Remote activation of phones by the police by Jacques Gascuel This article will be updated with any new information on the topic, and readers are encouraged to leave comments or contact the author with any suggestions or additions.
How does remote activation of phones by the police work?
An article of the bill on justice 2023-2027 raises controversy. It allows remote activation of mobile phones and capture of images or sound without the owner’s consent, for cases of organized crime or terrorism. How does this intelligence technique work? What are the conditions to use it? What are its advantages and disadvantages? What is the situation in other countries? We explain everything in this article.
2026 Cyber Doctrine Digital Security
February 24, 2026
2026 Digital Security
February 21, 2026
2026 Digital Security
February 18, 2026
2026 Digital Security
January 23, 2026
2026 Digital Security
January 17, 2026
2026 Digital Security
January 8, 2026
2026 Digital Security
January 7, 2026
2025 Digital Security
January 6, 2026
Discover our other articles on digital security
What is the new bill on justice and why is it raising concerns about privacy?
The bill on justice is a legislative project. It aims to modernize and simplify justice in France. It covers civil, criminal, administrative and digital justice. It also strengthens the investigation and prosecution of serious offenses, such as terrorism and organized crime.
One measure authorizes remote activation of phones by the police for some investigations. Article 3 “An unfailing commitment to better prevent radicalization and fight against terrorism” of the bill includes this measure. It modifies article 706-102-1 of the code of criminal procedure. This article defines how to activate remotely any electronic device that can emit, transmit, receive or store data.
This measure raises privacy concerns because it lets the police access personal or professional data in phones without the owners’ or possessors’ consent or knowledge. It also lets the police locate, record or capture sounds and images from phones without notification or justification. This measure may violate fundamental rights and freedoms, such as privacy, confidentiality, dignity, presumption of innocence and right to a fair trial.
What is remote activation of phones and how does it work?
Remote activation of phones by the police is an intelligence technique that allows law enforcement agencies to access data or record sounds and images from phones without the consent or knowledge of the phone users. This technique can be used for criminal investigations or national security purposes.
To remotely activate phones, law enforcement agencies need three factors: compatibility, connectivity, and security of the phones. They need to be compatible with the software or hardware that enables remote activation. They need to be connected to a network or a device that allows remote access. They need to have security flaws or vulnerabilities that can be exploited or bypassed.
Law enforcement agencies can remotely activate phones by three methods: exploiting vulnerabilities, installing malware, or using spyware on phones. Exploiting vulnerabilities means taking advantage of security flaws or weaknesses in the phone’s operating system, applications, or protocols. Installing malware means putting malicious software on the phone that can perform unauthorized actions or functions. Using spyware means employing software or hardware that can monitor or control the phone’s activity or data.
By remotely activating phones, law enforcement agencies can access data such as contacts, messages, photos, videos, location, browsing history, or passwords. They can also record sounds and images such as conversations, ambient noises, or camera shots. They can do this in real time or later by retrieving the data from the phone’s memory or storage.
What is the French bill on remote activation of phones by the police and what are its implications?
The French bill on remote activation of phones by the police is a legislative text that was promulgated on 25 May 2021. It is part of the justice orientation and programming bill for 2023-2027, which aims to modernize the justice system and reinforce its efficiency and independence.
The bill introduces a new article in the code of criminal procedure, which allows the judge of liberties and detention (at the request of the prosecutor) or the examining magistrate to order the remote activation of an electronic device without the knowledge or consent of its owner or possessor for the sole purpose of locating it in real time. This measure can be applied for crimes or misdemeanors punishable by at least five years’ imprisonment, a fairly broad criterion.
The bill also allows the judge of liberties and detention (at the request of the prosecutor) or the examining magistrate to order the remote activation of an electronic device without the knowledge or consent of its owner or possessor for the purpose of recording sounds and images from it. This measure can be applied only for crimes relating to organized crime and terrorism.
