
DataShielder HSM PGP: Advanced Data Encryption Datasheet
Product: DataShielder HSM PGP
Version: 2.0
Company: Freemindtronic
Date: 3 june 2025
Designed as an advanced data encryption tool, DataShielder HSM PGP secures sensitive information using the AES-256 CBC algorithm while implementing innovative key management techniques. By leveraging a secure key segmentation architecture, it effectively combines local and external storage in conjunction with the EviEngine for efficient serverless encryption management. As a result, it proves ideal for high-risk environments that demand Zero Trust and Zero Knowledge approaches. Moreover, by adhering to the OpenPGP protocol, it guarantees confidentiality and integrity of digital communications while simultaneously shielding against cyber threats.
In this system, two distinct key segments are generated: one resides locally in the web browser, while the other stores on an external device. This dual-segment approach, in turn, allows for unlimited combinations, enhancing the security and flexibility of encryption and decryption operations. Unlike a traditional 256-bit AES key, this innovative approach forms a robust 512-bit key, thereby significantly increasing security and providing enhanced protection against various attacks, including those exploiting classical and potentially quantum vulnerabilities.
Visual Encyclopedia of DataShielder Diagrams
This technical datasheet presents the core cryptographic processes within DataShielder HSM PGP’s advanced encryption system. It emphasizes key mechanisms such as key segmentation, AES-256 CBC encryption, secure key management, and quantum-resistant protocols. Designed for professionals, the content highlights how DataShielder ensures data integrity, confidentiality, and robust protection against cyber threats. You will find detailed workflows for encryption and decryption processes, alongside essential security features, reinforced by various diagrams to support understanding in high-risk environments.
Advanced Data Encryption Solution: Visual Encyclopedia of DataShielder Diagrams
✅ General Operation of Advanced Encryption
✅ License Activation Process for Secure Data Encryption
✅ Key Management for Enhanced Data Security
✅ Encryption and Decryption Process Using Advanced Techniques
Key Features of Advanced Encryption
✅ Symmetric Encryption with AES-256 CBC
✅ Patented Robust Key Segmentation for Enhanced Security
✅ Data Integrity and Hashing with SHA-256
✅ Automation via OpenPGP.js
✅ Protection via Volatile Memory
Technical Architecture of DataShielder Encryption
✅ Encryption Process with Key Segmentation
✅ Key Reconstitution
✅ Data Encryption with AES-256 CBC
✅ Integrity Verification
Cryptographic Libraries and Advanced Key Management
✅ Cryptographic Libraries and Patented Key Management
✅ Encryption and Decryption with Patented Key Segmentation
Advanced Data Encryption Decryption Process with Key Segmentation
✅ Initialization
✅ Key Reconstitution
✅ Data Decryption
✅ Integrity Verification
Advanced Data Encryption Quantum Security and Future Perspectives
✅ Preparing for Quantum Threats
✅ Transition to Post-Quantum Algorithms
Advanced Data Encryption with EviEngine
✅ Introduction to EviEngine and DataShielder HSM PGP
✅ EviEngine: A Serverless and Databaseless Technology
Operation and Architecture of EviEngine
✅ Communication Between Computer and Browser via DataShielder Engine
✅ License Management and Feature Authorization
Main Functions of EviEngine in DataShielder HSM PGP
✅ Serverless Automation
✅ License Management
✅ Key and Function Security
✅ Browser Interaction Management
Use Cases of Advanced Data Encryption in DataShielder HSM PGP
✅ Features in DataShielder HSM PGP
✅ Segmented Key Management
✅ License Activation
✅ Data Security and Privacy
Security and Benefits of EviEngine
✅ Advantages of License Management via EviEngine: Enhanced Security
✅ Supported Operating Systems
✅ Manual Update Protocol
How Works DataShielder HSM PGP
✅ 🎥 Video: How to Encrypt Files with DataShielder HSM PGP: One-Click & Drag-and-Drop Post-Quantum Encryption
✅ 🎥 Video: How to Secure Encrypted Messages with DataShielder HSM PGP in One-Click or via NFC
📘 User Guides for DataShielder HSM PGP
📖 Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Security Objectives for Advanced Data Encryption
The DataShielder HSM PGP effectively meets the following security requirements:
- Data Confidentiality: It utilizes AES-256 CBC to guarantee the confidentiality of both transmitted and stored information.
