Understanding OpenVPN Security Vulnerabilities: History, Risks, and Future Solutions
OpenVPN security vulnerabilities pose critical risks that could expose millions of devices to cyberattacks. This trusted tool for secure communication now faces serious challenges. This article delves into the history and discovery of these flaws while offering practical solutions to protect your data. Learn how to secure your network and stay ahead of these emerging threats.
Stay informed with our posts dedicated to Digital Security to track its evolution through our regularly updated topics.
Critical OpenVPN Vulnerabilities Pose Global Security Risks
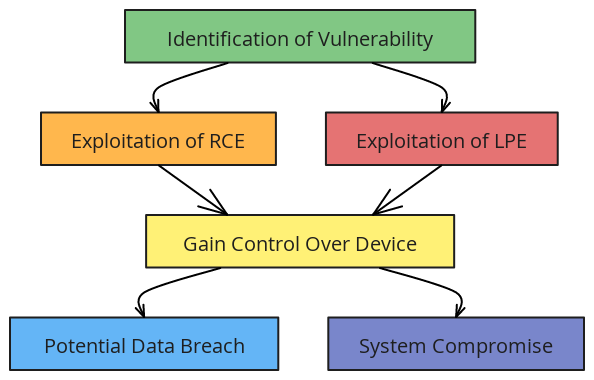
OpenVPN security vulnerabilities have come to the forefront, affecting millions of users globally. Microsoft recently highlighted these critical flaws, which are present in the widely-used open-source project OpenVPN. This project integrates with routers, firmware, PCs, mobile devices, and smart devices. Attackers could exploit these flaws to execute remote code (RCE) and escalate local privileges (LPE). Such exploitation could lead to severe security breaches.
These OpenVPN security vulnerabilities pose a substantial risk due to the extensive use of this technology. If exploited, malicious actors could take complete control of affected devices. These devices span various technologies globally, making the threat widespread. Therefore, the cybersecurity community must respond immediately and in a coordinated manner.
A Chronological Overview of OpenVPN and the Discovery of Vulnerabilities
To understand the current situation, we must first look at the historical context. This overview of OpenVPN highlights its evolution and the timeline leading to the discovery of its security vulnerabilities.
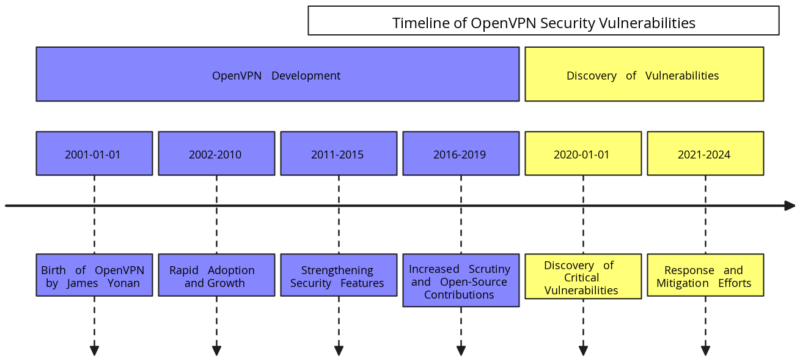
2001: The Birth of OpenVPN
OpenVPN security vulnerabilities did not exist at the beginning. OpenVPN was created by James Yonan in 2001 as an open-source software application implementing virtual private network (VPN) techniques. It aimed to provide secure site-to-site and point-to-point connections, making it a flexible and widely adaptable solution. The open-source nature of OpenVPN allowed developers and security experts worldwide to contribute to its codebase, enhancing its security and functionality over time.
2002-2010: Rapid Adoption and Growth
During the early 2000s, OpenVPN quickly gained traction due to its versatility and security features. Users and enterprises could easily customize it, which fueled its popularity. As organizations and individuals sought reliable VPN solutions, OpenVPN became a preferred choice. It was integrated into numerous routers, devices, and enterprise networks.
