2025, Cyberculture
Passwordless Security Trends 2025: Future of Digital Security
Passwordless Security Trends in 2025: Navigating the Digital Landscape
Explore the key passwordless security trends, challenges, and innovative solutions shaping our online security. This interactive report delves into user password habits, the escalating impact of cyber threats, and the critical transition towards more secure digital authentication methods. According to the Digital 2024 Global Overview Report by We Are Social and Hootsuite [Source A], over 5 billion people are connected to the Internet, spending an average of 6 hours and 40 minutes online daily.
423+ Billion
active online accounts worldwide, highlighting the immense scale of modern digital identity management.
The Burden of Passwords: Why Traditional Security Falls Short
This section examines prevalent user password habits, the fatigue they generate, and the resulting risky practices. Understanding these behaviors is crucial for grasping the full extent of the current password security problem and the need for passwordless authentication solutions.
How Many Passwords Do Users Manage?
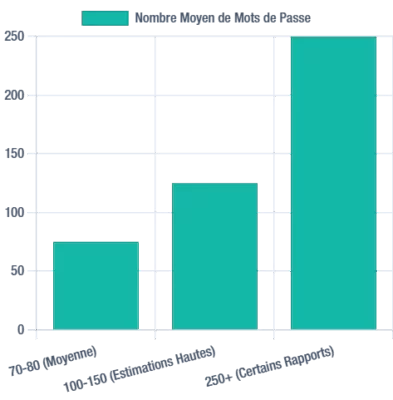
Individuals typically manage an average of 70 to 80 passwords, with some reports indicating figures as high as 100-150, or even over 250. According to Statista, a 2020 study estimated the average number of online accounts per internet user worldwide to be 90. This proliferation significantly contributes to password fatigue, pushing users towards less secure management methods.
Estimates of the average number of passwords per user, highlighting the scale of password management challenges.
Common & Risky Password Management Methods
Despite known security risks, many users opt for insecure password management methods: 54% rely on memory, 33% use pen and paper, 10% use sticky notes, and 15% use Excel or Notepad files. These practices underscore the urgent need for stronger authentication solutions.
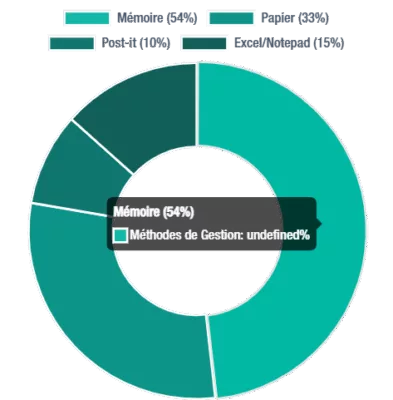
Distribution of password management methods, revealing widespread insecure password habits.
78%
of people admit to reusing passwords across multiple accounts, and 52% use the same one on at least three accounts, a significant security vulnerability.
76%
of users find password management stressful, contributing to password fatigue and poor security practices.
5-7 / 10-15
daily logins for private users and professionals respectively, highlighting the continuous authentication burden.
1 in 3
IT support tickets are related to password resets, indicating a major operational inefficiency.
Password Fatigue and Weakness: A Persistent Cyber Risk
The proliferation of online accounts leads to “password fatigue,” which encourages risky practices such as using weak passwords (e.g., “123456”, “password”, used by over 700,000 people) or widespread reuse. Nearly 60% of employees, including security personnel, admit to reusing passwords, and 48% reuse them on professional platforms. Furthermore, 59% of US adults include personal information in their passwords. This situation is worsened by the fact that 44% of internet users rarely or never change their passwords, creating gaping security flaws. Institutions like ANSSI and CISA consistently emphasize the importance of unique and complex passwords to mitigate these risks and enhance digital security in 2025.
The FBI’s Annual Internet Crime Report consistently highlights the devastating impact of password-related vulnerabilities, linking them to billions in financial losses due to various cybercriminal activities. This data underscores the urgent need for robust cybersecurity solutions beyond traditional passwords.
