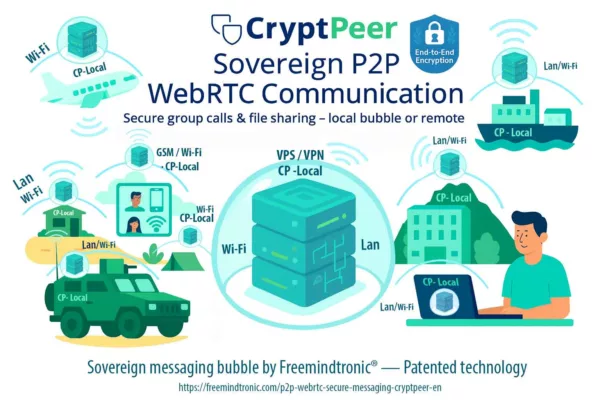
2025, Cyberculture
Tchap Sovereign Messaging — Strategic Analysis France
Executive Summary
Starting September 2025, the French government mandates the exclusive use of Tchap, a secure messaging platform built on the Matrix protocol, as formalized in the Prime Minister’s circular n°6497/SG dated 25 July 2025 (full text on Légifrance — PDF version). This structural shift requires a comprehensive review of Tchap’s resilience, sovereignty, and compliance with strategic standards (ANSSI, ZTA, RGS, SecNumCloud).
This sovereign chronicle, enhanced by Freemindtronic’s solutions (PassCypher, DataShielder), deciphers the challenges of identity governance, dual-layer encryption, disaster recovery (PRA/PCA), and hardware-based isolation beyond cloud dependencies.
Public Cost: According to DINUM, Tchap’s initial development was publicly funded at €1.2 million between 2018 and 2020, with an estimated annual operating budget of €400,000 covering maintenance, upgrades, hosting, and security. This moderate investment, compared to proprietary alternatives, reflects a strategic commitment to digital sovereignty.
Estimated reading time: 47 minutes
Complexity level: Strategic / Expert
Language specificity: Sovereign lexicon – High concept density
Accessibility: Screen reader optimized — semantic anchors in place for navigation
Editorial type: Chronique
About the Author: This analysis was authored by Jacques Gascuel, inventor and founder of Freemindtronic®. Specialized in sovereign security technologies, he designs and patents hardware-rooted systems for data protection, cryptographic sovereignty, and secure communications. His expertise spans compliance with ANSSI, NIS2, GDPR, and SecNumCloud frameworks, as well as countering hybrid threats through sovereign-by-design architectures.
In Cyberculture ↑ Correlate this Chronicle with other sovereign threat analyses in the same editorial rubric.
Strategic & Sovereign Navigation Index
- Executive Summary
- History of Tchap
- Adoption & Statistics
- Historical Security Vulnerabilities
- Auditability & Certifications
- Zero Trust Compatibility
- Element Technical Baseline
- Matrix Protocol Analysis
- Messaging & Device Comparison Table
- Geopolitical Messaging Map
- Sovereign Doctrine Timeline
- Sovereign Glossary
- Field Use & Mobility
- Crisis Continuity Scenarios
- Resilience Test Cases
- Compromise Scenarios & Doctrinal Responses
- AI & Quantum Threat Anticipation
- Automated Strategic Threat Monitoring
- CVE Intelligence & Vulnerability Governance
- Freemindtronic Use Case: Sovereign Complement to Tchap
- PassCypher / DataShielder Architecture: Runtime Sovereignty & Traceability
- PassCypher NFC HSM & PassCypher HSM PGP — Sovereign Access & Identity Control for Tchap
- PassCypher PGP HSM Use Case: Enhanced Diplomatic Passwordless Manager Offline
- Tchap Dual Encryption Extension
- Metadata Governance & Sovereign Traceability
- Sovereign UX: Cognitive Trust & Flow Visualization
- Trust Flow Diagram
- Software Trust Chain Analysis
- Sovereign Dependency Mapping
- Crisis System Interoperability
- Interoperability in Health & Education
- Ministerial Field Feedback
- Legal & Regulatory Framework
- Strategic Metrics & ROI
- Academic Indexing & Citation
- Strategic Synthesis & Sovereign Recommendations
Key Insights include:
- ⚠ Tchap (Matrix) operates with E2EE as an opt-in, leaving unencrypted channels active by default — increasing exposure to lawful interception or metadata harvesting.
- ⛓ DataShielder NFC HSM / DataShielder HSM PGP enable sovereign, client-side encryption of messages and files — pre-encrypting content before Tchap transport, with keys stored exclusively in hardware.
- ⚷ PassCypher NFC HSM / PassCypher HSM PGP securely store critical access secrets (logins, passwords, OTP seeds, recovery keys) entirely off-cloud with NFC/HID injection and zero local persistence.
- ⇔ Native Tchap lacks TOTP/HOTP generation — sovereign HSM modules can extend it to secure multi-factor authentication without relying on cloud-based OTP services.
- ⚯ Independent hardware key isolation ensures operational continuity and sovereignty — even during malware intrusion, insider compromise, or total network blackout.
- ☂ All Freemindtronic sovereign solutions comply with ANSSI guidance, NIS2 Directive, Zero Trust Architecture principles, GDPR requirements, and SecNumCloud hosting standards.
History of Tchap
The origins of Tchap date back to 2017, when the Interministerial Directorate for Digital Affairs (DINUM, formerly DINSIC) launched an initiative to equip French public services with a sovereign instant messaging platform. The goal was clear: to eliminate reliance on foreign platforms such as WhatsApp, Signal, or Telegram, which were deemed non-compliant with digital sovereignty standards and GDPR regulations.
Developed from the open-source client Element (formerly Riot), Tchap is based on the Matrix protocol, whose federated architecture enables granular control over data and servers. The first version was officially launched in April 2019. From the outset, Tchap was hosted in France under DINUM’s oversight, with a strong emphasis on security (authentication via FranceConnect Agent) and interoperability across ministries.
Between 2019 and 2022, successive versions enhanced user experience, resilience, and mobile compatibility. In 2023, an acceleration phase was initiated to prepare for the platform’s expansion to all public agents. By July 2024, a ministerial decree was drafted, leading to the structural measure effective on 1 September 2025: Tchap becomes the sole authorized messaging platform for communications between state agents.
⮞ Timeline
- 2017 – Project launch by DINUM
- 2019 – Official release of the first version
- 2021 – Advanced mobile integration, strengthened E2EE
- 2023 – Expansion to local authorities
- 2024 – Ministerial obligation decree drafted
- 2025 – Tchap becomes mandatory across central administration
Adoption Metrics and Usage Statistics
Since its official launch in April 2019, Tchap has progressively expanded across French public administrations. Initially deployed within central ministries, it later reached decentralized services and regional agencies.
As of Q2 2025, Tchap reportedly serves over 350,000 active users, including civil servants, security forces, and health professionals. The application registers an average of 15 million secure messages exchanged per month, according to DINUM figures.
In parallel, usage patterns indicate growing mobile access—over 65% of sessions originate from iOS and Android devices. The platform maintains 99.92% availability across certified infrastructure hosted under SecNumCloud constraints.
⮞ Key Indicators
- Active users: ~350,000 (projected to exceed 500,000 by 2026)
- Monthly messages: 15M+ encrypted exchanges
- Mobile access: 65% of sessions
- Infrastructure uptime: 99.92% (SecNumCloud-compliant)
Historical Security Vulnerabilities
Despite its security‑focused design, Tchap—based on the Element client and Matrix protocol—has faced several vulnerabilities since its inception. Below is a structured overview of key CVEs affecting the ecosystem, including the status of the 2025 entry:
| CVE | Description | Component | Severity (CVSS) | Disclosure Date |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CVE‑2019‑11340 | Email parsing flaw allowing spoofed identities | Sydent | High (7.5) | April 2019 |
| CVE‑2019‑11888 | Unauthorized access via email spoofing | Matrix / Tchap | Critical (9.8) | May 2019 |
| CVE‑2021‑39174 | Exposure through custom integrations | Element Web | Medium (6.5) | August 2021 |
| CVE‑2022‑36059 | Input validation flaw in federation | Synapse | High (7.4) | November 2022 |
| CVE‑2024‑34353 | Private key leak in logs | Rust SDK | Critical (9.1) | March 2024 |
| CVE‑2024‑37302 | DoS via media cache overflow | Synapse | Medium (5.3) | April 2024 |
| CVE‑2024‑42347 | Insecure URL preview in E2EE | React SDK | High (7.2) | May 2024 |
| CVE‑2024‑45191 | Weak AES configuration | libolm | Medium (6.3) | June 2024 |
| CVE‑2025‑49090 | State resolution flaw in Room v12 protocol (Reserved status) | Synapse | High (pending CVSS) | Reserved (Matrix planned server update 11 Aug 2025) |
This CVE is currently marked as “Reserved” on official databases (MITRE, NVD), meaning no technical details are publicly disclosed yet. However, Matrix.org confirms that the flaw concerns the state resolution mechanism of the Matrix protocol. It triggered the design of Room v12 and will be addressed via a synchronized server update on 11 August 2025 across the ecosystem.
The federated nature of Matrix introduces complexity that expands attack surfaces. Tchap’s alliance with sovereign infrastructure and rapid patch governance mitigates many risks—but proactive monitoring, particularly around Room‑v12 coordination, remains vital.