2011-2015: Strengthening Security Features
As cybersecurity threats evolved, so did OpenVPN. Between 2011 and 2015, the OpenVPN community focused on enhancing encryption methods and strengthening security protocols. This period saw the introduction of more robust features, including support for 256-bit encryption. OpenVPN became one of the most secure VPN solutions available. Millions of users worldwide relied on it for their privacy needs.
2016-2019: Increased Scrutiny and Open-Source Contributions
As OpenVPN’s popularity soared, it attracted more scrutiny from security researchers. The open-source nature of OpenVPN allowed for constant peer review, leading to the identification of potential vulnerabilities. During this period, the OpenVPN project continued to receive contributions from a global community of developers. This process further enhanced its security measures. However, the growing complexity of the codebase also made it challenging to ensure every aspect was fully secure.
2020: The Discovery of Critical Vulnerabilities
In 2020, security researchers began identifying critical OpenVPN security vulnerabilities. These flaws could be exploited for remote code execution (RCE) and local privilege escalation (LPE). Despite rigorous open-source review processes, these vulnerabilities highlighted the challenges of maintaining security in widely adopted open-source projects. The discovery was particularly concerning given the extensive use of OpenVPN across millions of devices worldwide.
2021-Present: Response and Mitigation Efforts
The discovery of these vulnerabilities prompted swift action. The OpenVPN community and associated manufacturers responded quickly to address the issues. They released a series of patches and updates to mitigate the risks. However, securing open-source software that is widely deployed in diverse environments remains challenging. Although many vulnerabilities have been addressed, the discovery sparked discussions about the need for ongoing vigilance and the adoption of complementary security measures, such as encryption solutions like DataShielder. The evolution of OpenVPN and the discovery of security vulnerabilities from 2001 to 2024.
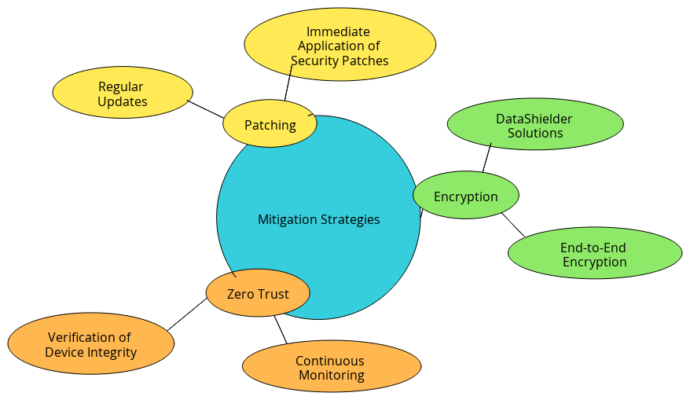
Understanding OpenVPN Security Vulnerabilities
For millions who rely on OpenVPN for secure communication, these security vulnerabilities are alarming. The possibility of remote code execution means an attacker could introduce malicious software onto your device without your consent. Additionally, local privilege escalation could give attackers elevated access. This access could potentially lead to a full takeover of the device.
Given the widespread use of OpenVPN across numerous devices, these security vulnerabilities could have far-reaching effects. The consequences of an exploit could include data theft and unauthorized access to sensitive information. It could also lead to widespread network compromises, affecting both individual users and large enterprises.
Why Encrypt Your Data Amid OpenVPN Security Vulnerabilities?
OpenVPN security vulnerabilities highlight the necessity of a multi-layered security approach. While VPNs like OpenVPN are essential for securing internet traffic, relying solely on them, especially if compromised, is insufficient to protect sensitive data.
A Zero Trust approach, which follows the principle of “never trust, always verify,” is vital in today’s cybersecurity landscape. This approach mandates not trusting any connection by default, including internal networks, and always verifying device identity and integrity.