These measures cannot concern parliamentarians, journalists, lawyers, magistrates and doctors, nor the defendants when they are in the judge’s office or with their lawyer.
The bill also specifies that the remote activation of an electronic device must be done in a way that does not alter its functioning or data, and that the data collected must be destroyed within six months after their use.
The bill aims to provide law enforcement agencies with more tools and information to prevent, investigate and prosecute crimes, especially in cases where phones are encrypted, hidden or destroyed. It also aims to harmonize the French legislation with other countries that have used or considered this technique, such as the United States, Germany, Italy, Israel, Canada, China, France, and the United Kingdom.
However, the bill also raises ethical and social challenges, as it involves a trade-off between security and privacy, as well as between effectiveness and legitimacy. It may undermine the right to respect for private life and the right to a fair trial, which are guaranteed by the European Convention on Human Rights and the French Constitution. It may also expose law enforcement agencies to legal or technical challenges or dangers, such as encryption technologies that can prevent or hinder remote activation. It may also create distrust or resistance among phone users or providers, who may use encryption technologies or legal remedies to protect their data or communications.
The bill has been criticized by several actors, such as lawyers, human rights defenders, digital rights activists, journalists and academics. They have denounced its lack of proportionality, necessity and oversight. They have also questioned its effectiveness and legitimacy. They have called for its withdrawal or amendment.
The bill is still subject to constitutional review by the Constitutional Council before its final promulgation.
How did the Senate vote on the bill and where to find the official sources?
The Senate adopted this measure on October 20, 2021, with some amendments. The Senate voted in favor of this measure by 214 votes against 121. The Senate also added some safeguards to this measure, such as limiting its duration to four months renewable once and requiring prior authorization from an independent judge.
The National Assembly still has to examine the bill before adopting it definitively. The National Assembly may approve, reject or modify this measure. The final text may differ from the one that the Senate voted.
The examination of the bill by the National Assembly will start on December 6, 2021. You can follow the progress of the bill on the website of the National Assembly. You can also find the official text of the bill and the report of the Senate on their respective websites. You can also consult the website of the Ministry of Justice for more information on the bill and its objectives.
What are the benefits and risks of remote activation of phones?
This technique can affect citizens’ and suspects’ behavior in different ways.
On one hand, it can deter people from serious offenses. It exposes them to a higher risk of detection and identification. It reduces their incentives for criminal activities.
On the other hand, it can also make people more cautious or paranoid. It increases their uncertainty and fear. It leads them to avoid electronic devices, encrypt their communications, or use countermeasures such as jamming devices.
This technique can also impact public safety and security positively and negatively.
On one hand, it can improve the efficiency and effectiveness of law enforcement agencies. It provides them with more information and evidence. It helps them prevent, investigate and prosecute crimes.
On the other hand, it can also pose risks for human rights and civil liberties. It allows intrusive and covert surveillance. It violates privacy, confidentiality and dignity. It can also be subject to abuse, misuse or error by law enforcement agents or hackers.
Finally, it can create a feeling of insecurity and mistrust towards institutions, which can access personal or professional data in phones. It can also harm respect for presumption of innocence by placing permanent suspicion on people targeted by this technique. It can also infringe on protection of journalistic sources or right to information by discouraging whistleblowers or witnesses from speaking freely. It can finally encourage people concerned to adopt avoidance or circumvention strategies, such as changing phones regularly, using encrypted applications or switching to airplane mode.
These strategies can reduce the actual effectiveness of this technique for preventing terrorism and organized crime.
What are the arguments in favor of remote activation of phones?
Some people support this technique because they think it has several advantages for law enforcement and public security.
How can remote activation of phones violate privacy and data protection?
One of the main arguments against this technique is that it can violate privacy and data protection for individuals and groups. Privacy and data protection are fundamental rights recognized by international standards and laws. They ensure human dignity and autonomy.
Remote activation of phones violates privacy and data protection by letting law enforcement agencies access personal or professional data without the owners’ or possessors’ consent or knowledge. It also lets law enforcement agencies access sensitive or confidential data without notification or justification. It also lets law enforcement agencies access excessive or irrelevant data without limitation or proportionality.