Auditability & Certifications
To ensure strategic resilience and regulatory alignment, Tchap operates within a framework shaped by France’s and Europe’s most stringent cybersecurity doctrines. Rather than relying on implicit trust, the platform’s architecture integrates sovereign standards that govern identity, encryption, and operational traceability.
First, the RGS (Référentiel Général de Sécurité) defines the baseline for digital identity verification, data integrity, and cryptographic practices across public services. Tchap’s authentication mechanisms—such as FranceConnect Agent—adhere to these requirements.
Next, the hosting infrastructure is expected to comply with SecNumCloud, the national qualification framework for cloud environments processing sensitive or sovereign data. While Tchap itself has not been officially declared as SecNumCloud-certified, it is hosted by DINUM-supervised providers located within France. Hosting remains under DINUM-supervised providers located in France; deployments align with SecNumCloud constraints.
In parallel, the evolving cybersecurity landscape introduces broader audit scopes. The NIS2 Directive and ANSSI’s Zero Trust Architecture (ZTA) require organizations to audit beyond static perimeters and adopt systemic resilience strategies:
- Real-time incident response capabilities
- Operational continuity and recovery enforcement
- Continuous access verification and segmentation by design
⮞ Sovereign Insight:
Before deploying any solution involving critical or classified data, public institutions must cross-verify the hosting operator’s status via the official ANSSI registry of qualified trust service providers. This validation is essential to ensure end-to-end sovereignty, enforce resilience doctrines, and prevent infrastructural drift toward non-conforming ecosystems.
Zero Trust Compatibility
As France transitions toward a sovereign digital ecosystem, Zero Trust Architecture (ZTA) emerges not merely as a technical framework but as a doctrinal imperative. Tchap’s evolution reflects this shift, where federated identity and sovereign infrastructure converge to meet the demands of runtime trust enforcement.
Although Tchap was not initially conceived under the ZTA model, its federated foundations and sovereign overlays allow progressive convergence toward strategic alignment with doctrines defined by ANSSI, ENISA, and the US DoD. ZTA mandates continuous, context-aware identity verification, no implicit trust across system boundaries, and runtime enforcement of least privilege.
Inherited from the Matrix protocol and Element client, Tchap supports identity federation and role-based access control. However, gaps remain regarding native ZTA requirements, including:
- Real-time risk evaluation or behavioral scoring
- Dynamic segmentation through software-defined perimeters
- Cryptographic attestation of endpoints before session initiation
To address these gaps, sovereign augmentations such as PassCypher NFC HSM and DataShielder HSM PGP (by Freemindtronic) enable:
- Offline cryptographic attestation of identities and devices
- Layered key compartmentalization independent of cloud infrastructures
- Runtime policy enforcement detached from network connectivity or software stack trust
While FranceConnect Agent provides federated SSO for public agents, it lacks endpoint verification and does not enforce runtime conditionality—thereby limiting full adherence to ZTA. Complementary sovereign modules can fill these architectural voids.
Doctrinal Gap Analysis
| ZTA Requirement | Tchap Native Support | Sovereign Augmentation |
|---|---|---|
| Continuous identity verification | Yes, via FranceConnect Agent | Not supported natively; requires endpoint attestation |
| Least privilege enforcement | Yes, via RBAC | Enhanced via PassCypher HSM policies |
| Cryptographic attestation of endpoints | No | Enabled via NFC HSM (offline attestation) |
| Dynamic segmentation | Absent | Enabled via DataShielder compartmentalization |
| Behavioral risk scoring | Not implemented | Possible via sovereign telemetry modules |
Strategic Enablers for Zero Trust Convergence
- 3DS Outscale, OVHcloud, Scaleway – SecNumCloud-certified infrastructures supporting secure trust zones
- ANSSI – Zero Trust Architecture Doctrine
- DoD – Zero Trust Reference Architecture v2.0
- ENISA – Zero Trust Guidance
- ENISA – NIS2 Technical Implementation Guidance
⮞ Sovereign Insight:
No Zero Trust framework can succeed without hardware-based verification and dynamic policy enforcement. By integrating Freemindtronic’s sovereign HSM NFC solutions into the Tchap perimeter, public entities reinforce runtime integrity and eliminate dependencies on foreign surveillance-prone infrastructures.
Zero Trust is not a feature—it is a posture. Sovereign cybersecurity demands runtime enforcement mechanisms that operate independently of cloud trust assumptions. Freemindtronic’s HSM modules embody this principle by enabling cryptographic sovereignty at the edge, even in disconnected or compromised environments.
Element Technical Baseline
Tchap relies on a modular and sovereign-ready architecture built upon the open-source Element client and the federated Matrix protocol. Element acts as the user interface layer, while Matrix handles decentralized message routing and data integrity. This combination empowers French public services to retain control over data residency, server governance, and communication sovereignty.
To strengthen its security posture, Element integrates client-side encryption libraries such as libolm, enabling end-to-end encryption across devices. Tchap builds on this foundation by enforcing authentication through FranceConnect Agent and disabling federation with non-approved servers. These adaptations reduce the attack surface and ensure closed-circle communication among state agents.
Nevertheless, several upstream dependencies remain embedded in the stack. These include:
- JavaScript-based frontends, which introduce browser-level exposure risks
- Electron-based desktop builds, requiring scrutiny of embedded runtime environments
- webRTC modules for voice and video, which may bypass sovereign routing controls
Such components must undergo continuous audit to ensure alignment with national security doctrines and to prevent indirect reliance on foreign codebases or telemetry vectors.
Dependency Risk Overview
| Component | Function | Risk Vector | Mitigation Strategy |
|---|---|---|---|
| JavaScript Frontend | UI rendering and logic | Browser-level injection, telemetry leakage | Code hardening, CSP enforcement |
| Electron Runtime | Desktop application container | Bundled dependencies, privilege escalation | Sandboxing, binary integrity checks |
| webRTC Stack | Voice and video communication | Peer-to-peer routing bypassing sovereign paths | Sovereign STUN/TURN servers, traffic inspection |
Strategic Considerations
While Element provides a flexible and customizable base for sovereign deployment, its upstream complexity demands proactive governance. Public entities must continuously monitor dependency updates, audit embedded modules, and validate runtime behaviors to maintain compliance with ANSSI and SecNumCloud expectations.
⮞ Sovereign Insight:
Sovereignty is not achieved through open source alone. It requires active and continuous control over software dependencies, runtime environments, and cryptographic flows. Freemindtronic’s hybrid hardware modules—such as PassCypher NFC HSM/HSM PGP and DataShielder NFC HSM/HSM PGP—strengthen endpoint integrity and isolate sensitive operations from volatile software layers. This approach reinforces operational resilience against systemic threats and indirect intrusion vectors.
Matrix Protocol Analysis
The Matrix protocol underpins Tchap’s sovereign messaging architecture through a decentralized model of federated homeservers. Each communication is replicated across servers using Directed Acyclic Graphs (DAGs), where messages are encoded as cryptographically signed events. This design promotes auditability and availability but introduces complex operational challenges when applied within high-assurance, sovereignty-bound infrastructures.
Its core advantage—replicated state resolution—enables homeservers to recover conversation history post-disconnection. While aligned with resilience doctrines, this function conflicts with strict requirements for data residency, execution traceability, and perimeter determinism. Any federation node misaligned with ANSSI-certified infrastructure may undermine the protocol’s sovereign posture.
Encryption is natively handled via libolm and megolm, leveraging Curve25519 and AES‑256. Although robust in theory, recent CVEs such as CVE‑2024‑45191 underscore critical lapses in software-only key custody. Without hardware-bound isolation, key lifecycle vulnerabilities persist—especially in threat environments involving supply chain compromise or rogue administrator scenarios.
The federated nature of Matrix—an asset for decentralization—creates heterogeneity in security policy enforcement. In cross-ministry deployments like Tchap, outdated homeservers or misconfigured peers may enable lateral intrusion, inconsistent cryptographic handling, or stealth metadata leakage. Sovereign deployments demand runtime guarantees not achievable through protocol specification alone.
Matrix establishes a robust foundation for distributed resilience and cryptographic integrity. However, sovereign deployments cannot rely solely on protocol guarantees. They require verified endpoints, consistent security policies across all nodes, and cloud-independent control over encryption keys. Without these sovereign enablers, systemic exposure remains latent.
• Enforce HSM-based secret isolation via PassCypher NFC
• Offload recovery credentials to air-gapped PGP modules
• Constrain federation to ANSSI-qualified infrastructures
• Inject ephemeral secrets through HID/NFC-based sandbox flows
• Visualize cryptographic flows using DataShielder traceability stack
⮞ Sovereign Insight:
Messaging sovereignty does not arise from protocol specifications alone. It stems from the capacity to control execution flows, isolate cryptographic assets, and maintain operational autonomy—even in disconnected or degraded environments. Freemindtronic’s PassCypher and DataShielder modules enable secure edge operations through offline cryptographic verification, zero telemetry exposure, and full lifecycle governance of sensitive secrets.