- Data Integrity: It protects data from unauthorized modifications through the implementation of SHA-256.
- Attack Resilience: It reduces attack surfaces with key segmentation, effectively eliminating the transmission of complete keys over networks.
- Post-Quantum Security: The system is built to withstand future threats posed by quantum computing, particularly by utilizing key segmentation to create a robust 512-bit key.
Advanced Data Encryption in DataShielder HSM PGP
Content: DataShielder HSM PGP employs Advanced Data Encryption techniques to provide robust protection against unauthorized access, leveraging AES-256 CBC and key segmentation technology. These methods ensure that data remains secure both in transit and at rest, and they are built to meet post-quantum security requirements. Additionally, DataShielder’s encryption protocols guarantee data confidentiality, integrity, and authenticity through the implementation of SHA-256 hashing and OpenPGP.js. The system’s segmented key storage splits encryption keys between local and external devices, combining two 256-bit key parts into a single 512-bit key. This approach increases the complexity of attacks and reduces the likelihood of key compromise.
Key Libraries:
- crypto-js (Version: 4.1.1) for AES-256 encryption and SHA-256 hashing. More details: CryptoJS Documentation
- js-base64 (Version: 3.7.4) for converting binary data to Base64, ensuring safe transmission of encrypted data. More details: JS-Base64 Documentation
- openpgp.js (Version: 5.11.2) for PGP encryption and signing. More details: OpenPGP.js Documentation
- bip39 (Version: 3.1.0) for mnemonic phrase generation and key management. More details: BIP39 Documentation
Key Features of Advanced Encryption
Symmetric Encryption with AES-256 CBC
DataShielder HSM PGP uses the AES-256 CBC algorithm to encrypt data with a 256-bit key. Each data block builds on the previous one, which greatly strengthens security by complicating the decryption of individual blocks. Additionally, this method makes unauthorized access much more difficult.
Patented Robust Key Segmentation for Enhanced Security
DataShielder HSM PGP splits the symmetric encryption key into two parts:
- First, Segment 1, a 256-bit key, remains in local browser storage.
- Next, Segment 2, another 256-bit key, stores on an external device like a USB or secure server.
By combining these two parts, the system creates a 512-bit key, which enhances security since the full key is never transmitted. In fact, only when both segments are accessed can the key be reconstituted, further reducing the risk of compromise.
Data Integrity and Hashing with SHA-256
DataShielder HSM PGP uses SHA-256 to create a data fingerprint before encryption. After that, it encrypts the hash alongside the data. As a result, the system can verify during decryption whether the data was altered, ensuring its integrity.
The OpenPGP.js library implements the cryptographic functions of DataShielder HSM PGP. Compliant with RFC 4880, it ensures interoperability with other PGP systems and supports AES-256, SHA-256, and CBC mode. This library facilitates the management of symmetric keys and encryption/decryption operations according to PGP security standards.
Protection via Volatile Memory
The key segments used for cryptographic operations store in volatile memory for a limited duration (less than a millisecond), minimizing the risk of key compromise during physical or software attacks. This mechanism guarantees that the keys do not remain in memory after cryptographic operations.
EviSign: Toward Qualified Electronic Signature Compliance
EviSign: Moving Toward Qualified Electronic Signature Compliance
EviSign actively bridges the gap between traditional electronic signatures and the stringent requirements of qualified electronic signatures. By adopting the patented segmented key system, EviSign not only enhances security but also simplifies the entire signing process. This evolution allows the system to maintain its offline and serverless architecture while aligning with eIDAS regulations.
Key Features for Seamless Integration
- Effortless Key Generation & Encryption Libraries
With EviSign, users can now generate cryptographic keys effortlessly. The tool fully supports both RSA (up to 4096 bits) and ECC, ensuring flexibility for different security needs. Thanks to the integration of crypto-js and OpenPGP.js, AES-256 encryption is handled smoothly. These libraries ensure data confidentiality and offer post-quantum resilience, making it future-proof. For more information, visit the CryptoJS Documentation and OpenPGP.js Documentation. - Streamlined Document Signing
Signing documents is now even easier with EviSign. It automates key generation through its segmented key technology, which fills passwords for users, enabling them to sign documents using private keys in .p7s format. This format is widely compatible across systems, ensuring seamless integration in various environments. - Robust Signature Verification
EviSign guarantees the authenticity and integrity of documents by providing clear, instant feedback during the verification process. Any modification to a signed file will trigger an invalid signature warning, ensuring that only authentic documents pass the verification stage. The drag-and-drop interface allows users to verify signed documents quickly, with green and red indicators clearly showing the verification result.