A related study, Time Spent on Login Method , explores the efficiency and security trade-offs of different authentication methods, underscoring the significant impact of time spent on login processes. User trust often remains disconnected from their actual practices: 60% feel confident in identifying phishing attempts, yet risky behaviors persist, reinforcing the need for phishing-resistant authentication.
Cybersecurity’s Financial Impact and Emerging Threats in 2025
Password-related vulnerabilities have direct and significant financial consequences for organizations and pave the way for increasingly sophisticated cyberattacks. This section explores the rising cost of data breaches and the new tactics cybercriminals are employing, including AI-driven cyber threats.
Rising Cost of Data Breaches and Credential Exposure
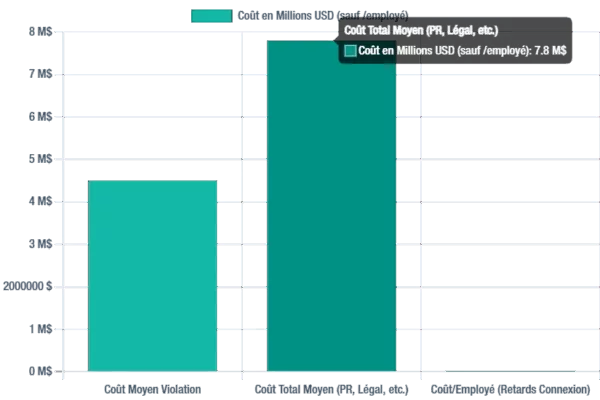
Data leaks related to passwords represent a significant financial burden for organizations. The average cost of a data breach in 2025 is projected to be $4.5 million, potentially reaching $7.8 million when including public relations, legal fees, and downtime. These figures highlight the critical need for robust data protection strategies.
Average financial impact of data breaches, illustrating the significant cybersecurity risks
3.8 Billion
credentials leaked in the first half of 2025. A broader study reveals 19 billion exposed passwords, of which 94% are reused or duplicated, creating massive credential stuffing vulnerabilities.
81%
of breaches involve weak or stolen passwords. 68% of breaches are directly attributable to human factors, emphasizing the need for user-centric security solutions.
41%
increase in DDoS attacks in 2024, costing up to $22,000/minute in downtime. SMEs suffer 198% more attacks than large enterprises, highlighting SME cybersecurity challenges.
Emerging Threats: AI, Deepfakes, and Advanced Phishing Attacks
Cybercriminals are increasingly leveraging advanced methods such as AI-assisted phishing and deepfakes to deceive users. Generative AI (GenAI) enables more sophisticated and large-scale attacks, with 47% of organizations citing GenAI-powered adversarial advancements as their primary concern. In 2024, 42% of organizations reported phishing or social engineering incidents. These threats exploit human psychology, making the distinction between legitimate and malicious communications increasingly difficult. Gartner predicts that by 2026, 30% of companies will consider identity verification solutions unreliable due to AI-generated deepfakes. Furthermore, IoT malware attacks increased by 400% in 2023, signaling growing vulnerabilities in connected devices and the broader IoT security landscape.
Toward a Passwordless Future: Adapting to New Authentication Models
Facing the inherent limitations of traditional passwords, the industry is rapidly moving towards passwordless authentication solutions. This section highlights the significant rise of passkeys, advancements in *biometric security, and the crucial integration of AI for enhanced security and a superior user experience.
Growth of the Passwordless Authentication Market
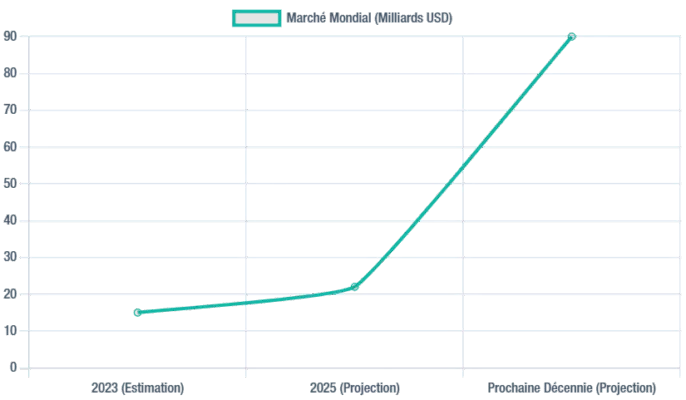
Projected growth of the global passwordless authentication market, demonstrating its rapid adoption.