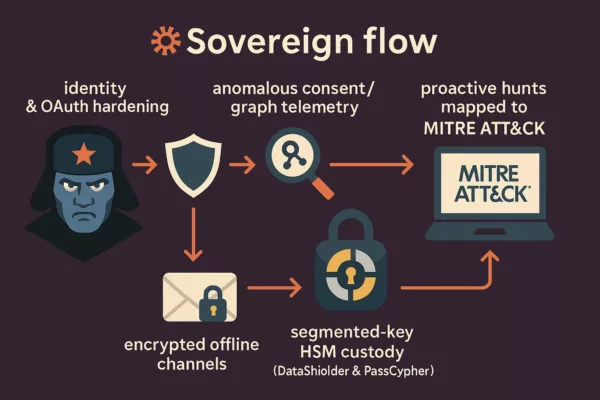
Given these vulnerabilities, implementing a robust strategy is crucial. This includes using advanced encryption tools like DataShielder, which protect data even before it enters a potentially compromised VPN.
DataShielder Solutions: Fortifying Security Beyond the VPN
OpenVPN security vulnerabilities underscore the importance of securing sensitive data before it enters the VPN tunnel. DataShielder NFC HSM Master, Lite, and Auth for Android, along with DataShielder HSM PGP for Computers, offer robust encryption solutions that protect your data end-to-end. These solutions adhere to Zero Trust and Zero Knowledge principles, ensuring comprehensive security.
Contactless Encryption with DataShielder NFC HSM for Android
DataShielder NFC HSM for Android, designed for NFC-enabled Android devices, provides contactless encryption by securely storing cryptographic keys within the device. Operating under the Zero Trust principle, it assumes every network, even seemingly secure ones, could be compromised. Therefore, it encrypts files and messages before they enter a potentially vulnerable VPN.
If the VPN is compromised, attackers might intercept data in clear text, but they cannot decrypt data protected by DataShielder. This is because the encryption keys are securely stored in distinct HSM PGP containers, making unauthorized decryption nearly impossible. This approach adds a critical layer to your security strategy, known as “defense in depth,” ensuring continuous protection even if one security measure fails.
End-to-End Security with DataShielder HSM PGP for Computers
The DataShielder HSM PGP for Computers brings PGP (Pretty Good Privacy) encryption directly to your desktop, enabling secure email communication and data storage. By fully aligning with Zero Trust practices, DataShielder ensures that your data is encrypted right at the source, well before any transmission occurs. The encryption keys are securely stored in tamper-resistant HSM hardware, strictly adhering to Zero Knowledge principles. This means that only you have access to the keys required to decrypt your data, thereby adding an additional layer of both physical and logical security.
Empowering Users with Complete Control
With DataShielder, you maintain complete control over your data’s security. This level of autonomy is especially vital when using potentially compromised networks, such as public Wi-Fi or breached VPNs. By fully embracing the Zero Trust framework, DataShielder operates under the assumption that every connection could be hostile, thereby maximizing your protection. The Zero Knowledge approach further guarantees that your data remains private, as no one but you can access the encryption keys. DataShielder integrates seamlessly with existing security infrastructures, making it an ideal choice for both individuals and enterprises aiming to significantly enhance their cybersecurity posture.
Proven and Reliable Security
DataShielder employs advanced encryption standards like AES-256 CBC, AES-256 CBC PGP, and RSA-4096 for secure key exchange between NFC HSM devices. It also utilizes AES-256 CBC PGP for segmented key sharing. These protocols ensure that your data is protected by the most robust security measures available. Distributed in France by AMG Pro and Fullsecure Andorre, these solutions provide reliable methods to keep your data encrypted and secure, even in the face of OpenVPN security vulnerabilities. Professionals who demand the highest level of security for their digital assets trust these solutions implicitly.
Why You Need This Now
In today’s digital landscape, where threats are constantly evolving and VPN vulnerabilities are increasingly exploited, adopting a Zero Trust and Zero Knowledge approach to data encryption is not just advisable—it’s essential. With DataShielder, you can confidently ensure that even if your VPN is compromised, your sensitive data remains encrypted, private, and completely inaccessible to unauthorized parties. Now is the time to act and protect your digital assets with the highest level of security available.
