Discover Russian Tactics by Midnight Blizzard
Midnight Blizzard, supported by Russian strategy, targeted Microsoft and HPE, orchestrating sophisticated cyberattacks. We delve into the facts, consequences, and effective protective measures such as PassCypher and DataShielder to combat this type of espionage.
Stay informed in our posts dedicated to Digital Security to follow its evolution thanks to our regularly updated topics
Explore our digital security feature on the Midnight Blizzard cyberattack against Microsoft and HPE by Jacques Gascuel. Stay updated and secure with our insights.
Updated March 20, 2024
Midnight Blizzard Cyberattack against Microsoft and HPE: A detailed analysis of the facts, the impacts and the lessons to learn
In 2023 and 2024, two IT giants, Microsoft and Hewlett Packard Enterprise (HPE), which has been using Microsoft 365 as its cloud messaging platform since 2017), fell victim to cyberattacks carried out by a hacker group linked to the Russian government. These attacks allowed hackers to gain access to the internal systems, source code, and sensitive data of companies and their customers. What are the facts, consequences and lessons to be learned from these incidents?
Update: Microsoft 365 Cyberattack Intensifies
Initial Underestimation: Researchers reveal the cyberattack on Microsoft 365 is far more severe than first anticipated.
APT Exploits Data: The APT group, orchestrating the attack, has leveraged exfiltrated data to delve deeper into Microsoft’s network.
Security Experts Raise Concerns: Security professionals express concerns over disjointed defense teams. They fear unidentified vulnerabilities may persist.
Microsoft’s Stance: Popular opinion suggests Microsoft is ‘caught off-guard’ against such sophisticated attacks.
Ongoing Efforts: Microsoft is now bolstering defenses, ensuring tighter coordination across security teams to address these challenges.
For more details, refer to the official Microsoft Security Response Center update.
How were the attacks carried out against Microsoft and HPE?
The attacks on Microsoft and HPE were carried out by the same hacker group, Midnight Blizzard, which is linked to the Russian government. The hackers used the same technique to infiltrate the networks of both companies: compromising Microsoft 365 email. This cloud-based messaging platform is used by many organizations to communicate and collaborate.
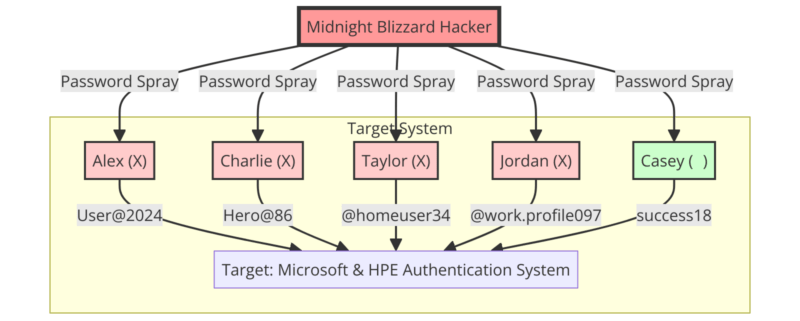
“Password Spray” Attack Method Against Microsoft and HPE
The compromise of Microsoft 365’s email and HPE’s email accounts was achieved through a simple but effective method known as “password spraying.” This technique, often used after a brute force attack, involves guessing a password by trying several combinations, usually from previous data breaches.
The hackers used this method to gain access to an old test account on Microsoft’s network. Once they gained access, they were able to infiltrate HPE’s email accounts.
“Password spraying” is a technique where hackers use common passwords to attempt to gain access to multiple accounts on the same domain. Using a list of commonly used weak passwords, a hacker can potentially gain access to hundreds of accounts in a single attack. This differs from “Credential Stuffing”, where a single set of credentials is used to attempt to access different accounts across multiple domains.
In the case of the Midnight Blizzard attack on Microsoft, the hacker group used a password spray attack to compromise a legacy non-productive test account and gain a foothold. They then used the account’s permissions to gain access to a very small percentage of Microsoft’s corporate email accounts, including members of the executive team and employees in cybersecurity, legal, and other functions. They managed to exfiltrate some emails and attached documents.