Enhanced User Experience & Legal Context
EviSign now integrates all critical signer information in one place. Every document signed through the system includes:
- Full name and email of the signer
- The organization and role of the signer
- Key creation date and its validity status (whether expired or revoked)
- Date and time of the signature
This process, combined with segmented key technology, guarantees authenticity and validity while eliminating the need for servers or databases. For more legal information on qualified electronic signatures and the requirements, refer to the official eIDAS Regulation.
Improved User Interface for Key Management
EviSign’s intuitive UI further simplifies cryptographic operations. The key generation and signature verification processes are now more straightforward than ever, with visual cues guiding users at every step. The tool automatically assesses password strength during key creation, enhancing both security and user experience.
By moving toward qualified electronic signature compliance, EviSign continues to offer a cutting-edge solution that merges advanced data encryption, user-friendly design, and top-tier security—all without the need for servers, databases, or centralized control.
EviSign: Key Generation, File Signing, and Verification Workflow
The diagram illustrates the comprehensive process of cryptographic operations within EviSign, part of the DataShielder HSM PGP ecosystem. It shows how users interact with the system to generate cryptographic keys, digitally sign files, and verify the integrity of those signed files. By detailing each step, the diagram highlights how EviSign ensures security and document authenticity, making it ideal for high-security environments. This streamlined workflow demonstrates the ease of managing sensitive files using advanced encryption standards.
EviSeed: Encrypted Mnemonic Phrases for BIP39
EviSeed provides encryption for BIP39 mnemonic phrases, used for cryptocurrency recovery. It uses AES-256 CBC encryption with segmented keys, providing additional protection for sensitive recovery phrases.
Key Features:
- Mnemonic Phrase Sizes: Supports 12, 15, 18, 21, and 24-word phrases.
- Languages Supported:
- English
- Spanish
- French
- Italian
- Simplified Chinese
- Traditional Chinese
- Japanese
- Checksum Validation: Each mnemonic phrase is validated using a BIP39 checksum to ensure correctness.
- QR Code Generation: The encrypted mnemonic phrase can be exported as a QR code for easy import into SeedNFC HSM devices.
Libraries Used:
- bip39 for mnemonic generation. BIP39 Documentation
- crypto-js for AES-256 CBC encryption. CryptoJS Documentation
Mnemonic Phrase Encryption Process in DataShielder HSM PGP
This diagram visualizes the process of securing mnemonic phrases through the EviSeed feature within DataShielder HSM PGP. It demonstrates the flow of generating, encrypting, and verifying mnemonic phrases, which are essential for cryptocurrency recovery. The diagram highlights how AES-256 CBC encryption is used in conjunction with segmented key storage, ensuring maximum security for BIP39 mnemonic phrases across multiple languages. The mnemonic phrase is validated with a checksum before encryption, further ensuring its integrity before being converted into a secure format such as a QR code for easy transfer.
Message and File Encryption in DataShielder HSM PGP
The EviCypher module within DataShielder HSM PGP provides powerful encryption for messages and files using AES-256 CBC with key segmentation, ensuring privacy protection and secure communication.
Key Features:
- Opacity Management: Protects against onlookers by adjusting the visibility of typed text, offering additional privacy in public spaces.
- Starred Display Mode: Displays text as asterisks, further enhancing privacy during message composition.
- Encryption for Secure Transmission: Messages are encrypted using AES-256 CBC and segmented into secure key portions. Encrypted messages can be copied, pasted, and transmitted securely across platforms.
- QR Code for Encrypted Messages: After encryption, messages can be represented as QR codes, allowing for easy sharing between devices.
File Encryption: The drag-and-drop functionality allows for easy file encryption with AES-256 CBC PGP encryption. Integration with NFC HSM devices ensures that encryption keys are securely managed through hardware, providing an extra layer of offline security.
Technical Architecture of DataShielder Encryption
Encryption Process with Key Segmentation
Initialization
- The user launches the DataShielder HSM PGP application in their browser. The application automatically retrieves Segment 1 of the key from local storage.