For example, remote activation of phones could let the police access medical records, financial transactions, political opinions, religious beliefs, sexual preferences, or other intimate information on a device or a communication. It could also let the police access information that is not related to the investigation or that is out of scope on a device or a communication. It could also let the police access information that is not necessary or appropriate for the investigation or that is disproportionate to the seriousness of the offense on a device or a communication.
How can remote activation of phones improve access to justice and evidence?
Another argument in favor of this technique is that it can improve access to justice and evidence for law enforcement agencies and victims of crimes. Justice and evidence ensure the rule of law and the protection of rights.
Remote activation of phones improves access to justice and evidence by letting law enforcement agencies obtain information that is otherwise inaccessible or difficult to obtain. It also lets law enforcement agencies obtain information that is more reliable and accurate than other sources. It also lets law enforcement agencies obtain information that is timelier and more relevant than other sources.
For example, remote activation of phones could help the police access data that is encrypted or password-protected on a device or a communication. It could also help the police access data that is authentic and verifiable on a device or a communication. It could also help the police access data that is up-to-date and pertinent on a device or a communication.
What are the arguments against remote activation of phones?
Some people oppose this technique because they think it has several disadvantages for human rights and civil liberties.
How can remote activation of phones violate privacy and data protection?
One of the main arguments against this technique is that it can violate privacy and data protection for individuals and groups. Privacy and data protection are fundamental rights recognized by international standards and laws. They ensure human dignity and autonomy.
Remote activation of phones violates privacy and data protection by letting law enforcement agencies access personal or professional data without the owners’ or possessors’ consent or knowledge. It also lets law enforcement agencies access sensitive or confidential data without notification or justification. It also lets law enforcement agencies access excessive or irrelevant data without limitation or proportionality.
For example, remote activation of phones could let the police access medical records, financial transactions, political opinions, religious beliefs, sexual preferences, or other intimate information on a device or a communication. It could also let the police access information that is not related to the investigation or that is out of scope on a device or a communication. It could also let the police access information that is not necessary or appropriate for the investigation or that is disproportionate to the seriousness of the offense on a device or a communication.
How can remote activation of phones undermine the presumption of innocence and the right to a fair trial?
Another argument against this technique is that it can undermine the presumption of innocence and the right to a fair trial for individuals and groups. The presumption of innocence and the right to a fair trial are fundamental rights recognized by international standards and laws. They ensure justice and accountability.
Remote activation of phones undermines the presumption of innocence and the right to a fair trial by letting law enforcement agencies access data that they can use against individuals or groups without any legal basis or due process. It also lets law enforcement agencies access data that they can manipulate or falsify by law enforcement agents or hackers. It also lets law enforcement agencies access data that individuals or groups can challenge or contest.
For example, remote activation of phones could let the police access data that they can incriminate individuals or groups without any warrant or authorization from a judge. It could also let the police access data that they can alter or corrupt by law enforcement agents or hackers. It could also let the police access data that individuals or groups can dispute or refute.
How can remote activation of phones create a risk of abuse and misuse by the authorities?
Another argument against this technique is that it can create a risk of abuse and misuse by the authorities for individuals and groups. Abuse and misuse are illegal or unethical actions that violate rights and obligations. They damage trust and legitimacy.
Remote activation of phones creates a risk of abuse and misuse by the authorities by letting law enforcement agencies access data that they can use for purposes other than those authorized or intended. It also lets law enforcement agencies access data that they can share or disclose to third parties without any oversight or control. It also lets law enforcement agencies access data that they can retain or store for longer than necessary or permitted.
For example, remote activation of phones could let the police access data that they can use for political, personal, commercial, or other interests on a device or a communication. It could also let the police access data that they can transfer or leak to other agencies, organizations, media, or individuals on a device or a communication. It could also let the police access data that they can keep or archive for indefinite periods on a device or a communication.