15+ Billion
online accounts are now compatible with passkeys, marking a significant milestone in phishing-resistant authentication adoption.
550%
increase in daily passkey creation (end of 2024, Bitwarden), with over a million new passkeys created in the last quarter of 2024, underscoring rapid user acceptance.
70%
of organizations are planning or implementing passwordless authentication. Furthermore, customer support costs related to passwords can be reduced by 50%, offering substantial operational benefits.
57%
of consumers are now familiar with passkeys, a notable increase from 39% in 2022, indicating growing public awareness of new authentication methods.
Benefits of Passkeys and Biometrics in Passwordless Security
Passkeys, based on FIDO standards, offer inherently superior security as they are phishing-resistant and unique to each site. They significantly improve user experience with faster logins (e.g., Amazon 6 times faster, TikTok 17 times faster) and boast a 98% success rate (Microsoft, compared to 32% for traditional passwords). The NIST updated its guidelines for 2025, now requiring phishing-resistant multi-factor authentication (MFA) for all federal agencies, a critical step towards secure digital identity.
Biometric authentication (facial recognition, fingerprints, voice, behavioral biometrics) is continuously gaining accuracy thanks to AI. Multimodal and contactless approaches are developing rapidly. Behavioral biometrics, which analyzes subtle patterns like typing rhythm or mouse movement, enables continuous background identity verification, offering advanced user authentication capabilities. Privacy protection remains a major concern, leading to designs where biometric data primarily stays on the user’s device or is stored in a decentralized manner (e.g., using blockchain for decentralized identity).
Innovative Solution: PassCypher NFC HSM and HSM PGP – A Secure Alternative for Advanced Passwordless Authentication
The PassCypher NFC HSM and PassCypher HSM PGP solutions represent a major advancement in authentication management. They fundamentally differ from traditional FIDO/Passkey systems in their security architecture, offering a truly secure alternative for digital identity.
Passkeys: Security Model and Potential Vulnerabilities
Passkeys rely on private keys that are encrypted and inherently securely stored in integrated hardware components of the device. These are true hardware security modules (integrated HSMs):
- TPM 2.0 (Trusted Platform Module) on Windows and Linux systems.
- Secure Enclave (Apple) and TEE (Trusted Execution Environment) on Apple and Android devices. These are dedicated and isolated hardware elements on the SoC, not just software areas of the OS.
Using a passkey requires local user authentication (biometrics or PIN). It is crucial to note that this human authentication is not a direct decryption key for the private key. It serves to authorize the secure hardware component (TPM/Secure Enclave) to use the key internally to sign the authentication request, without ever exposing the private key. More information can be found on Passkeys.com [Source L].
However, a vulnerability remains: if an attacker manages to obtain physical access to the device *and* bypass its local authentication (e.g., via a keylogger for the PIN, or a sophisticated biometric spoofing technique), they could then instruct this same secure component to use the passkeys stored on the device. Furthermore, although TPM 2.0 is used for FIDO keys, its NVRAM memory is limited and not designed to directly store thousands of “master keys,” rather protecting keys linked to user profiles. This highlights a potential area for enhanced authentication security.
PassCypher: A Revolutionary Hybrid Architecture for Advanced Passwordless Security
PassCypher adopts a fundamentally different architecture, offering significant independence from hardware and software flaws of a single device, including zero-days or espionage threats. This system positions itself as a hybrid HSM, combining external physical storage with secure volatile memory computation, making it an ideal next-gen authentication solution.