- Dual encryption barrier: DataShielder adds a sovereign AES-256 CBC encryption layer on top of Matrix’s native E2EE (Olm/Megolm), which remains limited to application-layer confidentiality
- Portable isolation: Credentials and messages remain protected outside the trusted perimeter
- Telemetry-free design: No identifiers, logs, or cloud dependencies
- Sovereign traceability: RGPD-aligned manufacturing and auditable key custody chain
- Anticipates future threats: Resistant to AI inference, metadata mining, and post-quantum disruption
• Chronique : Sovereign Messaging & Runtime Sovereignty
Messaging & Secure Device Comparison Table
This comparative analysis examines secure messaging platforms and sovereign-grade devices through the lens of national cybersecurity. It articulates five strategic dimensions: encryption posture, offline resilience, hardware key isolation, regulatory alignment, and overall sovereignty level. Notably, Freemindtronic does not offer a messaging service but provides sovereign cryptographic modules—PassCypher and DataShielder—which reinforce runtime autonomy, detached key custody, and non-cloud operational continuity.
| Platform / Device | Category | Sovereignty Level | Default E2EE | Offline Capability | Hardware Key Isolation | Regulatory Alignment |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tchap (Matrix / Element) | Messaging | Moderate to High | Partial (opt-in) | Absent | Optional via Freemindtronic | DINUM-hosted, aligned with SecNumCloud |
| Olvid | Messaging | High (France-native) | Yes (built-in) | Partial (offline pairing) | No hardware anchor | Audited, not SecNumCloud-certified |
| Cellcrypt | Messaging | High | Yes | Partial | Optional HSM | Gov & NATO alignment |
| Mode.io | Messaging | Moderate | Yes | Limited offline | No HSM | Commercial compliance |
| Wire | Messaging | High (EU) | Yes | Partial | No hardware anchor | GDPR-compliant |
| Threema Work | Messaging | High (Switzerland) | Yes | Partial | No hardware anchor | Swiss privacy law |
| Briar | Messaging | High | Yes (peer-to-peer) | Yes (offline mesh) | No hardware anchor | Community standard |
| CommuniTake | Device | Very High | OS-level encryption | Yes | Secure enclave | Gov-grade compliance |
| Bittium Tough Mobile | Device | Very High | OS-level encryption | Yes | Secure element | NATO-certified |
| CryptoPhone (GSMK) | Device | Very High | Secure VoIP & SMS | Yes | Secure module | Independent audits |
| Silent Circle Blackphone | Device | High | OS-level encryption | Yes | Secure enclave | Commercial compliance |
| Katim R01 | Device | Very High | Secure OS | Yes | Secure element | Gov & defense alignment |
| Sovereign Modules: Freemindtronic (PassCypher + DataShielder) | Sovereignty Enabler | Very High | N/A — not a messaging service | Yes — full offline continuity | Yes — physically external HSMs | Aligned with ANSSI, ZTA, NIS2 |
PassCypher secures authentication and access credentials via air-gapped injection through NFC or HID channels. DataShielder applies an independent AES-256 encryption layer that operates outside the messaging stack, with cryptographic keys stored in physically isolated sovereign HSMs—fully detached from cloud or application infrastructures.
Comparative Sovereignty Matrix
| Platform / Device | Jurisdictional Control | Runtime Sovereignty | Industrial Grade |
|---|---|---|---|
| Tchap | 🇫🇷 France (national) | Moderate | Rejected Thales |
| Olvid | 🇫🇷 France (independent) | High | No industrial backing |
| Cellcrypt | 🇬🇧 UK / 🇺🇸 US Gov alignment | High | Gov-certified |
| Mode.io | 🇪🇺 EU-based | Moderate | Commercial |
| Wire | 🇨🇭 Switzerland / 🇩🇪 Germany | High | Enterprise-grade |
| Threema Work | 🇨🇭 Switzerland | High | Enterprise-grade |
| Briar | 🌍 Open-source community | High | Peer-to-peer grade |
| CommuniTake | 🇮🇱 Israel (Gov alignment) | Very High | Industrial-grade |
| Bittium | 🇫🇮 Finland | Very High | NATO-certified |
| CryptoPhone | 🇩🇪 Germany | Very High | Independent secure hardware |
| Blackphone | 🇨🇭 Switzerland / 🇺🇸 US | High | Enterprise-grade |
| Katim R01 | 🇦🇪 UAE (Gov/Defense) | Very High | Defense-grade |
| Freemindtronic | 🏳️ Neutral | Full (air-gapped) | Sovereign modules |
Tchap Sovereign Messaging — Geopolitical Map & Strategic Context
This section maps the geopolitical positioning of Tchap within France’s sovereign communication strategy. It situates Tchap among European Union policy frameworks, emerging Global South sovereign messaging initiatives, and rival state-backed platforms, highlighting encryption policy divergences and sovereignty trade-offs.
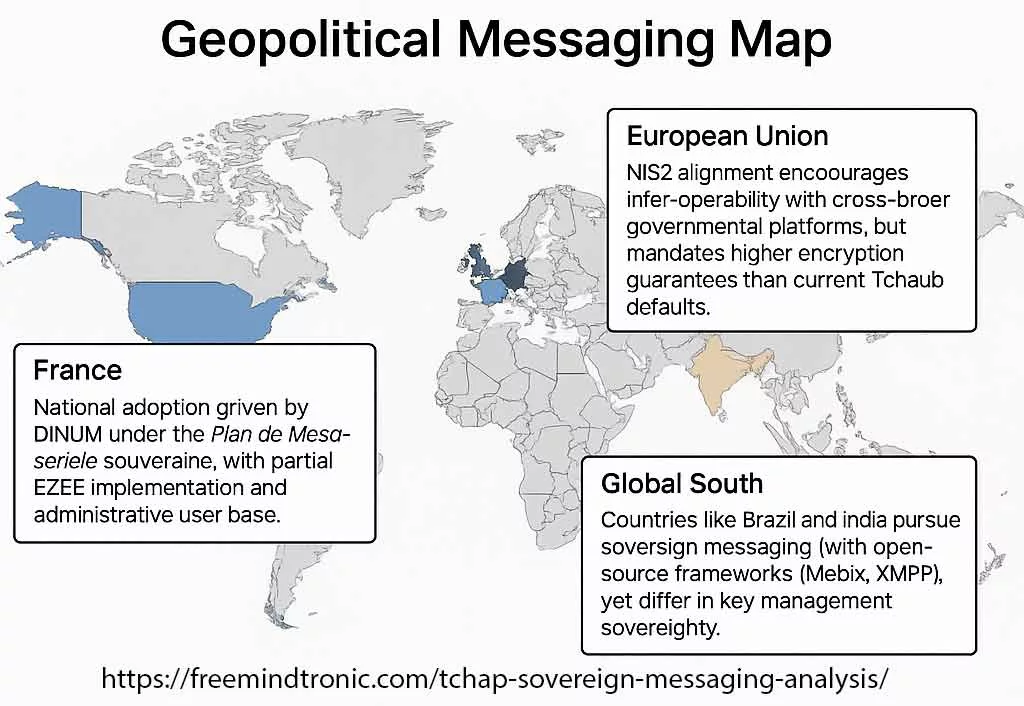
This map outlines the strategic positioning of Tchap within France’s sovereign communication landscape, while contextualizing its role against regional and global secure messaging initiatives.
- France — National adoption driven by DINUM under the Plan de Messagerie Souveraine, with partial E2EE implementation and administrative user base.
- European Union — NIS2 alignment encourages inter-operability with cross-border governmental platforms, but mandates higher encryption guarantees than current Tchap defaults.
- Global South — Countries like Brazil and India pursue sovereign messaging with open-source frameworks (Matrix, XMPP), yet differ in key management sovereignty.
- Strategic Rivals — U.S. and Chinese secure platforms (Signal derivatives, WeChat enterprise variants) influence encryption standards and geopolitical trust boundaries.
France’s sovereign messaging push with Tchap faces encryption policy gaps, while navigating competitive pressure from allied and rival state-backed secure platforms.
Sovereign Doctrine Timeline
This timeline consolidates key legal and strategic milestones that have shaped sovereign messaging policy in France and across the European Union. The progression illustrates a shift from compliance-centric frameworks to runtime sovereignty anchored in hardware isolation and jurisdictional control. This doctrinal evolution responds directly to emerging threat vectors—including extraterritorial surveillance, platform dependency, and systemic data exfiltration risks.
- 2016 — 🇪🇺 GDPR: Establishes the EU-wide foundation for data protection, enabling first-layer digital sovereignty through legal compliance.
- 2018 — 🇺🇸 CLOUD Act: Expands U.S. jurisdiction over foreign cloud providers, prompting sovereignty-centric policy responses across Europe.
- 2020 — 🇫🇷 SecNumCloud 3.2: Mandates full EU ownership, hosting, and administrative control for certified cloud services.
- 2021 — 🇫🇷 RGS v2 & Zero Trust: Introduces segmented access and cryptographic isolation aligned with Zero Trust architectures.
- 2022 — 🇪🇺 DORA: Reinforces operational resilience for EU financial entities through third-party dependency controls.
- 2023 — 🇪🇺 NIS2 Directive: Expands obligations for digital infrastructure providers, including messaging and cloud services.
- 2024 — 🇫🇷 Cloud au centre: Formalizes mandatory sovereign hosting for sensitive workflows; recommends endpoint-level cryptographic compartmentalization.
- 2025 — 🇪🇺 EUCS Draft: Proposes a European certification scheme for cloud services that excludes providers subject to foreign legal constraints.
- 2025 — 🇫🇷 Strategic Review on Digital Sovereignty: Positions runtime sovereignty and hardware-bound key custody as non-negotiable foundations for trusted communications.
Strategic Drift
From legal compliance to runtime containment, the doctrine now prioritizes execution control, key custody, and jurisdictional insulation. Sovereignty is no longer declarative—it must be cryptographically enforced and materially anchored. This shift reflects a strategic realization: trust cannot be outsourced, and resilience must be embedded at the hardware level.