What are the alternatives and safeguards for remote activation of phones?
Some people suggest that there are alternatives and safeguards for remote activation of phones that can balance security and privacy.
What are the existing legal tools to access phone data with judicial authorization?
One of the alternatives for remote activation of phones is to use existing legal tools to access phone data with judicial authorization. Judicial authorization is a legal requirement that ensures respect for rights and obligations. An independent and impartial judge grants it after evaluating the necessity and proportionality of the request.
Existing legal tools to access phone data with judicial authorization include search warrants, wiretaps, geolocation orders, data requisitions, and international cooperation agreements. These tools let law enforcement agencies obtain information from phones in a lawful and transparent manner. They also provide legal protection and recourse for individuals and groups.
For example, search warrants let law enforcement agencies physically seize phones and extract data from them with judicial authorization. Wiretaps let law enforcement agencies intercept calls and messages from phones with judicial authorization. Geolocation orders let law enforcement agencies track the location of phones with judicial authorization. Data requisitions let law enforcement agencies request data from phone operators or service providers with judicial authorization. International cooperation agreements let law enforcement agencies exchange data with foreign authorities with judicial authorization.
What are the principles and conditions for remote activation of phones according to the bill?
One of the safeguards for remote activation of phones is to follow the principles and conditions for remote activation of phones according to the bill. The bill on justice sets some rules and limits for this technique to prevent abuse and misuse.
The principles and conditions for remote activation of phones according to the bill include:
- The technique can only be used for terrorism and organized crime investigations.
- An independent judge who authorizes it must supervise the technique. The technique can only last for four months renewable once.
- The technique must respect necessity, proportionality, subsidiarity, and legality.
- Parliament and independent authorities must oversee and control the technique.
- Experts and stakeholders must evaluate and review the technique.
These principles and conditions aim to ensure a reasonable and accountable use of this technique. They also aim to protect the rights and interests of individuals and groups.
What are the possible ways to limit or challenge remote activation of phones?
Another safeguard for remote activation of phones is to use possible ways to limit or challenge remote activation of phones by individuals or groups. These ways can help protect rights and interests, as well as ensure accountability and transparency.
Some of the possible ways to limit or challenge remote activation of phones are:
-
Using encryption technologies:
Encryption technologies can make data on phones unreadable or inaccessible to law enforcement agencies, even if they remotely activate them. Encryption technologies can also protect communications from law enforcement agencies’ interception or recording. For example, using end-to-end encryption apps, such as Signal or WhatsApp, can prevent law enforcement agencies from accessing messages or calls on phones.
-
Using security features:
Security features can prevent law enforcement agencies from installing or activating software or applications on phones that enable remote activation. Security features can also detect or remove software or applications that enable remote activation. For example, using antivirus software, firewalls, passwords, biometrics, or VPNs can prevent law enforcement agencies from accessing phones.
-
Using legal remedies:
Legal remedies can let individuals or groups contest or oppose remote activation of phones by law enforcement agencies. Legal remedies can also let individuals or groups seek compensation or redress for damages caused by remote activation of phones. For example, using judicial review, administrative appeals, complaints, lawsuits, or human rights mechanisms can challenge law enforcement agencies’ actions or decisions regarding remote activation of phones.
How does this technique compare with other countries?
Law enforcement agencies in other countries, such as the United States, Germany, Italy, Israel, Canada, China, France, and the United Kingdom, have used or considered remote activation of phones by the police. This technique is not new or unique. However, the legal framework, the technical methods, and the ethical and social implications of this technique vary from country to country..
How does remote activation of phones by the police work in different countries?
Remote activation of phones by the police is an intelligence technique that varies from country to country. It depends on the legal framework, the technical methods and the ethical issues of each country. Here are some examples of how it works in different countries.