- The user retrieves Segment 2 from an external device
Key Reconstitution
- Segment 1 and Segment 2 combine in volatile memory to form a complete 512-bit key. This process leaves no permanent trace on the system.
Data Encryption with AES-256 CBC
- The data to be encrypted hashes using SHA-256 to generate a hash.
- AES-256 CBC encryption applies to the data using the complete 512-bit segmented key. Each data block encrypts based on the previous block, utilizing a unique initialization vector (IV) for each encryption operation.
Integrity Verification
- The SHA-256 hash undergoes comparison during decryption to ensure that the data remains unaltered.
Cryptographic Libraries and Advanced Data Encryption Key Management
Cryptographic Libraries and Patented Key Management (Protected by International Patent)
The DataShielder HSM PGP system incorporates advanced cryptographic libraries to handle encryption and manage keys securely. This includes AES-256 encryption and a patented key segmentation system, enhancing security by splitting a 512-bit encryption key into two separate 256-bit segments.
- crypto-js (Version: 4.1.1): Manages AES-256 CBC encryption and SHA-256 hashing, both essential for secure operations.
Documentation: CryptoJS - js-base64 (Version: 3.7.4): Converts binary data into Base64, facilitating safe transmission of encrypted data.
Documentation: JS-Base64 - openpgp (Version: 5.11.2): Implements OpenPGP encryption and signature capabilities.
Documentation: OpenPGP.js - bip39 (Version: 3.1.0): Generates mnemonic phrases for secure key management.
Documentation: BIP39
Patented Key Segmentation Technology
DataShielder HSM PGP is protected by your international key segmentation patent, which provides a unique approach to key management and authentication. This patent ensures the independence of the two 256-bit key segments. One segment is stored securely in the browser’s localStorage, while the other is kept on an external device, such as a USB, SSD, or NAS drive. The segmentation method ensures that no single location holds the entire key, significantly reducing the risk of compromise.
- Security by Design: The patented segmentation method guarantees that even if one segment is compromised, the full key remains inaccessible without access to the second segment.
- Flexible Key Management: Users can select segments from a variety of storage locations, including local and external devices. This dynamic flexibility in key selection creates numerous secure combinations, ensuring Zero Trust principles are upheld.
Encryption and Decryption with Patented Key Segmentation
The two key segments combine to form a 512-bit key during encryption and decryption, which is then used in AES-GCM. This patented approach strengthens security by ensuring that the key segments remain independent and are never stored together in one place.
Example:
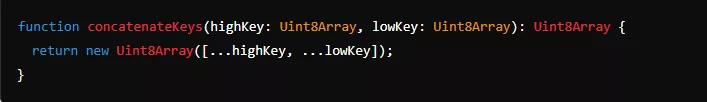
This process, managed by DataShielder Engine, ensures that sensitive information remains protected across various high-risk environments.
Encryption/Decryption
The concatenated 512-bit key is used in AES-GCM for secure handling of data. This method adds an initialization vector (IV) for additional encryption strength.
Example:
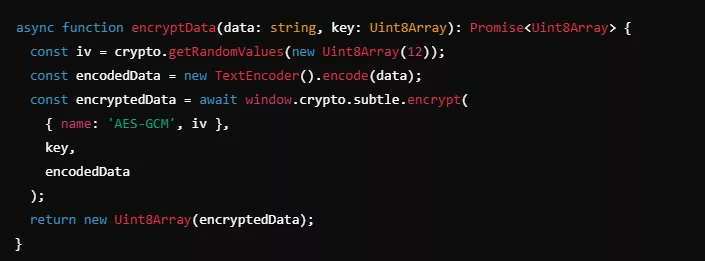
Decentralized Key Management with Segmented Keys
DataShielder HSM PGP enables a decentralized approach to key management where external key segments are stored across various devices (USB, SSD, etc.). Each user can receive a segment via separate channels (such as local storage on their USB), but the external segment may differ between users. This decentralized structure ensures security without relying on servers or databases, allowing complete autonomy over key management.
Following the explanation of both decentralized and intelligent centralized key management, the segmentation technology offers significant security benefits.
Intelligent Decentralized Key Management with EviEngine
Although the system is decentralized, DataShielder HSM PGP also enables intelligent centralized key management. Companies can securely distribute external key segments via shared services without requiring a centralized server or database. Employees can access external key segments stored on enterprise drives or remote storage services. Thanks to DataShielder HSM PGP’s path management system, it supports centralized key segment sharing while maintaining Zero Trust, Zero Knowledge, and avoiding the need for account creation or user identification.