Doctrinal Scope Comparison
| Doctrine | Jurisdictional Focus | Runtime Enforcement | Hardware Anchoring |
|---|---|---|---|
| 🇪🇺 GDPR | Legal compliance | None | None |
| 🇫🇷 RGS v2 / Zero Trust | National infrastructure | Segmented access | Optional |
| 🇪🇺 NIS2 / DORA | Critical operators | Third-party controls | Not required |
| 🇫🇷 Cloud au centre | Sovereign hosting | Mandatory isolation | Embedded cryptography |
| 🇪🇺 EUCS (draft) | Cloud sovereignty | Exclusion of foreign law | Pending specification |
This doctrinal progression reflects a decisive pivot—from declarative compliance to enforced containment. Protocols alone are insufficient. Runtime execution, key lifecycle, and cryptographic independence must be governed by mechanisms that resist legal coercion, telemetry leakage, and third-party inference—ideally through sovereign HSMs decoupled from cloud dependencies.
Sovereign Glossary
This glossary consolidates the key concepts that structure sovereign messaging architectures. Each term supports a precise understanding of how cryptographic autonomy, jurisdictional control, and runtime segmentation are deployed in national cybersecurity strategies.
- Runtime Sovereignty: Execution of security operations independently of third-party platforms, ensuring continuity and policy enforcement across disconnected or hostile environments.
- Hardware Security Module (HSM): Tamper-resistant hardware device that generates, stores, and processes cryptographic keys—physically decoupled from general-purpose systems.
- NFC HSM: Contactless hybrid hardware module enabling sovereign operations through segmented key architecture and proximity-based cryptographic triggering (via NFC).
- HSM PGP: Hybrid hardware system supporting OpenPGP-compatible operations. It separates key storage across multi-modal physical zones, allowing autonomous key management outside of networked environments.
- Segmented Key: Cryptographic architecture patented internationally by Freemindtronic. It distributes secret material across isolated and non-contiguous memory zones, ensuring no single component can reconstruct the full key. This architecture reinforces air-gapped trust boundaries and materially constrains key exfiltration.
- Key Custody: Continuous control over key material—covering generation, distribution, usage, and revocation—under a sovereign legal and operational perimeter.
- Zero Trust: Security posture assuming no default trust; it enforces identity validation, contextual access control, and endpoint integrity at every transaction stage.
- Cryptographic Compartmentalization: Isolation of cryptographic processes across hardware and software domains to limit propagation of breaches and enforce risk segmentation.
- Offline Cryptographic Verification: Authentication or decryption performed without network connectivity, typically through secure air-gapped or contactless devices.
- Federated Architecture: Decentralized structure allowing independent nodes to exchange and replicate data while retaining local administrative control.
- Cloud Sovereignty: Assurance that data and compute infrastructure remain subject only to the jurisdiction and policies of a trusted national or regional entity.
- Telemetry-Free Design: Architecture that excludes any form of behavioral analytics, usage logs, or identity traces—preventing metadata exfiltration by design.
These terms underpin the transition from compliance-based digital security to materially enforced sovereignty. They describe a framework where security posture depends not on trust declarations, but on physically enforced and verifiable constraints—aligned with national resilience doctrines.
Field Use & Mobility
Sovereign messaging architectures must operate seamlessly across disconnected, hostile, or resource-constrained environments. Field-deployed agents, tactical operators, and critical mobile workflows require tools that maintain full cryptographic continuity—without relying on central infrastructures or cloud relays.
- Offline Mode: Freemindtronic’s NFC HSM modules enable full message decryption and credential injection without network connectivity, ensuring functional isolation even in air-gapped conditions.
- Access Hardening: PassCypher secures mobile application access using segmented credentials injected through contactless proximity—blocking keyboard hijack and clipboard leakage.
- Data Overwatch: DataShielder enforces an external sovereign encryption layer, protecting files and messages independently of the hosting OS or messaging app integrity.
- Zero Emission: All modules operate without telemetry, persistent identifiers, or cloud dependencies—removing any digital trace of field activities.
- Portability: Solutions remain operational across smartphones, hardened laptops, and secure kiosks—even without firmware modification or dedicated middleware.
These capabilities enable trusted communications in non-permissive zones, cross-border missions, and sovereign diplomatic operations. They reduce reliance on vulnerable assets and ensure that security policies are not invalidated by connectivity loss or infrastructure compromise.
Crisis Continuity Scenarios
In the event of a large-scale disruption — whether due to network blackout, cyberattack, or loss of access to central infrastructure — sovereign messaging environments like Tchap must maintain operational capacity without compromising security. This section explores layered contingency plans combining Matrix-based private instances, DataShielder NFC HSM or PassCypher NFC HSM for secure credential storage, and alternative transport layers such as satellite relays (e.g. GovSat, IRIS²) or mesh networks.
Core objectives include:
- Ensuring end-to-end encrypted communications remain accessible via air-gapped or closed-circuit deployments.
- Providing double-layer encryption through hardware-segmented AES-256 keys stored offline.
- Allowing rapid redeployment to isolated Matrix homeservers with restricted federation to trusted nodes.
- Maintaining OTP/TOTP-based authentication without cloud dependency.
This approach complies with ANSSI’s Zero Trust doctrine (2024), LPM, and NIS2, while enabling field units — from civil security teams to diplomatic staff — to preserve confidentiality even in the face of total internet outage.
Resilience Test Cases
To validate the operational robustness of Tchap in conjunction with Freemindtronic hardware modules, specific resilience test cases must be executed under controlled conditions. These tests simulate degraded or hostile environments to confirm message integrity, authentication reliability, and service continuity.
Test Case 1 — Offline Authentication via NFC HSM: Store Tchap credentials in a DataShielder NFC HSM. Disconnect all internet access, connect to a local Matrix node, and inject credentials via Bluetooth/USB HID. Objective: verify successful login without exposure to local keystroke logging.
Test Case 2 — Double-Layer Encrypted Messaging: Pre-encrypt a text message with AES-256 CBC segmented keys on DataShielder, paste the ciphertext into a Tchap conversation, and have the recipient decrypt it locally with their HSM. Objective: confirm that even if native E2EE fails, content remains unreadable to unauthorized parties.
Test Case 3 — Network Isolation Operation: Connect clients to a private Matrix/Tchap instance via mesh or satellite link (GovSat/IRIS²). Send and receive messages with hardware-encrypted content. Objective: ensure minimal latency and maintained confidentiality over non-standard transport.
Each test must be logged with timestamps, error codes, and security event notes. Results feed into the Zero Trust Architecture compliance assessment and PRA/PCA readiness reports.
Compromise Scenarios & Doctrinal Responses
When operating a sovereign messaging platform such as Tchap, it is essential to anticipate potential compromise vectors and align mitigation strategies with national cybersecurity doctrines. Scenarios range from targeted credential theft to the exploitation of application-layer vulnerabilities or interception of metadata.
Scenario A — Credential Compromise: Stolen passwords or session tokens due to phishing, malware, or insider threat. Response: enforce multi-factor authentication using PassCypher NFC HSM, with secrets stored offline and injected only via physical presence, rendering remote theft ineffective.
Scenario B — Server Breach: Unauthorized access to Matrix homeserver storage or message queues. Response: adopt double-layer encryption with hardware-segmented AES-256 keys, ensuring content remains unintelligible even if server data is exfiltrated.
Scenario C — Network Surveillance: Traffic analysis to infer communication patterns. Response: leverage isolated federation nodes, onion-routing gateways, and adaptive padding to obfuscate metadata while maintaining service availability.
Scenario D — E2EE Failure: Misconfiguration or exploitation of the Olm/Megolm protocol stack. Response: apply pre-encryption at the client side with DataShielder, so that intercepted payloads contain only ciphertext beyond the native Matrix layer.
These countermeasures follow the ANSSI Zero Trust doctrine and support compliance with LPM and NIS2, ensuring that confidentiality, integrity, and availability are preserved under adverse conditions.
AI & Quantum Threat Anticipation
The convergence of advanced artificial intelligence and quantum computing introduces disruptive risks to sovereign messaging systems such as Tchap. AI-driven attacks can automate social engineering, exploit zero-day vulnerabilities at scale, and perform real-time traffic analysis. Quantum capabilities threaten the cryptographic primitives underlying current E2EE protocols, potentially rendering intercepted data decipherable.
AI-related risks: automated phishing with personalized lures, adaptive malware targeting specific operational contexts, and large-scale correlation of metadata from partial leaks. Mitigation: continuous anomaly detection, federated threat intelligence sharing between ministries, and proactive protocol hardening.
Quantum-related risks: Shor’s algorithm undermining RSA/ECC, Grover’s algorithm accelerating symmetric key searches. Mitigation: hybrid cryptography combining post-quantum algorithms (e.g. CRYSTALS-Kyber, Dilithium) with existing AES-256 CBC, stored and managed in DataShielder NFC HSM to ensure offline key custody.
Strategic planning requires embedding quantum-resilient cryptography into Tchap’s protocol stack well before large-scale quantum hardware becomes operational, and training operational teams to recognize AI-driven intrusion patterns in real time.
Maintaining the security posture of Tchap requires continuous surveillance of evolving threats, leveraging automation to detect, classify, and prioritize incidents in real time. Automated strategic threat monitoring combines machine learning, threat intelligence feeds, and sovereign infrastructure analytics to pre-emptively identify high-risk patterns. Core components: When combined with DataShielder NFC HSM and PassCypher modules, this framework ensures that even during a compromise window, authentication secrets and pre-encrypted payloads remain insulated from automated exploitation.