- In the United States, this technique is known as “roving bugs” or “mobile device tracking”. The Foreign Intelligence Surveillance Act (FISA) authorizes it for national security purposes and Title III of the Omnibus Crime Control and Safe Streets Act for criminal investigations. It requires a court order based on probable cause and limited in scope and duration. It can locate or record sounds and images from phones. It can be done by installing malware or exploiting vulnerabilities on phones.
- In Germany, this technique is known as “Quellen-TKÜ” or “source telecommunications surveillance”. The Code of Criminal Procedure and the Telecommunications Act regulate it for criminal investigations and the Federal Intelligence Service Act for national security purposes. It requires a court order based on reasonable suspicion and proportionality. It can intercept communications from phones. To do so, it installs software or uses spyware on phones.
- In Italy, this technique is known as “Trojan horse” or “spyware”. The Code of Criminal Procedure and the Data Protection Code regulate it for criminal investigations. It requires a court order based on serious indications of guilt and necessity. It can access data or record sounds and images from phones. To do so, it installs software or uses spyware on phones.
- In Israel, this technique is known as “IMSI catchers” or “stingrays”. The Wiretapping Law and the Privacy Protection Law regulate it for criminal investigations and the Security Service Law for national security purposes. It requires a court order based on reasonable grounds and proportionality. It can locate or intercept communications from phones. To do so, it uses devices that mimic cell towers and trick phones into connecting to them.
- In Canada, this technique is known as “cell site simulators” or “IMSI catchers”. The Criminal Code and the Charter of Rights and Freedoms regulate it for criminal investigations. It requires a court order based on reasonable grounds and proportionality. It can locate or intercept communications from phones. To do so, it uses devices that mimic cell towers and trick phones into connecting to them.
- In China, this technique is known as “network interception” or “remote control”. The Criminal Procedure Law and the Cybersecurity Law regulate it for criminal investigations and national security purposes. It does not require a court order but only an approval from a higher authority. It can access data or record sounds and images from phones. To do so, it installs software or uses spyware on phones.
- In France, real-time geolocation is regulated by the Criminal Procedure Code and the Intelligence Law for criminal and national security investigations. Article 706-102-1 of the Criminal Procedure Code allows police officers and agents to use a technical device to access, record, store and transmit computer data without the consent of the persons concerned. This requires a court order based on serious reasons and proportionality. Article 230-32 of the Criminal Procedure Code states that “Any technical means for real-time location, throughout the national territory, of a person, without his consent, a vehicle or any other object, without the consent of its owner or possessor, may be used if this operation is required by necessity: “. This also requires a court order based on serious reasons and proportionality.
- In the United Kingdom, this technique is known as “equipment interference” or “hacking”. The Investigatory Powers Act regulates it for criminal investigations and national security purposes. It requires a warrant based on necessity and proportionality. It can access data or record sounds and images from phones. To do so, it installs software or uses spyware on phones.
How does remote activation of phones by the police raise ethical and social challenges?
Remote activation of phones by the police raises ethical and social challenges in different contexts and situations because it involves a trade-off between security and privacy, as well as between effectiveness and legitimacy.
Security versus privacy
On one hand, remote activation of phones by the police can enhance security by providing law enforcement agencies with more information and evidence to prevent, investigate, and prosecute crimes. It can also deter criminals from using phones to plan or commit crimes.
On the other hand, remote activation of phones by the police can undermine privacy by letting law enforcement agencies access personal or professional data without consent or knowledge. It can also violate human rights and civil liberties by letting law enforcement agencies monitor or record sounds and images without notification or justification.
Effectiveness versus legitimacy
On one hand, remote activation of phones by the police can be effective by increasing the chances of finding relevant information or evidence on phones that may be encrypted, hidden, or destroyed. It can also be efficient by reducing the costs and risks of physical surveillance or interception.
On the other hand, remote activation of phones by the police can be illegitimate by violating the legal framework, the technical methods, or the oversight and control mechanisms that regulate this technique in each country. It can also be counterproductive by creating distrust or resistance among phone users or providers, who may use encryption technologies or legal remedies to protect their data or communications.