Advantages of Key Segmentation
- Security by Design: Key segments are never stored together, which ensures that even if one segment is compromised, the other remains inaccessible.
- Enhanced Protection: This method resists both local and network-based attacks since access to both segments is required for successful decryption.
Serverless Security with EviEngine (Protected by Copyright)
DataShielder’s EviEngine allows secure communication between the web browser and computer, eliminating the need for external servers or databases. Moreover, it retrieves and stores segmented encryption keys across multiple devices, including USBs and cloud storage, without relying on a central authority or data collection. This architecture ensures privacy while maintaining security.
Protected by copyright, EviEngine automates the management of license keys and activates browser extension features securely, by linking license usage directly to hardware. This provides users with greater flexibility in managing their own keys while ensuring Zero Trust architecture for data security.
Learn more about EviEngine here.
How EviEngine Works:
- Automates Actions in Web Services: EviEngine allows users to store and retrieve data across a variety of devices—removable, online, or networked—without needing a centralized server.
- License Management: License keys, linked to hardware and not user identity, are verified via EviEngine, acting like a dongle to activate features in DataShielder HSM PGP.
- Path Management: EviEngine manages paths where key segments are stored and retrieved, without needing a database, providing seamless integration with DataShielder HSM PGP.
With EviEngine, users enjoy full control over their keys, encrypted communications, and privacy, all protected by copyright innovation, making it the backbone for managing the secure and decentralized features of DataShielder HSM PGP.
Advanced Data Encryption Decryption Process with Key Segmentation
Initialization
- The user requests access to the encrypted data.
- Segment 1 of the key retrieves automatically from local storage, while Segment 2 retrieves from the external device.
Key Reconstitution
- The segments combine to form the complete 512-bit key.
Data Decryption
- The data decrypts using the AES-256 key and the initialization vector applied during encryption.
Integrity Verification
- The SHA-256 hash recalculates and compares to the original hash. If a difference is detected, the decryption fails, indicating data tampering.
Advantages of Advanced Data Encryption Key Segmentation
Enhanced Attack Protection
Key segmentation significantly complicates unauthorized access attempts. Even if one segment is compromised, decryption requires both segments, offering heightened protection against both local and remote attacks.
Post-Quantum Resilience
Although AES-256 remains secure, the ability to create a 512-bit key through segmentation enhances resilience against future quantum threats. An attacker must recover and combine two distinct segments before executing a successful attack.
Physical Protection of Segments
Each key segment physically separates, preventing complete compromise in the event of loss or theft of one segment. This mechanism introduces layered defense, especially in sensitive environments requiring increased protection.
Absence of Central Server or Database
The DataShielder HSM PGP system operates offline, without a central server or database. This ensures that keys never store or transmit over insecure public networks, thereby eliminating risks of key compromise through network attacks.
Advanced Data Encryption Quantum Security and Future Perspectives
Preparing for Quantum Threats
With the rise of quantum computing, traditional cryptographic algorithms like RSA or ECC will become vulnerable to attacks. The DataShielder HSM PGP system anticipates this threat by adopting key segmentation and integrating robust standards like AES-256 and SHA-256. This approach currently suffices for security, but long-term strategies may consider post-quantum algorithms for enhanced protection against quantum computers.
Transition to Post-Quantum Algorithms
Algorithms such as Kyber (post-quantum encryption) and Dilithium (post-quantum signatures) may incorporate into future versions of the DataShielder HSM PGP to ensure continuous security against evolving technological threats.
Advanced Data Encryption with EviEngine
Introduction to EviEngine and DataShielder HSM PGP
The DataShielder HSM PGP, founded on robust cryptographic principles (including AES-256 CBC and SHA-256), integrates a unique technology called EviEngine. This technology enables secure license management without servers or databases while ensuring seamless communication between the browser and the computer via the DataShielder Engine.
EviEngine: A Serverless and Databaseless Technology
EviEngine is designed to automate actions in web services without servers or databases. It allows users to store data on any accessible storage device, whether fixed, removable, online (cloud), or across local (LAN) or wide-area networks (WAN).