Automated Strategic Threat Monitoring
CVE Intelligence & Vulnerability Governance
Effective security governance for Tchap demands proactive tracking of vulnerabilities across its entire software stack — from the Matrix protocol and Synapse server to client forks and dependency libraries. CVE intelligence enables timely remediation, reducing the window of exposure for critical flaws.
Governance workflow:
- Maintain an updated software bill of materials (SBOM) for all Tchap components, including third-party modules and cryptographic libraries.
- Continuously monitor official CVE databases and sovereign CERT advisories for relevant disclosures.
- Implement a triage system: assess exploitability, potential impact on confidentiality, integrity, and availability, and required mitigation speed.
- Coordinate patch deployment through DINUM’s sovereign CI/CD infrastructure, ensuring integrity checks via reproducible builds.
Historical precedent — such as the April 2019 email validation flaw — highlights the need for immediate isolation of affected components, responsible disclosure channels, and post-mortem analysis to prevent recurrence. Leveraging PassCypher or DataShielder ensures that sensitive credentials remain protected even during active patch cycles.
Freemindtronic Use Case: Sovereign Complement to Tchap
The integration of PassCypher NFC HSM and DataShielder NFC HSM with Tchap strengthens sovereign security and operational resilience by keeping all credentials, encryption keys, and recovery codes under exclusive offline control — fully detached from Tchap’s native storage.
Scenario A — Hardware-Assisted Authentication: Tchap credentials are stored in a dedicated NFC HSM slot (≤61 ASCII characters, segmented into label, login, and password). Upon physical presence and PIN validation, credentials are injected directly into Tchap login fields via Bluetooth/USB HID, bypassing local OS storage and neutralizing keylogger or malware threats.
Scenario B — Dual-Layer Content Protection: Messages and files are pre-encrypted with AES-256 CBC using segmented keys generated in the NFC HSM. The ciphertext travels over Tchap, with decryption performed locally by the recipient’s sovereign module — ensuring confidentiality even if native E2EE is compromised.
Scenario C — Recovery & Continuity: Recovery keys, OTP/TOTP secrets, and export files are isolated in dedicated HSM slots, enabling rapid redeployment in crisis situations without reliance on external infrastructure.
Aligned with ANSSI’s Zero Trust Architecture and the July 2025 interministerial doctrine, this configuration ensures that critical secrets and content remain sovereign throughout their lifecycle, regardless of network or platform compromise.
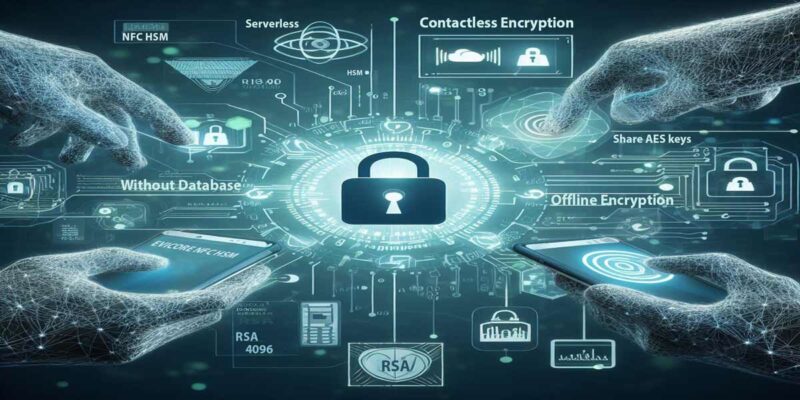
PassCypher / DataShielder Architecture: Runtime Sovereignty & Traceability
PassCypher HSM modules provide the hardware root of trust, while DataShielder orchestrates metadata governance and enforces a policy-driven chain of custody — ensuring operational sovereignty without exposing secrets.
Core Components:
PassCypher NFC HSM or HSM PGP (offline key custody), DataShielder (segmented vaults & policy engine), local middleware, Tchap client, and Matrix server.
- Runtime Sovereignty — HSM issues ephemeral cryptographic proofs; the host processes tokens only, with no long-term secrets in memory.
- Traceability — DataShielder logs policy outcomes and event hashes without storing plaintext content or keys.
- Compliance — Designed to meet Zero-Trust doctrine, GDPR data minimization principles, and NIS2 operational controls.
- Failure Isolation — Any compromise of client or server infrastructure cannot yield HSM-protected material.
Identity management, OTP workflows, and credential injection mechanisms are covered in the Sovereign Access & Identity Control section.
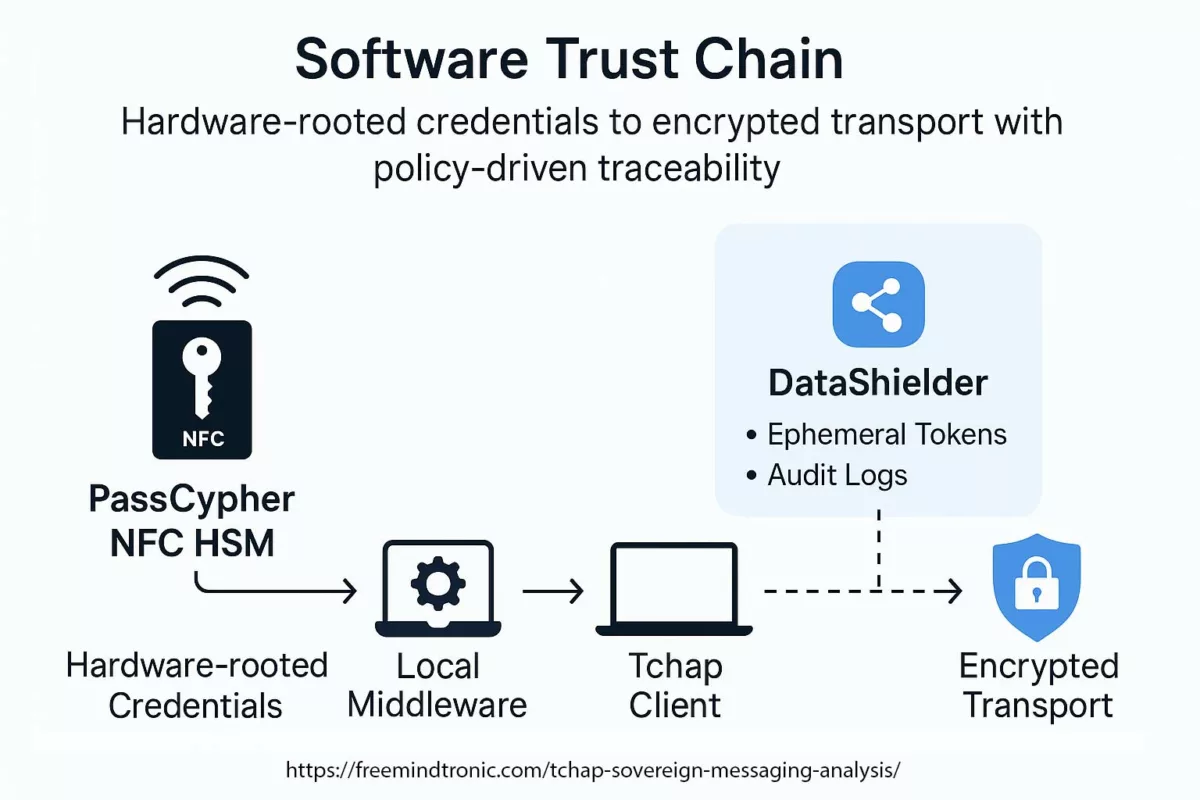
✪ Diagram — Software Trust Chain showing how sovereign trust flows from PassCypher HSM hardware credentials through encrypted Tchap transport, with DataShielder policy-driven traceability guaranteeing runtime sovereignty.
PassCypher NFC HSM & PassCypher HSM PGP — Sovereign Access & Identity Control for Tchap
Although Tchap implements secure end-to-end encryption (Olm/Megolm), safeguarding access credentials, recovery keys, and OTP secrets remains a critical challenge — especially under zero cloud trust and segmented sovereignty requirements.
PassCypher NFC HSM and PassCypher HSM PGP resolve this by managing and injecting all secrets entirely offline, ensuring they never appear in plaintext on any device.
- Credential Injection — Automated entry of login/password credentials via HID emulation (USB, Bluetooth, InputStick) for Tchap web or desktop clients.
- Recovery Key Custody — Secure storage of Matrix recovery phrases (≤61 printable ASCII characters on NFC HSM, unlimited on HSM PGP) with physical slot rotation.
- OTP/TOTP/HOTP Integration — Hardware-based generation and manual or policy-driven injection of one-time codes for MFA with Tchap services.
- Multi-Slot Separation — Distinct, labeled slots for each identity (e.g., ministry, local authority) to enforce physical separation.
- Offline-First Operation — Full capability in air-gapped or blackout environments via local middleware (HID or sandbox URL).
- Passwordless-by-Design — Hardware presence + PIN validation replace stored passwords, reducing attack vectors.
Deploying PassCypher with Tchap enables a sovereign, passwordless access model that prevents credential compromise from endpoint malware, phishing, or forensic extraction — while remaining compliant with ANSSI sovereignty requirements and the July 2025 interministerial doctrine.
PassCypher PGP HSM Use Case: Enhanced Diplomatic Passwordless Manager Offline
Diplomatic operations require sovereign, offline-first workflows with no credential persistence — even on trusted devices.