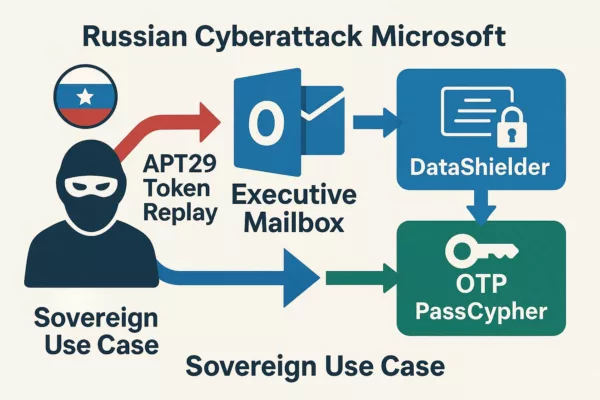
Real-World Exploitation of OpenVPN Security Vulnerabilities
In early 2024, cybercriminals actively exploited critical OpenVPN security vulnerabilities, leading to significant breaches across multiple sectors. These attacks leveraged zero-day flaws in OpenVPN, resulting in severe consequences for affected organizations.
January 2024: Targeted Exploits and Data Breaches
In January 2024, threat actors exploited several zero-day vulnerabilities in OpenVPN, which were identified under the codename OVPNX. These flaws were primarily used in attacks targeting industries such as information technology, finance, and telecommunications. The vulnerabilities allowed attackers to perform remote code execution (RCE) and local privilege escalation (LPE), leading to unauthorized access and control over critical systems.
One notable incident involved a major financial services firm that suffered a data breach due to the exploitation of these vulnerabilities. The attackers gained access to sensitive financial data, leading to significant financial losses and reputational damage for the firm. As a result, the company faced regulatory scrutiny and was forced to implement extensive remediation measures.
March 2024: Escalation of Attacks
By March 2024, the exploitation of OpenVPN vulnerabilities had escalated, with cybercriminals chaining these flaws to deploy ransomware and other malware across compromised networks. These attacks disrupted operations for several organizations, leading to service outages and data exfiltration. The impact was particularly severe for companies in the telecommunications sector, where attackers exploited these vulnerabilities to disrupt communication services on a large scale.
In response, affected organizations were compelled to adopt more robust security measures, including the immediate application of patches and the implementation of additional security controls. Despite these efforts, the incidents highlighted the ongoing risks associated with unpatched vulnerabilities and the need for continuous monitoring and vigilance.
Statistics Highlighting OpenVPN Security Vulnerabilities
Recent data reveals that OpenVPN is embedded in over 100 million devices worldwide. This includes routers, PCs, smartphones, and various IoT (Internet of Things) devices. Although exact user figures are challenging to determine, estimates suggest that the number of active OpenVPN users could range between 20 to 50 million globally. This widespread adoption underscores OpenVPN’s critical role in securing global internet communications.
Additionally, a survey by Cybersecurity Ventures indicates that nearly 85% of enterprises utilize VPN technology. OpenVPN is a top choice due to its open-source nature and remarkable flexibility. This extensive adoption not only solidifies OpenVPN’s importance in global internet security, but it also makes it a significant target for cyber exploitation. The vast number of devices relying on OpenVPN heightens its appeal to potential attackers.
Ensuring the security of OpenVPN is vital to maintaining the integrity of global internet infrastructure. Given its pervasive use, any vulnerabilities in OpenVPN could have widespread consequences. These could impact both individual users and large-scale enterprises across the globe.
Robust security measures and timely updates are essential to protect OpenVPN users from potential threats. As OpenVPN continues to play a pivotal role in global communications, safeguarding this technology must remain a top priority. This is crucial for maintaining secure and reliable internet access worldwide.