PassCypher HSM PGP: Ultimate Authentication for PC/Mac/Linux Environments
Operational Diagram: PassCypher HSM PGP for Enhanced PC/Mac/Linux Security
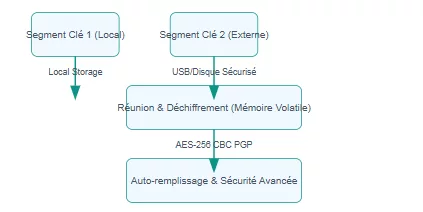
Key Segment 1 (Local)
Key Segment 2 (External)
Segments Recombination & Decryption (Volatile Memory)
Secure Auto-fill & Advanced Security
Browser Local Storage
USB/Secure Disk Enclave
AES-256 CBC PGP
- Segmented Keys and Robust Encryption: Uses a pair of 256-bit segmented keys. One is securely stored in the browser’s local storage, the other on a user-preferred external medium (USB drive, SD card, SSD, encrypted cloud, or even an enclave on a partitioned disk secured by BitLocker). Encryption and decryption are performed with a single click via AES-256 CBC secured by PGP, by concatenating the two segmented keys only in volatile memory and only for the duration of direct field auto-filling (without copy-pasting). This ensures robust data protection and key management.
- Advanced Protection against Cyberattacks: Integrates an anti-typosquatting URL sandbox and an anti-Browser-in-the-Browser (BITB) attack function, configurable in manual, semi-automatic, or automatic mode. Furthermore, with each connection, the “pwned” API is queried to check if the login and/or password have been compromised, displaying a visual alert message to the user (with a red hacker icon) if so. This provides proactive threat detection.
- Speed and Convenience: All these operations are performed in one click, or two clicks if two-factor authentication is required (including for complex accounts like Microsoft 365 with different redirection URLs). This emphasizes user experience in cybersecurity.
PassCypher NFC HSM: Mobile and Connected Passwordless Security
Operating Diagram: PassCypher NFC HSM

NFC HSM Module (EEPROM)
Android Phone (Freemindtronic App)
Website / App
Segmented Keys & Criteria (Volatile Memory)
Secure Auto-fill
PassCypher HSM PGP (Optional)
Encrypted Keys
NFC Communication
AES-256 Segmented
Via Secure Local Network
Login
- Multi-Segment Encrypted Containers: Stores encrypted containers via multiple segmented keys. By default, this includes a unique pairing key to the Android phone’s NFC device, a secure 128-bit signature key preventing HSM module counterfeiting, and the administrator password. This ensures robust mobile security.
- Encapsulation by Trust Criteria: Each container can be re-encrypted by encapsulation through the addition of supplementary trust criteria, such as:
- One or more geographical usage zones.
- One or more BSSIDs (Wi-Fi network identifiers).
- A password or fingerprint.
- A segmented key via QR code or barcode.
All this information, including access passwords to secure memory blocks of the EEPROM (e.g., M24LR64K from STM), is encrypted in the module’s memory, providing adaptable contextual authentication.
- Connectivity and Interoperability: Enables secure connection from an Android phone defined as a password manager, by filling login/password fields with a simple tap of the PassCypher NFC HSM module. A secure pairing system via the local network between the phone (with the Freemindtronic app embedding PassCypher NFC HSM) and PassCypher HSM PGP also allows auto-login from containers stored in NFC HSM modules, ensuring seamless and secure access.
- Secure Communication: All operations are performed in volatile memory via an innovative system of AES 256 segmented key encrypted communication between the phone and the extension, crucial for data integrity and privacy.
These PassCypher solutions, delivered internationally, offer unparalleled security and exceptional convenience, effectively addressing current and future cybersecurity challenges as a complete MFA authentication management solution. This segmented key system is protected by patents issued in the USA, Europe (EU), the United Kingdom (UK), Spain (ES), China, South Korea, and Japan, showcasing its innovative cybersecurity technology..