Scenario. In restricted or contested environments, where connectivity is intermittent or monitored, PassCypher HSM PGP securely stores PGP keypairs, OTP seeds, and recovery material entirely offline, ensuring credentials never enter device memory unencrypted.
- Passwordless Operation — Hardware presence + PIN initiate session bootstrap; no passwords are ever stored locally.
- Just-in-time Release — Time-bounded signatures and OTPs are issued only when all policy-defined conditions are met.
- Continuity — Operates fully in air-gapped or blackout conditions via local middleware.
- Multi-Role Utility — A single PGP HSM key set can protect diplomatic messages, classified documents, and external exchanges while Tchap maintains E2EE transport.
For details on credential injection, OTP generation, and multi-slot identity separation, see the Sovereign Access & Identity Control section.
Tchap Dual Encryption Extension
While Tchap already leverages end-to-end encryption through the Matrix protocol (Olm/Megolm), certain high-security operations demand an additional sovereign encryption layer. This dual-layer encryption model ensures that even if the native E2EE channel is compromised, sensitive payloads remain completely unintelligible to any unauthorized entity.
The second encryption layer is applied before content enters the Tchap client. Keys for this outer layer remain exclusively under the custody of a sovereign hardware security module — such as PassCypher NFC HSM or PassCypher HSM PGP — ensuring they never exist in Tchap, the operating system, or any network-accessible environment.
- Independent Key Custody — Encryption keys are stored and released solely upon physical presence and PIN validation via the HSM.
- Content-Agnostic Protection — Works with all Tchap content: messages, file attachments, exported session keys, and recovery codes.
- Operational Compartmentalization — Assign unique sovereign encryption keys for each Tchap room, mission, or operation to prevent cross-compromise.
- Post-Quantum Readiness — Supports composite or extended-length keys exceeding NFC HSM capacity via PassCypher HSM PGP.
By layering hardware-based sovereign encryption over Tchap’s native E2EE, organizations achieve resilience against insider threats, supply chain compromises, zero-day exploits, and future post-quantum cryptanalysis — without sacrificing day-to-day usability.
Even in the event of a complete Tchap infrastructure compromise, only holders of the sovereign HSM key can decrypt mission-critical data, maintaining absolute control over access.
Metadata Governance & Sovereign Traceability
Even when Tchap’s end-to-end encryption safeguards message content, metadata — sender, recipient, timestamps, room identifiers — remains a valuable target for intelligence gathering. Sovereign metadata governance ensures that all such transactional records are managed exclusively within the jurisdictional control of the French State, adhering to strict Zero Trust and compartmentalization policies.
Integrating PassCypher NFC HSM or PassCypher HSM PGP into Tchap access workflows enforces hardware-rooted identity binding to metadata events. Access keys and authentication proofs never reside on Tchap servers, drastically reducing correlation potential in the event of compromise or lawful intercept.
- Jurisdictional Data Residency — All metadata storage, audit logging, and trace generation occur within sovereign infrastructure, in compliance with ANSSI and interministerial doctrine.
- Identity-to-Event Binding — Sovereign HSMs ensure that only validated hardware-held identities can generate legitimate metadata entries.
- Audit-Ready Traceability — Each authentication or key release is cryptographically bound to a physical token and PIN verification.
- Exposure Minimization — No replication of credentials or identity markers into OS caches, browsers, or unprotected application logs.
This architecture strengthens operational sovereignty by making metadata trustworthy for internal audits yet opaque to external intelligence actors, even under full infrastructure compromise.
With sovereign metadata control, the State dictates the narrative — preserving forensic truth without reliance on foreign intermediaries.
Sovereign UX: Cognitive Trust & Flow Visualization
In high-security environments, operational sovereignty is not only about cryptographic strength — it also depends on how users perceive, verify, and interact with the system. With PassCypher NFC HSM or PassCypher HSM PGP securing Tchap sessions, the user experience must clearly communicate the real-time trust state at every step.
A well-designed sovereign UX implements hardware-based trust indicators and visual feedback loops to ensure operators always know when a key is in custody, released, injected, or locked. This cognitive trust framework reinforces proper operational behavior, reducing human error such as entering credentials into phishing prompts or skipping verification steps under pressure.
- Hardware Trust State Indicators — Device LEDs or secure displays confirm when a sovereign key is physically released or injected.
- Secure Credential Flow Mapping — On-screen diagrams illustrate the journey of credentials from the sovereign HSM to the Tchap session, with ⊘ marking non-transit zones.
- Contextual Slot Labels — Clear naming conventions (e.g., “Tchap-MinInt-OTP”) in PassCypher prevent identity or mission cross-use.
- Decision Checkpoints — Mandatory user confirmation before high-risk operations like recovery key release or OTP generation.
By merging security feedback with usability, sovereign UX aligns perfectly with Zero Trust Architecture (ZTA) — no secret is ever assumed safe without explicit verification, and the operator remains an active component of the security perimeter.
A transparent, user-driven trust model not only safeguards against technical compromise but also builds behavioral resilience in operators, making them allies in the defense of state communications.
Trust Flow Diagram
This diagram visualizes the hardware-rooted trust path linking PassCypher NFC HSM or PassCypher HSM PGP to a secure Tchap session. It illustrates where secrets exist only transiently (⇢), where they never transit (⊘), and how session trust can be renewed (↻) or revoked (⊥) via a temporal blockchain of trust without persistent secret storage.
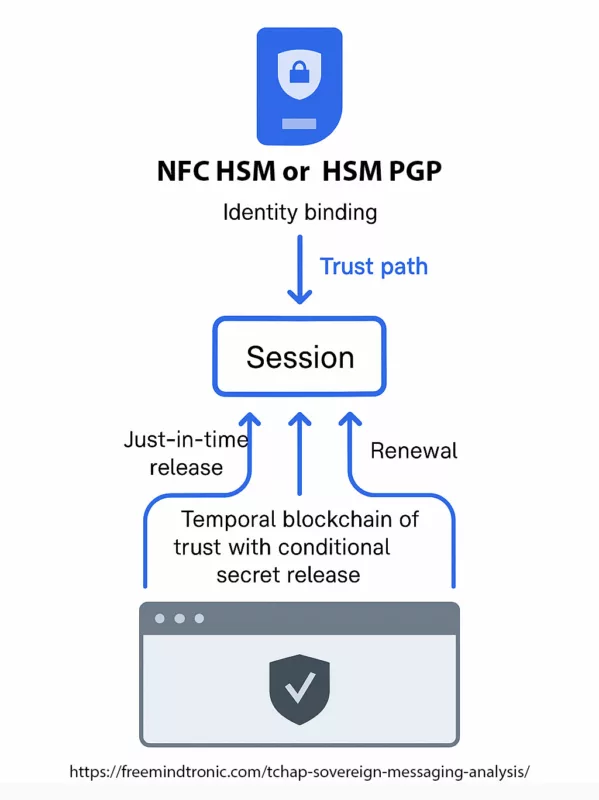
- Identity Binding — Configure a named slot (e.g., Tchap-Dir-OPS) in PassCypher; enforce policy with PIN, proximity, and OTP cadence.
- Local Attestation — Workstation validates HSM presence and slot integrity before any credential release.
- Just-in-Time Credential Release — A one-time secret or signature is injected into the login flow; credentials never leave the hardware in stored form.
- Sovereign Session Bootstrap — Tchap session starts with ephemeral authentication tokens only; no long-term secrets reside on the client.
- Renewable Proofs — Time-bound OTPs or signatures (↻) are issued for high-privilege operations; each action is audit-stamped.
- Policy-Driven Revocation — User or automated policy triggers ⊥; session tokens are invalidated and caches wiped (∅).
This trust path enforces hardware-rooted, just-in-time security with conditional secret access. Secrets remain locked in the sovereign HSM, while Tchap only receives temporary proofs, ensuring compliance with Zero Trust and national sovereignty mandates.