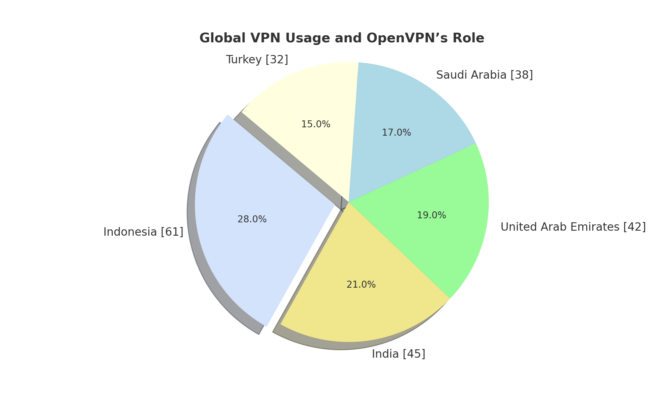
Global VPN Usage and OpenVPN’s Role
To understand the broader implications of these vulnerabilities, it’s crucial to consider the global landscape of VPN usage, particularly the countries with the highest adoption rates of VPN technology, where OpenVPN plays a pivotal role:
- Indonesia (61% VPN Usage): Indonesia has the highest VPN adoption globally, with 61% of internet users relying on VPNs to bypass censorship and secure their communications. The widespread use of OpenVPN in the country means that any vulnerability in the protocol could jeopardize the privacy and security of millions of Indonesians.
- India (45% VPN Usage): In India, 45% of internet users depend on VPNs to access restricted content and protect their privacy online. Given that OpenVPN is heavily utilized, any security flaws could expose millions of Indian users to potential cyber threats, impacting both personal and corporate data
- United Arab Emirates (42% VPN Usage): The UAE’s strict internet censorship drives 42% of the population to use VPNs, with OpenVPN being a key player. Any exploitation of vulnerabilities could severely compromise user privacy and security in the region
- Saudi Arabia (38% VPN Usage): In Saudi Arabia, 38% of internet users employ VPNs to circumvent government censorship and enhance their online privacy. OpenVPN’s vulnerabilities pose a significant risk, potentially leading to unauthorized data access and breaches of privacy
- Turkey (32% VPN Usage): Turkey’s 32% VPN adoption rate is primarily due to governmental restrictions on certain websites and social media platforms. OpenVPN is a widely used protocol, and any security flaws could increase the risk of surveillance and unauthorized data access for Turkish users
Broader Global Impact
Beyond these countries, OpenVPN’s vulnerabilities have far-reaching implications across North America, Europe, the Asia-Pacific region, the Middle East, and Africa:
- North America (35% VPN Usage): The United States, holding 35% of the global VPN market share, would be significantly impacted by any security flaws in OpenVPN. Given the critical role of VPNs in corporate and personal data protection, the consequences of an exploit could be extensive.
- Europe (17% VPN Usage): Although specific VPN usage percentages for the UK, Germany, and France might not be readily available, approximately 17% of internet users in Europe had used a VPN by 2020. This adoption is driven by stringent data protection regulations like GDPR and growing privacy concerns. Vulnerabilities in OpenVPN could undermine these protections, leading to potential regulatory challenges and widespread data breaches
- Asia-Pacific (20% VPN Usage in Australia): In the Asia-Pacific region, countries like Japan, Australia, and South Korea rely heavily on VPNs for secure communications in business and academic sectors. For example, in Australia, VPN usage reached around 20% in 2021. A compromised OpenVPN could disrupt critical infrastructure and expose sensitive information in these countries
- Middle East and Africa (69% VPN Usage in Qatar): VPN adoption rates are notably high in regions like Qatar, where over 69% of the population uses VPNs. In Nigeria, VPN adoption is steadily growing as users become more aware of internet security needs. OpenVPN’s vulnerabilities in these regions could lead to widespread disruption and privacy breaches, particularly where secure internet access is vital for maintaining information flow and protecting users from governmental surveillance
Implications of OpenVPN Security Vulnerabilities
OpenVPN security vulnerabilities pose a significant global threat, affecting around 20% of internet users worldwide who rely on VPNs for privacy, secure communications, and unrestricted access to online content. The extensive use of OpenVPN means that the potential attack surface is vast. When a single router is compromised, it can expose an entire network to unauthorized access. This type of breach can escalate rapidly, impacting both individual users and corporate environments.
The consequences of such a breach are far-reaching and severe. They can disrupt business operations, compromise sensitive data, and even jeopardize national security, especially in regions where VPN usage is prevalent. Users worldwide, particularly in areas with high VPN adoption, must act quickly. They should update their VPN software to the latest versions immediately. Additionally, they must implement supplementary security measures, such as robust encryption and multi-factor authentication, to protect against these vulnerabilities.