Global Cybersecurity Challenges in 2025: Beyond Passwordless
The AI Paradox and Emerging Quantum Threat
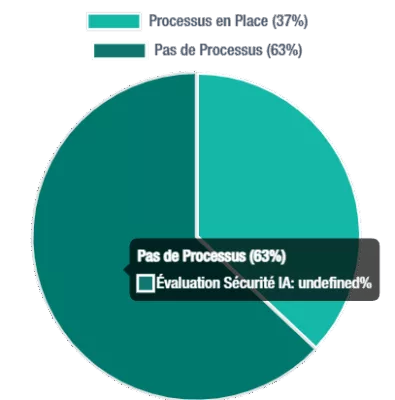
Organizational readiness for AI security assessment, revealing areas for improvement in cybersecurity preparedness.
Supply Chain Vulnerabilities and Third-Party Cybersecurity Risks
The increasing complexity of supply chains is now recognized as a primary cyber risk. A concerning 54% of large organizations view it as the biggest obstacle to their cyber resilience. A pervasive lack of visibility and control over supplier security creates systemic failure points, making the entire ecosystem vulnerable. Furthermore, 48% of CISOs cite third-party compliance as a major challenge in implementing crucial cyber regulations, complicating risk management strategies.
48%
of CISOs cite third-party compliance as a major challenge, highlighting the complexity of supply chain security management.
Skills Shortage and Regulatory Fragmentation in Cybersecurity
The global cybersecurity skills gap has grown by 8% in just one year. Two-thirds of organizations report critical shortages in cybersecurity talent, and only 14% feel they have the necessary expertise to address modern threats. In the public sector, 49% of organizations lack the talent required to achieve their cybersecurity goals, exacerbating talent retention issues.
Meanwhile, 76% of CISOs believe regulatory fragmentation significantly affects their ability to maintain compliance, creating “regulatory fatigue” and diverting resources from essential risk-based strategies. For comprehensive cyber threat landscape information, consult ENISA’s official publications. Geopolitical tensions also increasingly impact global cybersecurity strategies, with nearly 60% of organizations reporting such effects, adding another layer of complexity to national cybersecurity efforts.
Strategic Recommendations for Enhanced Passwordless Security in 2025
Actively explore and implement passkeys and advanced biometric authentication solutions. Emphasize the strong security benefits (especially phishing resistance) and improved user experience (faster, easier logins). Position passwordless technology as a strategic necessity to reduce support costs and enhance overall user satisfaction. Crucially, consider dedicated Hardware Security Module (HSM) solutions like PassCypher for optimal private key security and universal compatibility without extensive infrastructure adaptation.
Actively explore and implement passkeys and advanced biometric authentication solutions. Emphasize the strong security benefits (especially phishing resistance) and improved user experience (faster, easier logins). Position passwordless technology as a strategic necessity to reduce support costs and enhance overall user satisfaction. Crucially, consider dedicated Hardware Security Module (HSM) solutions like PassCypher for optimal private key security and universal compatibility without extensive infrastructure adaptation.
Actively explore and implement passkeys and advanced biometric authentication solutions. Emphasize the strong security benefits (especially phishing resistance) and improved user experience (faster, easier logins). Position passwordless technology as a strategic necessity to reduce support costs and enhance overall user satisfaction. Crucially, consider dedicated Hardware Security Module (HSM) solutions like PassCypher for optimal private key security and universal compatibility without extensive infrastructure adaptation.
Invest strategically in AI-driven defenses and thoroughly evaluate the security of all AI tools before deployment. Implement rigorous monitoring and enforce clear security requirements for the entire supply chain. Proactively anticipate and prepare for emerging threats from quantum computing, which could disrupt current encryption standards.
Actively support comprehensive cybersecurity training programs and leverage AI to augment human capabilities, addressing the critical skills shortage. Adopt “identity fabric” approaches to simplify access governance and streamline regulatory compliance, even amidst increasing fragmentation.

Pingback: The Future of Passwordless Authentication - Password Security