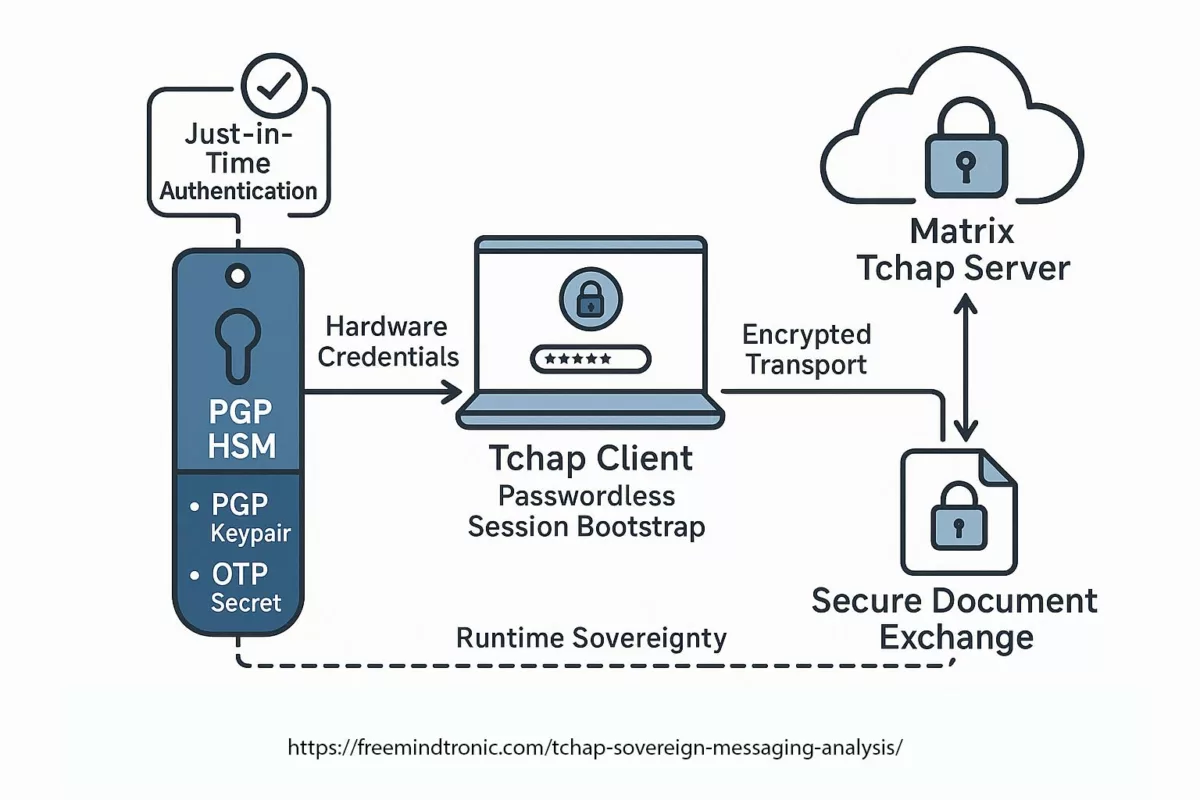
Software Trust Chain Analysis
The sovereign trust chain mapping in the Tchap ecosystem gains enhanced resilience when extended with PassCypher NFC HSM or PassCypher HSM PGP. This architecture ensures that every trust anchor — from hardware-rooted credentials to encrypted client-server transport — remains under sovereign control, with no exposure to cloud intermediaries or foreign infrastructure.
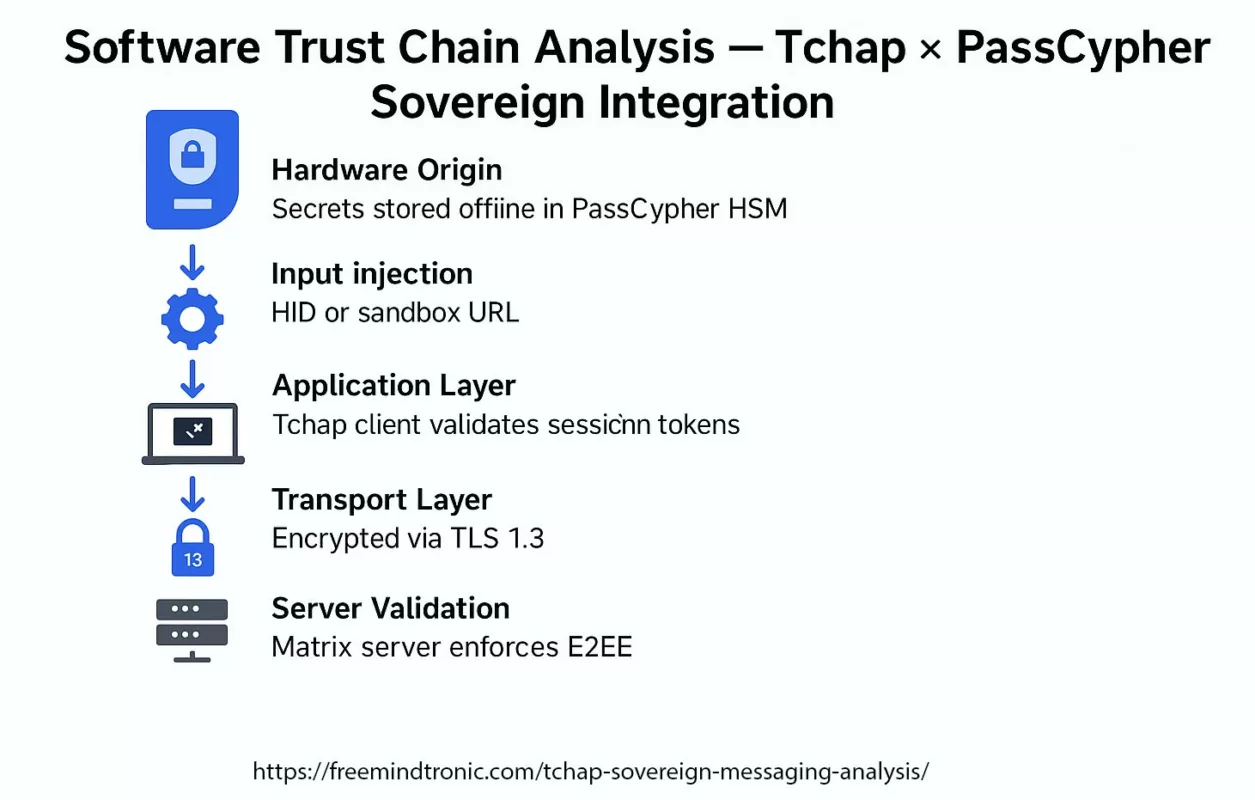 ✪ Software Trust Chain — Mapping the flow of sovereign trust from hardware-generated credentials in PassCypher HSM, through local middleware, Tchap client validation, TLS 1.3 mutual authentication, and E2EE server layers.</caption]
✪ Software Trust Chain — Mapping the flow of sovereign trust from hardware-generated credentials in PassCypher HSM, through local middleware, Tchap client validation, TLS 1.3 mutual authentication, and E2EE server layers.</caption]
- Hardware Origin — Credentials are generated and stored exclusively in the PassCypher HSM; immutable at rest and accessible only via NFC or PIN authentication.
- Local Middleware — Secure injection via HID or sandbox URL; no third-party or cloud service processes the secrets.
- Application Layer — The Tchap client validates ephemeral session tokens but never holds long-term secrets.
- Transport Layer — Protected by TLS 1.3 mutual authentication, strengthened with HSM-controlled OTPs for session hardening.
- Server Validation — The Matrix server stack enforces end-to-end encryption with hardware anchors; it cannot decrypt HSM-protected pre-authentication or metadata keys.
No single breach at the application, transport, or server layer can compromise user credentials. The sovereign trust anchor remains entirely in the user’s possession, enforcing zero cloud trust architecture principles.
Sovereign Dependency Mapping
Maintaining **sovereign control** over Tchap’s operational ecosystem requires a clear, auditable map of all **technical, infrastructure, and supply chain dependencies**. When extended with PassCypher NFC HSM or PassCypher HSM PGP, this mapping ensures every component—from client code to authentication workflows—is verified for jurisdictional integrity and security compliance.
- Direct Dependencies — Matrix protocol stack (Synapse, Olm/Megolm), Tchap-specific forks, and OS cryptographic APIs.
- Indirect Dependencies — External libraries, packaging frameworks, plugin ecosystems, and build toolchains.
- Sovereign Hardware Layer — PassCypher firmware, NFC interface libraries, secure element microcode—audited and maintained in a trusted environment.
- Infrastructure Control — On-premise hosting (OpenStack), state-controlled PKI, sovereign DNS resolution.
- Operational Workflows — Credential provisioning, OTP generation, and recovery processes anchored to hardware modules with offline key custody.
This dependency classification allows **selective hardening** of the most critical elements for national resilience, aligning with ANSSI supply chain security guidelines and Zero Trust Architecture doctrine.
Crisis System Interoperability
In high-pressure scenarios—ranging from nation-state cyberattacks to large-scale infrastructure outages—Tchap must interconnect seamlessly with other sovereign crisis communication platforms without compromising identity integrity or jurisdictional control. By pairing with PassCypher NFC HSM or PassCypher HSM PGP, authentication and key custody remain fully hardware-rooted across heterogeneous systems.
- Unified Cross-Platform Authentication — Single sovereign HSM credential usable across Tchap, GovSat, IRIS², and inter-ministerial coordination tools.
- Metadata Containment — Prevents identity trace leakage when bridging sovereign and sector-specific networks.
- Protocol Flexibility — Supports Matrix E2EE and external encrypted channels, with HSM-segmented key custody.
- Failover Readiness — Pre-provisioned crisis accounts and OTP workflows securely stored in HSM for rapid redeployment.
This architecture guarantees *operational continuity during emergencies without reverting to non-sovereign or ad-hoc insecure channels. The HSM acts as the **permanent trust anchor** across all interconnected systems.
Interoperability in Health & Education
Extending Tchap into sensitive domains such as healthcare and education demands strict compliance with sector-specific regulations, privacy mandates, and sovereign infrastructure controls. The integration of PassCypher NFC HSM or PassCypher HSM PGP brings offline, hardware-rooted credential custody and sovereign key management to these environments.
- Healthcare Integration — Secure linkage with Mon Espace Santé and hospital information systems, ensuring that professional identifiers, OTPs, and access tokens remain under sovereign HSM control.
- Education Systems — Seamless authentication with ENT (Espaces Numériques de Travail) platforms, eliminating the need to store staff or student credentials in third-party systems.
- Cross-Domain Identity Isolation — Dedicated slot-based credentials for each sector (e.g., Ministry, Hospital, University), preventing credential cross-contamination.
- Regulatory Compliance — Full alignment with ASIP Santé, MENJ security standards, GDPR, and RGAA accessibility requirements.