The ethical and social challenges of remote activation of phones by the police depend on the legal framework, the technical methods, and the oversight and control mechanisms that regulate this technique in each country. They also depend on the cultural and political values, the public opinion, and the media coverage that shape the perception and acceptance of this technique in each country.
Some of the ethical and social challenges of remote activation of phones by the police are how to :
- balance security and privacy in the use of this technique?
- ensure compliance with fundamental rights and freedoms in the use of this technique?
- prevent abuse, misuse, or error in the use of this technique?
- provide legal protection and recourse for individuals or groups affected by this technique?
- ensure accountability and transparency in the use of this technique?
- evaluate the effectiveness and legitimacy of this technique?
- foster trust and cooperation between law enforcement agencies and phone users in the use of this technique?
What is the impact of encryption technologies on this technique?
Encryption technologies are methods or systems that make data unreadable or inaccessible to unauthorized parties. Encryption technologies can have a significant impact on remote activation of phones by the police, as they can make this technique more difficult, risky, or controversial.
How can encryption technologies make remote activation of phones by the police more difficult or impossible?
Encryption technologies can make remote activation of phones by the police more difficult or impossible by preventing law enforcement agencies from accessing data or communications on phones, even if they remotely activate them. Encryption technologies can also protect phones from malware or spyware that enable remote activation.
For example, end-to-end encryption, which some apps such as Signal or WhatsApp use, can prevent law enforcement agencies from intercepting or reading messages or calls on phones, as only the sender and the receiver have the keys to decrypt them. Device encryption, which some operating systems such as iOS or Android use, can prevent law enforcement agencies from extracting or viewing data on phones, as they require a password or a biometric authentication to unlock them.
How can encryption technologies make remote activation of phones by the police more risky or harmful?
Encryption technologies can make remote activation of phones by the police more risky or harmful by exposing law enforcement agencies to legal or technical challenges or dangers. Encryption technologies can also harm phone users by compromising their security or privacy.
For example, breaking encryption, which law enforcement agencies sometimes do to access data or communications on phones, can expose them to legal challenges, as it may violate laws or regulations that protect encryption or privacy. It can also expose them to technical dangers, as it may weaken the security of phones or networks and create vulnerabilities for hackers or criminals. Hacking encryption, which law enforcement agencies sometimes do to install malware or spyware on phones, can harm phone users by compromising their security or privacy, as it may allow unauthorized access to their data or functions.
How can encryption technologies make remote activation of phones by the police more controversial or unacceptable?
Encryption technologies can make remote activation of phones by the police more controversial or unacceptable by raising ethical and social issues or debates. Encryption technologies can also create conflicts or tensions between law enforcement agencies and phone users or providers.
For example, undermining encryption, which law enforcement agencies sometimes request to facilitate remote activation of phones, can raise ethical and social issues or debates, as it may affect human rights and civil liberties, such as privacy, confidentiality, dignity, presumption of innocence, and right to a fair trial. It can also create conflicts or tensions between law enforcement agencies and phone users or providers. They may have different interests or values regarding encryption and security.