Operation and Architecture of EviEngine
Communication Between Computer and Browser via DataShielder Engine
The DataShielder Engine, manually installed on Windows or macOS systems, establishes secure communication between the web browser and the computer. Once installed, it operates offline, requiring no user intervention. It is signed by a Thales key for Windows and also signed for Apple macOS, ensuring a reliable and secure installation.
Unlike traditional systems that depend on servers and databases for updates and communication, DataShielder Engine functions in a Zero Trust and Zero Knowledge architecture. This means that there is no centralized storage of data, nor is there a need for account creation. Consequently, users must perform updates manually, preserving maximum security and isolation.
License Management and Feature Authorization
EviEngine, through DataShielder Engine, oversees the activation of features within the DataShielder HSM PGP using license keys provided by the publisher. This management occurs without reliance on servers or databases, ensuring that licenses tie to the user’s hardware rather than to a user account. This method greatly enhances security against unauthorized use.
Main Functions of EviEngine in DataShielder HSM PGP
Serverless Automation
EviEngine, via DataShielder Engine, automates actions in web services without the need for servers or databases. Users can freely store their keys and data in local devices, removable peripherals, or online.
License Management
The technology enables management of licenses for installed software (like DataShielder HSM PGP). Licenses link to the hardware, ensuring secure and simplified usage without a central server.
Key and Function Security
License keys encrypt and manage directly throughthe EviEngine, ensuring that only authorized features activate in DataShielder HSM PGP, effectively preventing unauthorized access.
Browser Interaction Management
EviEngine, via DataShielder Engine, manages interactions between the computer and the browser to execute commands securely and validated, all without external servers. This empowers users with complete control over their encryption environment.
Use Cases of Advanced Data Encryption in DataShielder HSM PGP
Features in DataShielder HSM PGP
When DataShielder HSM PGP pairs with EviEngine, it gains the following features:
Segmented Key Management
EviEngine manages the locations of segmented keys, allowing parts of the key to be stored in local browser storage and on external devices. Through EviEngine, DataShielder HSM PGP securely reconstructs and manages these segmented keys for encryption and decryption operations.
License Activation
EviEngine acts as a virtual dongle, verifying licenses tied to premium features of DataShielder HSM PGP. This enables strict usage rights management while adhering to the Zero Trust and Zero Knowledge architecture.
Data Security and Privacy
EviEngine does not collect or store personal or encryption data. All operations execute locally, ensuring that sensitive keys and data never leave the secure environment of the user’s device.
Security and Benefits of EviEngine
Advantages of License Management via EviEngine: Enhanced Security
By not relying on servers or databases, EviEngine and DataShielder Engine substantially mitigate the risks of third-party attacks or centralized data compromises.
Hardware-Tied Licenses
Licenses link to the device running DataShielder Engine, making unauthorized duplication or transfer of licenses more difficult.
Software Support and Compatibility
Supported Operating Systems
EviEngine via DataShielder Engine is compatible with both Windows and macOS, ensuring interoperability and enhanced security through official signatures recognized by Thales for Windows and Apple for macOS.
Manual Update Protocol
Since DataShielder Engine operates without servers or databases and within a Zero Trust framework, users must perform software updates manually to maintain the highest level of security.
Comprehensive Overview of DataShielder HSM PGP
Cutting-edge System Architecture
Explore the intricate architecture of DataShielder HSM PGP which supports advanced encryption and secure key management directly within your browser. This section details how local and external storage are utilized to enhance data security.
Diagram: General Operation Diagram
Understand the overall architecture and how different components interact to provide a secure environment for data handling. This diagram visualizes the secure architecture that underpins all encryption and decryption activities.
Tailored Licensing System
DataShielder HSM PGP’s licensing system is designed with security and user convenience in mind, anchored to the unique hardware ID of the motherboard, ensuring that each installation is as secure as possible.
Diagram: License Activation Process Diagram
This process diagram shows the step-by-step activation based on hardware identification, highlighting its role in secure data management.
Advanced Encryption & Key Management Features
Robust Key Management
Learn about the secure key management solutions offered by DataShielder HSM PGP, which include generating, storing, and managing encryption keys securely.
Diagram: Key Management Diagram
Delve into the specifics of key management that safeguard your encryption keys with utmost security.
Secure Encryption and Decryption Techniques
DataShielder HSM PGP uses AES-256 CBC PGP for all encryption and decryption processes, ensuring that your data remains protected against all forms of cyber threats.