This targeted interoperability transforms Tchap into a sovereign backbone for cross-sector collaboration, keeping high-value credentials and encryption keys entirely within national jurisdiction.
Ministerial Field Feedback
Operational deployments of Tchap in ministries and local administrations reveal that field conditions impose unique constraints on authentication, connectivity, and device security. When paired with PassCypher NFC HSM or PassCypher HSM PGP, several ministries report increased operator confidence and reduced credential compromise incidents.
- Interior & Security Forces — Mobile use in low-connectivity zones benefits from offline OTP generation and pre-provisioned crisis credentials stored on HSM.
- Prefectures — Staff rotation and multi-device use simplified via portable sovereign credential storage, eliminating the need for server-stored passwords.
- Defence & Diplomacy — Sensitive mission keys remain isolated in hardware; revocation possible even if the host device is lost or seized.
- Inter-ministerial Operations — Cross-team trust maintained via dedicated HSM slots per mission, preventing accidental credential overlap.
Feedback underscores that sovereign hardware custody reduces reliance on potentially compromised endpoints and fosters a higher adherence to Zero Trust operational discipline.
Field users value tangible, hardware-based trust anchors that remain operational under adverse conditions and disconnected environments.
Legal & Regulatory Framework
The deployment of Tchap in conjunction with PassCypher NFC HSM and PassCypher HSM PGP must comply with a robust set of French and European legal instruments, ensuring that every aspect of credential custody, encryption, and operational governance remains sovereign, compliant, and enforceable.
- French Doctrine Interministérielle — Circular of 25 July 2025 mandating sovereign control over all state communication platforms.
- ANSSI Guidelines — Full compliance with Référentiel Général de Sécurité (RGS) and alignment with SecNumCloud principles for certified secure infrastructure.
- GDPR (RGPD) — Adherence to European privacy protections, data minimisation, and lawful processing principles within sovereign jurisdiction.
- NIS2 Directive — Strengthening network and information system security, particularly for critical and strategic infrastructure.
- LPM (Loi de Programmation Militaire) — Reinforced cybersecurity measures for national defence and strategic communications.
- Zero Trust State Architecture — Integration of hardware-rooted identities, segmentation, and continuous verification in line with ANSSI’s 2024 doctrine.
Embedding these legal and regulatory safeguards into the technical design of Tchap + PassCypher ensures that digital sovereignty is not only a security posture but also a legally binding standard enforceable under national law.
Strategic Metrics & ROI
Evaluating the strategic return on investment for integrating PassCypher NFC HSM or PassCypher HSM PGP into the Tchap ecosystem requires performance metrics that extend beyond cost optimisation. The assessment must capture sovereignty gains, operational resilience, and measurable risk reduction — ensuring alignment with ANSSI’s Zero Trust guidelines and the NIS2 Directive.
- Credential Compromise Rate — Percentage reduction in password or cryptographic key leakage incidents per 1 000 active users following HSM deployment.
- Incident Response Time — Average reduction in time to revoke and reissue credentials during a security event.
- Operational Continuity Index — Share of uninterrupted Tchap sessions maintained during simulated or real crisis conditions.
- Sovereign Control Ratio — Proportion of authentication events executed exclusively within sovereign infrastructure and hardware-rooted credential custody.
- Training Efficiency — Average time for new operators to master secure login and OTP workflows with HSM integration.
These KPIs enable ministries and agencies to justify investment in sovereign hardware not merely as a security cost, but as a verifiable driver of digital sovereignty, operational assurance, and long-term strategic autonomy.
Quantifiable, reproducible metrics transform sovereignty from an abstract political principle into a validated, data-driven operational standard.
Academic Indexing & Citation
Positioning the integration of Tchap with PassCypher NFC HSM or PassCypher HSM PGP within academic research and policy studies ensures that sovereign communication strategies gain visibility, credibility, and replicability. By embedding the sovereign model into peer-reviewed and policy-referenced contexts, France reinforces its digital sovereignty leadership while encouraging cross-sector adoption.
- Standardised Citation Format — Use persistent identifiers (DOI, URN) for technical documentation, operational guides, and case studies.
- Repository Inclusion — Deposit white papers, audits, and security analyses into trusted repositories such as HAL and Zenodo.
- Cross-Disciplinary Integration — Link cybersecurity findings with political science, legal, and public administration research to address sovereignty holistically.
- Bibliometric Tracking — Monitor the citation impact of sovereign security implementations in academic literature and policy briefs.
- Peer-Reviewed Validation — Submit methods and results to independent academic review to enhance legitimacy and adoption potential.
Through structured academic referencing and open-access indexing, the Tchap + PassCypher integration evolves from an operational deployment to a documented reference model that can be replicated in allied jurisdictions and across strategic sectors.
Academic visibility transforms sovereign technology into a validated, globally recognised digital sovereignty framework.
Strategic Synthesis & Sovereign Recommendations
The integration of Tchap with PassCypher NFC HSM and PassCypher HSM PGP proves that sovereign communication platforms can combine operational efficiency with hardware-rooted, jurisdiction-controlled credential custody. This synergy mitigates immediate operational risks while fulfilling long-term digital sovereignty objectives.
- Maintain Hardware Custody by Default — All authentication, encryption, and recovery credentials should be generated, stored, and managed within sovereign-certified HSMs.
- Context-Specific Credential Segmentation — Use dedicated HSM slots for each mission, ministry, or sector to prevent cross-contamination of identities.
- Institutionalise Crisis Protocols — Predefine credential rotation and recovery workflows anchored in hardware trust to ensure continuity during incidents.
- Audit the Sovereign Supply Chain — Regularly verify firmware, microcode, and build environments for both PassCypher and Tchap to comply with ANSSI and legal requirements.
- Measure & Publish KPIs — Track sovereign performance metrics such as credential compromise rate, operational continuity index, and sovereign control ratio.
By embedding these sovereign-by-design principles into governance frameworks and operational doctrine, France strengthens its capacity to resist extraterritorial interference, maintain confidentiality, and ensure continuity of critical communications under all conditions.
Institutional adoption of sovereign communication security ensures that protection is not an afterthought but a permanent, verifiable state.
Strategic Synthesis & Sovereign Recommendations
1. Observations
To begin with, the mandatory deployment of Tchap across French ministries marks a pivotal shift toward sovereign digital infrastructure. Built on the Matrix protocol and hosted within SecNumCloud-compliant environments, Tchap clearly embodies France’s commitment to Zero Trust principles, GDPR alignment, and national resilience. Moreover, its open-source nature and strong institutional backing position it as a credible and strategic alternative to foreign messaging platforms.
However, it is important to note that sovereignty is not a static achievement — rather, it is a dynamic posture that requires continuous reinforcement across hardware, software, and operational layers.
2. Strategic Limitations
Despite its strengths, Tchap still presents certain limitations:
- Firstly, default E2EE is not enforced, leaving room for metadata exposure and unencrypted exchanges.
- Secondly, there is no native support for hardware-based cryptographic attestation, which limits runtime trust validation.
- Thirdly, the absence of offline continuity mechanisms makes it vulnerable in blackout or disconnected environments.
- Additionally, there is no integration of decentralised identity or multi-factor authentication via physical tokens (e.g., NFC HSMs).
- Finally, interoperability with sovereign enclaves or post-quantum cryptographic modules remains limited.
Consequently, these gaps expose Tchap to strategic risks in high-stakes environments such as diplomacy, defence, and crisis response.
3. Sovereign Recommendations
In order to address these challenges, several strategic measures are recommended:
- Integrate PassCypher NFC HSM modules to enable offline identity validation, secure OTP management, and cryptographic attestation without cloud reliance.
- Deploy DataShielder to govern metadata flows, enforce traceability, and visualise trust chains in real time.
- Extend encryption layers with OpenPGP support for diplomatic-grade confidentiality.
- Embed runtime sovereignty through hardware enclaves that isolate secrets and validate execution integrity.
- Establish a sovereign UX layer that cognitively reinforces trust perception and alerts users to potential compromise vectors.
Ultimately, these enhancements do not replace Tchap — instead, they complete it. In fact, they transform it from a secure communication channel into a resilient, sovereign ecosystem capable of withstanding hybrid threats and geopolitical pressure.
⧉ What We Didn’t Cover
Although this chronicle addresses the core components of the Tchap + PassCypher + DataShielder sovereign security model, certain complementary strategic and technical aspects remain beyond its current scope. Nevertheless, they are essential to achieving a fully comprehensive and future-proof architecture.
- Post-Quantum Roadmap — At present, PassCypher and DataShielder already implement AES-256 CBC with segmented keys, a symmetric encryption method widely regarded as quantum-resistant. Furthermore, this approach ensures that even in the face of quantum computing threats, confidentiality is preserved. However, a formal integration plan for post-quantum asymmetric algorithms — such as Kyber and Dilithium — across all Tchap clients is still under evaluation. For additional insights into the impact of quantum computing on current encryption standards, see Freemindtronic’s quantum computing threat analysis.
- SecNumCloud Evidence Pack — In addition, the full compliance documentation specific to Tchap hosting, aligned with ANSSI SecNumCloud certification requirements, remains to be formally compiled and published.
- Red Team Testing — Finally, the comprehensive results of adversarial penetration tests, particularly those targeting dual-encryption workflows under operational stress conditions, have yet to be released. These tests will play a pivotal role in validating the robustness of the proposed security architecture.
By addressing these points in forthcoming dedicated reports, the digital sovereignty and quantum security framework for state communications will move from a highly secure model to a demonstrably unassailable standard.