Once they gained access to email accounts, the hackers were able to exfiltrate sensitive data, such as emails, attachments, source code, and secrets.
Method of attack against Microsoft and HPE customers “phishing, malware or social engineering”
Midnight Blizzard also used this data to carry out subsequent attacks against Microsoft and HPE customers, using phishing, malware, or social engineering techniques.
Why were the attacks successful?
- Hackers exploited security vulnerabilities such as the lack of multi-factor authentication, the persistence of legacy test accounts, or weak passwords.
- The hackers acted in a discreet manner, using advanced and persistent techniques, such as encrypting communications, masking IP addresses, or imitating legitimate behavior.
- The hackers were supported by the Russian government, which provided them with resources, information, and diplomatic protection.
Here’s a diagram that summarizes the steps to Microsoft 365 email compromise:
Microsoft 365 email compromise diagram
Stages of Microsoft’s Security Breach
Microsoft endured a multi-phase assault:
November 2023 saw the initial breach when attackers cracked an outdated test account via password spray attacks, cycling through many potential passwords.
By December, those intruders had penetrated select executive and security team email accounts, extracting sensitive emails and documents.
January 2024 brought Microsoft’s detection and countermeasures to thwart further unauthorized access. The company identified Midnight Blizzard, known by aliases such as APT29 and Cozy Bear, as the culprits.
Come March, it was disclosed that the invaders had also accessed Microsoft’s code repositories and internal systems, utilizing the stolen intel for subsequent assaults on Microsoft’s clientele, targeting to exploit vulnerabilities or clone functionalities.
The different consequences of this attack on Microsoft
Consequences for Microsoft and its customers
The attack had significant consequences for Microsoft and its customers. On the one hand, Microsoft had to tighten its security measures, notify affected customers, investigate the extent of the compromise, and restore trust in its services.
On the other hand, Microsoft’s customers faced the risk of being targeted by subsequent attacks using information stolen from Microsoft, such as secrets, source code, or sensitive data. Some customers may have suffered financial losses, reputational damage, or privacy breaches.
Geopolitical consequence
The attack also had geopolitical consequences, as it revealed the Russian government’s involvement in large-scale cyber espionage operations against Western interests. It has drawn condemnation from several countries, including the United States, the United Kingdom, France and Germany, which have called for a coordinated and proportionate response to the threat. It also reinforced the need to strengthen international cooperation on cybersecurity and to define common standards to prevent conflicts in cyberspace.
Steps to attack HPE
Midnight Blizzard executed the attack on HPE, leveraging Microsoft 365 email for entry—the platform HPE adopted in 2017.
Initially, in May 2023, the hackers infiltrated SharePoint, extracting a select set of files. Post-breach, HPE, alongside cybersecurity experts, promptly engaged in containment and recovery efforts.
Come December, new breaches surfaced; targeted mailboxes related to cybersecurity and business operations were compromised. These intrusions were suspected to be connected to the earlier SharePoint incident.
Finally, in January 2024, HPE disclosed the breach to the SEC, affirming the implementation of measures to remove the threat, alert impacted clients, gauge the breach’s scope, and reinstate service integrity.
The different consequences of this attack on HPE
First, the attack had similar consequences to the attack on Microsoft, but on a smaller scale.
Restoring trust in its services to their customersOn the one hand, HPE had to strengthen its security measures, inform affected customers, and restore trust in its services. HPE’s customers faced the risk of being targeted by subsequent attacks using information stolen from HPE, such as sensitive data.
Justify the lack of economic impact as a result of this attack
On the other hand, HPE stated that the incident did not have a material impact on its operations, financial condition or results of operations.
The similarities and differences between the two attacks
Both attacks were carried out by the same hacking group, Midnight Blizzard, which is linked to the Russian government. Both attacks used the same means of access, Microsoft 365 email, which is a cloud-based email platform used by many organizations. Both attacks allowed hackers to exfiltrate sensitive data, such as emails, attachments, source code, or secrets. Both attacks had consequences for the victim companies, their customers, and geopolitics.