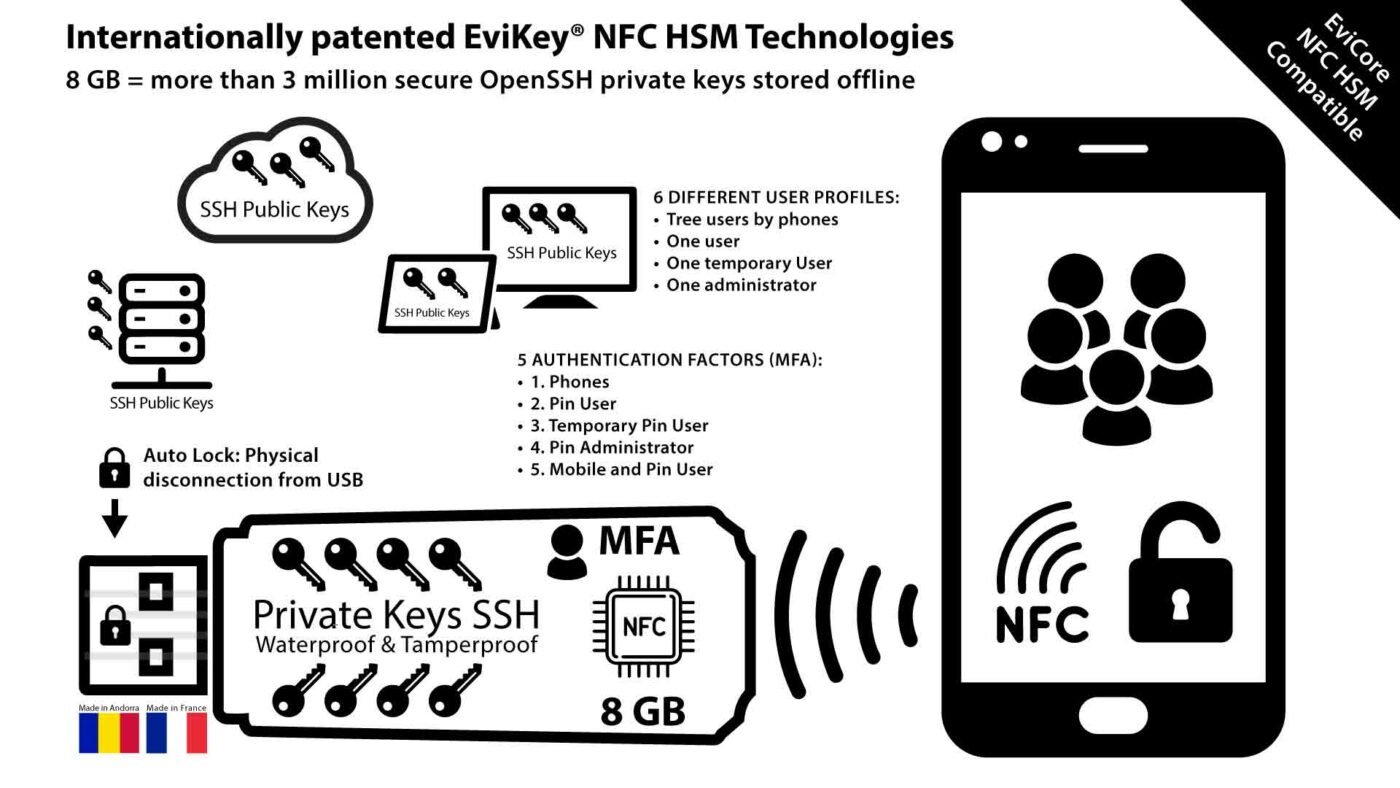
How does EviCore NFC HSM technology developed by Freemindtronic offer a high level of protection for phone users?
Remote activation of phones by the police can be facilitated by exploiting security flaws, installing malware, or requesting backdoors in encryption technologies. However, some encryption technologies may be resistant to these measures and offer a higher level of protection for phone users. One of them is the EviCore NFC HSM technology developed by Freemindtronic.
This technology lets users create their own encryption keys in a random way and store them in a physical device that communicates with the phone via NFC (Near Field Communication). The device also lets users define their own trust criteria that must be met to use the keys or their segments. The encryption is done in post-quantum AES-256 mode from either a device compatible with the EviCore NFC HSM technology or from an encrypted enclave in the phone created in the Key chain (Apple) or the Key store (Android) via the EviCore HSM OpenPGP technology. The encryption keys are segmented and superior to 256 bits. Moreover, they are physically externalized from computer systems. Everything is designed by Freemindtronic to effectively fight against espionage and corruption of telephone, computer, communication and information systems. Finally, without a server, without a database, even in air gap and airplane mode works EviCore NFC HSM or EviCore HSM OpenPGP technology. Everything is designed to work in volatile memory to leave no trace in telephone and computer systems.