Diagram: Encryption/Decryption Process Diagram
Visual representation of the encryption and decryption processes that safeguard your communications.
🎥 Video Tutorials: Master DataShielder HSM PGP
Learn how to effectively use DataShielder HSM PGP with these step-by-step video tutorials. Whether you are encrypting files or securing messages, these guides demonstrate the ease of operation and the power of FullSecure architecture.
✅ Video: How to Encrypt Files with DataShielder HSM PGP
Watch this tutorial on encrypting files using one-click and drag-and-drop post-quantum encryption.
Video: How to Encrypt Files with DataShielder HSM PGP: One-Click & Drag-and-Drop Post-Quantum Encryption
This video demonstrates how to encrypt files using DataShielder HSM PGP, leveraging an intuitive drag-and-drop feature with one-click post-quantum encryption.
✅ Video: How to Secure Encrypted Messages with DataShielder HSM PGP
Learn how to secure encrypted messages effortlessly, either with a single click or via NFC, for quick and secure communication.
Watch this tutorial on securing encrypted messages with DataShielder HSM PGP in a single click or through NFC for rapid, secure communication.
📖 Available Tutorials
➤ Guide Categories:
- ⏩ Quick Start Guide – Step-by-step instructions for immediate setup.
- 📜 Comprehensive Tutorial – Detailed explanations covering segmented key encryption, security layers, and NFC integration.
⏬ Access Your Guide
| 🌍 Language | ⚡ Quick Start Guide | 📜 Comprehensive Tutorial |
|---|---|---|
| 🇬🇧 English | ⏩ Get Started | 📜 Full Manual |
| 🇫🇷 Français | ⏩ Accéder | 📜 Consulter |
| 🇪🇸 Español | ⏳ Coming soon | ⏳ Coming soon |
| 🇦🇩 Català | ⏳ Coming soon | ⏳ Coming soon |
🛡 Comprehensive Guide for NFC HSM DataShielder Module
➤ Complete Guide on NFC Integration:
- 🔗 Covers full usage when the NFC HSM DataShielder module is paired with DataShielder HSM PGP.
- 🔗 Step-by-step instructions for setup, security protocols, and webmail encryption.
| 🌍 Language | 🔗 NFC Card Guide |
|---|---|
| 🇬🇧 English | 🔗 NFC Guide |
| 🇫🇷 Français | 🔗 Guide NFC |
| 🇪🇸 Español | ⏳ Coming soon |
| 🇦🇩 Català | ⏳ Coming soon |
Real-world Application Scenarios DataShielder HSM PGP
Efficient Key Sharing ProtocolsSummary of DataShielder HSM PGP
Explore how DataShielder HSM PGP facilitates secure key sharing between individuals, enhancing collaborative security without compromising data integrity.
Diagram: Key Sharing Between Bob and Alice
A practical example of how encrypted key sharing is implemented securely between users.
Expansion of Key Management Capabilities
Illustration of how DataShielder HSM PGP supports the creation and distribution of new key pairs, demonstrating flexibility and security in high-stakes environments.
Diagram: Generating and Sharing New Key Pairs with Arthur
Showcasing the process of generating new keys while maintaining security protocols.
DataShielder HSM PGP stands at the forefront of “data encryption software,” offering “browser-based encryption tools” that are essential for both civil and military applications. It delivers not just functionality but the assurance of top-tier security.
Appendix: Diagram Collection
A comprehensive collection of all diagrams used throughout the document to provide visual support for the technical descriptions, enhancing understanding and engagement.
Summary
DataShielder HSM PGP offers a suite of Advanced Data Encryption tools designed to secure sensitive data, whether in communication, document signing, or cryptocurrency management. Each component—EviSign, EviCypher, and EviSeed—ensures top-tier security through advanced cryptographic measures like AES-256 CBC encryption, key segmentation, and post-quantum resilience. This robust system guarantees that even in high-risk environments, data remains secure and confidential.
3 thoughts on “DataShielder HSM PGP: Segmented Key Encryption”
Comments are closed.
Pingback: Software version history application & extension - Freemindtronic
Pingback: Reputation Cyberattacks in Hybrid Conflicts — Anatomy of an Invisible Cyberwar - Freemindtronic
Pingback: Quantum computer 6100 qubits ⮞ Historic 2025 breakthrough - Freemindtronic