There were also differences between the two attacks. The attack on Microsoft was longer, deeper, and more widespread than the attack on HPE. The attack on Microsoft lasted several months, while the attack on HPE lasted a few weeks. The attack on Microsoft allowed the attackers to gain access to the company’s source code repositories and internal systems, while the attack on HPE was limited to email and SharePoint files. The attack on Microsoft affected thousands of customers, while the attack on HPE did not specify how many customers were affected.
What types of data does Midnight Blizzard exfiltrate?
What types of data does Midnight Blizzard exfiltrate?
Midnight Blizzard is the name given to a group of cybercriminals who have carried out cyber attacks against Microsoft, HPE, and their customers. This group is also known as Nobelium, Cozy Bear, or APT29. It managed to break into these companies’ cloud email systems and steal sensitive data. Microsoft said that Midnight Blizzard also accessed some of its source code and internal systems, but that it did not compromise Microsoft-hosted client systems.
“In recent weeks, we have seen Midnight Blizzard [Nobelium] use information initially exfiltrated from our corporate email systems to obtain, or attempt to obtain, unauthorized access,” Microsoft said in a blog post. “This includes access to some of the company’s source code repositories and internal systems. To date, we have found no evidence that Microsoft-hosted client systems have been compromised.”
Midnight Blizzard Exfiltrated Data Category
The data exfiltrated by Midnight Blizzard can be grouped into three main categories:
Communication data
Communication data is data that relates to interactions between Microsoft and HPE employees, partners, or customers. They include emails, attachments, contacts, calendars, notes, or instant messages. This data may contain confidential, strategic or personal information, such as trade secrets, project plans, contracts, reports, opinions, identifiers. This data was exfiltrated at Microsoft and HPE.
Source code data
Source code data is data that relates to the development of Microsoft’s products or services. They include files, repositories, versions, comments, or tests related to the source code. This data may reveal technical, functional, or security information, such as algorithms, architectures, features, vulnerabilities, patches, or backdoors. This data was exfiltrated only at Microsoft.
Internal system data
Communication and internal system data is data that relates to the exchange and operation of Microsoft and HPE’s internal systems. This includes emails, attachments, contacts, calendars, notes, instant messages, files, configurations, logs, audits, or scans of internal systems. This data may contain confidential, strategic or personal information, such as trade secrets, project plans, contracts, reports, opinions, identifiers. This data can also provide information about the performance, security, or reliability of internal systems. This data was exfiltrated at Microsoft and HPE.
What are the estimated values of the data exfiltrated by Midnight Blizzard?
It is difficult to estimate the exact value of the data exfiltrated by Midnight Blizzard, as it depends on several factors, such as the quantity, quality, freshness, rarity, or usefulness of the data. However, an approximate range can be attempted based on official sources or existing studies.
HPE’s SEC filing indicates that the security incident’s repercussions on their operational, financial, or business performance were minimal. This suggests the exfiltrated data’s worth is on the lower end, possibly just a few thousand dollars. On the other hand, Microsoft’s annual report documents a staggering $168.1 billion in revenue for 2023, with $60.7 billion attributed to their cloud division. Such figures lead to the conclusion that the stolen data from Microsoft could be highly valuable, potentially in the millions. Further, the Ponemon Institute’s study reports the average data breach cost in 2023 at $4.24 million, the highest to date, encompassing various associated costs. These costs include activities like detection and response, as well as indirect losses like diminished productivity and tarnished reputation. Therefore, it stands to reason that the value of data taken from Microsoft and HPE’s customers is similarly high, potentially reaching tens of millions of dollars.
What are the potential consequences of the data exfiltrated by Midnight Blizzard?
The data exfiltrated by Midnight Blizzard can have serious potential consequences for the victim companies, their customers, and geopolitics. Here are a few examples:
- Communication data can be used to carry out phishing, malware, or social engineering attacks, impersonating trusted individuals, exploiting security vulnerabilities, or manipulating emotions. These attacks can aim to steal other data, take control of systems, destroy or alter data, or extort ransoms.
- Source code data can be used to discover and exploit vulnerabilities, to copy or modify functionality, to create competing products or services, or to infringe intellectual property. These actions may adversely affect the security, quality, innovation, or competitiveness of Microsoft or HPE products or services.