This technology offers a high level of security and privacy for phone users who want to protect their data from unauthorized access, including by the police. It also offers a high level of performance and usability for phone users who want to encrypt or over-encrypt all types of messaging in the world, including SMS and MMS. It also works with other applications that use encryption, such as email, cloud storage or blockchain.
Furthermore, this technology is designed to be totally anonymous, autonomous, unconnected, without a database, without collecting any information of any kind on the identity of the user, nor on the hardware, nor on the terminals used. The technology is designed to be totally isolated and totally independent of the security of the terminal used whether it is connected or not. Freemindtronic does not keep the unique pairing keys for each NFC HSM device. And even if it did, the user at installation will automatically generate segmented complementary keys for encryption with administrator and user passwords. Each NFC device has a unique 128-bit signature dedicated to fighting against counterfeiting of NFC devices. It is also used as a key segment. The secret stored in eprom memories or in enclaves of the phone and/or computer can be individually secured by other segmented keys characterized by additional trust criteria such as a geozone, a random hexadecimal code via an existing or generated QR code or Bar Code via EviCore HSM. It is therefore physically impossible for Freemindtronic but under judicial assignment to decrypt data encrypted via EviCore HSM technologies even with a quantum computer.
Conclusion
Remote activation of phones by the police is an intelligence technique. It aims to fight terrorism and crime by accessing data or sounds and images from phones without consent or knowledge. Law enforcement agencies in various countries have used or considered this technique. For example, France, the United States, Germany, Italy, Israel, Canada, China, and the United Kingdom. However, this technique raises technical, legal, ethical, and social challenges. They need to be addressed.
On the technical side, remote activation of phones by the police depends on three factors: compatibility, connectivity, and security of the phones. It can be done by three methods: exploiting vulnerabilities, installing malware, or using spyware on phones.For example, EviCore NFC HSM technology developed by Freemindtronic protects data and communications on phones from remote activation by the police. Encryption technologies can make this technique more difficult or impossible by preventing law enforcement agencies from accessing data or communications on phones, even if they remotely activate them.
On the legal side, remote activation of phones by the police requires a legal framework that regulates its use and scope. Laws or regulations can authorize it and specify the conditions and criteria for its application. Legal remedies can also challenge it and contest or oppose its validity or legality.
On the ethical side, remote activation of phones by the police involves a trade-off between security and privacy, as well as between effectiveness and legitimacy. It can enhance security by providing more information and evidence to law enforcement agencies to prevent, investigate, and prosecute crimes. It can also undermine privacy by letting law enforcement agencies access personal or professional data without notification or justification.
On the social side, remote activation of phones by the police raises issues or debates that affect human rights and civil liberties. For example, privacy, confidentiality, dignity, presumption of innocence, and right to a fair trial. It can also create conflicts or tensions between law enforcement agencies and phone users or providers, as they may have different interests or values regarding encryption and security.
Therefore, remote activation of phones by the police is a complex and controversial technique that requires a careful and balanced approach that respects the rights and interests of all parties involved. The French bill on remote activation of phones by the police and the EviCore NFC HSM Open PGP technology developed by Freemindtronic illustrate the complex and evolving relationship between intelligence and encryption in the digital age. They raise questions about finding a balance. It is between security and privacy, between public interest and individual rights, between innovation and regulation.
: According to Okta, privacy is the right to control how your information is viewed and used, while security is protection from threats or dangers (https://www.okta.com/identity-101/privacy-vs-security/).
: According to Carnegie Endowment for International Peace, finding a balance between security and privacy requires addressing technical, legal, and social questions (https://carnegieendowment.org/2019/09/10/moving-encryption-policy-conversation-forward-pub-79573).
: According to Springboard, finding a balance between innovation and regulation requires cooperation among stakeholders and respect for human rights (https://www.springboard.com/blog/cybersecurity/privacy-vs-security-how-to-balance-both/).