These actions are not just advisable—they are essential. As threats continue to evolve, the urgency for proactive security measures grows. Protecting your network and sensitive data against potential exploits requires immediate and decisive action.
Update on Patches for OpenVPN Security Vulnerabilities
The discovery of multiple vulnerabilities in OpenVPN, including those tied to OVPNX, underscores the urgency for organizations to stay vigilant. On August 8, 2024, the Microsoft Security Blog confirmed vulnerabilities that could lead to remote code execution (RCE) and local privilege escalation (LPE). These vulnerabilities, identified as CVE-2024-27903, CVE-2024-27459, and CVE-2024-24974, were initially discovered by security researcher Vladimir Tokarev.
These vulnerabilities primarily impact the OpenVPN GUI on Windows, stressing the importance of promptly applying security updates. If left unaddressed, they could lead to significant financial losses and severe reputational damage.
To protect against these risks, organizations should:
- Apply Patches Promptly: Ensure that all OpenVPN installations are updated to the latest versions, which include the necessary fixes released in March 2024.
- Implement Robust Security Measures: Use advanced encryption solutions like DataShielder to add an extra layer of protection.
- Conduct Regular Security Audits: Continuously evaluate your network infrastructure to identify and address any potential vulnerabilities.
- Monitor for Unusual Activity: Keep a close watch on network traffic and respond swiftly to any signs of compromise.
For more detailed information, please visit the Microsoft Security Blog and the OpenVPN Security Blog.
Additional Resources for Technical Readers
For those interested in a deeper technical dive into the vulnerabilities:
- OpenVPN CVEs and Vulnerability Details: Explore a comprehensive list of OpenVPN-related CVEs.
- CVE-2024-27903 Documentation: Access official documentation, including release notes and CVE registration.
Limitations of Available Patches
Despite the release of several patches, some OpenVPN security vulnerabilities may persist. These limitations are often due to design constraints in certain devices or the OpenVPN protocol itself. Older or unsupported devices may remain vulnerable, making them perpetual targets for attackers. Users of such devices should adopt additional security practices, such as network segmentation, to minimize exposure.
The Future of VPN Security
The discovery of these OpenVPN security vulnerabilities suggests a possible shift in the future of VPN technology. This shift may favor more secure alternatives and innovative protocols. Emerging solutions like WireGuard, known for its simplicity and modern cryptographic methods, are gaining popularity as safer alternatives to traditional VPNs. Adopting these new technologies could enhance both performance and security, providing a more resilient defense against potential threats.
Adoption of Alternative Protocols
As OpenVPN security vulnerabilities come under scrutiny, the adoption of alternative protocols like WireGuard is on the rise. WireGuard offers simplicity, speed, and robust encryption, making it an attractive option for users seeking a more secure VPN solution. While OpenVPN remains widely used, WireGuard’s growing popularity signals a shift towards more secure and efficient VPN technologies.
Resources and Practical Guides for Addressing OpenVPN Security Vulnerabilities
To assist users in securing their devices against OpenVPN security vulnerabilities, here are practical resources:
- OpenVPN Security Blog: Follow updates on OpenVPN’s official blog for the latest security patches and advice.
- Microsoft Security Response Center: Stay informed with the Microsoft Security Response Center for guidelines on mitigating risks.
- Patch Guides: Access comprehensive guides on applying security patches for various devices, ensuring that your network remains protected.
- Diagnostic Tools: Use recommended tools to check your device’s vulnerability status and confirm the successful application of updates.
Impact on Businesses and Regulatory Compliance
For businesses, the implications of these OpenVPN security vulnerabilities extend beyond immediate security concerns. With regulations like the GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation) in Europe, organizations are obligated to protect personal data. They may face significant penalties if found non-compliant. The discovery of these vulnerabilities necessitates a re-evaluation of current security measures to ensure ongoing compliance with data protection laws.
Businesses should also consider updating their Business Continuity Plans (BCPs) to account for the potential impact of these vulnerabilities. By preparing for worst-case scenarios and implementing robust incident response strategies, organizations can minimize the risk of data breaches and maintain operational resilience.