- Internal system data may be used to understand and disrupt Microsoft or HPE’s operations, organization, or performance, to reveal sensitive or confidential information, to create false information or rumors, or to influence decisions or behaviors. These actions may damage the reputation, trust, satisfaction, or loyalty of Microsoft or HPE customers, partners, or employees.
How could PassCypher HSM have prevented the cyberattack on Microsoft and HPE?
The cyberattack on Microsoft and HPE used weak or reused passwords to access email accounts. PassCypher NFC HSM or PassCypher HSM PGP is a hardware-based password manager, which allows you to create and use strong, unique, and random passwords, without knowing, remembering, displaying, or entering them manually. It uses Freemindtronic’s EviCore HSM PGP or EviCore NFC HSM technology to communicate contactlessly with compatible devices, and has a complicated and complex random password generator with self-entropy control based on shannon mathematical calculation.
With PassCypher NFC HSM or PassCypher HSM PGP solutions, users can effectively protect themselves against password spray attacks quickly, easily, and even free of charge. This is because PassCypher HSM PGP is originally completely free. He presented for the first time in Marseille on 6-7 March 2024 at AccessSecurity at the PhosPhorus Technology stand, partner of Fullsecure Andorra.
How could DataShielder have protected email messages and email attachments from being exfiltrated by hackers?
As you read more in this article, the cyberattack against Microsoft and HPE exfiltrated communication data, such as emails, attachments, contacts, notes, or instant messages. DataShielder NFC HSM or DataShielder HSM PGP are solutions for encrypting post-quantum data via NFC HSM or HSM PGP. Users encrypt and decrypt their communication data, only from their HSMs via physically outsourced segmented keys from the IT or phone systems. It works without a server or database and without any dependency on the security of communication systems. Of course, without the need to connect to an online service, or entrust your encryption keys to a third party. They have a random AES-256 encryption key generator. In particular, it embeds Freemindtronic’s EviCypher technology, which also encrypts webmail such as Outlook. With DataShielder solutions, users can protect themselves from data exfiltration by hackers and ensure the confidentiality, integrity, and authenticity of their communications.
Recommendations to protect yourself from cyber threats
The cyberattacks against Microsoft and HPE show that cyber threats are real, growing, and sophisticated. They also show that businesses of all sizes, industries, and locations need to take cybersecurity seriously and adopt best practices to protect themselves effectively. Here are some recommendations:
- Enable multi-factor authentication, which involves requiring two or more credentials to log in to an account, such as a password and a code sent via SMS or email. This helps reduce the risk of being compromised by a password spray attack.
- Review account permissions, which determine access rights to company resources and data. This helps limit the risk of an attack spreading from a compromised account.
- Monitor suspicious activity, which may indicate an attempted or successful attack, such as unusual logins, file changes, data transfers, or security alerts. This makes it possible to detect and stop an attack as early as possible.
- Use security solutions that provide protection, detection, and response to cyber threats, such as antivirus, firewalls, intrusion detection and prevention systems, or monitoring and analytics services. This makes it possible to strengthen the security of the information system and to benefit from the expertise of cybersecurity professionals.
- Educate users, who are often the weakest link in the security chain, and who can fall victim to phishing, malware, or social engineering. This includes training them in good cybersecurity practices, informing them of the risks and instructions to follow in the event of an incident, and encouraging them to adopt responsible and vigilant behavior.
In conclusion
In conclusion, Midnight Blizzard’s cyberattacks expose critical vulnerabilities in global tech infrastructure. Through these incidents, we learn the importance of robust security measures like PassCypher and DataShielder. Moving forward, adopting advanced defenses and staying informed are key to combating future threats. Let’s embrace these lessons and protect our digital world.
Sources:
- Microsoft’s official blog, which published several articles about the Midnight Blizzard attack, including the exfiltrated communication, source code, and internal system data.
- The official document from HPE, which reported the security incident to the SEC, and which mentioned the exfiltrated internal communications and system data.
- The official report from FireEye, which analyzed Midnight Blizzard’s activities, and confirmed the exfiltrated communication and source code data.









